Maps
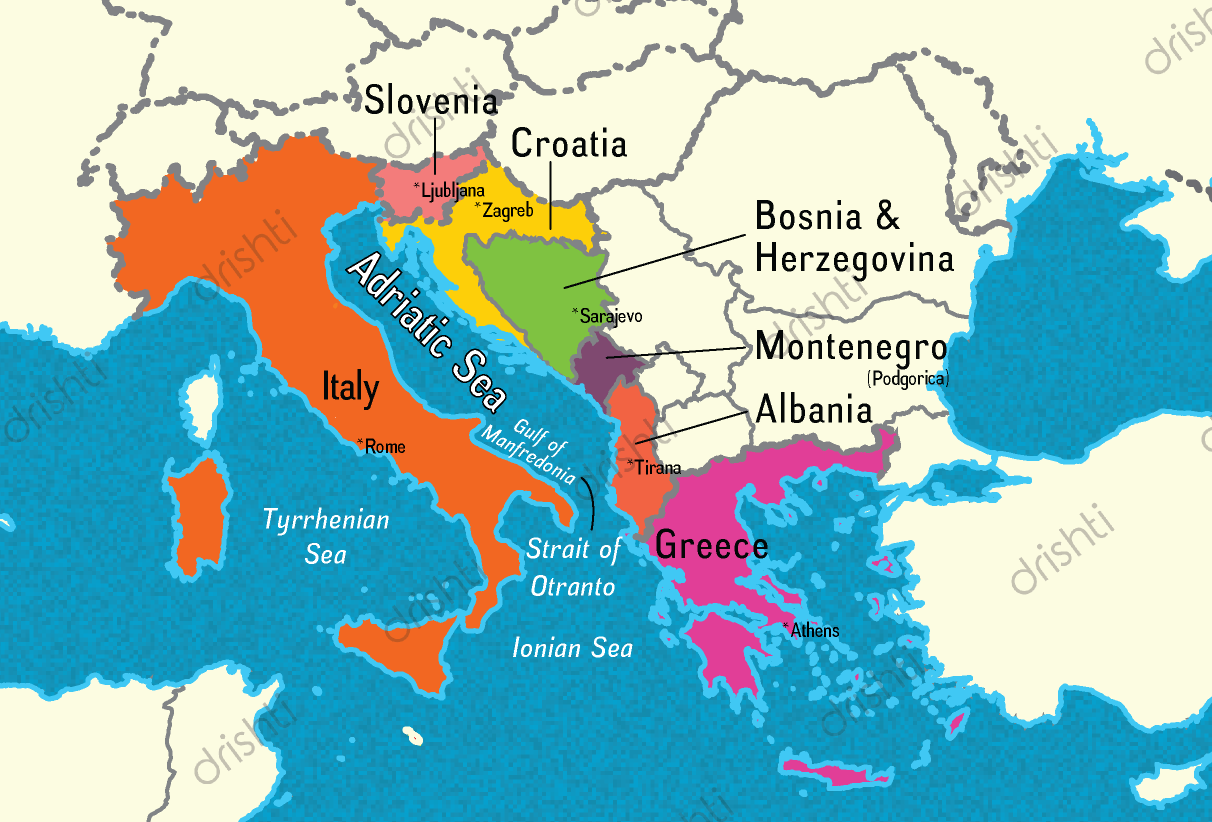
Adriatic Sea
Key Points
- Physical Geography:
- Arm of the Mediterranean Sea, lying between Italy and the Balkan Peninsula.
- It extends from the Gulf of Venice south to the Strait of Otranto, linking it to the Ionian Sea.
- Bordering Countries: Italy, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania and Slovenia.
Economy
World Economic Outlook: IMF
For Prelims: World Economic Outlook, IMF, Global Financial Stability Report, World Economic Outlook.
For Mains: Important International Institutions, Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests, Growth & Development, World Economic Outlook, International Monetary Fund.
Why in News?
Recently, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) released the latest edition of World Economic Outlook 2022.
What are the Highlights of the World Economic Outlook?
- Indian Scenario:
- It cut its forecast for India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth in 2022 to 6.8%, from 7.4% for India in the fiscal year that started in April 2022.
- For 2023, India has been projected to grow at 6.1%.
- Global Scenario:
- Global growth is forecast to slow from 6% in 2021 to 3.2% in 2022 and 2.7% in 2023. This is the weakest growth profile since 2001, except for the global financial crisis and the acute phase of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- The global growth is expected to slow further in 2023. The worst is yet to come and, for many people 2023 will feel like a recession.
- A slowdown in the Euro area is expected to deepen in 2023, and growth in China is projected to hit its lowest rate in decades apart from during the initial coronavirus outbreak.
