Infographics
Indian Economy
India's Fiscal Deficit Targets
For Prelims: Union Budget for 2023-24, Fiscal Deficit, Subsidies, Capital spending, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Balance of payments, India's external debt.
For Mains: Economic Survey 2022-23, Positive Aspects of Fiscal Deficit, Negative Aspects of Fiscal Deficit.
Why in News?
In the Union Budget for 2023-24, the government announced the adoption of relative fiscal prudence and projected a decline in fiscal deficit to 5.9% of gross domestic product (GDP) in FY24, compared with 6.4% in FY23.
- The government planned to continue on the path of fiscal consolidation and reach a fiscal deficit below 4.5% by 2025-26.
What is the Direction on Deficit Given in the Budget?
- In the revenue budget, the deficit was 4.1% of GDP in 2022-23 (revised estimate). In Union Budget 2023-24, revenue deficit is 2.9% of GDP.
- If interest payments are deducted from fiscal deficit, which is referred to as primary deficit, it stood at 3% of GDP in 2022-23 (RE).
- The primary deficit, which reflects the current fiscal stance devoid of past interest payment liabilities, is pegged at 2.3% of GDP in Union Budget 2023-24.
What are the Major Steps of Government Towards Fiscal Consolidation?
- Reduced Subsidies:
- The government has reduced the amount of money allocated for food, fertiliser and petroleum subsidies.
- The food subsidy in 2022-23 (RE) was ₹2,87,194 crore. In 2023-24, it has been reduced to ₹1,97,350 crore.
- Similarly, the fertilizer subsidy in 2022-23 was ₹2,25,220 crore (RE); it has been reduced to ₹1,75,100 crore for FY24.
- The petroleum subsidy in 2022-23 was ₹9,171 crore (RE); it has declined to ₹2,257 crore in 2023-24 (Budget estimate/BE).
- The decrease in subsidies compared to the previous year is not as sharp, but it is still a positive step towards reaching a fiscal deficit target of 4.5% by 2025-26.
- The government has reduced the amount of money allocated for food, fertiliser and petroleum subsidies.
- Capital Expenditure:
- In the Budget for 2023-24, capital spending is planned to rise to 3.3% of GDP, and the government has provided an interest-free loan of ₹1.3 lakh crore for 50 years to states to boost growth.
- Debt Management:
- The majority of the fiscal deficit is financed through internal market borrowings, with a small portion coming from securities against savings, provident funds, and external debt.
- In the 2023 Union Budget, India's external debt is only 1% of the total fiscal deficit, which is estimated at ₹22,118 crore.
- The states are free to maintain a fiscal deficit of 3.5% of their Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) with 0.5% tied to power sector reforms.
- The majority of the fiscal deficit is financed through internal market borrowings, with a small portion coming from securities against savings, provident funds, and external debt.
Why is Fiscal Consolidation Important for an Emerging Economy?
- Fiscal consolidation refers to the ways and means of narrowing the fiscal deficit. A government typically borrows to bridge the deficit. It will then have to allocate a part of its earnings to service the debt.
- The interest burden will increase as the debt increases. In the Budget for FY22, of the total government expenditure of over ₹34.83 lakh crore, more than 8.09 lakh crore (around 20%) went towards interest payment.
What is Fiscal Deficit?
- About:
- Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue (excluding borrowings).
- It is an indicator of the extent to which the government must borrow in order to finance its operations and is expressed as a percentage of the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- A high fiscal deficit can lead to inflation, devaluation of the currency and an increase in the debt burden.
- While a lower fiscal deficit is seen as a positive sign of fiscal discipline and a healthy economy.
- Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue (excluding borrowings).
- Positive Aspects of Fiscal Deficit:
- Increased Government Spending: Fiscal deficit enables the government to increase spending on public services, infrastructure, and other important areas that can stimulate economic growth.
- Finances Public Investments: The government can finance long-term investments, such as infrastructure projects, through fiscal deficit.
- Job Creation: Increased government spending can lead to job creation, which can help reduce unemployment and increase the standard of living.
- Negative Aspects of Fiscal Deficit:
- Increased Debt Burden: A persistent high fiscal deficit leads to an increase in government debt, which puts pressure on future generations to repay the debt.
- Inflationary Pressure: Large fiscal deficits can lead to an increase in money supply and higher inflation, which reduces the purchasing power of the general public.
- Crowding out of Private Investment: The government may have to borrow heavily to finance the fiscal deficit, which can lead to a rise in interest rates, and make it difficult for the private sector to access credit, thus crowding out private investment.
- Balance of Payments Problems: If a country is running large fiscal deficits, it may have to borrow from foreign sources, which can lead to a decrease in foreign exchange reserves and put pressure on the balance of payments.
What are the Other Types of Deficits in India?
- Revenue Deficit: It refers to the excess of government’s revenue expenditure over revenue receipts.
- Revenue Deficit = Revenue expenditure – Revenue receipts
- Primary Deficit: Primary deficit equals fiscal deficit minus interest payments. This indicates the gap between the government’s expenditure requirements and its receipts, not taking into account the expenditure incurred on interest payments on loans taken during the previous years.
