Governance
Global Sustainable Development Report, 2022
For Prelims: Global Sustainable Development Report, 2022, TERI, SDGs
For Mains: Environmental Pollution & Degradation, India’s SDG targets and its achievements
Why in News?
Recently, the global Sustainable Development Report, 2022 was released.
- India was ranked 121 out of the 163 countries. It was ranked 117 in 2020 and 120 in 2021.
- Earlier, in February 2022, the Prime Minister addressed the The Energy and Resources Institute’s (TERI) World Sustainable Development Summit.
What is a Sustainable Development Report?
- About:
- It is a global assessment of countries' progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.
- It is published by a group of independent experts at the Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN).
- SDSN was launched in 2012 to mobilize global scientific and technological expertise to promote practical problem solving for sustainable development and implement the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Following their adoption, SDSN is now committed to supporting the implementation of the SDGs at national and international levels.
- Ranking:
- Countries are ranked by their overall score.
- The overall score measures the total progress towards achieving all 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDG)
- The score can be interpreted as a percentage of SDG achievement.
- A score of 100 indicates that all SDGs have been achieved.
- Performance of the Countries:
- The 2022 SDG Index is topped by Finland, followed by three Nordic countries –Denmark, Sweden and Norway.
- East and South Asia is the region that progressed most on the SDGs since their adoption in 2015.
- Bangladesh and Cambodia are the two countries that progressed most on the SDGs since 2015.
- By contrast Venezuela has declined the most on the SDG Index since their adoption in 2015.
What are the key Highlights of the Report?
- About World:
- Multiple and simultaneous health, climate, biodiversity, geopolitical and military crises are major setbacks for sustainable development globally.
- The SDG Index world average has slightly decreased in 2021 for the second year in a row, largely due to the impact of the pandemic on SDG1 (No Poverty) and SDG8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) and poor performance on SDG11-15 (climate, biodiversity, and sustainable urban development goals).
- Besides their massive humanitarian costs, military conflicts – including the war in Ukraine – have major international spill overs on food security and energy prices, which are amplified by the climate and biodiversity crises.
- About India:
- India’s Preparedness Worsened:
- India is not placed well to achieve the United Nations-mandated Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) and its preparedness has worsened over the years in comparison with other countries.
- Major Challenges:
- The country continues to face major challenges in achieving 11 of the 17 SDGs, which has pushed down its global ranking on SDG preparedness.
- Ensuring decent work (SDG 8) has become more challenging.
- According to the report, India is on track to achieving SDG 13 on climate action.
- However, The State of India’s Environment, 2022 flagged that the country was facing major challenges in this area.
- India’s performance on climate action — (SDG) 13 — has slipped from 2019-2020.
- This decline in India’s overall performance is primarily due to eight states — Bihar, Telangana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab and Jharkhand — whose scores have dipped under SDG 13 in the two years.
- However, The State of India’s Environment, 2022 flagged that the country was facing major challenges in this area.
- Progress Made:
- The progress in around 10 of these goals is similar to those in 2021.
- These include SDG 2 on ending hunger, SDG 3 on good health and well being and SDG 6 on clean water and sanitation.
- The progress in around 10 of these goals is similar to those in 2021.
- India’s Preparedness Worsened:
What are the Recommendations?
- New partnerships and innovations should be Scaled-up:
- New partnerships and innovations that emerged during the Covid-19 pandemic, including in scientific cooperation and data, should be scaled-up to support the SDGs.
- Science and Technological Innovations:
- Science, technological innovations, and data systems can help identify solutions in times of crises and can provide decisive contributions to address the major challenges of our times.
- These call for increased and prolonged investments in statistical capacities, Research & Development and education and skills.
- Increasing Investment:
- Achieving the SDGs is fundamentally an investment agenda in physical infrastructure (including renewable energy, digital technologies) and human capital (including health, education).
- Yet the poorest half of the world lacks market access to capital on acceptable terms.
- Poor and vulnerable countries have been hit hard by the multiple crises and their spill overs.
- Achieving the SDGs is fundamentally an investment agenda in physical infrastructure (including renewable energy, digital technologies) and human capital (including health, education).
What are Sustainable Development Goals (SDG)?
- The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) also known as the Global Goals, were adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that by 2030 all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
- The 17 SDGs are integrated—they recognize that action in one area will affect outcomes in others, and that development must balance social, economic and environmental sustainability.
- Countries have committed to prioritize progress for those who're furthest behind. The SDGs are designed to end poverty, hunger, Acquired ImmunoDeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) and discrimination against women and girls.

UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Sustainable Development Goals were first proposed in 1972 by a global think tank called the ‘Club of Rome’.
- The Sustainable Development Goals have to be achieved by 2030.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
- The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, are a universal call for action to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
- They are built upon the success of the Millennium Development Goals, including new areas such as climate change, economic inequality, innovation, sustainable consumption, peace and justice, among other priorities.
- The goals are interconnected – often the key to success on one will involve tackling issues more commonly associated with another.
- Adopted in 2015, SDGs came into effect in January 2016. They are meant to be achieved by 2030. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The SDGs were born at the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development in Rio de Janeiro in 2012. The Club of Rome advocated resource conservation for the first time in a more systematic way in 1968. Hence, statement 1 is not correct. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Science & Technology
India's first Biotech Startup Expo 2022
For Prelims: India's first Biotech Startup Expo 2022, Biotechnology
For Mains: Potential of Biotech Sector and Associated Challenges
Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister has inaugurated the Biotech Startup Expo - 2022.
- It is a reflection of the expansive growth of the biotech sector in the country.
What are the Key Highlights of the Expo?
- About:
- The Biotech Startup Expo 2022 will provide a common platform to connect investors, entrepreneurs, scientists, researchers, industry leaders, manufacturers, bio-incubators, regulators and government officials.
- The expo is being organised by the Department of Biotechnology and Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) to mark the completion of ten years of BIRAC.
- It will showcase applications of biotechnology in various fields including healthcare, agriculture, genomics, clean energy, biopharma, industrial biotechnology and waste-to-value.
- Theme: 'Biotech Startup Innovations: Towards AatmaNirbhar Bharat'.
What is Biotechnology and its Application?
- Biotechnology is technology that utilizes biological systems, living organisms or parts of this to develop or create different products.
- Brewing and baking bread are examples of processes that fall within the concept of biotechnology (use of yeast (= living organism) to produce the desired product).
- Such traditional processes usually utilize the living organisms in their natural form (or further developed by breeding), while the more modern form of biotechnology will generally involve a more advanced modification of the biological system or organism.
- Biotechnology deals with industrial scale production of biopharmaceuticals and biologicals using genetically modified microbes, fungi, plants and animals.
- The applications of biotechnology include therapeutics, diagnostics, genetically modified crops for agriculture, processed food, bioremediation, waste treatment, and energy production.
What is the Status of Biotech Sector?
- About:
- India is among the top 12 destinations for biotechnology globally and 3rd largest biotechnology destination in the Asia Pacific region.
- The country is also the world’s third-largest producer of recombinant Hepatitis B vaccine and second-largest producer of BT cotton (genetically modified pest resistant plant cotton).
- India’s Biotech sector is categorised into Biopharmaceuticals, BioIndustrial, Bioagriculture, BioIT & BioServices.
- Within bio-services, India offers a strong capability in contract manufacturing, research and clinical trials, and is home to the most US FDA approved plants globally outside of the US.
- Statistics:
- The Indian bioeconomy grew from USD 62.5 billion in 2019 to USD 70.2 billion in 2020 at a growth rate of 12.3%.
- The Indian biotechnology industry, which stood at USD 63 billion in 2019, is expected to reach USD 150 billion by 2025, with a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 16.4%.
- By 2025, the contribution of the Indian biotechnology industry to the global biotechnology market is expected to grow to 19%.
- As of 2021, India’s biotech industry clocks in about USD 12 billion in annual revenue.
- Potential of Biotechnology:
- Multi-Faceted Domain: Biotechnology is a multi-faceted domain encompassing applications in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, scientific discoveries, etc. The biotech sector can be broadly divided into five major segments:
- Biopharma
- Bio-agriculture
- Bio-services
- Bio-industrial Applications
- Bioinformatic
- Growing Biotech Start-ups: As one of India's pioneering achievements in biotechnology, the sector employs the best minds and contributes to the development of generic and affordable medicines.
- Currently, there are over 2,700 biotech start-ups and are expected to touch the 10,000-mark by 2024.
- Role of BIRAC: Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), established under the Department of Biotechnology in 2012, continues to play a crucial role in the development of the biotech sector in India.
- BIRAC brings innovators and funders on to a common table, enabling ideas to become a reality and facilitate technological advances that make human progress possible.
- Other Factors:
- India is seen as a potential land of opportunity by the biotech sector.
- These factors include a diverse population, diverse climates, a talented workforce, initiatives to relax corporate regulations and a growing demand for bio goods.