- Inflation:
- Global inflation is forecast to rise from 4.7% in 2021 to 8.8% in 2022 but to decline to 6.5% in 2023 and to 4.1% by 2024.
- The slowdown in global economic activity is broad-based and sharper-than-expected, with inflation higher than seen in decades. The economic outlook depends on a successful calibration of monetary and fiscal policies, the course of the war in Ukraine, and growth prospects in China.
What are IMF’s Recommendations?
- Fighting Inflation:
- The priority must be to tackle inflation, normalize central bank balance sheets, and raise real policy rates above their neutral level fast enough and for long enough to keep inflation and inflation expectations under control.
- Monetary and Fiscal Policy Coordination:
- Fiscal policy also needs to support monetary policy in softening demand in economies with excess aggregate demand and overheating labor markets.
- Without price stability, any gains from future growth are at risk of being eaten up by a renewed cost-of-living squeeze.
- Central banks need to act resolutely while communicating clearly the objectives and the steps to achieve them.
- Protecting the Vulnerable during the Adjustment:
- As the cost of living continues to rise, policymakers will need to protect the most vulnerable members of society from the impact of higher prices.
- Climate Policies:
- Without prompt remedial action, climate change will eventually have catastrophic impacts on health and economic outcomes the world over.
- Current global targets are not aligned with global temperature goals. Meeting these goals will require emission cuts of at least 25% by the end of the decade.
- The ongoing energy crisis has also sharpened the energy security benefits countries can derive from transitioning to clean and reliable energy sources to steadily replace their reliance on fossil fuels with renewables and low-carbon energy sources.
What is the International Monetary Fund?
- About:
- The IMF was set up along with the World Bank after the Second World War to assist in the reconstruction of war-ravaged countries.
- The two organizations agreed to be set up at a conference in Bretton Woods in the US. Hence, they are known as the Bretton Woods twins.
- Created in 1944, the IMF is governed by and accountable to the 190 countries that make up its near-global membership. India joined on 27th December 1945.
- The IMF came into formal existence in December 1945.
- The IMF's primary purpose is to ensure the stability of the international monetary system — the system of exchange rates and international payments that enables countries (and their citizens) to transact with each other.
- The Fund's mandate was updated in 2012 to include all macroeconomic and financial sector issues that bear on global stability.
- The IMF was set up along with the World Bank after the Second World War to assist in the reconstruction of war-ravaged countries.
- Reports by IMF:
- World Economic Outlook
- It is a survey by the IMF that is usually published twice a year in the months of April and October.
- It analyzes and predicts global economic developments during the near and medium term.
- In response to the growing demand for more frequent forecast updates, the WEO Update is published in January and July, between the two main WEO publications released usually in April and October.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. "Rapid Financing Instrument" and "Rapid Credit Facility" are related to the provisions of lending by which one of the following? (2022)
(a) Asian Development Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
(d) World Bank
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI) provides quick financial assistance, which is available to all member countries facing urgent balance of payments requirements. The RFI was created as part of a broader reform to make IMF financial support more flexible to meet the diverse needs of member states. The RFI replaces the IMF's previous emergency assistance policy and can be used in a wide variety of circumstances.
- The Rapid Credit Facility (RCF) provides immediate balance of payments (BoP) requirements to low-income countries (LICs) with no ex-post condition, where a full economic program is neither necessary nor feasible. RCF was set up as part of a comprehensive reform to make the fund's financial support more flexible and better suited to suit the diverse needs of LIC including times of crisis.
- There are three areas under the RCF: (i) a "regular window" for immediate BoP needs due to a wide range of sources such as household instability, emergencies and fragility (ii) for immediate BoP needs due to sudden, exogenous shocks. an “exogenous shock window” and (iii) a “large natural disaster window” for immediate BoP needs due to natural disasters where the damage is estimated to be equal to or greater than 20% of the member's GDP.
Q2. “Gold Tranche” (Reserve Tranche) refers to (2020)
(a) a loan system of the World Bank
(b) one of the operations of a Central Bank
(c) a credit system granted by WTO to its members
(d) a credit system granted by IMF to its members
Ans: (d)
Q3. ‘Global Financial Stability Report’ is prepared by the (2016)
(a) European Central Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
(d) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. The World Bank and the IMF, collectively known as the Bretton Woods Institutions, are the two inter-governmental pillars supporting the structure of the world’s economic and financial order. Superficially, the World Bank and the IMF exhibit many common characteristics, yet their role, functions and mandate are distinctly different. Elucidate. (2013)


Indian Economy
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE)
For Prelims: PM-DevINE, PM Gati Shakti, North East Region
For Mains: Significance of North East for India, Challenges Related to North East India
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved a new Scheme, Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE).
