Governance
10 Years of Skill India Mission
For Prelims: Skill India Mission, SANKALP Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0), Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme, National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF), PM JANMAN, Understanding of Lifelong Learning for All in Society (ULLAS)
For Mains: Key Achievements and Challenges Related to Skill India Mission, Key Initiatives Related to Skill Development in India, Emerging Sectors where India can Prioritize Skilling Efforts
Why in News?
The Skill India Mission launched on 15th July 2015 (World Youth Skills Day) has completed 10 years in 2025, marking a decade of efforts to empower India's youth with job-ready skills.
Note:
- World Youth Skills Day, declared by the United Nations General Assembly’s (UNGA) in 2014, is celebrated annually on 15th July to emphasise the strategic importance of skilling youth.
- The 2025 theme focuses on empowering youth through Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital skills.
What is the Skill India Mission?
- About: The scheme is designed to skill, reskill, and upskill India's youth by offering industry-relevant training through a vast network of centers and programs, addressing the increasing demand for employability, entrepreneurship, and quality job opportunities.
- Over 6 crore individuals have been trained under various schemes, including in emerging sectors like artificial intelligence, robotics, green energy, and Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Restructured Skill India Mission (2022–26): In February 2025, the restructured Skill India Mission was approved for 2022-23 to 2025-26, merging Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0), Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme into a single Central Sector Scheme.
- Key Features: All the courses and certifications under the Skill India Program are aligned with the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF) and integrated with DigiLocker & National Credit Framework (NCrF).
What are the Key Initiatives Launched Under Skill India Mission?
|
Scheme |
About & Objectives |
Achievements |
|
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): |
PMKVY, launched on 15th July 2015 under the Skill India Mission, aims to provide free, short-term, quality-assured skill training to enhance the employability of youth. Phases:
|
As of July 2025, over 1.63 crore candidates have been trained across sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, IT, and construction.
|
|
Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme: |
JSS is a community-based vocational training programme for non-literates, neo-literates, and school dropouts.
|
Over 26 lakh individuals trained between FY 2018–19 and 2023–24. |
|
Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS): |
PM-NAPS aims to boost apprenticeship training by providing 25% stipend support Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) for individuals aged 14–35 years. |
As of May 2025, over 43.47 lakh apprentices have been engaged across 36 States/UTs. |
Skill Development Schemes in India
- Rural Self Employment and Training Institutes (RSETIs): These are bank-led residential training centres providing entrepreneurship development to rural youth.
- As of June 2025, over 5.67 million candidates have been trained, significantly rising from 2.29 million in FY 2016–17.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY): Launched under NRLM in 2014, it targets rural youth unemployment through demand-driven, placement-linked skill training, ensuring wage employment and inclusive rural development.
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana: Launched on 17th September 2023, this scheme supports traditional artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 identified trades (e.g., carpenter, potter, blacksmith). It provides toolkits, digital incentives, collateral-free credit, and market linkage support.
- Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH): A tech-driven platform enabling Aadhaar-based verification, real-time monitoring of skilling outcomes, and integration with education and entrepreneurship ecosystems.
- Centres of Excellence at NSTIs: Launched in 2025 at Hyderabad and Chennai, these centres focus on advanced instructor training and skilling in AI, robotics, and green technologies, boosting national skilling capacity.
|
Click Here to Read: Key Issues Associated with India’s Skilling Initiatives Click Here to Read: Strategic Measures to Reform India’s Skilling Ecosystem |
Conclusion
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) has been a key pillar of India’s skilling ecosystem, promoting inclusivity, industry-relevance, and future-readiness. As India advances toward a knowledge-based economy, alignment of skill development with digital governance, demand-driven training, and demographic dividend utilization will be critical for sustained growth and employment generation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Despite multiple initiatives, skill development in India often lacks industry linkage and regional balance. Examine the causes and suggest corrective steps. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? (2016)


Biodiversity & Environment
Just Transition in the Global Plastics Treaty
For Prelims: Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee, India Plastics Pact, Project REPLAN , GoLitter Partnerships Project
For Mains: Just Transition, Environmental Governance and Multilateral Agreements, Inclusive Development and Vulnerable Sections
Why in News?
The negotiations for the Global Plastics Treaty initiated under the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) resolution 5/14 (March 2022), have brought attention to the need for a Just Transition ensuring that efforts to end plastic pollution are both environmentally sustainable and socially fair.
