Indian Polity
Defamation Law and Disqualification of MPs
For Prelims: Parliament, Indian Penal Code, RPA Act 1951, Supreme Court, Fundamental Rights
For Mains: Defamation Law
Why in News?
Recently, an MP (Member of Parliament) was sentenced to two years in jail in a 2019 Defamation Case over his remarks about another political leader by the Surat Court.
- The case was filed under Indian Penal Code (IPC) sections 499 and 500, dealing with defamation.
What do IPC sections 499 and 500 say?
- Section 499 of the IPC elaborates on how defamation could be through words – spoken or intended to be read, through signs, and also through visible representations.
- These can either be published or spoken about a person with the intention of damaging the reputation of that person, or with the knowledge or reason to believe that the imputation will harm his reputation.
- Section 500 stipulates imprisonment of up to two years, with or without a fine, for someone held guilty of criminal defamation.
What Is Defamation?
- About:
- Defamation is the act of communicating false statements about a person that injure the reputation of that person when observed through the eyes of an ordinary man.
- Any false and unprivileged statement published or spoken deliberately, intentionally, knowingly with the intention to damage someone's reputation is defamation.
- History of defamation can be traced in Roman law and German law. Abusive chants were capital punishment in Roman.
- Defamation Law in India:
- Article 19 of the Constitution grants freedom of speech to its citizens. However, Article 19(2) has imposed certain reasonable exemptions to this freedom such as - Contempt of Court, defamation and incitement to an offense.
- In India, defamation can both be a civil wrong and a criminal offense, depending on the objective they seek to achieve.
- A Civil Wrong sees a wrong being redressed with monetary compensation, while a criminal law seeks to punish a wrongdoer and send a message to others not to commit such acts, with a jail term.
- In a Criminal Offense, defamation has to be established beyond reasonable doubt but in a civil defamation suit, damages can be awarded based on probabilities.
- Free Speech v/s Defamation laws:
- It is argued that the defamation laws are a violation of Fundamental Rights guaranteed under Article 19 of the constitution.
- The Supreme Court has ruled that the criminal provisions of defamation are constitutionally valid and are not in conflict with the right to free speech.
- The SC has also held that it is valid to treat defamation as a public wrong and that criminal defamation is not a disproportionate restriction on free speech, because protection of reputation is a fundamental right as well as a human right.
- The Court relied on the judgments of other countries and reaffirmed the right to reputation as a part of the right to life under Article 21.
- Using the principle of ‘balancing of fundamental rights’, the court held that the right to freedom and speech and expression cannot be “allowed so much room that even reputation of an individual which is a constituent of Article 21 would have no entry into that area”.
- It is argued that the defamation laws are a violation of Fundamental Rights guaranteed under Article 19 of the constitution.
What are the Previous Defamation Judgements?
- Mahendra Ram Vs. Harnandan Prasad (1958): A letter written in Urdu was sent to the plaintiff. Therefore, he needed another person to read it to him. It was held that since the defendant knew the plaintiff does not know Urdu and he needs assistance, the act of the defendant amounted to defamation.
- Ram Jethmalani Vs. Subramanian Swamy (2006): The High Court of Delhi held Dr. Swamy for defaming Ram Jetmalani by saying that he received money from a banned organization to protect the then Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu from the case of assassination of Rajiv Gandhi.
- Shreya Singhal Vs. Union of India (2015): It is a landmark judgment regarding internet defamation. It held unconstitutional Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, 2000 which punishes for sending offensive messages through communication services.
What Happens if a Lawmaker/MP is Convicted?
- The conviction may disqualify an MP if the offense for which he is convicted is listed in Section 8(1) of the Representation of the People (RPA) Act of 1951.
- This section includes offences such as section 153A (offence of promoting enmity between different groups on ground of religion, race, place of birth, residence, language, etc., and doing acts prejudicial to maintenance of harmony) or section 171E (offence of bribery) or section 171F (offence of undue influence or personation at an election) and a few others.
- Section 8(3) of the RPA mandates that an MP can be disqualified if convicted and sentenced to at least 2 years of imprisonment.
- However, the section also states that the disqualification takes effect only “after three months have elapsed” from the date of conviction.
- Within that period, the convicted MP can file an appeal against the sentence before the High Court.
Conclusion
- Intentional acts of defamation are also punished with imprisonment which prohibits defaming a person with malice intention. The defamation law is also constitutional and is a reasonable restriction on the right to free speech and expression.