- PM-DevINE was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 to address development gaps in the North Eastern Region (NER).
What is PM-DevINE Scheme?
- About:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% Central funding.
- The new scheme, to be implemented during the remaining four years of the 15th Finance Commission from 2022-23 to 2025-26 have an outlay of Rs.6,600 crore.
- The PM-DevINE is in addition to the quantum of resources available for the development of the NE region. It will not be a substitute for existing central and state schemes.
- Implementation:
- The scheme will be implemented by the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region through North Eastern Council or Central Ministries/ agencies.
- Objectives:
- Fund infrastructure convergently, in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti
- Support social development projects based on felt needs of the NER
- Enable livelihood activities for youth and women
- Fill the development gaps in various sectors
What is the Significance of North East for India?
- Strategic Significance: North-East India is the gateway to South-East Asia and beyond. It is India’s land-bridge to Myanmar.
- India's Act East Policy places the northeastern states on the territorial frontier of India's eastward engagement.
- Cultural Significance: North East India is one of the most culturally diverse areas of the world. It is home to over 200 tribes. Popular festivals include the Hornbill Festival of Nagaland, Pang Lhabsol of Sikkim, etc.
- Economic Significance: Economically, the Region is rich in natural resources of “TOT” (Tea, Oil, and Timber).
- It is a veritable powerhouse with a potential of 50000 MW of hydroelectric power and an abundant reserve of fossil fuels.
- Ecological Significance: North East is a part of Indo-Burma biodiversity hotspot. It represents one of the highest avian and plant biodiversity of the Indian subcontinent.
- This area has the prestige of having all the bear species present in India.
What are Current Challenges Pertaining to North-East India?
- Isolation From the Rest of India: The region’s accessibility has always remained weak due to geographical reasons and underdeveloped transport links with the rest of India.
- Lack of Efficient Infrastructure: Infrastructure i.e., physical (like roadways, waterways, energy and so on) as well as social infrastructure (for instance educational institutions, health facilities) plays an important role in human development and economic growth of any region
- One of the reasons for the economic backwardness of the North-Eastern states is the poor state of basic infrastructural facilities.
- Slow Pace of Industrial Growth: North-East India has remained historically underdeveloped in terms of industrial growth.
- Territorial Conflicts: There are existing inter-state and international territorial conflicts within the Northeast that are often based on historical border disputes and differing ethnic, tribal or cultural affinities. Example: Assam-Mizoram Border Dispute.
- Insurgency and Political Issues: Insurgency or terrorism is a political weapon and is often the result of accumulated anger due to political, economic and social causes.
- The North-Eastern states have witnessed a rise of insurgent activities and regional movements with a feeling of exploitation and alienation from other Indian states.
What are the Major Infrastructure Projects in the Northeast?
- Rail, Road and Air Connectivity:
- 4,000 km of roads, 20 railway projects for 2,011 km and 15 air connectivity projects are being developed.
- Waterways Connectivity:
- National waterways on the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Barak rivers (National Waterways (NW)-1 on the Ganges, NW-2 on Brahmaputra and NW-16 on Barak) are under development to provide better connectivity.
- Eastern Waterways Connectivity Transport Grid:
- It will connect the northeast with the rest of India by providing 5,000 km of navigable waterways.
- North Eastern Region Power System Improvement Project (NERPSIP):
- (NERPSIP) is a major step towards economic development of the North Eastern Region through strengthening of Intra - State Transmission and Distribution systems.
- Government is also emphasizing on projects related to power transmission and distribution, mobile networks, 4G, and broadband connectivity.
Way Forward
- Investing in infrastructure would generate employment and would play a major role in thwarting secessionist movements in the North-East region.
- India’s North East is surrounded by national and international borders, so, national and international infrastructure development will be the best choice for inclusive development in India’s Northeast.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Cross-border movement of insurgents is only one of the several security challenges facing the policing of the border in North-East India. Examine the various challenges currently emanating across the India- Myanmar border. Also, discuss the steps to counter the challenges. (2019)


Indian Economy
Railways to Bid for 16 Stations Through PPP Model
For Prelims: Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model, Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT), Build-Own-Operate (BOO), Build-Operate-Lease-Transfer (BOLT), Design-Build-Operate-Transfer (DBFOT), Lease-Develop-Operate (LDO), Operate-Maintain-Transfer (OMT), Adarsh Station Scheme.
For Mains: Significance of various investment Models of Public-Private Partnership.
Why in News?
Recently, the railway ministry is planning to bid out 16 stations under the public-private partnership (PPP) model. These railway stations will be upgraded to ensure improved basic facilities and accessibility for passengers.