- Multi-Faceted Domain: Biotechnology is a multi-faceted domain encompassing applications in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, scientific discoveries, etc. The biotech sector can be broadly divided into five major segments:
- Associated Challenges:
- Structural Issues: Considering that manufacturing in the biopharma sector is capital intensive, such investments have been suboptimal in India due to limited access to capital, inadequate infrastructure and complex and ever-evolving regulatory framework.
- As Biotechnology products and solutions often require ethical and regulatory clearance, making the process long, expensive and cumbersome.
- Further, low remuneration of scientists (compared to the developed economies) and a few institutional research bases have not helped create more jobs in biotechnology.
- Heavily Public Sector Dominated: Compared to the developed economies (the United States), biotechnology research in India is mainly funded by the public exchequer.
- Unless the private sector starts supporting applied research and engages with academic institutions, the innovation in applied and translational biotechnology will be minimal.
- Lack of Innovation: In terms of innovation, entrepreneurship, and technology creation, the biotechnology sector requires years of experience in the domain, access to labs with sophisticated instruments, sustained and long-term funding to innovate.
- However, India has not done well enough in improving innovation culture.
- Structural Issues: Considering that manufacturing in the biopharma sector is capital intensive, such investments have been suboptimal in India due to limited access to capital, inadequate infrastructure and complex and ever-evolving regulatory framework.
What are the Related Initiatives?
Way Forward
- Given the long history of diseases in India, the country has accumulated years of experience and scientific knowledge to prevent and treat them. India is working to boost the biotechnology sector under various flagship programmes such as 'Make in India' and 'Start-up India'.
- Increase in the number of biotech incubators will boost research and promote growth of start-ups, which is critical for the success of the Indian biotech industry.
- The favourable location of the biotech hubs will depend on critical factors like research and technology development competence, market, industry policies, infrastructure, investments.
- Setting up the integrated biotech hubs will facilitate Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs), build the confidence of investors, enhance Indian export potential for quality products, boost in-house capacity towards import substitution, and nurture and support innovations to generate more IP for India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. Mycorrhizal biotechnology has been used in rehabilitating degraded sites because mycorrhiza enables the plants to (2013)
- resist drought and increase absorptive area
- tolerate extremes of pH
- resist disease infestation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Mycorrhiza: It is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term ‘mycorrhiza’ refers to the role of the fungus in the plant’s rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhiza plays important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology and soil chemistry.
- Mycorrhizal biotechnology improves plant growth and survival in soils contaminated by heavy metals. It enables in:
- Increasing the efficiency of nutrient and water uptake.
- Enhancing the plant’s capacity to tolerate extremes of pH. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Enhancing resistance to pathogens. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Buffering plant species against several environmental stresses and drought resistance. Hence, 1 is correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
International Relations
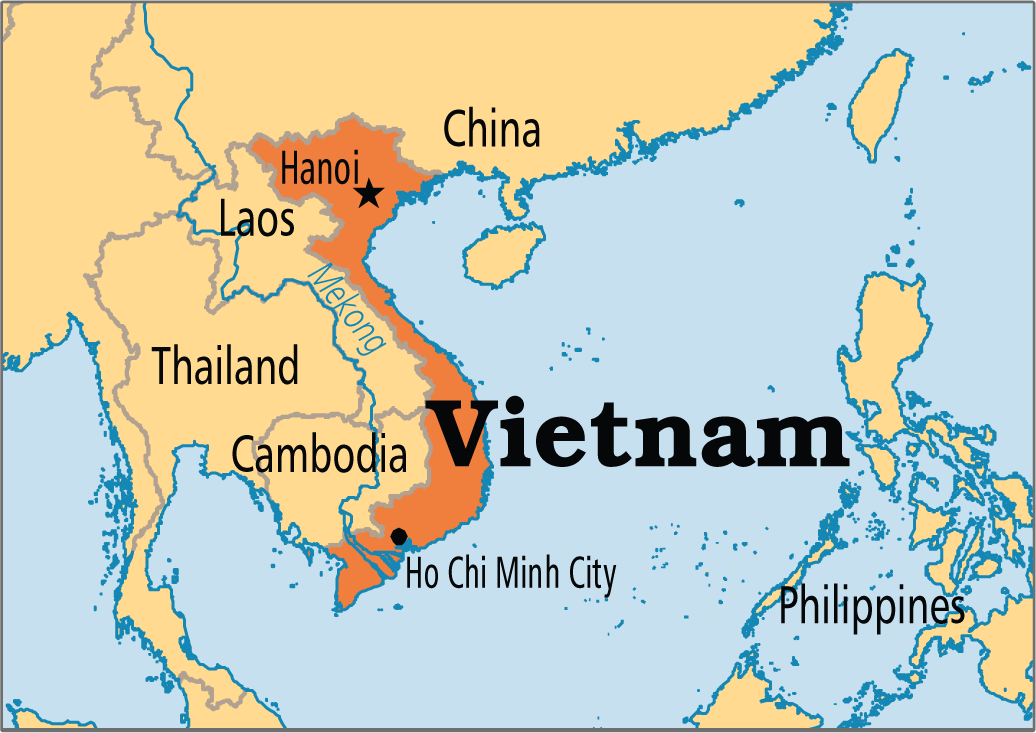
India Vietnam Partnership
For Prelims: Vietnam and neighboring countries
For Mains: Significance of India and Vietnam relations and the common area of interest between two countries in recent times
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Defence Minister visited Vietnam, where he signed some Defence Agreements, which will significantly enhance the scope and scale of existing defence cooperation.