- However, it is no defamation if the acts done fall within the exceptions provided. Over the seventy-one years of Independence, there have been numerous cases of defamation and the court has interpreted each and every case with utmost care and they serve as precedents.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ):
Mains
Q. What do you understand by the concept of “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. (2014)


Social Justice
World Tuberculosis Day 2023
For Prelims: TB-free by 2025, WHO, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, World TB Report 2022, Nikshay Poshan Yojna, DBT.
For Mains: World Tuberculosis Day 2023.
Why in News?
World Tuberculosis (TB) Day is observed on 24th March every year to spread awareness about the disease and how best to combat it.
- India aims to make the nation TB-free by 2025, whereas the Global Target for TB elimination is 2030.
- Theme for 2023: Yes! We can end TB!
Why is World TB Day Observed and What is its Significance?
- On this day in 1882, Dr. Robert Koch announced the discovery of Mycobacterium tuberculosis that causes TB, and his discovery opened the way towards diagnosing and curing this disease.
- Even today TB is one of the world's deadliest infectious killers. As per WHO (World Health Organisation), every day, over 4100 people lose their lives to TB and about 28,000 people fall ill with this disease. Deaths from tuberculosis have risen in 2020 for the first time in more than a decade.
- According to the WHO, in 2020, around 9,900,000 people fell ill with TB and died, around 1,500,000. Since the year 2000, 66,000,000 lives have been saved by efforts taken globally to end TB.
- India accounts for roughly 28% of TB cases in the world, as per the Global TB Report 2022.
- Therefore, World TB Day is observed to educate people around the world about the disease TB and its impact.
What is Tuberculosis?
- About:
- Tuberculosis is an infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can practically affect any organ of the body. The most common ones are lungs, pleura (lining around the lungs), lymph nodes, intestines, spine, and brain.
- Transmission:
- It is an airborne infection that spreads through close contact with the infected, especially in densely populated spaces with poor ventilation.
- Symptoms:
- Common symptoms of active lung TB are cough with sputum and blood at times, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever and night sweats.
- Treatment:
- TB is a treatable and curable disease. It is treated with a standard 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs that are provided with information, supervision and support to the patient by a health worker or trained volunteer.
- Anti-TB medicines have been used for decades and strains that are resistant to 1 or more of the medicines have been documented in every country surveyed.
- Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful, first-line anti-TB drugs.
- MDR-TB is treatable and curable by using second-line drugs such as Bedaquiline.
- Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) is a more serious form of MDR-TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to the most effective second-line anti-TB drugs, often leaving patients without any further treatment options.
- Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful, first-line anti-TB drugs.
What are the Initiatives to Combat TB?
- Global Efforts:
- The WHO has launched a joint initiative “Find. Treat. All. #EndTB” with the Global Fund and Stop TB Partnership.
- WHO also releases the Global Tuberculosis Report.
- India’s Efforts:
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Tuberculosis Elimination (2017-2025), The Nikshay Ecosystem (National TB information system), Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY- financial support), TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign.
- Currently, two vaccines VPM (Vaccine Projekt Management) 1002 and MIP (Mycobacterium Indicus Pranii) have been developed and identified for TB, and are under Phase-3 clinical trial.
- In 2018 Nikshay Poshan Yojna was launched, which aimed to support every Tuberculosis (TB) Patient by providing a Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) of Rs 500 per month for nutritional needs.


Indian Economy
Technology and Innovation Report 2023: UNCTAD
For Prelims: United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), Technology and Innovation Report 2023, Green technologies, Electric vehicles, Green Energy Corridor, Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles, International Solar Alliance.
For Mains: Reports Released by United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, India’s Initiatives Related to Green Technologies.
Why in News?
In its Technology and Innovation Report 2023, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has stated that developed countries are benefiting more from green technologies than developing countries, and this could deepen global economic inequality.
What are the Key Findings and Recommendations of the Report?
- Findings:
- Green technologies can create a market worth USD 9.5 trillion by 2030, up from USD 1.5 trillion in 2020.
- The total exports of green technologies from developed countries jumped to more than USD 156 billion in 2021 from about USD 60 billion in 2018.
- While exports from developing countries rose to only about USD 75 billion from USD 57 billion.
- According to the ‘frontier technology readiness index’ included in the report, only a few developing countries have the capacity to take advantage of frontier technologies such as blockchain, drones, and solar power.
- Green frontier technologies such as electric vehicles, solar and wind energy, and green hydrogen are expected to reach a market value of USD 2.1 trillion in 2030.