- Part one of the 5th session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-5.1) on plastic pollution held in Busan (2024) emphasized the need for stronger legal recognition and protections for informal waste workers and other vulnerable communities.
Note: The INC, set up by United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) under the UNEA resolution 5/14, is tasked with creating a legally binding treaty to tackle plastic pollution across its full life cycle.
- INC-1 was held in Uruguay (2022), INC-2 in Paris (2023), INC-3 in Nairobi (2023), INC-4 in Ottawa (2024), and INC-5.1 in Busan (2024). INC-5.2 is scheduled for Geneva (August 2025).
Why is the Inclusion of 'Just Transition' Critical in the Global Plastics Treaty?
- Ensuring Fairness, and Inclusivity: A just transition ensures fairness and inclusivity in the shift to low-carbon, sustainable economies by protecting workers and vulnerable communities. It seeks to avoid creating new injustices while trying to fix existing ones.
- It promotes green jobs, retraining, and social protection, especially for informal waste workers.
- Protecting Workers in Transition to a Plastic-Free Economy: Workers across the value chain (from production to disposal) are at risk of exclusion or economic displacement as countries move towards banning plastics and promoting sustainable alternatives.
- Informal waste pickers contribute significantly to plastic recycling (often over 50% of urban waste recovery in developing nations), yet lack recognition and legal protection.
- Gaps in the Draft Treaty on Just Transition: The draft Global Plastics Treaty recognizes waste pickers' contributions but lacks binding protections.
- It fails to define their roles in informal sectors, and Articles 8 and 9 of the Treaty merely encourage inclusion without mandating obligations, excluding informal workers from engagement. Article 11 lacks financial support for just transition programs.
- A 'Just Transition' ensures waste pickers are not marginalized in the shift to sustainability. Without binding protections, they risk economic displacement. A clear framework is essential for their inclusion, social protection, and retraining for greener jobs.
Where do Countries Stand on Just Transition in the Global Plastics Treaty?
- India: It agrees with Just Transition provisions but stresses that implementation should align with national regulations and local contexts.
- At INC-5.1 in Busan, India called for a clear scope for the Global Plastics Treaty. It urged avoiding overlaps with existing agreements like the Basel, Rotterdam, and Stockholm Conventions or the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- India also stressed the treaty must follow Rio Declaration (1992) principles, especially common but differentiated responsibilities, national priorities, and the right to development for developing countries.
- European Union (EU): Advocates for safe working conditions and legal recognition of informal workers, emphasizing fair conditions across the plastics lifecycle.
- Pacific Small Island Developing States (PSIDS): Proposes inclusion of indigenous people and local communities in the Just Transition process, recognizing their vulnerability to environmental degradation.
- US and African Group: Both support existing provisions, with an emphasis on involving children, youth, and waste pickers. The African Group has reservations on the legal recognition of informal workers.
- Iran: Calls for financing, technology transfer, and capacity-building, but disagrees on terms like 'vulnerable groups' and 'workers' and resists legal recognition of waste management cooperatives.
Global Plastic Pollution
- According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature, over 460 million tonnes of plastic is produced yearly, with 20 million tonnes leaking into the environment, threatening ecosystems, biodiversity, and the climate.
- In 2019, macro-plastics made up 88% of the 20 million tonnes of plastic leaking into the environment, mostly from single-use items like bags, bottles, and cups.
Plastic Pollution in India
- Plastic Pollution: According to the UN Development Programme (UNDP), India generates 9.46 million tonnes of plastic waste annually, with 40% uncollected polluting rivers, streets, and contributing 4% to national emissions.
- Rapid urbanisation and rising demand for plastic packaging are worsening the problem. Growth of e-commerce has led to more non-recyclable plastic waste.
- Waste management infrastructure is weak, with more uncontrolled dumpsites than sanitary landfills. Open burning is widespread, causing toxic emissions and health hazards. The EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) system is poorly enforced.
- According to the FICCI, India may lose USD 133 billion in material value from plastic packaging waste by 2030.
- India’s Initiatives to Curb Plastics:
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2024: Strengthen plastic waste governance by mandating annual waste assessments by local bodies, introducing a centralized registration portal, and requiring online reporting for better monitoring.
- India Plastics Pact: It unites stakeholders to cut plastic use through time-bound targets, innovation, and accountability, aligned with global circular economy principles.