- Primary deficit = Fiscal deficit – Interest payments
- Effective Revenue Deficit: It is the difference between revenue deficit and grants for creation of capital assets.
- The concept of effective revenue deficit has been suggested by the Rangarajan Committee on Public Expenditure.
Conclusion
India’s priority is to recover the economy through capital expenditure (capex). With increased government investment in infrastructure, private investment will also increase, boosting the economic (GDP) growth, and as a result the ratio of fiscal deficit to GDP will decrease.
UPSC Civil Services, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. In the context of governance, consider the following: (2010)
- Encouraging Foreign Direct Investment inflows
- Privatization of higher educational Institutions
- Down-sizing of bureaucracy
- Selling/offloading the shares of Public Sector Undertakings
Which of the above can be used as measures to control the fiscal deficit in India?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: D
Q2. Which one of the following is likely to be the most inflationary in its effect? (2021)
(a) Repayment of public debt
(b) Borrowing from the public to finance a budget deficit
(c) Borrowing from the banks to finance a budget deficit
(d) Creation of new money to finance a budget deficit
Ans: (d)
Q3. Which of the following is/are included in the capital budget of the Government of India? (2016)
- Expenditure on acquisition of assets like roads, buildings, machinery, etc.
- Loans received from foreign governments
- Loans and advances granted to the States and Union Territories
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q1. One of the intended objectives of the Union Budget 2017-18 is to ‘transform, energise and clean India’. Analyse the measures proposed in the Budget 2017-18 to achieve the objective. (2017)
Q2. Distinguish between Capital Budget and Revenue Budget. Explain the components of both these Budgets. (2021)


Geography
Earthquakes in Turkey and Causes
Prelims: Tectonic Plates, Types of Earthquakes, Earthquake, its Distribution and Types, Strike-Slip Earthquake.
Mains: Earthquake, its types and Distribution.
Why in News?
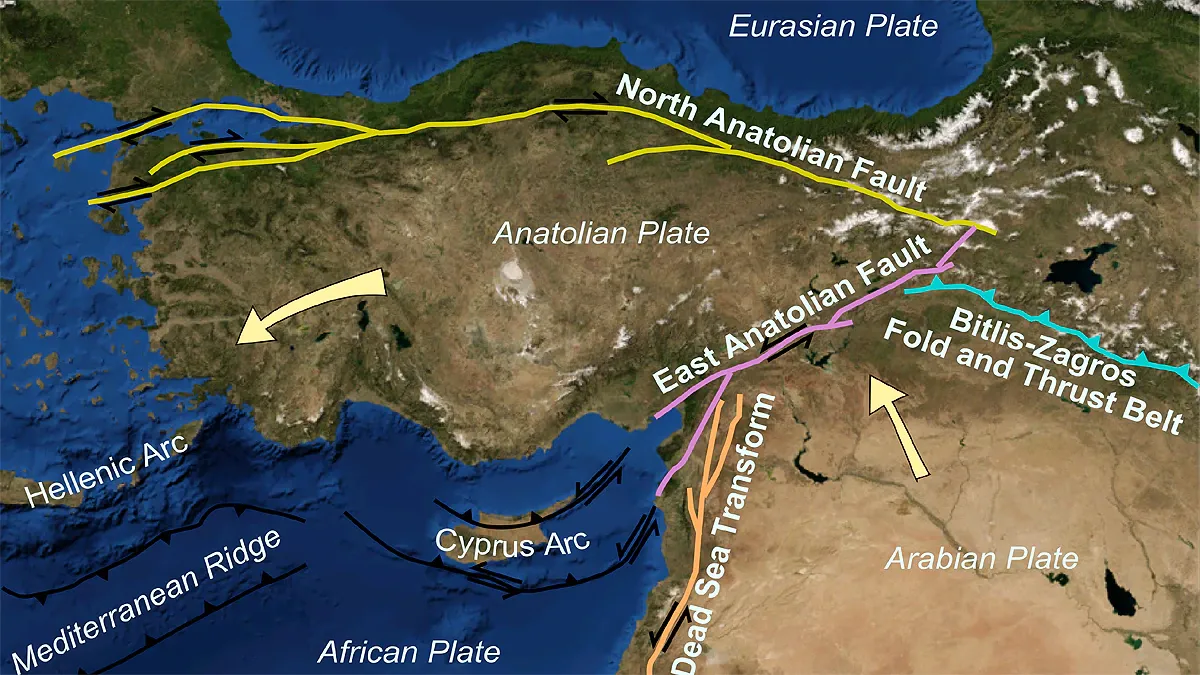
Recently, powerful tremors were felt in Turkey after an earthquake of magnitude 7.8 struck along a well-known fault line called the Anatolia tectonic block.
- The earthquakes emerged from relatively shallow depths and were a “strike-slip quake”.
- It is being described as the strongest Earthquake that Turkey has experienced in over a century and the worst disaster since 1939. The 1939 earthquake was the Erzincan Earthquake that had caused “extreme damage in the Erzincan Plain and the Kelkit River Valley.