- India and Vietnam are marking 50 years of the establishment of bilateral diplomatic relations.
- Earlier, India and Vietnam signed a Letter of Intent (LOI) to collaborate in the field of digital media, paving the way for further strengthening the partnership between the two countries.
What are the Key Highlights of the Visit?
- India-Vietnam Defence Partnership towards 2030:
- Both the Defence Ministers signed the ‘Joint Vision Statement on India-Vietnam Defence Partnership towards 2030’ to bolster bilateral defence cooperation.
- Defence Line of Credit:
- The two ministers agreed on the finalisation of the USD 500 million Defence Line of Credit extended to Vietnam with implementation of the projects under it adding substantially to Vietnam’s defence capabilities and furthering the government’s vision of ‘Make in India, Make for the World.’
- Mutual Logistics Support:
- Both inked a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on Mutual Logistics Support.
- This is a major step towards simplifying procedures for mutually beneficial logistic support and is the first such major agreement which Vietnam has signed with any country.
- India has signed several logistics agreements including all Quad countries, France, Singapore and South Korea beginning with the Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement with the U.S. in 2016.
- Logistics agreements are administrative arrangements facilitating access to military facilities for exchange of fuel and provisions on mutual agreement simplifying logistical support and increasing operational turnaround of the military when operating away from India.
- Simulators and a Monetary Grant:
- India will gift two simulators and a monetary grant towards setting up of Language and IT (Information Technology) Lab at the Air Force Officers Training School for capacity building of the Vietnamese Armed Forces.
How has been the India-Vietnam Relations?
- Background:
- While defence cooperation has been one of the most significant pillars of the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership initiated by the two countries in 2016, the relationship between the two countries was established much earlier.
- India had established the Consul General’s office in Hanoi as early as 1956.
- Vietnam established its diplomatic mission in 1972.
- India had stood by Vietnam in opposing US intervention in that country at the cost of embittering Indo-US relations.
- The relationship was further strengthened when India, in the early 1990s, initiated its “Look East Policy” with the specific objective of economic integration and political cooperation with Southeast Asia and East Asia.
- Areas of Cooperation:
- Strategic Partnership:
- India and Vietnam agreed to strengthen their strategic partnership “in line with India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI) and the ASEAN’s Outlook on Indo-Pacific to achieve shared security, prosperity and growth for all in the region.”
- Economic Cooperation:
- Trade and economic relations for mutual benefit, which have significantly improved over the years particularly after the ASEAN- India Free Trade Agreement was signed.
- India realises that Vietnam is a potential regional power in South East Asia with great political stability and substantial economic growth.
- India is investing in development and capacity assistance for Vietnam through quick impact projects (QIP), proposals in the area of water resource management in Vietnam’s Mekong Delta region, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and digital connectivity.
- Trade relations:
- During the Financial Year (FY) April 2020 – March 2021, bilateral trade between India and Vietnam reached USD 11.12 billion.
- Indian exports to Vietnam amounting to USD 4.99 billion and Indian imports from Vietnam at USD 6.12 billion.
- During the Financial Year (FY) April 2020 – March 2021, bilateral trade between India and Vietnam reached USD 11.12 billion.
- Defence Cooperation:
- While Vietnam is interested in modernising its armed forces, India is interested in developing defence capabilities of its South-East Asian partners sufficiently to maintain peace in the strategic region.