- Project REPLAN (REducing PLAstic from Nature): Initiated by the Khadi and Village Industries Commission, focuses on reducing plastic waste by incorporating it into handmade paper production.
- Un-Plastic Collective: Voluntary initiative launched by the UNEP-India, CII, and WWF-India, where companies commit to time-bound actions to eliminate, reuse, and replace plastics through a circular economy approach.
What Should be the Roadmap for Operationalizing Just Transition within the Global Plastics Treaty?
- Binding Provisions: Ensure key provisions related to Just Transition should be legally binding rather than voluntary to ensure accountability.
- Ensure Just Transition references International Labour Organization (ILO) Conventions, national labour laws, and UN human rights frameworks to ensure strong enforcement and protection of workers' rights within the Global Plastics Treaty.
- Definitional Clarity and Inclusivity: Definitions must explicitly recognize informal waste workers, especially waste pickers, as critical stakeholders in plastic recovery and management.
- Legal recognition of these workers will ensure they are integrated into both national and international policy frameworks and are provided with appropriate protections.
- Institutional Mechanisms: Establish a global Just Transition Fund to support vulnerable workers and facilitate green infrastructure.
- A dedicated fund can better help retrain workers to integrate them into formal waste systems, boost circular economy efforts, and prevent rising inequality or job loss during the plastic phase-out.
- Link Just Transition to Technology Transfer and Capacity Building: Access to clean plastic management technologies should come with safeguards for affected workers. This ensures they’re not pushed out or left behind during the shift to greener alternatives.
- Support South-South collaboration on low-cost, decentralised recycling tech. Include mandatory capacity-building programs to help countries integrate informal workers into formal waste systems.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the significance of integrating 'Just Transition' into the Global Plastics Treaty. How can it address both environmental and social inequalities? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2016)
|
|
Terms sometimes seen in the news |
Their origin |
|
1. |
Annex-I Countries |
Cartagena Protocol |
|
2. |
Certified Emissions Reductions |
Nagoya Protocol |
|
3. |
Clean Development Mechanism |
Kyoto Protocol |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. In India, ‘extend producer responsibility’ was introduced as an important feature in which of the following? (2019)
(a) The Bio-medical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 1998
(b) The Recycled Plastic (Manufacturing and Usage) Rules, 1999
(c) The e-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011
(d) The Food Safety and Standard Regulations, 2011
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q: What are the impediments in disposing the huge quantities of discarded solid waste which are continuously being generated? How do we remove safely the toxic wastes that have been accumulating in our habitable environment? (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
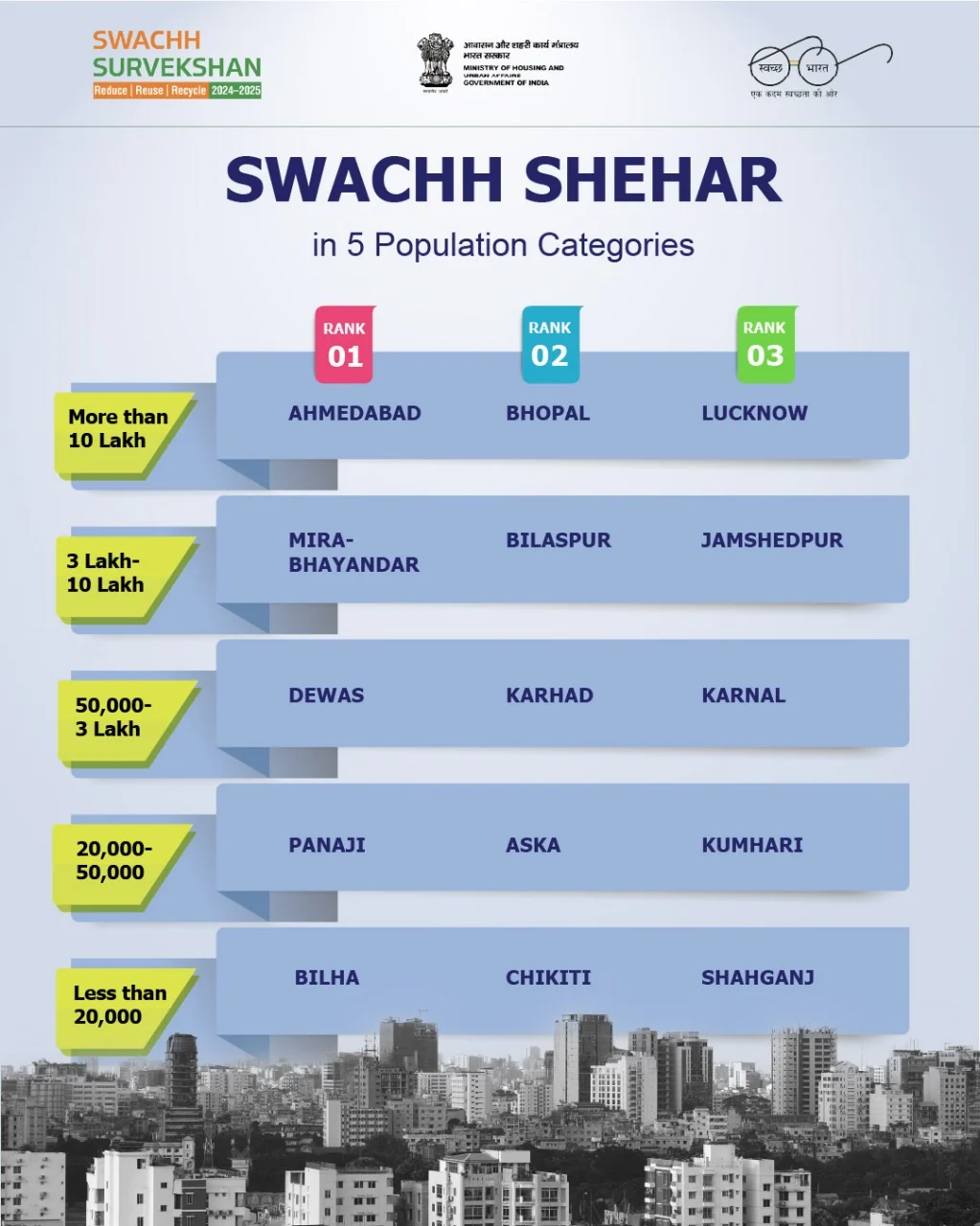
Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 Awards
Why in News?
The President of India conferred Swachh Survekshan Awards 2024-25 (9th edition) hosted by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) in New Delhi.
What are the Key Highlights of Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 Awards?
- Revamped Format & Super Swachh League: To ensure a level playing field and acknowledge consistent top performers like Indore (ranked No. 1 for 7 consecutive years), MoHUA introduced a new category- Super Swachh League (SSL) Cities.
- These SSL cities were excluded from regular rankings to promote fairness and encourage emerging cities.
- City Classification Based on Population: For the first time, city classification based on population was introduced, enabling fair comparison and targeted improvement across Urban Local Bodies (ULBs). Cities were ranked in 5 categories:
- Very Small Cities (< 20,000)
- Small Cities (20,000 – 50,000)
- Medium Cities (50,000 – 3 lakh)
- Big Cities (3 – 10 lakh)
- Million Plus Cities (> 10 lakh)
- Special Awards:
- Recognition for Special Initiative of Swachh Mahakumbh 2025: Prayagraj (for waste management during the Mahakumbh 2025)
- Cleanest Ganga Town: Prayagraj
- Safaimitra Surakshit Shehar Awards: Visakhapatnam, Jabalpur, and Gorakhpur recognized for ensuring the safety and dignity of sanitation workers.
- Cleanest Cantonment Board: Secunderabad Cantonment
- Promising Swachh Shehar of State: 35 cities across 33 States/UTs were recognized as “Promising Swachh Shehar” for their notable progress in urban sanitation.
- Key cities included Rajahmundry, Patna, Guwahati, Pimpri Chinchwad, Agra, and Bhubaneswar.
What is Swachh Survekshan under Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM)?
Swachh Survekshan
- About: Swachh Survekshan, conducted by the MoHUA since 2016, is the world’s largest urban sanitation and cleanliness survey under Swachh Bharat Mission–Urban (SBM-U).
- Swachh Survekshan Awards are annual rankings and recognitions given to cities and urban local bodies (ULBs) under the Swachh Survekshan.
- Objective: It aims to foster citizen participation, generate awareness on sanitation, and promote competitive federalism through performance benchmarking.
- Key Features:
- Launched with just 73 cities, it has expanded to cover 4,589 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in the 2024–25 edition.
- Cities are evaluated based on parameters such as waste segregation, processing, sanitation in public spaces, and citizen feedback.
- The 9th edition was conducted from April 2024 to March 2025.
- Swachh Survekshan 2025: Under the revamped framework of Swachh Survekshan 2025, indicators have been simplified and restructured into 10 comprehensive sections, with a special focus on tourist and high-footfall areas and the sanitation of public spaces.
- The annual theme for 2025 is “Reduce, Reuse, Recycle (3R)”, promoting circular economy principles in line with the Jaipur Declaration adopted at the 12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum (March 2025).
- Additionally, new indicators have been introduced for Project Grounding and City Transport Unit (CTU) transformation, along with the launch of school-level assessments to inculcate Swachhta values among the youth.
Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM)
- About: Launched on 2nd October 2014, the SBM is a nationwide cleanliness drive, divided into SBM-Gramin (under the Ministry of Jal Shakti) and SBM-Urban (under MoHUA), with funding support from the Swachh Bharat Kosh for CSR and philanthropic contributions.
- Objective: The mission’s initial goal was to make India Open Defecation Free (ODF) by 2nd October 2019, through large-scale construction of toilets and behavioral change campaigns.
- Phase-II (SBM-Gramin) was launched in 2020–21 with the aim to achieve ODF Plus status by 2024–25 through solid and liquid waste management in rural areas.
- SBM-Urban 2.0, introduced in 2021, focuses on garbage-free cities, faecal sludge and plastic waste management, greywater treatment, and capacity building to sustain urban sanitation outcomes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. As per the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 in India, which one of the following statements is correct? (2019)
(a) Waste generator has to segregate waste into five categories.
(b) The Rules are applicable to notified urban local bodies, notified towns and all industrial townships only
(c) The Rules provide for exact and elaborate criteria for the identification of sites for landfills and waste processing facilities.
(d) It is mandatory on the part of the waste generator that the waste generated in one district cannot be moved to another district.
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
Black Hole Merger
Why in News?
An international team of scientists has detected the most massive black hole merger ever observed. The event, named GW231123, was observed by the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA (LVK) collaboration, which forms the Gravitational Wave Network.
What is a Black Hole Merger?
- About: A black hole merger occurs when two black holes orbit each other and gradually move closer by emitting gravitational waves (ripples in space-time caused by some of the most violent and energetic processes in the universe).
- As they spiral inward, they eventually collide and merge into a single, larger black hole.
- These gravitational waves are detected on Earth by observatories like the LVK network of gravitational wave observatories.
- Significance of GW231123: It involved two black holes, approximately 100 and 140 times the mass of the Sun, colliding to form a single, massive black hole about 225 times the Sun's mass.
- The waves from GW231123 actually originated billions of years ago, but only reached Earth in 2025.
- This black hole merger, unlike typical stellar black holes under 60 solar masses, GW231123 is much bigger and spinning unusually fast, making the discovery even more intriguing.
- Implications: Black holes this big are typically thought to come from the collapse of huge stars. This event suggests that some may instead form through mergers of smaller black holes.
Gravitational Wave Network
- The gravitational wave network, often referred to as the LVK collaboration, is a global alliance of observatories that work together to detect gravitational waves.
- LVK:
- LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory): The first to detect gravitational waves in 2015, LIGO has two detectors located in the US.
- That historic gravitational wave detection confirmed a prediction made by Einstein (predicted their existence in his general theory of Relativity in 1916) and earned the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Virgo: Located in Italy, Virgo joined the network to increase detection accuracy and help pinpoint the location of events.
- KAGRA (Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector): A newer detector in Japan, KAGRA adds sensitivity and a broader geographic spread.
- LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory): The first to detect gravitational waves in 2015, LIGO has two detectors located in the US.
Note: India in collaboration with the US is building the third detector of LIGO, which will be known as LIGO-India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
(a) ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
(b) ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
(c) Possibility of intergalactic space travel through ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
(d) It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’
Ans: (b)
Q. What is the purpose of ‘evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (eLISA)’ project? (2017)
(a) To detect neutrinos
(b) To detect gravitational waves
(c) To detect the effectiveness of missile defence system
(d) To study the effect of solar flares on our communication systems
Ans: (b)


Rapid Fire
SC Overrides Spousal Privilege for Fair Trial
The Supreme Court, in a landmark judgment, has ruled that secretly recorded conversations between spouses are admissible as evidence in matrimonial disputes, including divorce proceedings.
- This judgment has significantly impacted the interpretation of spousal privilege in Indian law and emphasizes the balance between the right to privacy (Article 21) and the right to a fair trial.
Spousal Privilege
- Spousal privilege, as codified under Section 122 of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872, safeguards communications between married individuals.
- The law prevents one spouse from being compelled to testify against the other or disclose any communication made during the marriage, unless the other spouse consents.
- However, it is not absolute and can be waived in specific circumstances, such as in criminal and divorce cases, where the claims are supported by evidence, including electronic communication.
Right to Privacy & Fair Trial
- The court’s interpretation of Section 122 of the Evidence Act recognizes that privacy cannot be an absolute right, especially when it impedes the pursuit of justice in matrimonial matters.
- The court acknowledged the balance between privacy and the right to a fair trial. It noted that while secret recordings infringe upon privacy rights, a fair trial may require the admission of such evidence, especially when it is crucial to determining the facts.
| Read More: Right to Privacy, Supreme Court's Role in Upholding Civil Liberties |


Rapid Fire
Right to Peace Over Noise
The Madras High Court has ruled that religious gatherings, which include loud public prayers, cannot be held in residential premises without prior permission from the District Collector.
- The respondents argued they had neighbours’ consent and protection under Article 25 (freedom of religion), claiming the chants promoted peace.
- However, the court ruled that religious freedom cannot override others’ right to peace, stressing that prayer should be personal and not cause public disturbance.
- This ruling echoes an earlier Supreme Court of India judgment that prioritized the right to peace and protection from noise pollution.
- In 2005, the Supreme Court ruled that noise pollution violates Article 21, which ensures the right to life and peaceful living. It clarified that using loudspeakers, even for religious purposes, is not a fundamental right.
- The Court made it clear that it’s not about religion, but about protecting others from being a forced audience to noise.
- Article 21 ensures the right to peace, and no one has a right to create noise that disturbs others, even in their own home.
- In 2005, the Supreme Court ruled that noise pollution violates Article 21, which ensures the right to life and peaceful living. It clarified that using loudspeakers, even for religious purposes, is not a fundamental right.
- Under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, "air pollutant" includes noise if present in harmful concentrations that can harm humans, animals, plants, property, or the environment.
| Read more: Regulating Right to Freedom of Religion |


Rapid Fire
Noise Effect on Quantum Entanglement
Scientists from Raman Research Institute (RRI), IISc Bangalore, IISER Kolkata have found that quantum noise can sometimes enhance, revive, or even create entanglement, challenging earlier beliefs that it only disrupts quantum systems.
Quantum Entanglement
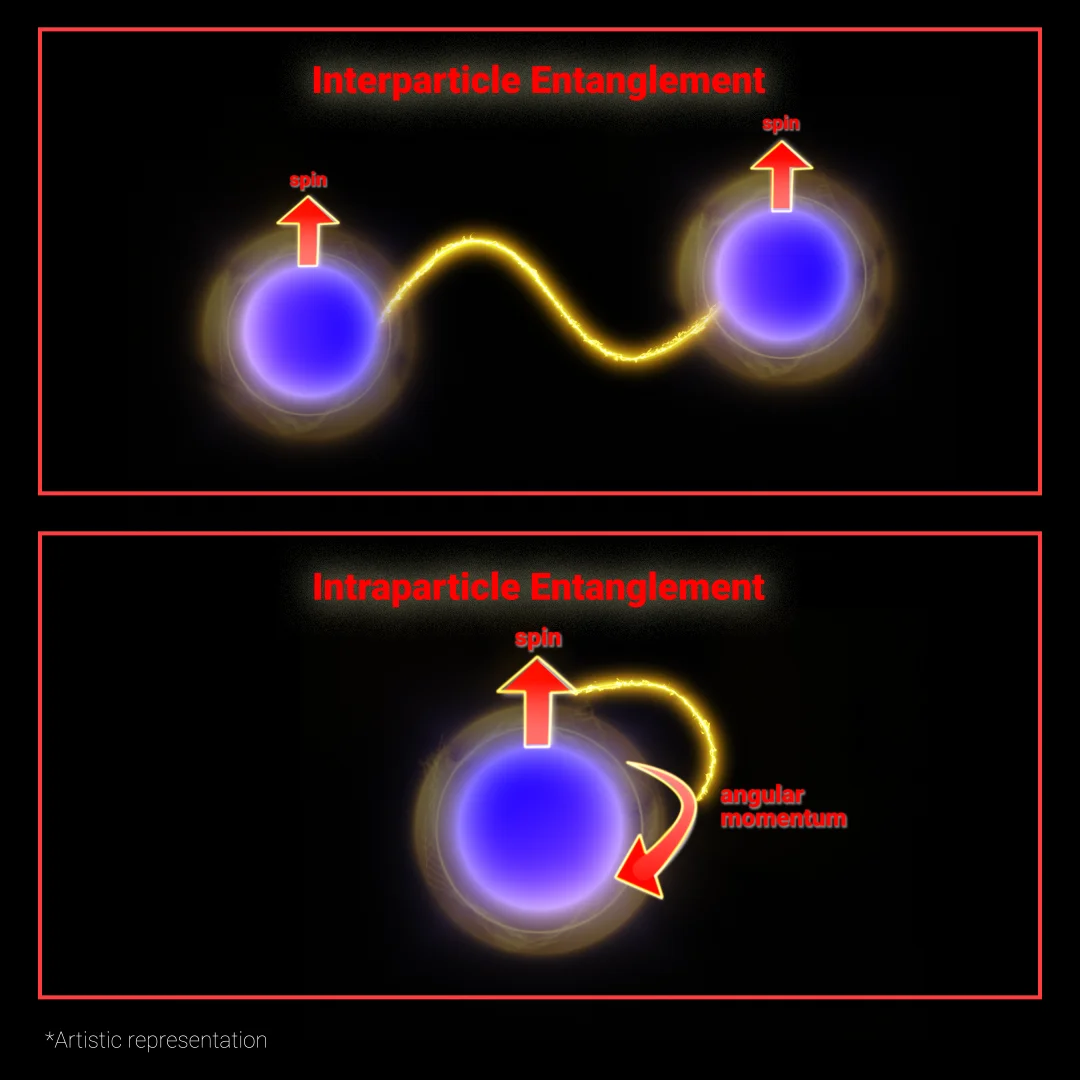
- Quantum entanglement refers to a phenomenon in quantum mechanics where two or more particles become interlinked, such that the state of one particle instantly determines the state of the other, regardless of the distance.
- It forms the basis of advanced technologies like quantum computing, quantum cryptography, and quantum communication,
- Types of Quantum Entanglement:
- Intraparticle entanglement, where different properties (e.g., spin and path) of a single particle are entangled.
- Interparticle entanglement, the more common form, involving entanglement between separate particles.
Quantum Noise
- About: Quantum noise refers to random disturbances arising from a system’s interaction with its environment, often leading to loss of coherence (decoherence) and degradation of quantum properties like entanglement.
- Types: Amplitude damping (energy loss), Phase damping (loss of phase coherence), and Depolarizing noise (randomization of the quantum state).
Noise Effects on Entanglement
- The study found that amplitude damping can create, preserve, or revive entanglement in intraparticle systems, while phase damping and depolarizing noise are less effective.
- Also, intraparticle entanglement was found to be more resilient to noise compared to interparticle entanglement, which showed only steady decay with no revival or generation under noise.
- The study introduced a realistic Global Noise Model and developed a precise analytical formula to predict entanglement behavior under various noise types, providing a valuable tool for designing resilient quantum systems suited for real-world, noisy environments.
| Read More: Quantum Entanglement, Ultra-Secure Communication Using Quantum Technology |


Rapid Fire
Birth Anniversary of Adikabi Sarala Das
The President of India participated in the birth anniversary celebrations of Adikabi Sarala Das (15th July 2025).
Adikabi Sarala Das
- Adikabi Sarala Dasa, originator of Odia literature, was born around the 15th century A.D.
- He was the first scholar to write in Odia language.
- His early name was Siddheswara Parida and was a contemporary of Gajapati king Kapilendra Dev.
- He wrote his epic poems at a religious establishment known as Munigosain.
- Besides the three epics for which he is best known — the Mahabharata, Vilanka Ramayana, and Chandi Purana — he also wrote the Laxmi Narayana Vachanika.
Odia Language
- Oldest of the eastern group of the Indo-Aryan family, Odia is derived from Ardhamagadhi Prakrit.
- Odia has also been influenced by the Dravidian languages as well as Arabic, Persian, and English.
- In 2014, Odia became the 6th language of the country to get 'classical language' status, after Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam.
- In 2024, Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali were included in the category of classical languages.
- Odia is one of the 22 official languages included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
| Read More: 5 New Classical Languages and Change in Criteria |