- The frontier technology readiness index which has ranked 166 countries, is dominated by high-income economies, notably the US, Sweden, Singapore, Switzerland, and the Netherlands.
- The second quarter of the list includes emerging economies – notably Brazil - ranked at 40, China at 35, India at 46, the Russian Federation at 31, and South Africa at 56.
- Here, India remains the greatest performer by ranking at 67 positions better than expected.
- The second quarter of the list includes emerging economies – notably Brazil - ranked at 40, China at 35, India at 46, the Russian Federation at 31, and South Africa at 56.
- Green technologies can create a market worth USD 9.5 trillion by 2030, up from USD 1.5 trillion in 2020.
- Recommendations:
- UNCTAD calls on governments in developing countries to align environmental, science, technology, innovation, and industrial policies.
- It urges them to prioritise investment in greener and more complex sectors, to provide incentives to shift consumer demand towards greener goods and to boost investment in research and development.
- It recommends that international trade rules permit developing countries to protect emerging green industries through tariffs, subsidies, and public procurement, so that they not only meet local demand but also reach economies of scale that make exports more competitive.
- Lastly, UNCTAD urged developed countries to provide support to their less well-off counterparts and ensure all nations can participate and take full economic advantage of the green tech revolution.
- UNCTAD calls on governments in developing countries to align environmental, science, technology, innovation, and industrial policies.
What is the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)?
- UNCTAD is a permanent intergovernmental body of the United Nations.
- It was established in 1964 and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It aims to promote sustainable development, particularly in developing countries, through international trade, investment, finance, and technology transfer.
- UNCTAD's work focuses on four main areas: trade and development, investment and enterprise, technology and innovation, and macroeconomics and development policies.
What are India's Initiatives Related to Green Technologies?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
- It is a Public Limited Government Company.
- It is a Non-Banking Financial Company.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”. Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
India’s Traditional New Year Festivals
Why in News?
Recently, India celebrated Chaitra Sukladi, Ugadi, Gudi Padwa, Cheti Chand, Navreh and Sajibu Cheiraoba. These festivals of the spring season mark the beginning of the traditional new year in India.
What are the Traditional New Year Festivals in India?
- Chaitra Sukladi:
- It marks the beginning of the new year of the Vikram Samvat also known as the Vedic [Hindu] calendar.
- Vikram Samvat is based on the day when the emperor Vikramaditya defeated Sakas, invaded Ujjain and called for a new era.
- It is the first day during the waxing phase (in which the visible side of moon is getting bigger every night) of the moon in the Chaitra (first month of Hindu calendar).
- Gudi Padwa and Ugadi:
- These festivals are celebrated by the people in the Deccan region including Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- A famous concoction served is jaggery (sweet) and neem (bitter), called bevu-bella in the South, signifying that life brings both happiness and sorrows.
- Gudi is a doll prepared in Maharashtrian homes.
- For Ugadi, doors in homes are adorned with mango leaf decorations called toranalu or Torana in Kannada.
- Cheti Chand:
- Cheti Chand is the new year festival of the Sindhi community.
- The festival is celebrated to commemorate the birth anniversary of Jhulelal, the patron saint of the Sindhi community.
- Vaishakhi:
- It is also pronounced as Baisakhi, observed by Hindus and Sikhs.
- It commemorates the formation of Khalsa panth of warriors under Guru Gobind Singh in 1699.
- Baisakhi was also the day when colonial British empire officials committed the Jallianwala Bagh massacre at a gathering, an event influential to the Indian movement against colonial rule.
- Navreh:
- Navreh is the Kashmiri New Year's Day.
- The day is marked by performing various rituals, decorating houses with flowers, preparing traditional dishes, and offering prayers to the deities.
- Sajibu Cheiraoba:
- It is considered one of the most important festivals of Manipur.
- It is celebrated with great pomp and joy, especially by the Meiteis of the state.
- Vishu:
- It is a Hindu festival celebrated in the Indian state of Kerala, Tulu Nadu region in Karnataka, Mahé district of Union Territory of Pondicherry, neighbouring areas of Tamil Nadu and their diaspora communities.
- The festival marks the first day of Medam (falls in the middle of April in the Gregorian calendar), the 9th month in the solar calendar in Kerala.
- Puthandu:
- Also known as Puthuvarudam or Tamil New Year, is the first day of the year on the Tamil calendar and traditionally celebrated as a festival.