- This is in addition to the 1253 railway stations that have been identified for development under the Adarsh Station Scheme.
What is Public Private Partnership Model?
- About:
- It is an arrangement between the government and private sector for the provision of public assets and/or public services. Public-private partnerships allow large-scale government projects, such as roads, bridges, or hospitals, to be completed with private funding.
- In this type of partnership, investments are undertaken by the private sector entity, for a specified period of time.
- As PPP involves full retention of responsibility by the government for providing the services, it doesn’t amount to privatization.
- There is a well-defined allocation of risk between the private sector and the public entity.
- The private entity is chosen on the basis of open competitive bidding and receives performance-linked payments.
- PPP route can be an alternative in developing countries where governments face various constraints on borrowing money for important projects.
- It can also give required expertise in planning or executing large projects.
- Benefits:
- The PPP model can bring opportunities for investment, operating efficiency and modern and clean technology.
- PPP railway projects provide for shared use of rail tracks may lead to efficiency gains and an increased revenue basis (or reduced cost basis) for states and private investors.
- Further, it could lead to increased competition and modernization of railway infrastructure.
- Challenges:
- PPP projects have been stuck in issues such as disputes in existing contracts, non-availability of capital and regulatory hurdles related to the acquisition of land.
- Indian government has a poor record in regulating PPPs in practice, as there are delays in land acquisition.
- Loans for infrastructure projects are believed to comprise a large share of the non-performing asset portfolio of public sector banks in India.
- In many sectors, PPP projects have turned into conduits of crony capitalism.
- Many PPP projects in infrastructure sector are run by “politically connected firms” which have used political connections to win contracts.
- PPP firms use every opportunity for renegotiating contracts by citing reasons like lower revenue or a rise in costs which becomes a norm in India.
What are Types of Public Private Partnership (PPP) Models?
- Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT): It is a conventional PPP model in which the private partner is responsible to design, build, operate (during the contracted period) and transfer back the facility to the public sector.
- The private sector partner has to bring the finance for the project and take the responsibility to construct and maintain it.
- The public sector will allow private sector partners to collect revenue from the users. The national highway projects contracted out by NHAI under PPP mode is a major example for the BOT model.
- Build-Own-Operate (BOO): In this model ownership of the newly built facility will rest with the private party.
- On mutually agreed terms and conditions the public sector partner agrees to ‘purchase’ the goods and services produced by the project.
- Build, Own, Operate, Transfer (BOOT): In this variant of BOT, after the negotiated period of time, the project is transferred to the government or to the private operator.
- BOOT model is used for the development of highways and ports.
- Build-Operate-Lease-Transfer (BOLT): In this approach, the government gives a concession to a private entity to build a facility (and possibly design it as well), own the facility, lease the facility to the public sector and then at the end of the lease period transfer the ownership of the facility to the government.
- Design-Build-Operate-Transfer (DBFO): In this model, entire responsibility for the design, construction, finance, and operation of the project for the period of concession lies with the private party.
- Lease-Develop-Operate (LDO): In this type of investment model either the government or the public sector entity retains ownership of the newly created infrastructure facility and receives payments in terms of a lease agreement with the private promoter.
- It is mostly followed in the development of airport facilities.
- Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) Model: Under this model, the cost is completely borne by the government. Government invites bids for engineering knowledge from the private players. Procurement of raw material and construction costs are met by the government. The private sector’s participation is minimal and is limited to the provision of engineering expertise. A difficulty of the model is that financial is the high financial burden for the government.
- The Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM): In India, the new HAM is a mix of BOT-Annuity and EPC models. As per the design, the government will contribute 40% of the project cost in the first five years through annual payments (annuity). The remaining payment will be made on the basis of the assets created and the performance of the developer.
What is Adarsh Station Scheme?
- About: Adarsh station scheme of the Ministry of Railways aims to upgrade the suburban stations of India to Adarsh stations. It was introduced in 2009.
- The selection of railway stations under this scheme is based on the identified need for up-gradation of amenities.
- Key features:
- Adarsh stations will be beautified and upgraded with modern facilities like:
- Improvement of facade of the station building.
- Duly streamlining traffic flow
- Improvement of platform surface
- Improvement of existing waiting halls and retiring rooms
- Toilet facilities
- Provision of foot over bridges
- Provision of lifts and escalators etc.
- The upgradation process will be monitored by the Indian Government and Indian Railways.
- Adarsh stations will be beautified and upgraded with modern facilities like:
Way Forward
- New projects, especially large-scale transit projects, are significant for increasing mobility and for the series of changes in land use patterns. PPPs have the potential to deliver infrastructure projects better and faster. Currently, PPP contracts focus more on fiscal benefits.
