Infographics
Indian Polity
Special Category Status
Prelims: Special category States, Gadgil formula
Mains: Benefits and issues associated with Special category status.
Why in News?
Recently, Union Finance Minister made it clear that the Centre will not consider demands for “special category status” for any state as the 14th Finance commission has clearly said no special status can be given.
- This comes as a blow to states like Odisha, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh which have been pushing for it for some years now.
What is Special Category Status (SCS)?
- About:
- SCS is a classification given by the Centre to assist development of states that face geographical and socio-economic disadvantages.
- Constitution does not make a provision for SCS and this classification was later done on the recommendations of the Fifth Finance Commission in 1969.
- Status was first accorded to Jammu and Kashmir, Assam and Nagaland in 1969.
- SCS for plan assistance was granted in the past by the National Development Council of the erstwhile Planning Commission.
- Eleven States including Assam, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Sikkim, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Uttarakhand and Telangana have been accorded the special category state status.
- Telangana, the newest State of India, was accorded the status as it was carved out of another state Andhra Pradesh.
- The 14th Finance Commission has done away with the 'special category status' for states, except for the Northeastern and three hill states.
- It suggested to fill the resource gap of such states through tax devolution by increasing it to 42% from 32%.
- SCS is different from Special status which imparts enhanced legislative and political rights, while SCS deals with only economic and financial aspects.
- For instance, J&K used to have Special status before Article 370 was repealed.
- Parameters (Based on Gadgil Formula):
- Hilly Terrain;
- Low Population Density and/or Sizeable Share of Tribal Population;
- Strategic Location along Borders with Neighbouring Countries;
- Economic and Infrastructure Backwardness; and
- Nonviable Nature of State finances.
What are the Benefits of Special Category Status?
- The Centre pays 90% of the funds required in a centrally-sponsored scheme to special category status states as against 60% or 75% in case of other states, while the remaining funds are provided by the state governments.
- Unspent money in a financial year does not lapse and is carried forward.
- Significant concessions are provided to these states in excise and customs duties, income tax and corporate tax.
- 30% of the Centre’s Gross Budget goes to Special Category states.
What are the Concerns regarding Special Category Status?
- It causes Increased burden on Central Finances.
- Also, giving special status to a state leads to demands from other states too. For instance, demands from Andhra Pradesh, Odisha and Bihar.
Conclusion
- As suggested by 14th Finance commission, tax devolution to states has been increased to 42% and the same has been continued by 15th FC (41%) too to fill the resource gap without extending SCS.


Indian Economy
49th GST Council Meeting
Prelims: GST, GST appellate Tribunal, Cess, Indirect tax, Tax Evasion.
Mains: GST, its significance and Related Issues.
Why in News?
Recently, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council in its 49th Meeting has reached consensus on the constitution of the GST Appellate Tribunal to resolve the rising number of disputes under the old indirect tax regime.
What are the Key Highlights of the GST Meeting?
- GST Appellate Tribunal:
- The council has approved the creation of a national tribunal mechanism with state benches for the redressal of disputes.
- The Tribunal will resolve the rising number of disputes under the GST regime that are now clogging High Courts and other judicial fora.
- This year’s Finance Bill can incorporate the enabling legislative provisions for the Tribunal.
- The GST Tribunal will have one principal bench in New Delhi and many benches or boards in states. The principal bench and state boards would have two technical and two judicial members each, with equal representation.
- But all four members would not sit to hear each case, which is likely to be decided based on the threshold or value of dues involved.
- Cleared Pending Compensation Dues:
- It has cleared the balance of Rs 16,982 crore (for June 2022).
- It has finalized GST compensation of Rs 16,524 crore to six states/UTs including, Delhi, Karnataka, Odisha, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana
- Lower Penal Charges:
- It approved lower penal charges for delayed filing of annual returns by businesses with a turnover of up to Rs 20 crore a year.
- The council has approved an Amnesty Scheme for taxpayers unable to file three statutory returns, that entail conditional waivers or reductions in late fees for such filings.
- The GST Amnesty Scheme was introduced to encourage non-filers to voluntarily come forward and file their GST returns by providing a one-time relief from late fees.
- Rate Changes:
- The GST rate on several items has been changed, such as pencil sharpeners, rab (liquid jaggery).
- The Council also decided to extend the GST exemption to educational institutions and central and state educational boards from conducting entrance examinations through any authority, including the National Testing Agency.
- Plugging Tax Evasion:
- The Council has decided to switch the compensation cess levied on pan masala and gutkha commodities from an ad valorem basis to a specific tax-based levy.