- The festival date is set with the solar cycle of the lunisolar Hindu calendar, as the first day of the Tamil month Chithirai.
- It therefore falls on or about 14th April every year on the Gregorian calendar.
- Bohag Bihu:
- Bohag Bihu or Rongali Bihu also called Xaat Bihu (seven Bihus) is a traditional aboriginal ethnic festival celebrated in the state of Assam and other parts of northeastern India by the indigenous ethnic groups of Assam.
- It marks the beginning of the Assamese New Year.
- It usually falls in the 2nd week of April, historically signifying the time of harvest.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Chaitra 1 of the national calendar based on the Saka Era corresponds to which one of the following dates of the Gregorian calendar in a normal year of 365 days? (2014)
(a) 22nd March (or 21st March)
(b) 15th May (or 16th May)
(c) 31st March (or 30th March)
(d) 21st April (or 20th April)
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
City Finance Rankings 2022
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has launched the ‘City Finance Rankings 2022’ under which Urban Local Bodies (ULB) in the country will be evaluated on the basis of their financial health.
What is City Finance Rankings 2022?
- About:
- All the Participating cities or ULBs will be evaluated on 15 indicators across three key municipal finance assessment parameters, namely:
- Resource Mobilization
- Expenditure Performance
- Fiscal Governance.
- The cities will be ranked at the national level based on their scores under any one of the following four population categories:
- Above 4 million
- Between 1-4 million
- 100,000 to 1 million
- Less than 100,000
- The top 3 cities in each population category will be recognized and rewarded at the national level as well as within each state/state cluster.
- All the Participating cities or ULBs will be evaluated on 15 indicators across three key municipal finance assessment parameters, namely:
- Significance:
- It will help identify areas in the financial performance of the cities where they can make further improvements.
- It will motivate city/state officials and decision-makers to implement municipal finance reforms.
- It will enable them to deliver quality infrastructure and services, and hence a good quality of life to citizens.
- At a state- and national level, the rankings will highlight the outcomes achieved by municipalities and provide critical insights to key policymakers into the state of finances of urban local bodies.


Important Facts For Prelims
QS World University Rankings by Subject-2023
Why in News?
Recently, QS World University Rankings 2023 by subject were released.
- Earlier in 2022, QS World University Ranking 2023 was released.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- About: The rankings cover 54 academic disciplines, the India universities perform well in the fields of Computer Science, Chemistry, Biological Sciences, Business Studies, and Physics.
- Global Rankings:
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) of US is ranked first followed by University of Cambridge of UK, Stanford University of US respectively.
- India’s Performance:
- Improvement:
- Led by its Institutes of Eminence (IoE), India has improved its position in the QS World University Rankings by Subject, with 44 courses, in their respective subject categories, offered in the country’s higher educational institutes ranked among the global top 100.
- Top Performing Institutions:
- Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Science (in dentistry programme) - best performer among Indian institutes obtaining the 13th rank globally
- IIT-Kanpur (Electrical engineering, ranked 87th), featuring in the top 100 categories for the first time
- IIT-Madras (in Petroleum Engineering, ranked 21st )
- IIT-Bombay (Mathematic, ranked 92nd)
- IIT-Delhi (Electrical engineering, ranked 49th)
- Jawaharlal Nehru University (Sociology, ranked 68th)
- Comparison:
- India is the second-most improved nation in Asia with its overall performance improving by 17.2% year on year, after Mainland China which improved by 21.9%.
- Improvement:
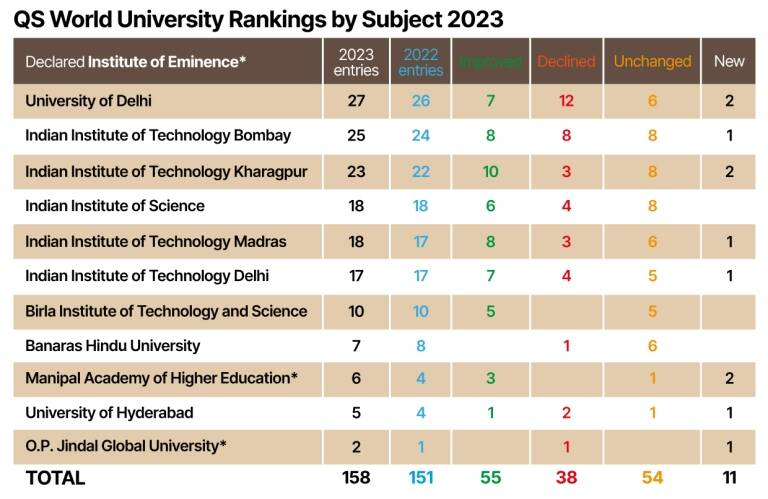
What is QS World University Rankings by Subject?