- There is a need for a serious assessment of the efficacy and the likely benefits of increasing private sector participation in rail projects before the adoption of this model.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Examine the development of Airports in India through joint ventures under Public–Private Partnership (PPP) model. What are the challenges faced by the authorities in this regard? (2017)
Q. Why is Public Private Partnership (PPP) required in infrastructural projects? Examine the role of PPP model in the redevelopment of Railway Stations in India. (2022)


Governance
Online Gaming Market in India
For Prelims: Online Gaming, Gambling, Digital India, Game of Skill, Game of Chance, Betting
For Mains: Online Gaming and its Impact
Why in News?
A task force set up by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has prepared a final report of its recommendations to regulate the online gaming industry in India.
What are the Recommendations of the Task Force?
- Central-Level Law for Online Gaming:
- A central-level law for online gaming should apply to real money and free games of skill, including e-sports, online fantasy sports contests, and card games among others.
- Casual games with no real money element in the form of stakes may be kept outside the scope of such rules, unless they have a high number of users in India.
- A Regulatory Body for the Online Gaming Industry:
- It has also recommended creating a regulatory body for the online gaming industry.
- The body will determine what qualifies as a game of skill or chance, and accordingly certify different gaming formats, seek compliance and enforcement.
- A “game of skill” is based mainly on the mental or physical level of expertise of a player, rather than a chance.
- A “game of chance” however is determined mainly by a random factor of any type. In games of chance, the usage of skill is present but a higher level of chance determines success.
- Three-Tier Dispute Resolution Mechanism:
- A three-tier dispute resolution mechanism, similar to that prescribed under the Information Technology Rules, 2021 for online streaming services, consisting of:
- A grievance redressal system at the gaming platform level,
- Self-regulatory body of the industry, and
- An oversight committee led by the government.
- A three-tier dispute resolution mechanism, similar to that prescribed under the Information Technology Rules, 2021 for online streaming services, consisting of:
- Online Gaming Platform as a Legal Entity:
- Any online gaming platform (domestic or foreign) offering real money online games to Indian users will need to be a legal entity incorporated under Indian law.
- These platforms will also be treated as ‘reporting entities’ under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002.
- These platforms will also be required to report suspicious transactions to the Financial Intelligence Unit-India.
- Regulation of the Sector:
- By MeitY:
- MeitY may act as the nodal ministry to regulate online gaming, except for the e-sports category on which the Department of Sports can take the lead.
- The scope of the regulation by MeitY should only cover online gaming, that is, games of skill.
- The issues of online betting and gambling being games of chance in nature should be excluded from its scope, the task force is learnt to have recommended.
- By Information and Broadcasting Ministry:
- Certain other aspects of online gaming such as advertisements, code of ethics relating to content classifications etc. could be regulated by the Information and Broadcasting Ministry.
- Consumer Affairs Ministry:
- The Consumer Affairs Ministry can regulate the sector for unfair trade practices.
- By MeitY:
What is the Purpose of a Law at the Central Level?
- Online Gaming being a State Subject:
- Online gaming so far has been a state subject, but according to the state governments, they find it extremely difficult to enforce certain rules like geo-blocking certain apps or websites within the territory of their state.
- Also, there is a concern that rules passed in one state are not applicable in another, which has caused inconsistency in how the online gaming industry is regulated in the country.
- State governments also do not have enough blocking powers like the Centre to issue blocking orders for offshore betting sites.
- Societal Concerns:
- A number of societal concerns that can arise from the proliferation of online games in the country has also been highlighted.
- There have been a number of reported incidents of people losing large sums of money on online games, leading to suicides in various parts of the country.
- No Regulatory Framework:
- Along with that, there is currently no regulatory framework to govern various aspects of online gaming companies such as having a grievance redressal mechanism, implementing player protection measures, protection of data and intellectual property rights, and prohibiting misleading advertisements.
What is the Size of India's Online Gaming Market?
- Revenue and Industry Growth:
- The revenue of the Indian mobile gaming industry is expected to exceed USD1.5 billion in 2022, and is estimated to reach USD 5 billion in 2025.
- The industry in the country grew at a CAGR of 38% between 2017-2020, as opposed to 8% in China and 10% in the US.
- It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% to reach Rs 153 billion in revenue by 2024.
- Users Growth:
- India’s percentage of New Paying Users (NPUs) in gaming has been the fastest growing in the world for two consecutive years, at 40% in 2020 and reaching 50% in 2021.
- According to a report by EY FICCI (Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry), transaction-based games’ revenues grew 26% in India, with the number of paying gamers increasing by 17% from 80 million in 2020 to 95 million in 2021.