What Makes Turkey Prone to Earthquakes?
- In the Eastern Mediterranean region comprising Turkey, Syria and Jordan, tectonics are dominated by complex interactions between the African, Arabian, and Eurasian tectonic plates, and the Anatolian tectonic block.
- Turkey sits on the Anatolian tectonic plate, which borders two major faults, the North Anatolian Fault (NAF) that cuts across the country from west to east, and the East Anatolian Fault (EAF) in the southeast.
- The NAF line is the meeting point of the Eurasian and Anatolian tectonic plates that is known to be “Particularly Devastating”.
- NAF is right-lateral strike-slip structure in northern Turkey accommodating much of the translational motion of the Anatolia block westwards with respect to Eurasia and Africa.
- The EAF is the tectonic boundary between the Anatolian Plate and the northward-moving Arabian Plate. It runs 650 kilometers from eastern Turkey and into the Mediterranean.
- The NAF line is the meeting point of the Eurasian and Anatolian tectonic plates that is known to be “Particularly Devastating”.
- In addition to this, the Aegean Sea Plate, located in the eastern Mediterranean Sea under southern Greece and western Turkey, is also a source of seismic activity in the region.
- According to one estimate, almost 95% of Turkey's land mass is prone to earthquakes, while about a third of the country is at high risk, including the areas around the major cities of Istanbul and Izmir and the region of East Anatolia.
How Regular Earthquake is Different from Strike Slip Earthquake?
- Plate Movement: In a strike-slip earthquake, two tectonic plates move horizontally past each other, whereas in a regular earthquake, the movement is vertical.
- Fault Zones, Tectonic Earthquakes, Volcanic Earthquake, Human Induced Earthquakes are the different types of Earthquakes.
- Fault Type and Location: Strike-slip earthquakes occur along transform boundaries such as the San Andreas Fault in California while regular earthquakes occur along divergent or convergent plate boundaries where the plates move vertically such as along the Pacific "Ring of Fire.
- Causes: The cause of strike-slip fault earthquakes is due to the movement of the two plates against one another and the release of built-up strain.
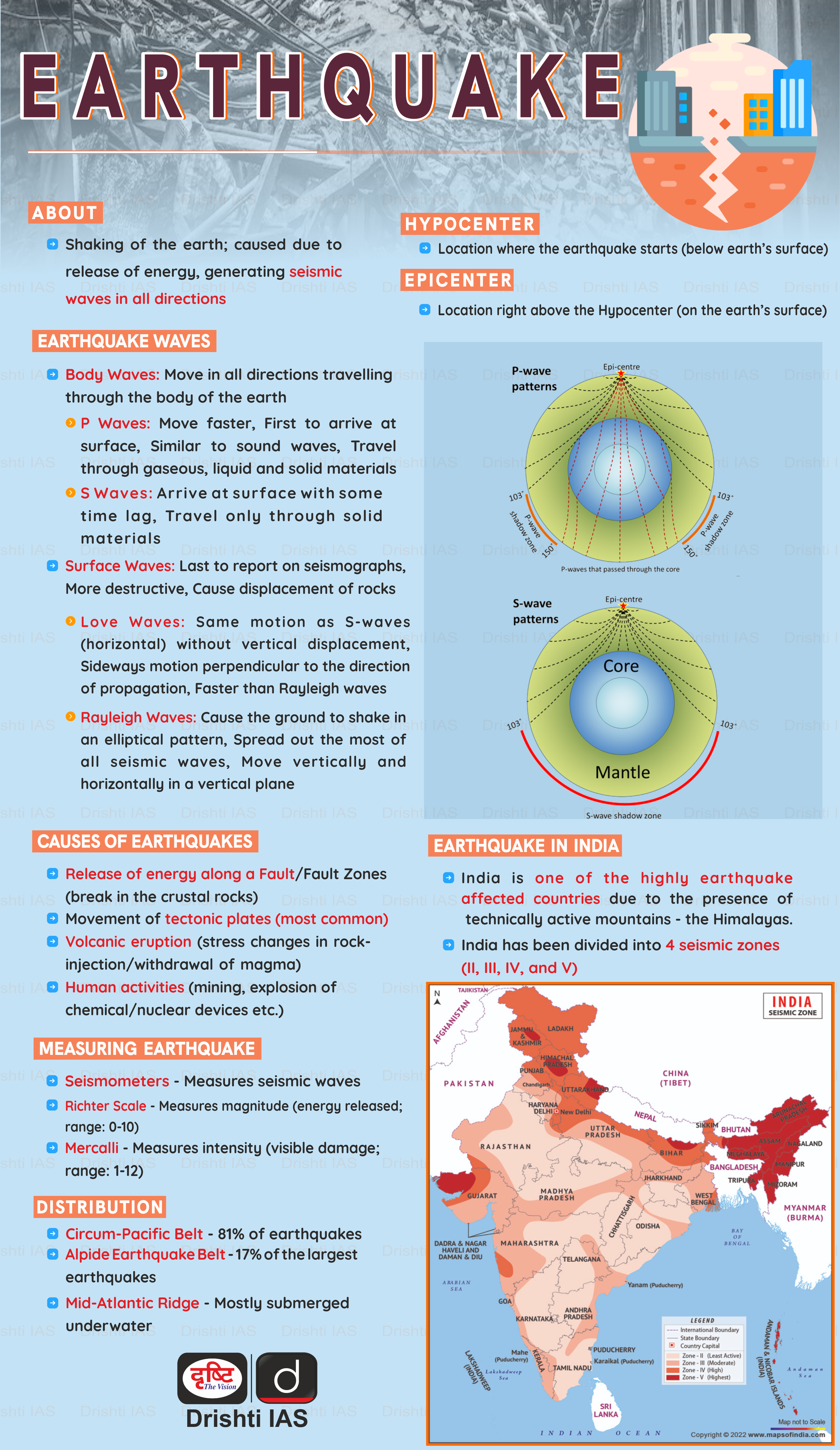
Do Shallow Earthquake cause greater Damage?
- A shallow earthquake is an earthquake that occurs at a shallow depth, usually within the Earth's crust, near the surface. They typically have a depth of less than 70 km and can result in strong ground shaking and surface faulting.
- They are often more damaging than deep earthquakes because the energy from the seismic waves is released closer to the surface, leading to stronger ground motion and more intense shaking.
- This can cause damage to buildings and infrastructure, as well as triggers landslides, rockfalls, and other secondary hazards.
- However, the amount of damage caused by an earthquake depends on a number of factors, including the magnitude of the earthquake, the distance from the epicenter, the depth of the earthquake, the type of soil and geological conditions at the surface.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The frequency of earthquakes appears to have increased in the Indian subcontinent. However, India’s preparedness for mitigating their impact has significant gaps. Discuss various aspects. (2015)
Q. Discuss about the vulnerability of India to earthquake related hazards. Give examples including the salient features of major disasters caused by earthquakes in different parts of India during the last three decades. (2021)


Indian Polity
National Commission for Scheduled Tribes
For Prelims: NCST, Constitutional Provisions related to STs.
For Mains: NCST: Functions, Scheduled Tribes: Provisions, Initiatives.
Why in News?
The recent data presented by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) revealed that the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) is currently functioning with less than 50% of its sanctioned strength.
What is the NCST?
- Formation: NCST was set up in 2004 by amending Article 338 and by inserting a new article 338A in the Constitution through the 89th Constitution Amendment Act, 2003. Hence, it is a constitutional body.
- By this amendment, the erstwhile National Commission for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes was replaced by two separate Commissions namely:
- the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC), and
- the NCST
- By this amendment, the erstwhile National Commission for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes was replaced by two separate Commissions namely:
- Objective: Article 338A inter-alia gives powers to the NCST to oversee the implementation of various safeguards provided to Scheduled Tribes (STs) under the Constitution or under any other law for time being in force or under any other order to the Government and to evaluate the working of such safeguards.
- Composition: It consists of a Chairperson, a Vice-Chairperson and 3 other Members who are appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal.
- At least one member should be a woman.
- The Chairperson, the Vice-Chairperson and the other Members hold office for a term of 3 years.
- The Chairperson has been given the rank of Union Cabinet Minister, the Vice Chairperson has the rank of a Minister of State and other Members have the rank of Secretary to the Government of India.
- The members are not eligible for appointments for more than two terms.
What are the Duties and Functions of the NCST?
- To investigate and monitor all matters relating to the safeguards provided for the STs under the Constitution or under any other law for the time being in force or under any order of the Government.
- To inquire into specific complaints with respect to the deprivation of rights and safeguards of the STs.
- To participate and advise in the planning process of the socio-economic development of the STs and to evaluate the progress of their development.
- The Commission shall provide reports on the operation of those safeguards to the President annually and as necessary.
- To make in such reports recommendations as to the measures that should be taken by the Union or any State for effective implementation of those safeguards.
- The President, subject to the provisions of any law made by Parliament, may, by rule, discharge any other functions relating to the protection, welfare, development, and advancement of the STs.
What are the Provisions Related to STs in India?
- Definition:
- The Constitution of India does not define the criteria for recognition of STs. As per Census-1931, STs are termed as "backward tribes” living in the "Excluded" and "Partially Excluded" areas.
- The Government of India Act of 1935 called for the first time for representatives of "backward tribes" in provincial assemblies.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 366(25): It only provides a process to define STs:
- “STs means such tribes or tribal communities or parts of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to be Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this Constitution.”
- Article 342(1): The President with respect to any State/UT (after consultation with the Governor in case of state) may specify the tribes/tribal communities/part of or groups within tribes/ tribal communities as a Scheduled Tribe in that State/UT.
- Fifth Schedule: It lays out provisions for the Administration and Control of Scheduled Areas and STs in states other than 6th Schedule States.
- Sixth Schedule: Deals with the administration of the tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- Article 366(25): It only provides a process to define STs:
- Statutory Provisions:
- Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955 against Untouchability.
- Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989.
- Provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to the Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996.
- Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
Conclusion
The vacancies should be immediately filled as there should be no reason now for any further delay since the recruitment rules have been suitably revised. Moreover, the lack of manpower is leading to difficulties in performing the functions as well which also makes it important to fill the vacancies immediately for the effective performance of the commission.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Every year, a month long ecologically important campaign/festival is held during which certain communities/tribes plant saplings of fruit-bearing trees. Which of the following are such communities/ tribes? (2014)
(a) Bhutia and Lepcha
(b) Gond and Korku
(c) Irula and Toda
(d) Sahariya and Agariya
Ans: (b)
Q2. The provisions in Fifth Schedule and Sixth Schedule in the Constitution of India are made in order to (2015)
(a) protect the interests of Scheduled Tribes
(b) determine the boundaries between States
(c) determine the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats
(d) protect the interests of all the border States
Ans: (a)
Q3. Under which Schedule of the Constitution of India can the transfer of tribal land to private parties for mining be declared null and void? (2019)
(a) Third Schedule
(b) Fifth Schedule
(c) Ninth Schedule
(d) Twelfth Schedule
Ans: (b)
Q4. If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
(a) This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
(b) This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
(c) This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
(d) The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (2017)


Governance
Hate Crimes in India
For Prelims: Hate Crimes, Article 14, IPC Sections (153A 153B, 295A).
For Mains: Indian Laws Against Hate Crimes, Major Factors Responsible for Hate Crime, Possible Ways to Deal with Hate Crimes in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) observed that there is a growing consensus around hate speech and stressed there is no scope for hate crimes on the basis of religion in a secular country like India. And, it is the primary duty of the State to protect citizens from hate crimes.
What are Hate Crimes?
- About:
- Hate crimes refer to violent or abusive acts committed against individuals or groups based on their religion, caste, ethnicity, sexual orientation, or other identities.
- These crimes often involve acts of violence, intimidation, or threats, and they target individuals or groups who are perceived as being different or marginalized.
- The Indian Constitution guarantees equality and prohibits discrimination on the grounds of religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth, (Article 14) but despite this, hate crimes remain a persistent problem in the country.
- Hate crimes refer to violent or abusive acts committed against individuals or groups based on their religion, caste, ethnicity, sexual orientation, or other identities.
- Indian Laws Against Hate Crimes:
- Hate crime is neither well defined in the Indian legal framework nor can it be easily reduced to a standard definition due to the myriad forms it can take.
- However, Hate speeches are dealt under IPC under Sections 153A, 153B, 295A, 298, 505(1) and 505(2) that declares that word, spoken or written, that promotes disharmony, hatred, or insults on basis of religion, ethnicity, culture, language, region, caste, community, race etc., is punishable under law.
- Hate crime is neither well defined in the Indian legal framework nor can it be easily reduced to a standard definition due to the myriad forms it can take.
- Major Factors Responsible for Hate Crime:
- Religious and Ethnic Tensions: India is a diverse country with a multitude of different religious and ethnic groups. These tensions often lead to violence and hate crimes.
- Caste-based Discrimination: India has a long history of caste-based discrimination, which has contributed to the marginalization of certain groups and the perpetration of hate crimes against them.
- Lack of Political Will: Despite the presence of laws and regulations to address hate crimes, the lack of political will to enforce them effectively has created a permissive environment for such crimes to occur.
- Social Media and Misinformation: The spread of hate speech and misinformation on social media can further fuel tensions and contribute to the perpetration of hate crimes.
What are Possible Ways to Deal with Hate Crimes in India?
- Awareness Campaigns: The first step in addressing hate crime is to raise awareness about its harmful effects on individuals and society as a whole.
- Mass media campaigns and community outreach programs can be used to educate people about the consequences of hate crime and encourage them to report such incidents.
- Community Engagement: Communities can play an important role in addressing hate crime. This can be done by creating spaces where people can come together and have open and honest discussions about the issues that divide them.
- This can also help to build bridges between different communities and foster greater understanding and respect.
- Use of Technology: Technology can be used to improve reporting and tracking of hate crimes. This can include developing online reporting systems and using data analytics to identify trends and hotspots for hate crime.
- Restorative Justice Programs: Restorative justice programs aim to repair harm and build relationships between victims, offenders and the community.
- These programs can be used in cases of hate crime to promote healing and reconciliation between affected communities.
- Stiffer Penalties: Another way to deal with hate crime is to impose stiffer penalties on those who engage in such behaviour. This can serve as a deterrent to others who may be considering committing hate crimes.


Important Facts For Prelims
Muons Penetrate Ancient Xi'an Fortress Wall
Why in News?
As per a new study, researchers are examining the fortress wall of Xi’an, an ancient city in China, by using tiny outer space particles Muons that can penetrate hundreds of metres of stone surfaces.
- Scientists have used a muon detector, called CORMIS (Cosmic Ray Muon Imaging System), to examine the wall of Xi’an city.
What are Muons?
- About:
- Muons are subatomic particles raining from space. They are created when the particles in Earth’s atmosphere collide with cosmic rays.
- Cosmic rays are the clusters of high-energy particles that move through space at almost the speed of light.
- According to Scientific American magazine, “about 10,000 muons reach every square metre of the Earth’s surface a minute”.
- Muons are subatomic particles raining from space. They are created when the particles in Earth’s atmosphere collide with cosmic rays.
- Properties:
- These particles resemble electrons but are 207 times as massive. Therefore, they are sometimes called “fat electrons”.
- Because muons are so heavy, they can travel through hundreds of metres of rock or other matter before getting absorbed or decayed.
- In comparison, electrons can penetrate through only a few centimetres.
- Also, muons are highly unstable and exist for just 2.2 microseconds.
What is Muography?
- About:
- The method of scanning large structures owing to the penetration power of muons is called Muography.
- Applications of Muography:
- Archaeology:
- With unique advantages, muography has gained increasing attention from archaeologists as a novel and innovative tool to investigate large-scale archaeological sites.
- Example: The first use of muography was in the late 1960s when a Nobel Prize-winning physicist named Luis Alvarez teamed up with Egyptologists to look for hidden rooms in the Pyramid of Khafre in Giza.
- With unique advantages, muography has gained increasing attention from archaeologists as a novel and innovative tool to investigate large-scale archaeological sites.
- Other Applications:
- Muography has also found use in customs security, internal imaging of volcanoes and others.
- In 2015, scientists used the technique to look inside the Fukushima nuclear reactors after the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan.
- It is also being used by researchers to analyze Mount Vesuvius, a volcano in Italy.
- Muography has also found use in customs security, internal imaging of volcanoes and others.
- Archaeology:


Important Facts For Prelims
Visva-Bharati to be World’s First Living Heritage University
Why in News?
Visva-Bharati University, founded by Rabindranath Tagore in 1921, is set to become the world's first "living heritage university". The university is expected to receive the heritage tag from UNESCO in April or May 2023.
- Normally heritage tag is given to a dead monument. For the first time in the world, a living university which is functioning is going to get the heritage tag from UNESCO.
What are the Key Points Related to Visva-Bharati University?
- It is located in Shantiniketan, West Bengal, India. When founded in 1921, it was named after Nobel Laureate Rabindranath Tagore until Visva-Bharati Society was registered as an organization in May 1922.
- Rabindranath believed in open-air education and introduced that system at the university, which prevails to date.
- According to UNESCO, in 1922, Visva-Bharati was inaugurated as a Centre for Culture with exploration into the arts, language, humanities, music and these are reflected in diverse institutes that continue in their educational programmes like including Hindi studies, Sino-Asian studies, humanities, fine arts, and music.
- They are based on the founding principles of excellence in culture and culture studies.
- Until Independence, it was a college and the institution was given the status of Central University in 1951 through a Central Act.
- The structures within the institutes of Visva-Bharati University are diverse in architectural expression.
- Examples include the
- Kalo Bari (a mud structure with coal tar finish and sculpture panels)
- Mastermoshai studio (a single-story structure built for the first principal of Kala Bhavan, Nandalal Bose)
- Murals and paintings on Cheena and Hindi Bhavan
- Examples include the
What is UNESCO?
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) is a specialised agency of the United Nations that promotes cooperation among nations through education, science, culture, and communication.
- Major Initiatives of UNESCO:


Important Facts For Prelims
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
Why in News?
As per the sample survey conducted at the national level by Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE) to assess employment generation under Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY), the scheme helped in generating 1.12 crore net additional employment during a period of approximately 3 years (i.e., from 2015 to 2018).
What are the Other Highlights of the Survey?
- Out of 81 lakh loans given in the state of Rajasthan, over 52 lakh were given to women entrepreneurs in the last three financial years, which is 64% of all loans.
- The PMMY has been expanded over time:
- In 2016-17, the scheme was expanded to cover activities related to agriculture, such as fishing, dairy, and food processing.
- In 2017-18, loans for tractors and power tillers became eligible under PMMY, with a maximum limit of Rs. 10 lakhs.
- From 2018-19 onwards, loans for two-wheelers for commercial use were included in PMMY.
What is Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana?
- About:
- PMMY was launched by the Government of India in 2015.
- The PMMY provides collateral-free institutional loans up to Rs. 10 lakhs for small business enterprises.
- Funding Provision:
- It is provided by Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) i.e. Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs).
- Types:
- The loan can be used for income-generating activities in the manufacturing, trading, services sector, and agriculture.
- There are three loan products under PMMY:
- Shishu (loans up to Rs. 50,000)
- Kishore (loans between Rs. 50,000 and Rs. 5 lakh)
- Tarun (loans between Rs. 5 lakh and Rs. 10 lakh).
- Steps Taken for the Improvement of the Scheme:
- Provision for online applications through udyamimitra portal.
- Some Public Sector Banks (PSBs) have put end-to-end digital lending for automated sanctions under PMMY.
- Intensive publicity campaigns by PSBs and Mudra Ltd. for increased visibility of the scheme amongst the stakeholders.
- Nomination of Mudra Nodal Officers in PSBs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at (2016)
(a) bringing the small entrepreneurs into formal financial system
(b) providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
(c) providing pensions to old and destitute persons
(d) funding the voluntary organizations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
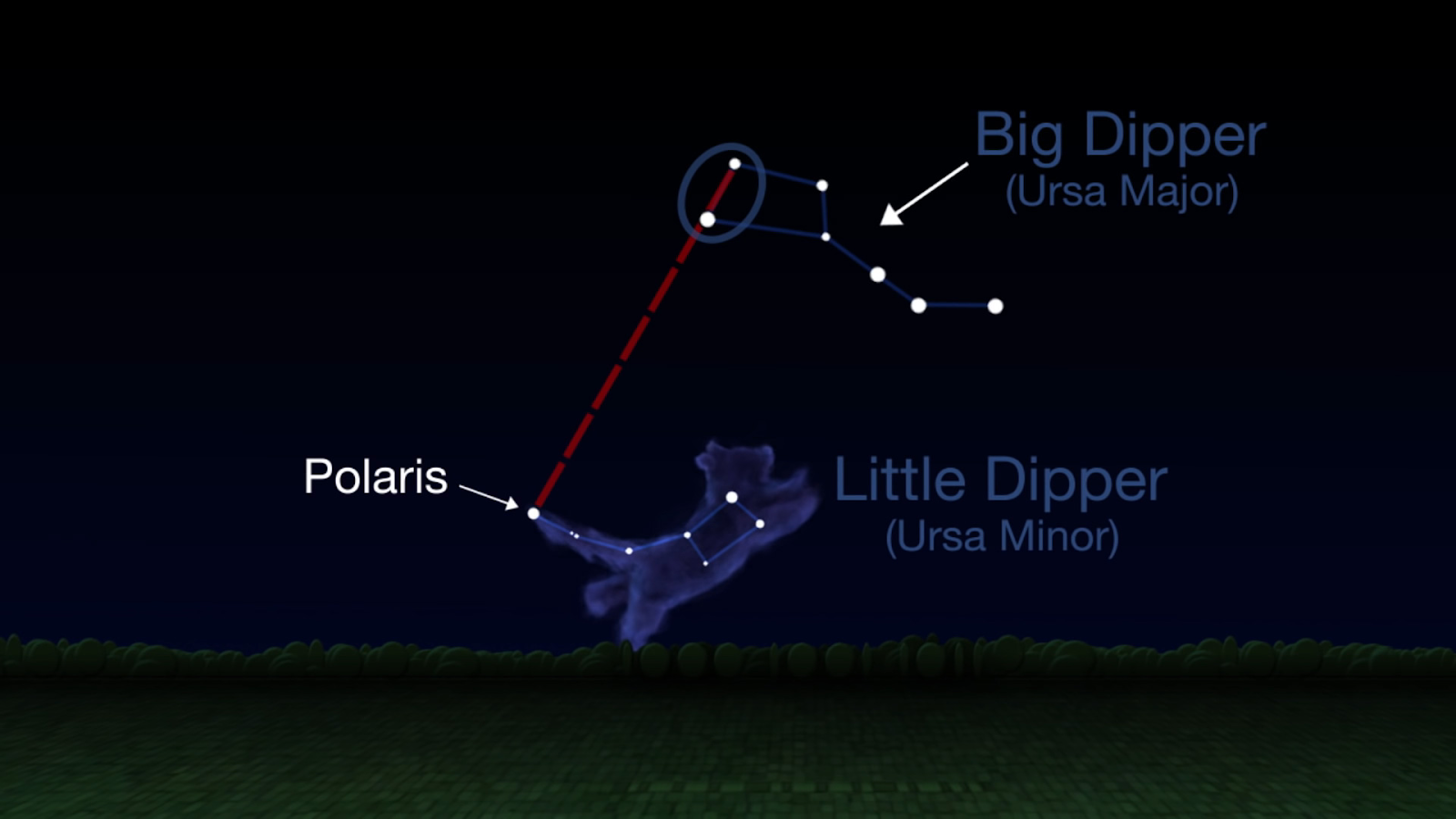
North Star
Polaris, known as the North Star/Pole Star, is a very bright star (~2,500 times more luminous than the Sun) and is part of the constellation Ursa Minor (~323 LY away from the Earth).
Polaris is less than 1° away from the north celestial pole, almost in direct line with the Earth’s rotational axis, therefore, it appears to sit motionless in the northern sky with all the other stars appearing to rotate around it.Its position and brightness have allowed humans to use it for navigation since late antiquity. The elevation of the star above the horizon gives the approximate latitude of the observer. However, upon crossing the equator to the south, the North Star is lost over the horizon, and hence stops being a useful navigational aid.
Polaris seems to have been first charted by the Roman mathematician/astronomer Ptolemy (165 - 85 BC).
As per NASA, “North Star” is “a title that passes to different stars over time”; as the Earth’s axis of rotation wobbles, the celestial pole “wanders in a slow circle over the eons, sweeping past different stars”. About 14,000 years ago, the celestial pole pointed towards the bright star Vega, and “it will again point to Vega in about 12,000 years”.
Naval LCA Lands on INS Vikrant
The Naval variant of India’s indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) made its maiden landing on board the INS Vikrant, marking a milestone towards the Navy’s self-reliance plans. This was followed by a landing and take-off by a twin-engine MiG-29K fighter jet (Russian origin).
INS Vikrant, India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier commissioned in Sept 2022, is currently in the process of getting operationalised.
In Jan 2020, DRDO demonstrated a successful landing of Naval LCA on INS Vikramaditya along the lines of which the DRDO is in the process of developing a Twin Engine Deck- Based Fighter (TEDBF) for INS Vikrant.
Read More - INS Vikrant
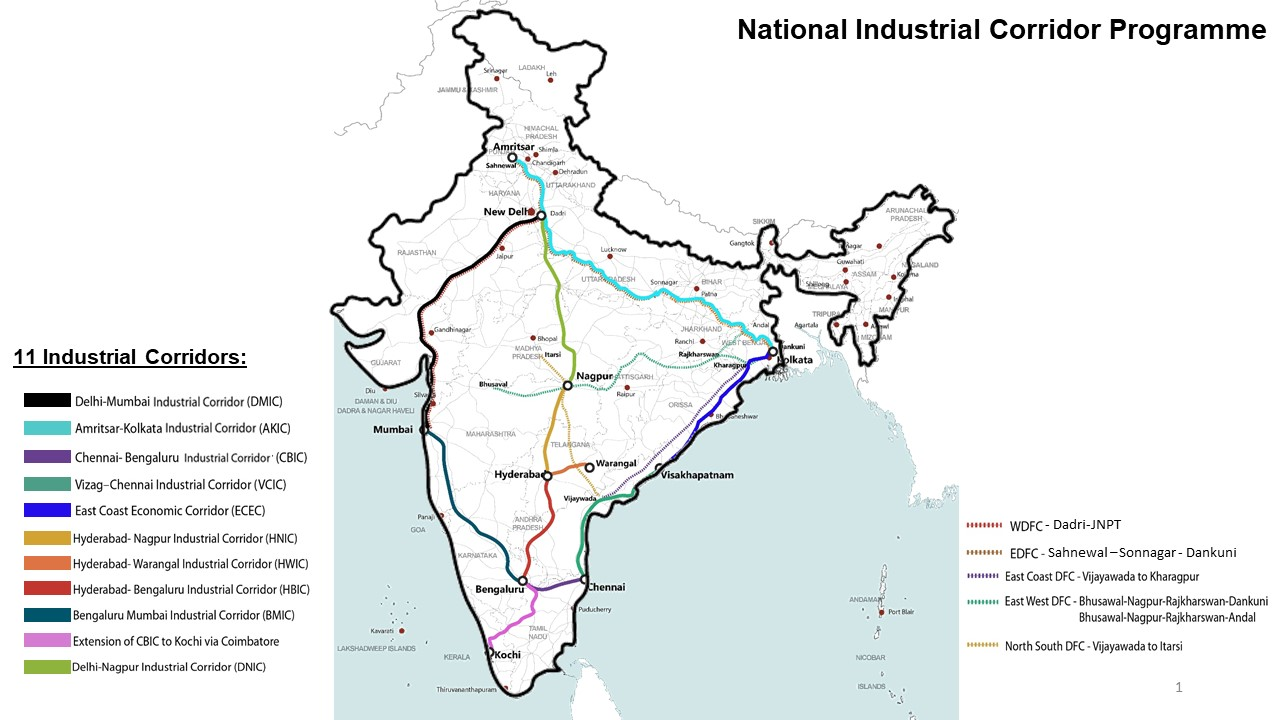
Southern India’s First Industrial Corridor Project
The Prime Minister of India laid the foundation stone of southern India’s 1st Industrial Corridor Project to be implemented at Tumakuru, spread over 8500 Acre of land, under the Chennai-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
The Tumakuru Industrial Township has been planned in line with the principles of PM-GatiShakti to ensure last mile multimodal connectivity to the economic zone.
The Govt of India (via NICD and Implementation Trust) and the Govt of Karnataka are developing the Industrial Township at Vasanthanarasapura in 3 phases in Tumakuru district through the project Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV).
Under the National Industrial Corridor Development (NICD) Programme, 32 greenfield industrial smart cities under 11 industrial corridors are being developed with world class Plug-n-Play infrastructure.
Read More - PM Gati Shakti
Yuva Sangam Portal
The “Yuva Sangam” registration portal was recently launched at Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA), New Delhi.
Yuva Sangam is an initiative to build close ties between the youth of the Northeast Region and the rest of India under the spirit of Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat. Under this initiative, over 20000 youth will travel across India and gain a unique opportunity of cross-cultural learning. The program is an opportunity for the youth of NER to see India.
Read More - North-East India