- The ad valorem tax is levied according to value.
- This will boost the first stage collection of the revenue.
- The Council also mandated that exports only be allowed against letters of undertaking assuring of GST compliance.
- The Council has decided to switch the compensation cess levied on pan masala and gutkha commodities from an ad valorem basis to a specific tax-based levy.
What is the GST Council?
- About:
- It is a joint forum of the Centre and the states.
- It was set up by the President as per Article 279A (1) of the amended Constitution.
- Members:
- The members of the Council include the Union Finance Minister (chairperson), the Union Minister of State (Finance) from the Centre.
- Each state can nominate a minister in-charge of finance or taxation or any other minister as a member.
- Functions:
- According to Article 279 of the Constitution, the council can make recommendations to the Union and the states on important issues related to GST, like the goods and services that may be subjected or exempted from GST, model GST Laws”.
- Article 279 as well as Article 279A of the Indian Constitution deal with the financial provisions of the country.
- They are specifically related to the calculation of “net proceeds” from Union duties and taxes on goods and the formation of the Goods and Services Tax Council, respectively.
- It also decides on various rate slabs of GST.
- For instance, an interim report by a panel of ministers has suggested imposing 28 % GST on casinos, online gaming and horse racing.
- According to Article 279 of the Constitution, the council can make recommendations to the Union and the states on important issues related to GST, like the goods and services that may be subjected or exempted from GST, model GST Laws”.
What is the Concept of Goods and Services Tax?
- About:
- GST is a value-added tax system that is levied on the supply of goods and services in an economy.
- It is a comprehensive indirect tax that was introduced in India on 1st July 2017, through the 101st Constitution Amendment Act, 2016, with the slogan of ‘One Nation One Tax’.
- The GST has subsumed indirect taxes like excise duty, Value Added Tax (VAT), service tax, luxury tax etc.
- It is essentially a consumption tax and is levied at the final consumption point.
- Tax Structure under GST:
- Central GST to cover Excise duty, Service tax etc,
- State GST to cover VAT, luxury tax etc.
- Integrated GST (IGST) to cover inter-state trade.
- IGST per se is not a tax but a system to coordinate state and union taxes.
- Under GST, Goods and services are divided into five different tax slabs for collection of tax: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%.
What are the Issues Related to GST?
- Complexity:
- The GST system in India is quite complex, with multiple tax rates, exemptions, and compliance requirements.
- It hampers the progress of a single indirect tax rate for all the goods and services in the country.
- High Tax Rates:
- Some industries and goods are subject to high GST rates, which can make them unaffordable for many consumers.
- For example, the tax rate on luxury goods and services is 28%, which is quite high.
- Though rates are rationalized, 50% of items are under the 18% bracket.
- Some industries and goods are subject to high GST rates, which can make them unaffordable for many consumers.
- Compliance Burden:
- The GST regime has a lot of compliance requirements, including filing of returns, maintaining records, and regular audits. This can be a burden for businesses, especially small and medium enterprises.
- Technical Issues:
- There have been reports of technical glitches in the GST network, leading to delays in filing returns and claiming input tax credits.
- Impact on the Unorganized Sector:
- The unorganized sector, which forms a significant part of the Indian economy, has been adversely affected by the GST.
- Many small businesses and traders have found it challenging to comply with the new tax regime.
- Lack of Clarity:
- There is still a lack of clarity on some aspects of the GST regime, such as the classification of goods and services and the applicability of tax rates. This lack of clarity can create confusion and disputes.
Way Forward
- Simplifying the compliance process, providing easier access to information, and increasing support for taxpayers can help address this issue.
- Technical issues such as system downtimes, portal errors, and other glitches can cause significant disruptions for businesses. Addressing these technical issues can help businesses comply with GST requirements more effectively.
- Many small businesses and traders are not fully aware of the GST system and its implications. Increasing awareness and education about the GST system can help improve compliance and reduce errors.
- GST is a collaborative effort between the central and state governments, and coordination between them is crucial to its success. Improving communication and coordination can help ensure a smooth implementation of the GST system.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following items: (2018)
- Cereal grains hulled
- Chicken eggs cooked
- Fish processed and canned
- Newspapers containing advertising material
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Good and Services Tax)?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Q2. What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Explain the rationale behind the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act of 2017. How has COVID-19 impacted the GST compensation fund and created new federal tensions? (2020)
Q. Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on the revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017. (2019)
Q. Explain the salient features of the Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act, 2016. Do you think it is efficacious enough “to remove cascading effect of taxes and provide for common national market for goods and services”? (2017)
Q. Discuss the rationale for introducing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Bring out critically the reasons for the delay in roll out for its regime. (2013)


Indian Economy
Stock Market Regulation
Prelims: Stock Market Regulation, SC, SEBI, SCRA, Free-Market Economy, BSE, NSE.
Mains: Stock Market Regulation and Safeguards against Frauds.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court asked the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the government to produce the existing regulatory framework in place to protect investors from Stock Market volatility.
What is the Stock Market?
- About:
- Stock markets are venues where buyers and sellers meet to exchange equity shares of public corporations.
- Stock markets are components of a Free-Market economy because they enable democratized access to investor trading and exchange of capital.
- A free-market economy is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand, without interference from government regulation.
- India has two stock exchanges – the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE).
- SEBI is the regulator of the securities market in India. They set the legal framework and regulate all entities interested in operating in the market.
- The SCRA (Securities Contracts Regulation Act) has empowered SEBI to recognise and regulate stock exchanges and later commodity exchanges in India; this was earlier done by the Union government.
- Laws for Regulation:
- Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (SEBI Act):
- The SEBI Act empowers SEBI to protect the interests of investors and to promote the development of the capital/securities market, besides regulating it.
- It sets out the functions and powers of SEBI and establishes its structure and management.
- Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 (SCRA):
- This law provides the legal framework for the regulation of securities contracts in India.
- It covers the listing and trading of securities, the registration and regulation of stockbrokers and sub-brokers, and the prohibition of insider trading.
- Companies Act, 2013:
- This law regulates the incorporation, management, and governance of companies in India.
- It also sets out the rules for the issue and transfer of securities by companies.
- Depositories Act, 1996:
- This law provides for the regulation and supervision of depositories in India. It sets out the procedures for the dematerialization and transfer of securities held in electronic form.
- Insider Trading Regulations, 2015:
- These regulations prohibit insider trading in securities listed on Indian stock exchanges. They prescribe the code of conduct for insiders, the procedures for disclosures, and the penalties for violations.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (SEBI Act):
What is the Role of SEBI at Curbing Market Volatility?
- While SEBI does not interfere to prevent market volatility, exchanges have circuit filters — upper and lower — to prevent excessive volatility.
- But SEBI can issue directions to those who are associated with the market, and has powers to regulate trading and settlement on stock exchanges.
- Using these powers, SEBI can direct stock exchanges to stop trading, totally or selectively.
- It can also prohibit entities or persons from buying, selling or dealing in securities, from raising funds from the market and being associated with intermediaries or listed companies.
What are the Safeguards Against Fraud?
- SEBI notified the Prohibition of Fraudulent and Unfair Trade Practices Regulations in 1995 and the Prohibition of Insider Trading Regulations in 1992 to prevent the two key forms of fraud, market manipulation, and insider trading.
- These regulations define a species of fraud, who is an insider and prohibit such fraudulent activity and provide for penalties including disgorgement of ill-gotten gains.
- Violations of these regulations are predicate offenses that can lead to a deemed violation of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act 2002.
- SEBI has notified the Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers Regulations to ensure that acquisitions and changes of management are done only after giving an opportunity to public shareholders to exit the company if they want to.
- Appeals against orders of SEBI and the stock exchanges can be made to the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) comprising three members.
- Appeals from the SAT can be made to the Supreme Court.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is issued by registered foreign portfolio investors to overseas investors who want to be part of the Indian stock market without registering themselves directly? (2019)
(a) Certificate of Deposit
(b) Commercial Paper
(c) Promissory Note
(d) Participatory Note
Ans: (d)


Science & Technology
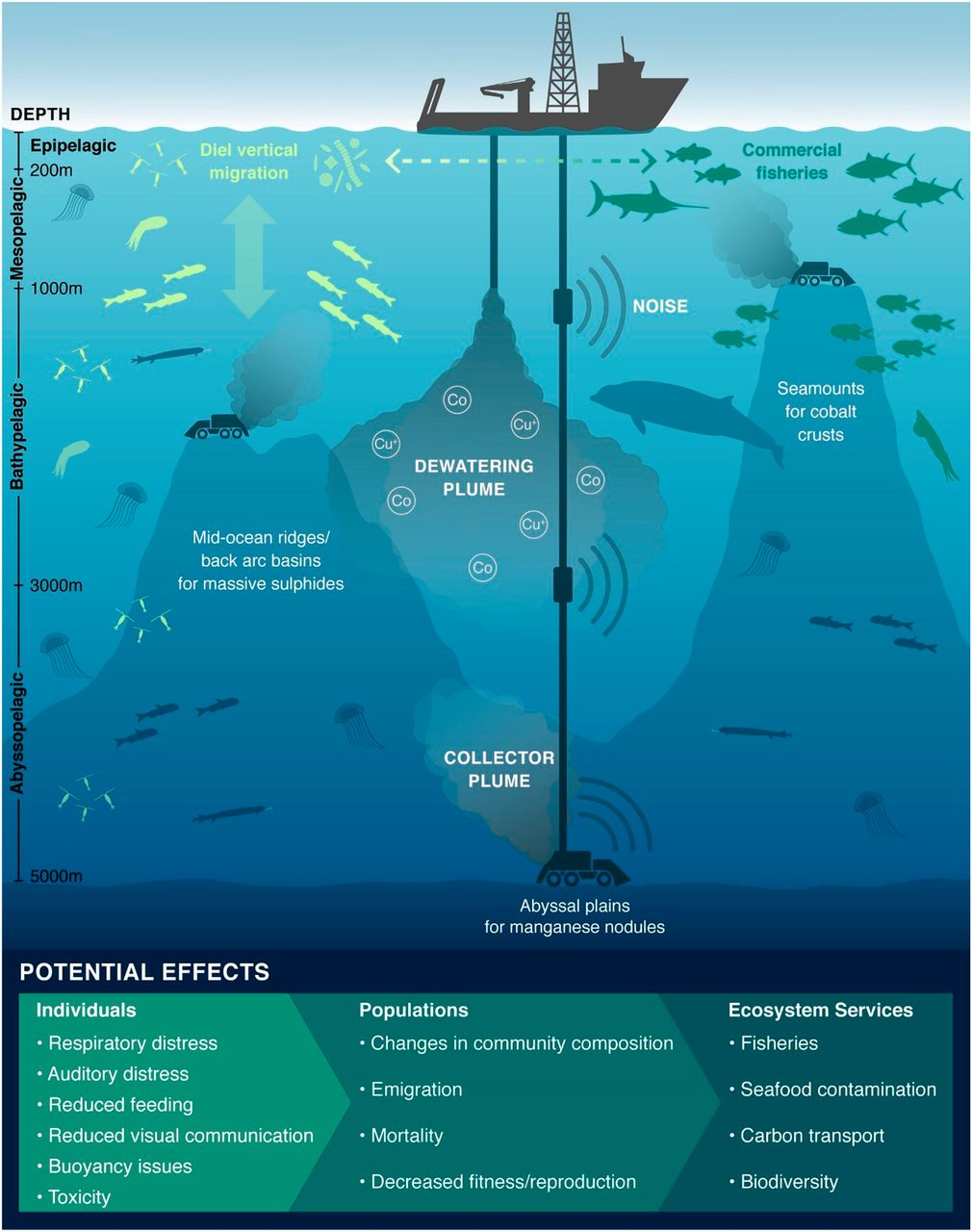
Deep Sea Mining and its Threats
Prelims: Deep Sea mining, UNCLOS, Frontiers in Marine Science report, Deep Sea mission
Mains: Deep-Sea mining and its Impacts.
Why in News?
Recently, a study suggested that commercial-scale Deep seabed mining operations can potentially harm the oceans and endangered species, such as cetaceans including blue whales and several dolphin species.
- The evaluation emphasizes the need for continued conservation efforts to protect these species.
What is Deep Sea Mining?
- About:
- Deep-sea mining is the process of retrieving mineral deposits from the deep seabed the ocean below 200 metres and covers two-thirds of the total seafloor.
- According to International Seabed Authority (ISA), an agency under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) for monitoring all activities related to mineral resources in the deep sea, the international seabed is the area that lies beyond the limits of national jurisdiction and represents around 50% of the total area of the world’s oceans.
- ISA has issued 32 contracts to explore deep sea mineral deposits. More than 1.5 million square kilometres of the international seabed have been set aside for mineral exploration.
- Governance:
- ISA is required by UNCLOS to put in place the governance infrastructure including rules, regulations and procedures governing the contours of deep-sea mining within 2 years.
- In case of failure, the ISA must at least evaluate the mining proposal by the end of two years.
- The 11th Annual Deep Sea Mining Summit 2023 is to be held in London, United Kingdom. Agenda includes the “economic landscape and growth for deep sea mining and technological developments associated with commercialising”.
- Reasons for Growing Interest:
- Depleting Terrestrial Deposits: Depleting stocks of metals such as copper, nickel, aluminium, manganese, zinc, lithium and cobalt caused shift in focus towards Deep Sea Deposits.
- Mineral resources are extracted from Polymetallic nodules found in various deep ocean regions including deep pacific and Indian oceans.