Way Forward
- Robust Policy Framework:
- India’s e-gaming industry needs robust policy frameworks and digital infrastructure to fulfill its potential, maximize revenue and foray toward being a global leader.
- A government body that oversees operations, drafts progressive policies preventing societal issues, suitably classifies games of skill or chance, ensures consumer protection and combats illegality and crime is required.
- Cooperation between Government and Gaming Companies:
- Gaming companies should also continue to work with the government to promote responsible gaming by educating gamers and establishing best practices like conducting KYC checks, user authentication, etc to prevent illegal activities and financial dealings on their platforms.


Governance
2nd World Geospatial Information Congress
For Prelims: UN World Geospatial Information Congress,
For Mains: Geospatial sector of India - Challenges and Opportunities, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, 2nd United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress was inaugurated in Hyderabad under the theme ‘Geo-Enabling the Global Village: No one should be left behind’.
- India’s geospatial economy is expected to cross Rs. 63,100 crores by 2025 at a growth rate of 12.8%.
What is the UN World Geospatial Information Congress?
- The first United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress was held in Deqing, Zhejiang Province, China in 2018.
- The United Nation Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM) organizes the United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress (UNWGIC) every four years.
- The objectives are enhancing international collaboration among the Member States and relevant stakeholders in Geospatial information management and capacities.
What is Geospatial Technology?
- About:
- Geospatial technology is a term used to describe the range of modern tools contributing to the geographic mapping and analysis of the Earth and human societies.
- The term 'geospatial' refers to a collection of technologies that help to collect, analyse, store, manage, distribute, integrate, and present geographic information.
- Broadly, it consists of the following technologies:
- Geospatial technology is a term used to describe the range of modern tools contributing to the geographic mapping and analysis of the Earth and human societies.
- Significance:
- Employment Generation:
- It will provide employment to more than 10 lakh people mainly through Geospatial start-ups in India.
- Socio-Economic Development:
- Geospatial technology has become one of the key enablers in socio-economic development by enhancing productivity, ensuring sustainable infrastructure planning, effective administration, and aiding the farm sector.
- Other Advantages:
- Other advantages include sustainable urban development, managing and mitigating disasters, tracking the impact of climate change, forest management, water management, stopping desertification and food security.
- Intelligent maps and models can be created using geospatial technology.
- It can be used to reveal spatial patterns hidden in large amounts of data that are complex to access collectively through mapping.
- Geospatial technology has been driving inclusion and progress in national development projects like SVAMITVA, PM Gati Shakti master plan, Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) Trinity etc.
- Employment Generation:
What are the Challenges related to the Sector in India?
- Absence of Sizeable Market:
- Among the most prominent hurdles is the absence of a sizable geospatial market in India.
- There is no demand for geospatial services and products on a scale linked to India’s potential and size.
- This lack of demand is mainly a consequence of the lack of awareness among potential users in government and private sectors.
- Lack of Skilled Manpower:
- The other hurdle has been the lack of skilled manpower across the entire pyramid.
- Though India has many who are trained in geospatial this is mostly either through a master’s level programme or on-job training.
- Unlike the West, India lacks a strata of core professionals who understand geospatial end-to-end.
- Unavailability of Data:
- The unavailability of foundation data, especially at high-resolution, is also a constraint.
- The lack of clarity on data sharing and collaboration prevents co-creation and asset maximisation.
- No-Ready-to-use Solutions:
- Additionally, there are still no ready-to-use solutions especially built to solve the problems of India.
What are the Related Initiatives?
- Google Street View is launched in ten cities of India under the Guidelines of the National Geospatial Policy (NGP), 2021.
- The Survey of India has developed a web Geographic Information System (GIS) called Sarthi. It will help users in creating applications for geospatial data visualisation, manipulation, and analysis without a lot of resources at their end.
- The online maps portal of Survey of India has over 4,000 maps with national, state, district, and tehsil level data that have been indexed for end users.
- National Atlas and Thematic Mapping Organization (NATMO) has released thematic maps such as the cultural map of India, the climactic map, or the economic map, on Manchitran portal.
- NATMO, functioning as a subordinate department under the Department of Science & Technology, Ministry of Science & Technology, with its headquarters at Kolkata.
- Bhuvan, is the national Geo-portal developed and hosted by ISRO comprising Geo Spatial Data, Services and Tools for Analysis.
- The Association of Geospatial Industries has released a report titled “Potential of Geospatial Technologies for the Water Sector in India''.
Way Forward
- India needs to be aggressive to make a leapfrog; special attention is required as far as the geospatial sector is concerned.
- There is a need to establish a geo-portal to make all public-funded data accessible through data as a service model, with no or nominal charge.