- QS is the world’s leading provider of services, analytics, and insight to the global higher education sector.
- The QS World University Rankings by Subject are compiled annually to help prospective students identify the leading universities in a particular subject.
- This year’s rankings include three new subjects: data science, history of art, and marketing.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Sarus Crane
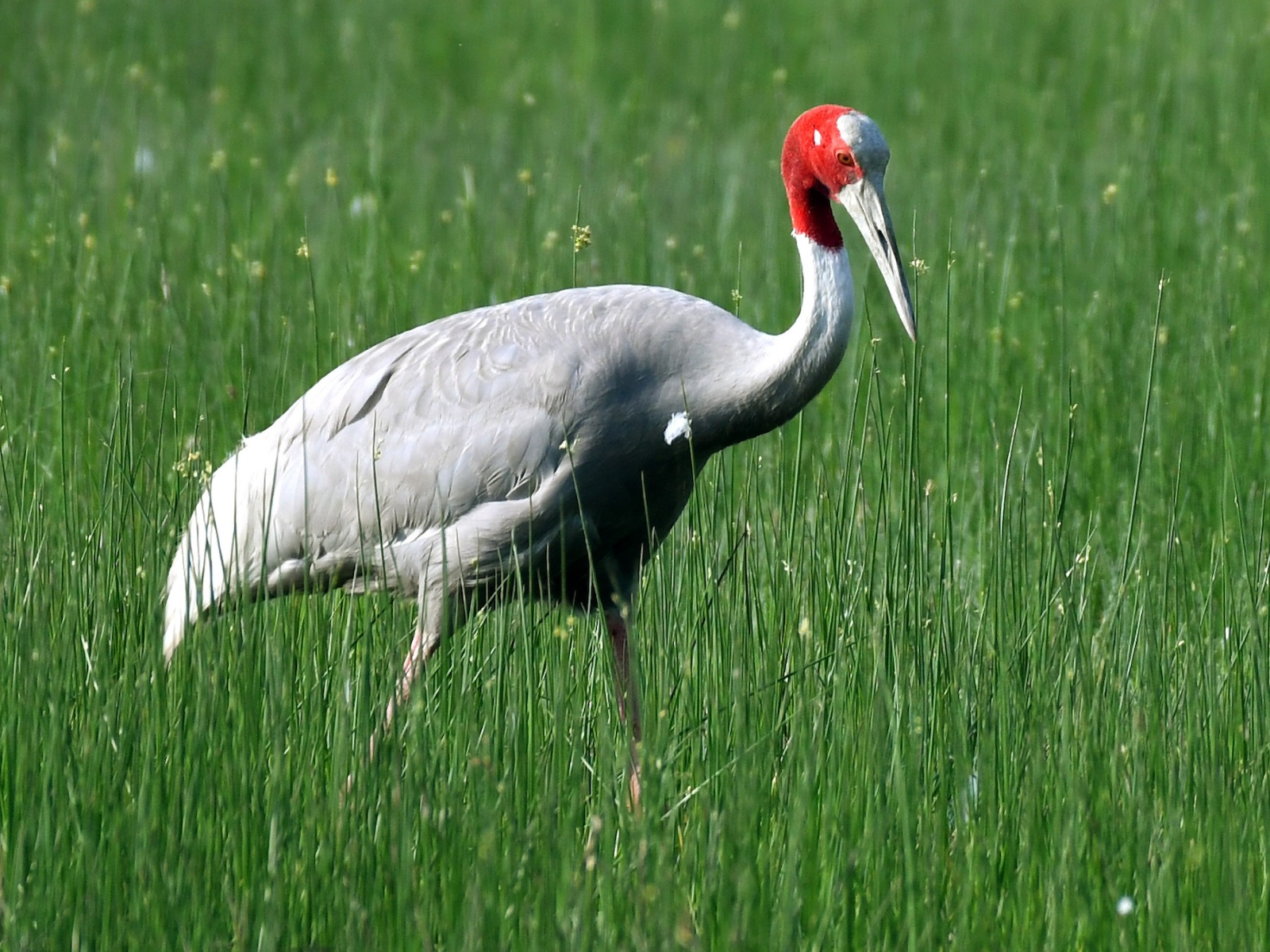
Recently, Sarus Crane, Uttar Pradesh's state bird, was recently rescued and transported to Raebareli's Samaspur Bird Sanctuary. A day after the bird was taken to the sanctuary, it was claimed that the bird was missing.
The scientific name of Sarus Crane is Grus Antigone. It is the tallest flying bird in the world, standing 152-156 cm tall with a wingspan of 240cm. The Sarus crane has predominantly grey plumage with a naked red head and upper neck and pale red legs. It is known to mate for life with a single partner, and its breeding season coincides with heavy rains during the monsoon season.
The sarus crane is listed in Schedule IV of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, and it is predominantly found in India, Southeast Asia, and Australia.
Read more: Sarus Crane
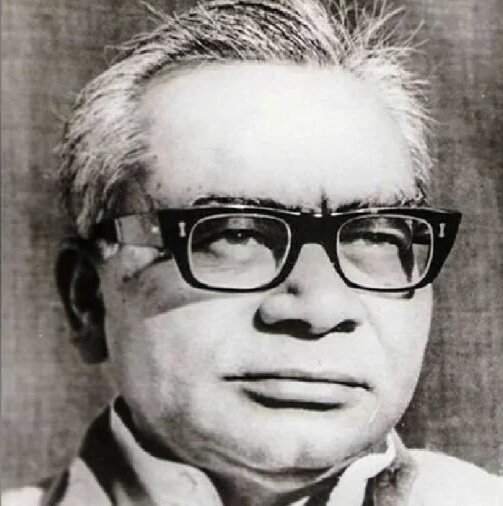
Ram Manohar Lohia
The Prime Minister paid tribute to Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia on his birthday (March 23, 1910 – October 12, 1967).
Ram Manohar Lohia was a prominent figure in socialist politics and in the movement towards Indian independence. He was a committed supporter of Mahatma Gandhi's non-violent struggle against British rule and participated in the Quit India movement in 1942.
Lohia's early political career began with the Congress Party, where he held the position of secretary of the Foreign Department of the All-India Congress Committee (A.I.C.C.), the Congress Party's highest body.
In 1963 Lohia became a member of the Lok Sabha after a by-election in Farrukhabad (Lok Sabha constituency). He also won the Lok Sabha general election of 1967 from Kannauj (Lok Sabha constituency) but died a few months later.
Read more: Ram Manohar Lohia
Lingayats, Vokkaligas’ Share in Reservation
The Karnataka High Court removed a stay imposed on the state government’s order to create new subgroups of Other Backward Classes (OBC) reservation for the dominant Lingayat and Vokkaliga castes in the state. The removal of the stay was allowed by a division bench headed by Chief Justice P B Varale. At present, the reservation of Lingayat and Vokkaliga castes stands in Category III (B) with 5% reservation and in Category III (A) with 4% reservation respectively.
The Panchamasalis, which is the largest sub-sect within the Lingayats have been demanding their inclusion under the OBC 2A Category to avail of the 15% quota in government jobs and educational institutions.
As per the proposed recommendations, the dominant Vokkaligas and the Lingayats will be identified under the new OBC categories (2C and 2D) and by allotting to them 6% of the 10% Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) quota created by the Centre.
Read more: Vokkaligas, Lingayats share in Reservation.
Exercise Konkan 2023
The Annual Bilateral Maritime Exercise Konkan 2023 was a joint maritime exercise conducted between the Indian Navy and the Royal Navy of Britain. The annual military drill was held from 20 to 22 March-2023 off the Konkan coast in the Arabian Sea.
The Konkan exercise series began in 2004. The exercise exhibited op-readiness, enhanced interoperability, and conducted joint operations. Participating ships included INS Trishul (Indian Navy), HMS Lancaster (Royal Navy) and Type 23 guided missile frigate.
The exercises covered all domains of maritime operations, air, surface and sub-surface, and included gunnery shoots on surface inflatable target ‘Killer Tomato', helicopter operations, anti-air and anti-submarine warfare drills, Visit Board Search and Seizure (VBSS), ship manoeuvres and exchange of personnel.
Other military exercises of India and the UK include - Konkan Shakti 2021 (first-ever tri-services joint exercise), Exercise Indradhanush (joint air force exercise), Exercise Ajeya Warrior (joint military exercise between India’s & UK’s soldiers)
Read more: India – UK Relations