- The nodules are approximately potato-sized and sit on the sediment surface across abyssal plains in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), a region spanning 5,000 kilometres (3,100 miles) across the central Pacific Ocean at depths of 4,000 - 5,500 metres.
- Increasing Demand: Demand for these metals is also increasing to produce smartphones, wind turbines, solar panels and batteries.
- Depleting Terrestrial Deposits: Depleting stocks of metals such as copper, nickel, aluminium, manganese, zinc, lithium and cobalt caused shift in focus towards Deep Sea Deposits.
What are the Cetaceans?
- Cetaceans are exclusively aquatic placental mammals (including Whales, Dolphins, Porpoises, etc.) constituting the order Cetacea. They are found in oceans worldwide and in some freshwater environments.
- They have a tapered body, no external hind limbs, and a tail ending in a horizontal blade of two lobes, or flukes.
- Cetaceans must come to the water’s surface to breathe through blowholes located on top of their head.
What are the Threats?
- Commercial-scale mining is expected to operate 24 hours a day, causing noise pollution.
- It can overlap with the frequencies at which cetaceans communicate, which can cause auditory masking and behaviour change in marine mammals.
- Settlement of sediment plumes generated by mining vehicles could harm/kill the species at the bottom of the ocean (benthic species) in the vicinity.
- Sediment discharged from processing vessels can also increase turbidity in the water column. Also, far from sight impacts could go largely unquantified.
What is India’s Deep Ocean Mission?
- Deep Ocean Mission seeks to develop the technologies required for exploring and then, extracting minerals in the deep seabed.
- Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) will be the nodal Ministry implementing this multi-institutional ambitious mission.
- It would develop a manned submersible (MATSYA 6000) that can carry three people to a depth of 6,000 meters in the ocean with a suite of scientific sensors and tools.
- It will pursue technological innovations for exploration and conservation of deep-sea biodiversity through "bioprospecting of deep-sea flora and fauna and studies on sustainable utilization of deep-sea bio-resources.
- The mission will seek to explore the prospects of deriving energy and freshwater from the ocean through "studies and detailed engineering design for offshore ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC)-powered desalination plants.
What are other Blue Economy Initiatives?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ) nation
Prelims
Q1. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC) is a regional cooperation initiative of the Indian Ocean Rim countries which was established in Mauritius in March 1997 with the aim of promoting economic and technical cooperation among its members. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- IOR-ARC is the only pan-Indian ocean grouping. It has 23 Member States and 9 Dialogue Partners.
- It aims to create a platform for trade, and socio-economic and cultural cooperation in the Indian Ocean Rim area, which constitutes a population of about two billion people. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The Indian Ocean Rim is rich in strategic and precious minerals, metals and other natural resources, marine resources, and energy, all of which can be sourced from Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ), continental shelves, and the deep seabed. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2021)
- The Global Ocean Commission grants licences for seabed exploration and mining in international waters.
- India has received licences for seabed mineral exploration in international waters
- ‘Rare earth minerals’ are present on the seafloor in international waters.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
- International Seabed Authority (ISA) is a UN body set up to regulate the exploration and exploitation of marine non-living resources of oceans in international waters. It considers applications for exploration and exploitation of deep-sea resources from contractors, assesses environmental impact assessments and supervises mining activities. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- India was the first country to receive the status of a ‘Pioneer Investor’ in 1987 and was given an area of about 1.5 lakh sq. km in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB) for nodule exploration. India’s exclusive rights to explore polymetallic nodules from seabed in the Central Indian Ocean Basin was extended in 2017 for five years. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Rare earth minerals are present on the seafloor in international waters. The sea floor of various oceans boasts one of the world’s largest untapped collections of rare-earth minerals. Hence, statement 3 is correct. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Critically evaluate the various resources of the oceans which can be harnessed to meet the resource crisis in the world. (2014)


Governance
Odisha’s Initiative to Curb Child Marriage
For Prelims: Advika, Prevention of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill 2021
For Mains: Major Developments in Minimum Marriageable Age in India, Associated Issues with Child Marriage.
Why in News?
Odisha has been taking a long-term approach to bring about social and behavioral change regarding child marriage over the past 4-5 years.
- Odisha recorded an overall decline in the prevalence of child marriage: from 21.3% in National Family Health Survey-4 to 20.5% in NFHS-5.
How Odisha is Tackling the Problem of Child Marriage?
- The state has implemented a multi-pronged approach to tackle child marriage, including tracking the absence of girls in schools and villages, counseling, and using a platform called "Advika" to link all schemes targeting girls aged 10 to 19 years.
- It has issued guidelines to declare villages child-marriage-free and there are also monetary incentives for particularly vulnerable tribal groups.
- The approaches to prevent child marriages differ from district to district, with some maintaining a database of adolescent girls and others making the production of Aadhaar number mandatory in all marriages.
- Various districts have come up with their own ways of tackling the problem, such as weaving a Kathak performance into a local celebration to raise awareness about child marriage.
- The emphasis is on engaging with the community, especially girls in the age group of 15 to 18 who are dropouts, and retaining them in educational institutions.
- The Odisha police have also been involved in the effort, conducting monthly meetings in the community to discuss dropping out from school and child marriages with representatives of the panchayat, parents, and children.
- Police stations have been made child-friendly so that girls would feel empowered to approach the police.
- Various community leaders of different caste, tribe, and religious groups have been roped in to build awareness about child marriages.
What are the Major Developments in Minimum Marriageable Age in India?
- At the time of India’s independence, the minimum marriageable age stood at 15 years for females and 18 years for men.
- In 1978, the government increased it to 18 for girls and 21 for men.
- The Law Commission Report of 2008, on reforming family law, recommended a uniform age of marriage for boys and girls at 18 years and not 21.
- In 2021, the Central government sought to introduce the Prevention of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill 2021, to raise the manageable age for women across all religions, from 18 to 21 years.
- The proposed law will apply to all communities in the country and, once enacted, will supersede existing marriage and personal laws.
What are the Associated Issues with Child Marriage?
- Health Complications During Childbirth: Child brides are often not physically mature enough to safely carry and deliver a child, leading to a higher risk of health complications for both the mother and child.
- Interrupted Education: Marriage often interrupts a girl's education, which can limit her future opportunities and perpetuate the cycle of poverty.
- Limited Economic Opportunities: Child brides often have limited opportunities to pursue a career or earn a living, which can leave them financially dependent on their husband and vulnerable to abuse.
- Domestic Violence: Child brides are more likely to experience domestic violence from their husbands, who may view them as subservient and less deserving of respect than older wives.
- Child marriage also have a significant impact on a girl's mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
Way Forward
- Leveraging Technology: Technology can be used to raise awareness about the harms of child marriage and to provide education and support to girls at risk of child marriage.
- For example, mobile apps can be developed that provide information on legal rights, health, and education, and enable girls to connect with support networks.
- Involving Religious and Community Leaders: Religious and community leaders can play a key role in ending child marriage.
- They can be encouraged to speak out against child marriage, and to use their influence to promote education, gender equality, and women's empowerment.
- Focus on the Success Stories: While it is important to raise awareness about the harms of child marriage, it is also important to focus on the positive.
- This means celebrating successful programs and initiatives that have helped to reduce the incidence of child marriage, and highlighting positive stories of girls who have been able to break free from the cycle of poverty and discrimination through education and empowerment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016).


Important Facts For Prelims
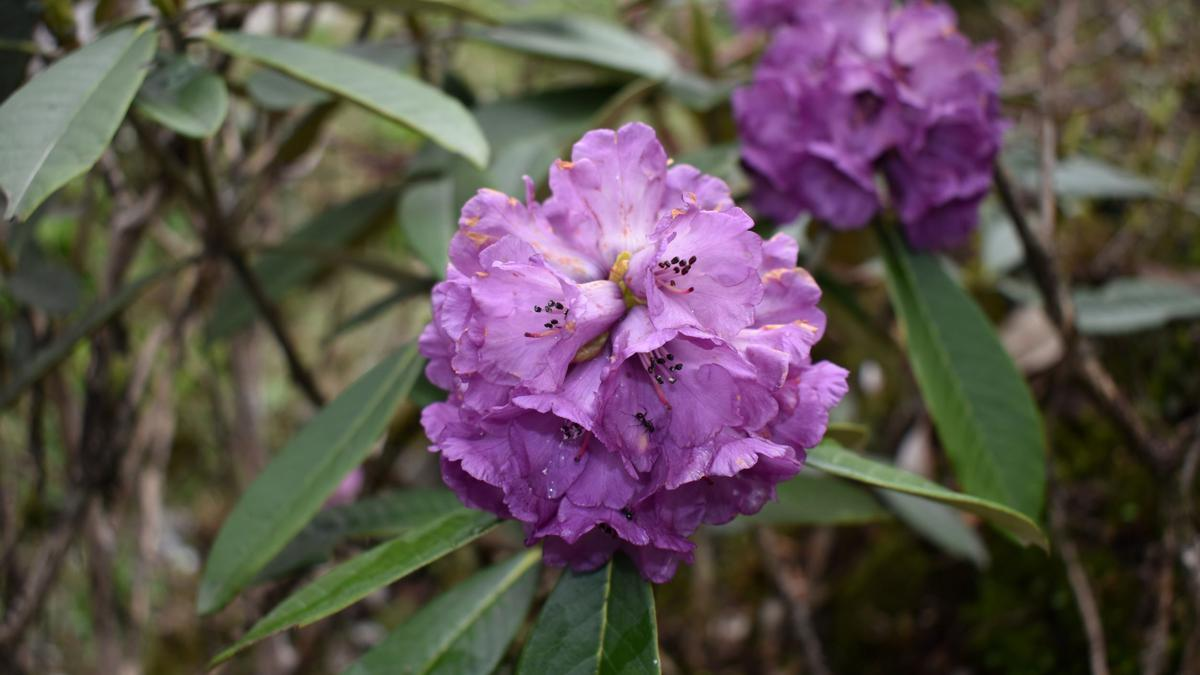
Rhododendron
Why in News?
