Science & Technology
Ultra-Secure Communication Using Quantum Technology
- 19 Jun 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Quantum Communication, Quantum Computing, National Quantum Mission, Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
For Mains: Quantum Key Distribution Technology and its Significance Applications of Quantum Technology, National Quantum Mission, Other India’s Initiative in Quantum Computing.
Why in News?
Scientists from IIT Delhi and DRDO have successfully demonstrated an ultra-secure communication system using entanglement-based free-space quantum secure communication.
- This method uses light particles (photons) and the principle of quantum entanglement to transmit information through air, ensuring that any attempt to intercept the communication is immediately detectable.
- It marks a significant step forward in India’s efforts to build quantum-secure networks under the National Quantum Mission (2023–2031).
What are the Key Highlights of DRDO-IIT-Delhi Breakthrough in Quantum Communication?
- Scientists demonstrated entanglement-based Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) over a 1 km free-space link, transmitting quantum keys through air, recording a secure key rate of 240 bps (bits per second), showing resilience to atmospheric turbulence, detector noise, and artificial lighting.
- Earlier, in 2022, India’s first intercity quantum link (Vindhyachal–Prayagraj) was set up using commercial-grade fibre.
- In 2023, QKD was extended to 380 km over standard telecom fibre (QBER 1.48%), followed by a 100 km demo in 2024.
What is Quantum Communication and Quantum Entanglement?
- Quantum communication is the transmission of secure information using principles of quantum mechanics, particularly quantum entanglement.
- It includes protocols like Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), quantum teleportation, and dense coding and techniques such as free-space communication, quantum repeaters, and decoherence-free subspaces to enable secure, long-distance transmission.
- It holds strategic value for defence and cybersecurity.
- Quantum Entanglement is a phenomenon in quantum physics where two or more particles become linked in such a way that the state of one instantly determines the state of the other, regardless of the distance between them.
- It defies classical physics and enables applications like quantum communication, quantum cryptography, and quantum computing.
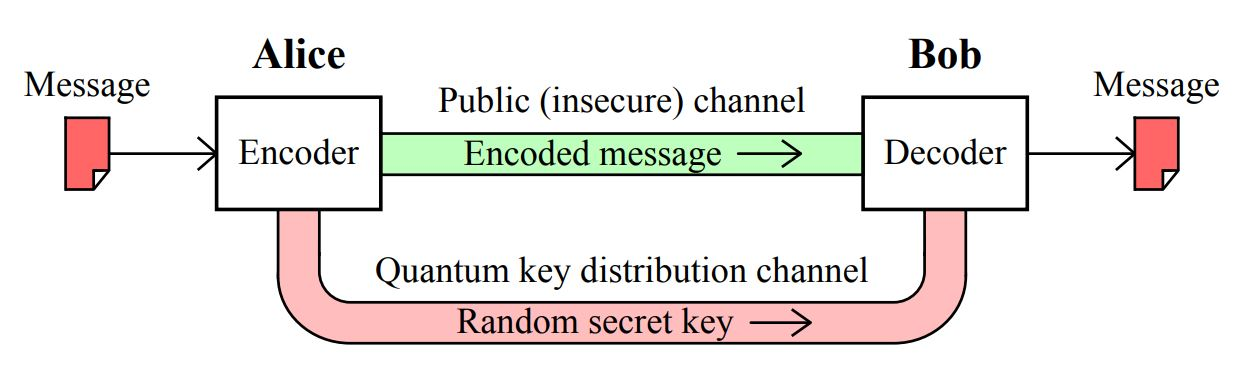
What is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)?
- About: Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is a secure communication method that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to generate and share cryptographic keys between two parties.
- Working:
- QKD uses qubits (quantum bits), transmitted through optical fibres based on total internal reflection, to securely exchange encryption keys between two users.
- Unlike classical bits, qubits are encoded on photons and are highly sensitive to disturbance.
- QKD enables two distant users, who do not initially share a secret key, to generate a common, random secret key. These interactions must be authenticated using classical cryptographic methods.
- If an eavesdropper tries to intercept the communication, it disturbs the qubits, causing transmission errors that alert the legitimate users. Thus, QKD transforms an authenticated classical channel into a secure quantum channel, ensuring tamper-evident encryption.
- QKD uses qubits (quantum bits), transmitted through optical fibres based on total internal reflection, to securely exchange encryption keys between two users.
- Types of QKD:
- Prepare-and-Measure QKD: One party prepares photons in specific quantum states, and the other measures them. Any interference alters the state, revealing intrusion.
- Entanglement-Based QKD: A source generates entangled photon pairs and sends one to each party. The entangled nature ensures that the measurement outcomes are correlated and secure.
What is the National Quantum Mission (NQM)?
- About: The National Quantum Mission (NQM) is a strategic national initiative aimed at advancing India’s capabilities in quantum technologies.
- It is one of the 9 key missions under the PM-STIAC (Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council).
- It seeks to position India as a global leader in quantum science by fostering innovation in quantum communication, quantum computing, and precision sensing.
- It was approved by the Union Cabinet in 2023 for the period 2023–24 to 2030–31.
- Significance: Crucial for advancing India’s position in the global quantum race, with applications in defence, cybersecurity, space, banking, and telecommunications.
- Key Objectives:
- Quantum Computing: Develop intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50–1000 physical qubits using platforms such as superconducting and photonic technologies over the next eight years.
- Secure Quantum Communication:
- Enable satellite-based quantum communication between Indian ground stations over distances exceeding 2000 km.
- Facilitate long-distance secure quantum links with international partners.
- Quantum Sensing and Metrology: Develop high-sensitivity magnetometers and atomic clocks to enhance precision in navigation, communication, and timing applications.
- Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs): Establish four T-Hubs at premier academic and national R&D institutions focused on:
- Quantum computation
- Quantum communication
- Quantum Sensing & Metrology
- Quantum Materials & Devices
- Key Initiatives Under NQM:
- DRDO Initiatives: DRDO is developing and testing quantum-resilient security protocols and quantum-safe symmetric and asymmetric cryptographic algorithms to protect defence and strategic communications.
- SETS (Society for Electronic Transactions and Security): Under the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA), SETS is advancing Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) research and has implemented PQC for FIDO authentication and IoT security applications.
- C-DoT (Centre for Development of Telematics): Under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), C-DoT has developed cutting-edge solutions, including Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), Post-Quantum Cryptography, and Quantum-Secure Video IP Phones.
Related Government Initiatives on Quantum Technology
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the key objectives and initiatives under the NQM and their strategic importance for India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following is the context in which the term "qubit" is mentioned?
(a) Cloud Services
(b) Quantum Computing
(c) Visible Light Communication Technologies
(d) Wireless Communication Technologies
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)