- Vietnam is interested in India’s Akash surface-to-air systems and Dhruv advanced light helicopters and Brahmos missiles.
- Apart from this, the defence relations include capacity building, dealing with common security concerns, training of personnel, and cooperation in defence R&D.
- Indian Naval Ship INS Kiltan undertook a visit to Ho Chi Minh City in 2020 to deliver flood relief materials for the people of Central Vietnam (Mission Sagar III).
- It also participated in the PASSEX Exercise with the Vietnam People’s Navy.
- The China factor also weighs heavily in the respective strategic calculus of India and Vietnam.
- Both countries had fought wars with China and both have border problems with that country. China aggressively continues to encroach in the territories of the two countries.
- Hence, it is natural for both the countries to come closer with a view to restrain China from its aggressive actions.
- Cooperation at Multiple Fora:
- At the UN Security Council, both India and Vietnam are serving concurrently as non-permanent members in 2021.
- India and Vietnam closely cooperate in various regional forums such as East Asia Summit, Mekong Ganga Cooperation, Asia Europe Meeting (ASEM).
- People-to-People Contacts:
- The year 2019 was celebrated as the ASEAN-India Year of Tourism. Both countries have facilitated a simplified visa regime to promote bilateral tourism.
- The Embassy of India organised various events to celebrate Mahatma@150 in 2018-19. These include Jaipur artificial limb fitment camps, which were organised in four provinces of Vietnam, benefitting 1000 people, under the ‘India for Humanity’ initiative of the Government of India.
- Strategic Partnership:
Way Forward
- In 2016, the first time in 15 years, an Indian Prime Minister visited Vietnam signaling India is no longer hesitant to expand its presence in China’s periphery.
- India's foreign policy envisages India to play an anchor for peace, prosperity and stability in Asia and Africa, deepening ties with Vietnam will only strengthen this narrative.
- As India and Vietnam geographically lie at the heart of the emerging Indo-Pacific construct, both would play a major role in this strategic space which is becoming a core theatre for competition for power and influence amongst the major powers.
- The strategic partnership under the broad India-Vietnam cooperation framework would be critical towards building the vision laid out under India’s ‘Act East’ Policy, which looks to expand engagement that is mutually positive and which ensures inclusive growth for all in the region.
- Strengthening ties with Vietnam will eventually lead a step towards the realisation of SAGAR (Security and Growth all in the region) initiative as hailed by the Indian PM.
- India and Vietnam both can mutually benefit each other in the arena of Blue Economy and ocean security.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
- The Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC) is an initiative by six countries – India and five ASEAN countries, namely, Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam for cooperation in tourism, culture, education, as well as transport and communications. It was launched in 2000 in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
- Both the Ganga and the Mekong are civilizational rivers and the MGC initiative aims to facilitate closer contacts among the people inhabiting these two major river basins.
- The MGC is also indicative of the cultural and commercial linkages among the member countries of the MGC down the centuries. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Economy
Sustainable Fashion
For Prelims: Slow Environment Movement, United nations Sustainable development Goals (SDG)
For Mains: Need of sustainable fashion for a healthy and inclusive environment
Why in News?
Responsible production and consumption — the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 12 — has become an increasingly important conversation within the ‘slow fashion’ movement, especially since the 2013 Rana plaza Tragedy in Bangladesh.
- On 24th April 2013, the collapse of the Rana Plaza building in Dhaka, Bangladesh, which housed five garment factories, killed at least 1,132 people and injured more than 2,500. It brought the attention of the international community and consumers towards the conditions of workers and sustainable fashion.
What is Slow Fashion Movement?
- Slow Fashion is an approach to producing clothing which takes into consideration all aspects of the supply chain and in doing so, aims to respect people, the environment, and animals.
- It also means spending more time on the design process, ensuring that each piece of apparel is quality made.
- Fast Fashion retailers have taught us that more is better, and thereby have created a huge consumption issue. The fast fashion industry is driving down quality, exploiting the environment and their workers to create cheap garments that do not last.
- Slow fashion is the exact opposite of this. It’s about creating mindful, curated collections based on quality finishes, versus pumping out large quantities of seasonal and trendy clothing.
What is the significance of Sustainable Fashion?
- Textiles and clothes contribute USD 2.4 trillion to global manufacturing.
- It provides employment to 300 million people worldwide along the value chain around the world, many of them are women.
- It is responsible for 2-6 % greenhouse gases emissions of the world.
- It consumes around 215 billion litres of water per year.
- It faces annual material loss of USD 100 billion due to underutilization.
- Textiles account for approximately 9% microplastics losses to the ocean.
What are the Initiatives for Sustainable Fashion?
- At Global level:
- United Nations Alliance for Sustainable Fashion:
- It is an initiative of United Nations agencies and allied organizations designed to contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals through coordinated action in the fashion sector.
- Specifically, the Alliance works to support coordination between UN bodies working in fashion and promoting projects and policies that ensure that the fashion value chain contributes to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals’ targets.
- Traceability for Sustainable Garment and Footwear: As part of this initiative, UNECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe) has launched "The Sustainability Pledge" inviting governments, garment and footwear manufacturers and industry stakeholders to pledge to apply toolkit of measures and take a positive step towards improving the environmental and ethical credentials of the sector.
- World Cotton Day (7th October): It creates awareness of the need of market access for cotton and cotton-related products from least developed countries, fosters sustainable trade policies and enables developing countries to benefit more from every step of the cotton value chain.
- United Nations Alliance for Sustainable Fashion:
- At National Level:
- Project SU.RE: SU.RE stands for ‘Sustainable Resolution’. It is the first ever holistic effort towards gradually introducing a broader framework for establishing critical sustainability goals for the Indian textile industry. It was launched in 2020.
- Objective: The project aims to move towards sustainable fashion that contributes to a clean environment.
- Khadi Promotion: Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) promotes khadi products. They have tied up with leading brands—Arvind Mills and Raymonds—and are also working with Air India to promote khadi products.
- Bamboo Promotion: NITI Aayog’s Forum for North East has highlighted the role of bamboo in development of the North East region. Over 60% of India’s bamboo is grown in the North East.
- Brown Cotton: Brown Cotton, is a local (to Karnataka) indigenous variety of desi cotton that is recognised for its natural brown colour. This effort is a larger encompassing exercise that involves the environment, the economy as well as local communities.
- Project SU.RE: SU.RE stands for ‘Sustainable Resolution’. It is the first ever holistic effort towards gradually introducing a broader framework for establishing critical sustainability goals for the Indian textile industry. It was launched in 2020.
What are the challenges associated with sustainable Fashion?
- Economic and financial barriers.
- A new categorization of barriers: human perceptions, resource constraints and weak legislation.
- Issues in finding an eco-friendly and ethical alternative to the standard manufacturing process.
- Lack of Technological advantage.
- Increase in cost of manufacturing due to increase in investment in environment saving efforts and hike in wages of labourers.
- Eco-Friendly brands find it challengi
Way Forward
- Environmental awareness: The people all around the world should be made aware that climate change is a reality and not a hoax, so they should understand their responsibility of protection and conservation of environment.
- Public Campaigns: There should be public campaigns by the environmentalists against the companies which do not adhere to environmental standards and should refrain from purchasing any product manufactured by them.
- Increase in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): The governments around the world should increase the CSR which companies need to pay on causing harm to the environment. This will prompt them to adopt sustainable practices.
Important Facts For Prelims
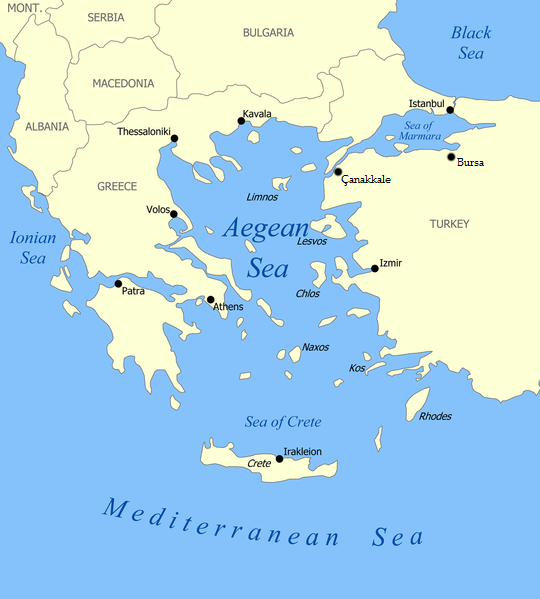
Aegean Sea
Why in News?
Recently, Turkish President warned Greece to demilitarize islands in the Aegean Sea.
What is the Dispute?
- Turkey’s Stand:
- Turkey says Greece has been building a military presence in violation of treaties that guarantee the unarmed status of the Aegean islands.
- It argues the islands were ceded to Greece on the condition they remained demilitarised.