- Solution developers and start-ups should be engaged to build solution templates for various business processes across departments.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: (c)


Governance
Section 66A of the IT Act, 2000
For Prelims: Section 66A of the IT Act, 2000, Article 19(1)(a)
For Mains: Freedom of Speech and Expression, Issues Arising Out of Design & Implementation of Policies, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court ordered States and their police forces to stop prosecuting free speech on social media under Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- However, the court clarified that this direction would apply only to a charge under Section 66A and not extend to other offences in a case.
What is Section 66A of the IT Act?
- About:
- Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, of 2000 made it a punishable offence for any person to send offensive information using a computer or any other electronic device.
- The provision also made it punishable for a person to send information that they believed to be false.
- Section 66A had prescribed three years' imprisonment if a social media message caused "annoyance" or was found "grossly offensive".
- Even sending emails for causing annoyance, inconvenience, or to deceive or mislead the recipient about the origin of the message was punishable under this section.
- The court struck down the provision as unconstitutional and a violation of free speech in 2015 in the Shreya Singhal Case.
- The section relating to restrictions on online speech was declared unconstitutional on grounds of violating the freedom of speech guaranteed under Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution of India.
- It held that online intermediaries would only be obligated to take down content on receiving an order from a court or government authority.
- Issues with Section 66A:
- Based on Undefined Actions:
- The weakness of Section 66A lay in the fact that it had created an offence on the basis of undefined actions: such as causing “inconvenience, danger, obstruction and insult”, which do not fall among the exceptions granted under Article 19 of the Constitution, which guarantees the freedom of speech.
- No Procedural Safeguards:
- Section 66A did not have procedural safeguards like other sections of the law with similar aims, such as the need to obtain the concurrence of the Centre before action can be taken.
- Local authorities could proceed autonomously, literally on the whim of their political masters.
- Section 66A did not have procedural safeguards like other sections of the law with similar aims, such as the need to obtain the concurrence of the Centre before action can be taken.
- Against the Fundamental Rights:
- Section 66A was contrary to both Articles 19 (free speech) and 21 (right to life) of the Constitution.
- Right to know is the species of the right to speech and expression provided by the Article 19(1) (a) of the constitution of India.
- Section 66A was contrary to both Articles 19 (free speech) and 21 (right to life) of the Constitution.
- Based on Undefined Actions:
Way Forward
- There is a pressing need to move from a system where communication about judicial decisions is at the mercy of initiatives by scrupulous officers, to a method not contingent on human error to the greatest possible extent. The urgency cannot be overstated.
- Enforcing unconstitutional laws is sheer wastage of public money.
- But more importantly, until this basic flaw is addressed, certain persons will remain exposed to denial of their right to life and personal liberty in the worst possible way imaginable.
- They will suffer the indignity of lawless arrest and detention, for no reason other than their poverty and ignorance, and inability to demand their rights.


Important Facts For Prelims
IBSAMAR VII
Why in News?
INS Tarkash reached Port Gqeberha (also known as Port Elizabeth), South Africa to participate in the seventh edition of India-Brazil-South Africa Maritime (IBSAMAR) i.e., IBSAMAR VII.
- IBSAMAR is an important part of IBSA trilateral defence cooperation.
What is IBSAMAR VII?
- It is a joint Multinational Maritime Exercise between the Indian, Brazilian and South African Navies currently being held in South Africa from 10-12 October, 2022.
- The previous edition of IBSAMAR (IBSAMAR VI) was conducted in Simons Town, South Africa in 2018.
- The Indian Navy is represented by the Teg class guided missile frigate, INS Tarkash, a Chetak helicopter and the personnel from the Marine Commando Force (MARCOS).
- The harbour phase of IBSAMAR VII includes professional exchanges such as damage control and fire-fighting drills, Visit, Board, Search, and Seizure (VBSS)/cross boarding lectures and interaction among special forces.
- The Joint Maritime Exercise will strengthen maritime security, joint operational training, sharing of best practices and building interoperability to address common maritime threats.
What are India’s Other Maritime Exercises?
- Thailand: India-Thailand Coordinated Patrol (Indo-Thai CORPAT)
- United Kingdom: Konkan - Shakti
- Indonesia: Samudra Shakti
- Singapore: Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX)
- Qatar: Zair-Al-Bahr
- Japan: Maritime Partnership Exercise (MPX)
What is IBSA?
- About:
- The IBSA is a trilateral, developmental initiative between India, Brazil and South Africa to promote South-South cooperation and exchange.
- The idea of South-South Cooperation (SSC) is not new. Its genesis can be traced back to the decades of efforts by countries and groupings working together to ensure South-South solidarity such as Bandung conference 1955, Non-Aligned Movement 1961, G77 grouping, United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the Buenos Aires Plan of Action 1978, and the 2009 Nairobi declaration.