Recently, the Botanical Survey of India has published a new report titled 'Rhododendrons of Sikkim and Darjeeling Himalaya- An Illustrated Account', which lists 45 taxa of rhododendrons.
What is Rhododendron?
- Rhododendron is a genus of flowering plants that includes about 1,000 species, primarily native to the temperate regions of Asia, North America, and Europe, as well as to the tropical regions of southeast Asia and northern Australia.
- They are known for their showy clusters of large, brightly coloured flowers, and many species are popular ornamental plants in gardens and parks.
- Rhododendrons are evergreen or deciduous shrubs or small trees, with woody stems and broad, leathery leaves.
- In India, Pink Rhododendron is the state flower of Himachal Pradesh, while Rhododendron arboreum is the state flower of Nagaland and the official State Tree of Uttarakhand.
What are the Major Highlights of the Report?
- The report reveals that the Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalayas are home to more than one-third (34%) of all rhododendron types found in India, despite the region comprising only 0.3% of India's geographical area.
- There are 132 taxa (80 species, 25 subspecies and 27 varieties) of rhododendrons found in India.
- Of the 45 taxa listed in the report, five are facing high threats due to anthropological pressures and climate change.
- Rhododendron edgeworthii, Rhododendron niveum, Rhododendron baileyi, Rhododendron lindleyi, and Rhododendron maddenii are among the threatened species.
- Rhododendron is considered an indicator species for climate change as the flowering season for rhododendrons has been found to begin as early as January for some species.


Important Facts For Prelims
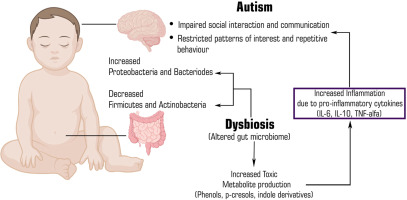
Microbiome Link to Autism
Why in News?
It is found that Gut Microbiome composition in humans implicates several diseases, including Autism, Crohn’s disease etc.
- Gut microbiome or gut microbiota, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of humans, they affect the body from birth and throughout life by controlling the digestion of food, immune system, central nervous system and other bodily processes.
What is Autism?
- About:
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is the term for a group of neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Researchers are yet to fully understand the aetiology of ASD. However, they are beginning to find that a disorder in the gut-brain axis could have a prominent part.
- Aetiology is the study of the factors that cause a condition or disease.
- It is a complex brain development disability which makes itself visible during the first 3 years of a person’s life.
- It is not mental retardation as people with autism may show excellent skills in spheres like art, music, writing etc. The level of intellectual functioning in individuals with ASDs is extremely variable, extending from profound impairment to superior levels.
- Causes:
- There are probably many factors that make a child more likely to have an ASD, including environmental and genetic factors.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), ASD affects one in 100 children.
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Children with ASD have impaired social interactions, lack verbal and nonverbal communication skills, and display restricted and repetitive behaviours.
- Cure:
- Although autism is not curable, its symptoms can be addressed with appropriate interventions like evidence-based psychosocial interventions, behavioral treatment and skills training programmes for parents and other caregivers, health promotion, care, rehabilitation services, etc.
What is the Link Between Gut Microbiome and Autism?
- The human microbiome, sometimes called the “forgotten organ”, plays a significant role in an array of host processes, including growth, development, physiology, immunity, nutrition, and disease.
- The gut microbiome is believed to have a big impact on immune modulation and metabolic activities in the human body.
- Immune modulation refers, among other things, to the efforts of the immune system to ensure its response is proportionate to a threat.
- Some scientists have disputed the significance of the gut microbiome by contending that the microbiome can’t cause ASD and therefore its role in the pathophysiology of ASD is limited.
- But research on this topic has shown that even if the gut microbiome doesn’t play a causative role, abnormalities in it can challenge a person with toxic metabolites and keep the person from synthesizing the metabolites required to produce neurotransmitters involved in cognition, behaviour, mood, and sleep.
- As a result, ‘fixing’ the gut in ASD can reduce the toxic burden, including that which moves through the blood-brain barrier, and/or help complete the necessary neurotransmitter synthesis pathways.
What are the Initiatives Related to ASD?
- United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), Sustainable Development Goals deal with rights of people with disabilities including autism.
- The Right of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 increased the types of disabilities from 7 to 21. It also added autism spectrum disorder among others, which were largely ignored in earlier Act.
- In 2014, the World Health Organisation (WHO) adopted a resolution entitled "Comprehensive and coordinated efforts for the management of ASD," which was supported by more than 60 countries.
- In 2008, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously declared 2nd April as World Autism Awareness Day.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ) nation
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of probiotics:
- Probiotics are made of both bacteria and yeast.
- The organisms in probiotics are found in foods we ingest but they do not naturally occur in our gut.
- Probiotics help in the digestion of milk sugars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Probiotics are a combination of live beneficial bacteria and/or yeasts that naturally live in your body. Bacteria is usually viewed in a negative light as something that makes you sick. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Acidophilus is a probiotic bacteria that naturally occurs in the human gut and other parts of the body.This bacteria helps the digestive system break down sugars, such as lactose, into lactic acid. Trillions of bacteria and other micro-organisms live in every person's gut. There are several ways you can take a probiotic supplement. They come in a variety of forms, including in Foods,Drinks,Capsules or pills, Powders, Liquids. Hence, statement 2 is not correct but statement 3 is correct.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Kamala Kasturi
Recently, Mrs. Kamala Kasturi passed away. She was an environmentalist who contributed to protecting the environment and was the founder of the Environment Society, Chennai. She was involved in several environmental protection projects and the campaign to save the Cauvery River from several dyeing units and take up the cleaning of the river. She had participated in several tree planting campaigns and was also a petitioner in the public interest litigation (PIL) petition against the slaughterhouse which was proposed to be constructed in Red Hills (Sengundram, Tamil Nadu).
Read More: Cauvery River & Related Disputes
Sansad Ratna Awards
The 13th edition of the Sansad Ratna award function will be held on 25th March 2023 in New Delhi. The Sansad Ratna Awards were instituted at the suggestion of Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam to honour top-performing Parliamentarians. He himself launched the first edition of the Award function in 2010 in Chennai. Till now, 90 top-performing Parliamentarians have been honoured. The 13th edition will be making history as it crosses the century of awards mark.
Read More: Parliament, Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam
Vinyl Chloride: A Threat to Human Body
Vinyl chloride, the chemical in several of the train cars that derailed and burned in East Palestine, Ohio recently can be extremely harmful to the human liver. The liver is the body's filter for removing toxicants from the blood. Specialized cells known as hepatocytes help reduce the toxicity of drugs, alcohol, caffeine and environmental chemicals and then send away the waste to be excreted.
The chemical has been shown to cause liver cancer, as well as a nonmalignant liver disease known as TASH, or toxicant-associated steatohepatitis. Vinyl chloride is used to produce Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), a hard plastic used for pipes, as well as in some packaging, coatings and wires.
India’s First Hybrid Rocket
Recently, India’s first hybrid-sounding rocket by private players was launched from Chengalpattu, Tamil Nadu. Martin Foundation, in association with Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam International Foundation and Space Zone India, launched the Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Satellite Launch Vehicle Mission- 2023.
The organisations mentioned that 5,000 students were involved in the project. The selected students designed and constructed a student satellite launch vehicle (rocket) and 150 PICO satellites (satellites at a mass below 1 kg, implemented by use of modern miniaturization techniques) research experiment cubes that contained different payloads. The rocket can be used for research in weather, atmospheric conditions and radiation.
Hybrid rocket is a bipropellant rocket engine which uses propellants that are in two different states, typically liquid and solid, which when reacted, create exhaust gases suitable for rocket propulsion.
In 2022, the Space technology startup Skyroot Aerospace also sent India’s first privately developed rocket Vikram-S. It is a single-stage spin-stabilised solid propellant rocket with a mass of approximately 545 kgs.
Read More: India’s Space Ecosystem, Vikram -S