- Turkey says Greece has been building a military presence in violation of treaties that guarantee the unarmed status of the Aegean islands.
- Greece Stand:
- Greece maintains Turkey has deliberately misinterpreted the treaties and says it has legal grounds to defend itself including a long-standing threat of war if Greece extended its territorial waters.
- Greek-Turkish differences are not presently about land, but water.
- They currently each have six nautical miles (11km) of territorial water in the Aegean.
- The UN Convention on the International Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), concluded in 1982 and ratified by 158 countries, says states may claim up to 12 miles (about 20km).
- Related Treaty:
- Greece absorbed the islands of Limnos, Samothrace, Lesvos, Samos, Chios and Ikaria from the Ottoman Empire in the Balkan Wars of 1912-13.
- It was officially awarded sovereignty over them in the Treaty of Lausanne of 1923.
- Another treaty drawn up in London in 1914 had made Greek possession of the islands conditional on their demilitarisation.
- According to Turkey, the Lausanne Treaty makes reference to the 1914 treaty, it implies the same conditionality.
- Greece rejects that interpretation.
- Greece absorbed the islands of Limnos, Samothrace, Lesvos, Samos, Chios and Ikaria from the Ottoman Empire in the Balkan Wars of 1912-13.
What are the Key Highlights about the Aegean Sea?
- Aegean Sea an arm of the Mediterranean Sea, located between the Greek peninsula on the west and Asia Minor on the east.
- The Aegean is connected through the straits of the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmara, and the Bosporus to the Black Sea, while the island of Crete can be taken as marking its boundary on the south.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2019)
| Sea | Bordering Country | |
| 1. | Adriatic Sea | Albania |
| 2. | Black Sea | Croatia |
| 3. | Caspian Sea | Kazakhstan |
| 4. | Mediterranean Sea | Morocco |
| 5. | Red Sea | Syria |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Adriatic Sea is a part of the Mediterranean Sea positioned between the eastern coastline of Italy, and countries of the Balkan Peninsula, from Slovenia, through Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and to Albania. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- The Black Sea is an inland sea located between far southeastern Europe and the far western edges of the continent of Asia and the country of Turkey. It is bordered by Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Russia and Georgia. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- The Caspian Sea is an enclosed body of water between Asia and Europe. It is bordered by Iran, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan and Russia. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.
- There are 21 countries which border the Mediterranean Sea. These are Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Malta, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Cyprus, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco.
- Morocco’s Mediterranean coast represents the westernmost edge of the Northern African coast. The coastline features the Strait of Gibraltar that marks the link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Hence, pair 4 is correctly matched.
- There are six countries (Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti) bordering the Red Sea. Hence, pair 5 is not correctly matched. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q. Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries? (2017)
- Jordan
- Iraq
- Lebanon
- Syria
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The following countries have a coastline on the Mediterranean Sea:
- Northern shore (from west to east): Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey.
- Eastern shore (from north to south): Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt. Hence, 3 and 4 are correct.
- Southern shore (from west to east): Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt.
- Island nations: Malta, Cyprus. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Important Facts For Prelims
Biodiversity Park in Sirumalai Hills: Tamil Nadu
Why in News?
The Government of Tamil Nadu is developing a biodiversity park in the Sirumalai Hill Range in Dindigul district.
- The main aim is to create awareness for the sustainable management of the ecologically sensitive area.
What are the Key Points of this Park?
- This park is a nature reserve that harbours the natural heritage of the area and has conservation, education and cultural values and will enhance the quality of the environment.
- Various biodiversity components such as mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, etc, have been showcased here.
- Different types of flowering plants have been planted all around the park and necessary irrigation facilities have been provided.
- Assemblage of nectar plants to attract butterflies and host plants has also been planned.
What is a Biodiversity Park?
- About:
- The biodiversity park is a unique landscape of wilderness where ecological assemblages of native plant and animal species in the form of biological communities are recreated in a region.
- The underlying principle of the park is to recreate self-sustaining ecosystems with native flora and fauna which are characteristics of the area.
- Objectives:
- Creating awareness among the forest stakeholders, the public and the student community about biological diversity and its significance.
- Creating plant diversity that is endangered, threatened and highly valuable for human existence.
- Creating a gene bank with important plant species including rare and endemic ones.
- Creating a carbon sink for future generations with indigenous species to mitigate problems of global warming and climate change.
- Promoting the culture of conservation and appreciation towards natural resources and its management.
- Creating livelihood opportunities for local communities, especially the tribal community who are part and parcel of the forest ecosystem from time immemorial.
What are the Key Points Related to Sirumalai Hill Range?
- About:
- The Sirumalai Hills are spread over 60,000 acres in Dindigul District of Tamil Nadu.
- They are considered to be the spur of the Eastern Ghats. They are located about 25 kilometres from Dindigul town, at an altitude of 400 to 1,650 metres from mean sea level.
- The hills act as a repository of several rare and endemic plants.
- Flora:
- The lower hill range consists of highly disturbed scrub forest while the major portion of the middle hill ranges are occupied by tropical mixed dry deciduous forest.
- The higher elevations are occupied by semi evergreen forest. The woodland savannahs are found along the slopes in the higher altitudes.
- Fauna:
- Animals like Gaur, Leopard, spotted deer, mouse deer, barking deer, Jackal, Sloth Bear, wild boar, Indian pangolin, slender loris and several species of reptiles and avifauna (Birds) are found in the region.
Important Facts For Prelims
QS World University Ranking 2023
Why in News?
Recently, QS World University Ranking 2023 was released.
What is QS World University Rankings?
- Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) a leading global career and education network for ambitious professionals looking to further their personal and professional development.
- QS develops and successfully implements methods of comparative data collection and analysis used to highlight institutions’ strengths.
- The ‘QS World University Rankings’ is an annual publication of university rankings which comprises the global overall and subject rankings.
- Six parameters and their weightage for the evaluation:
- Academic Reputation (40%)
- Employer Reputation (10%)
- Faculty/Student Ratio (20%)
- Citations per faculty (20%)
- International Faculty Ratio (5%)
- International Student Ratio (5%)
What are Key Highlights of the Report?
- Global Rankings:
- Top Ranks:
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) of the US is the top university for the 11th consecutive year.
- The second place went to the University of Cambridge, followed by Stanford University
- Top Ranks:
- Indian Institutions:
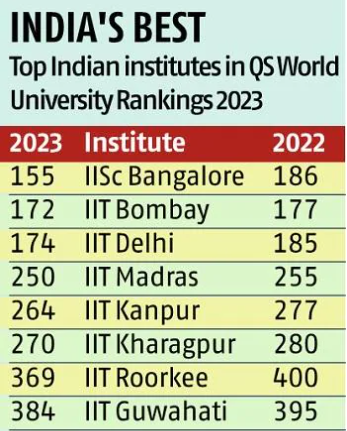
- The Indian Institute Science (IISC) was ranked highest followed by IIT Bombay and IIT Delhi. The total number of Indian institutes among the top 1,000 globally has risen to 27 from 22.
- IISc Bengaluru is the world’s top research university, achieving a perfect score of 100/100 for this metric.
- Furthermore, IISc Bengaluru is the fastest rising South Asian university among the QS World University Rankings top-200.
- Overall, Indian education institutes, 41 of which made it to the rankings, have performed poorly across many key metrics.
- For instance, 30 out of 41 ranked universities have suffered declines in the Faculty Student Ratio (FSR) indicator, with only four recording improvements.
- The report shows that India's presence in the top 500 category is also IIT-driven like other IITs around the world.
- Apart from IISc, eight IITs (Delhi, Bombay, Madras, Kanpur, Kharagpur, Roorkee, Guwahati, Indore) are ranked among the top 500 globally.
- No other Indian university, public or private, has found a place in the top 500 category globally, since the launch of the Institute of Eminence scheme.
- The Indian Institute Science (IISC) was ranked highest followed by IIT Bombay and IIT Delhi. The total number of Indian institutes among the top 1,000 globally has risen to 27 from 22.
What are the Related Indian Initiatives?
- Institutions of Eminence (IoE) Scheme:
- It is a government's scheme to provide the regulatory architecture for setting up or upgrading of 20 Institutions (10 from public sector and 10 from the private sector) as world-class teaching and research institutions called ‘Institutions of Eminence’.
- National Education Policy, 2020:
- It aims to introduce several changes in the Indian education system - from the school to college level and make India a global knowledge superpower.
- Impacting Research Innovation and Technology (IMPRINT):
- It is a first-of-its-kind Pan-IIT and IISc joint initiative to develop a new education policy and a roadmap for research to solve major engineering and technology challenges that India must address and champion to enable, empower and embolden the nation for inclusive growth and self-reliance.
- Uchhatar Avishkar Yojana (UAY):
- It was announced with a view to promote innovation of a higher order that directly impacts the needs of the Industry and thereby improves the competitive edge of Indian manufacturing.