- Formation:
- The grouping was formalized and named the IBSA Dialogue Forum when the Foreign Ministers of the three countries met in Brasilia (Brazil) on 6th June 2003 and issued the Brasilia Declaration.
- Headquarters:
- IBSA does not have a headquarters or a permanent executive secretariat.
- IBSA Fund:
- Established in 2004, IBSA Fund (India, Brazil and South Africa Facility for Poverty and Hunger Alleviation) is a unique Fund through which development projects are executed with IBSA funding in fellow developing countries.
- The fund is managed by the United Nations (UN) Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC). Each IBSA member country is required to contribute $1 million per annum to the fund.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The ‘Indian Ocean Naval Symposium’ (IONS) is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral States of the Indian Ocean Region by providing an open and inclusive forum for discussion of regionally relevant maritime issues. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- It provides a forum to increase maritime security cooperation, and promote friendly relationships among the member nations.
- The inaugural IONS-2008 was held in New Delhi, India in Feburary, 2008. The Chief of the Naval Staff, Indian Navy was designated as the Chairman of IONS for the period 2008-10. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Therefore, option B is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
World Sloth Bear Day
Why in News?
The first World Sloth Bear Day was observed on October 12, 2022 to generate awareness and strengthen conservation efforts around the unique bear species endemic to the Indian subcontinent.
- It was proposed by Wildlife SOS India, an organisation involved in sloth bear conservation and protection for over two decades and the (International Union for Conservation of Nature) IUCN-Species Survival Commission (SSC) sloth bear expert team accepted and declared the day to be celebrated worldwide.
What is Sloth Bear?
- About:
- Sloth Bear is one of the 8 bear species found across the globe.
- Sloth bears primarily eat termites and ants, and unlike other bear species, they routinely carry their cubs on their backs.
- They are also very fond of honey, hence their alternative name of “honey bear”.
- Sloth bears do not hibernate.
- They are agile and considered one of the most formidable wild animals.
- They are also known as the least researched bear species.
- Scientific Name: Melursus Ursinus.
- Habitat: Presently Sloth bears are only found in the Indian subcontinent, Nepal and a sub-species in Sri Lanka.
- About 90% of the global Sloth Bear population is found in India.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable.
- Wildlife protection Act (1972): Schedule I.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES): Appendix I.
- Threats:
- An ethnic group named Kalandars, who were mostly poor performed a practice known as a dancing bear, where the captured sloth bears are tortured to make them dance.
- According to several reports, their population has dropped by 40 to 50% over the last three decades mainly due to habitat loss, habitat fragmentation, poaching and increasing human-bear conflict.
- Conservation efforts:
- The Wildlife SOS Bear rescue centres are rescuing Sloth bears and reintroducing them to their natural habitat where they also received veterinary care.
- Further, to ensure the Kalandar community did not fall back on poaching wild animals for a living, Wildlife SOS worked with the Kalandars to provide them with alternative forms of livelihood and access to education.
- Through the declaration of World Sloth Bear Day, Wildlife SOS and the IUCN-SSC, (Species Survival Commission) Sloth Bear Expert Team aim to set precedence for the rest of the world to promote the conservation of Sloth bears and their habitats throughout their distribution range.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
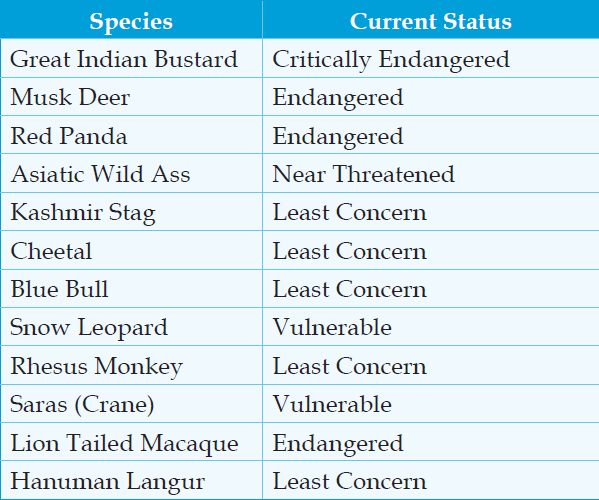
Q. Which one of the following groups of animals belongs to the category of endangered species? (2012)
(a) Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda and Asiatic Wild Ass
(b) Kashmir Stag, Cheetal, Blue Bull and Great Indian Bustard
(c) Snow Leopard, Swamp Deer, Rhesus Monkey and Saras (Crane)
(d) Lion-tailed Macaque, Blue Bull, Hanuman Langur and Cheetal
Ans: (a)
Exp: