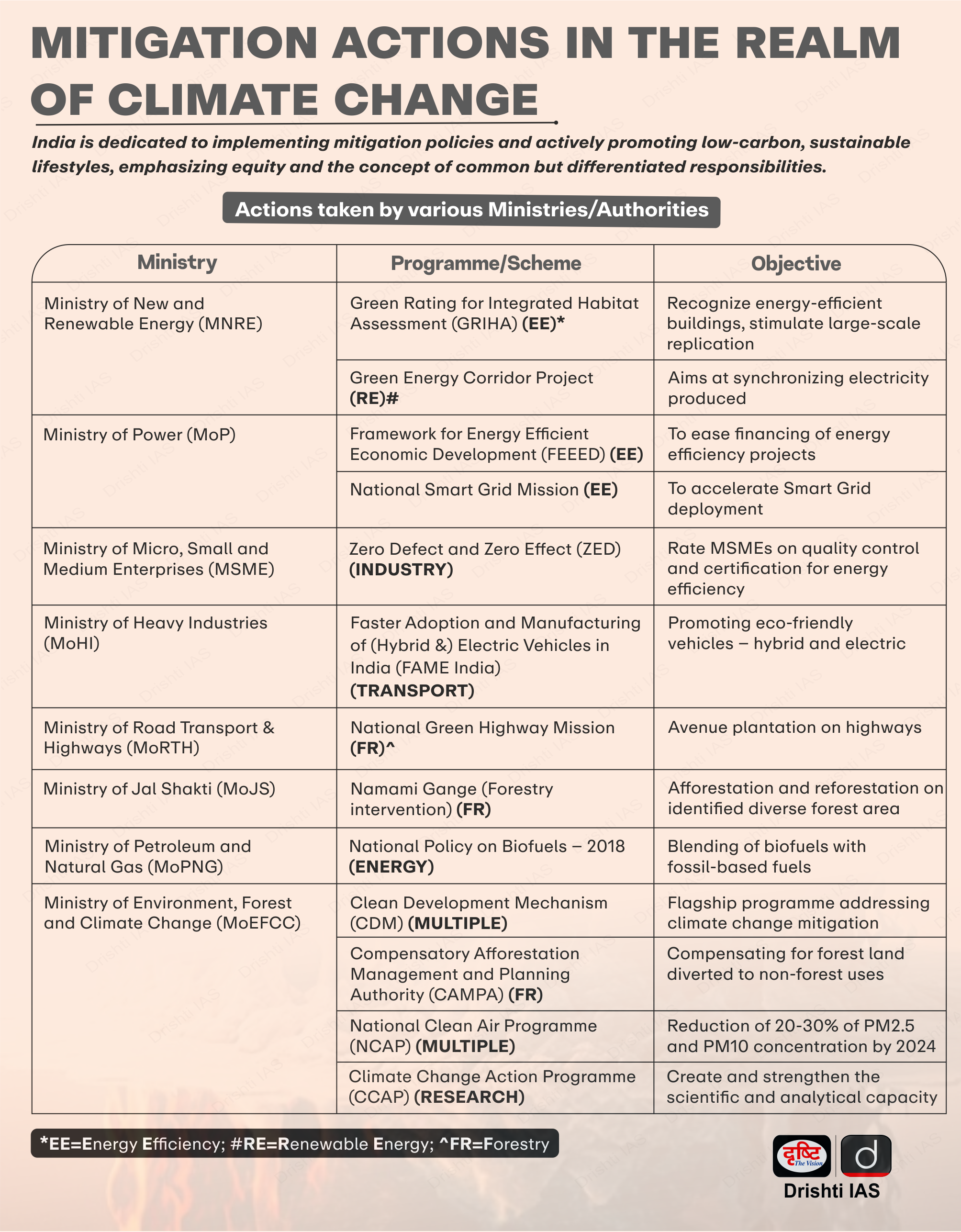
Infographics
International Relations
Africa at Centre of India’s Vision for Global South
For Prelims: Global South, India-Africa Relations, Voice of Global South Summit, United Nation Security Council, Brandt Line, Group of 77, African Union, Horn of Africa.
For Mains: India’s Vision for the Global South, Prioritizing Africa in its Global South Vision.
Why in News?
India's increased emphasis on Africa has been highlighted during various state visits. This shift is significant as it reflects India's growing stature as a major global power, providing an opportunity to champion the interests of the Global South.
What is India’s Vision for the Global South?
- Giving Voice to the Global South: India sees itself as a representative for developing countries, ensuring their issues are heard at forums like G20.
- This includes initiatives like the "Voice of Global South Summit" aimed at creating a platform for developing countries to discuss common challenges.
- Advocacy and Reform: India advocates for reforms in global institutions to better reflect the interests of developing countries.
- This could involve changes in areas like international taxation, climate finance or giving greater decision-making power to developing nations within organisations like the United Nations Security Council.
- South-South Cooperation: India promotes cooperation among developing countries by sharing best practices, technologies, and resources.
- The India-UN Development Partnership Fund, launched in 2017 aids Southern-led sustainable development projects, prioritising least developed countries and small island developing States.
- Climate Change Mitigation: India's vision for the Global South includes collaborative efforts to address climate change.
- Through initiatives like the International Solar Alliance (ISA), India aims to promote renewable energy adoption in countries across Asia, Africa, and Latin America, contributing to sustainable development and climate resilience.
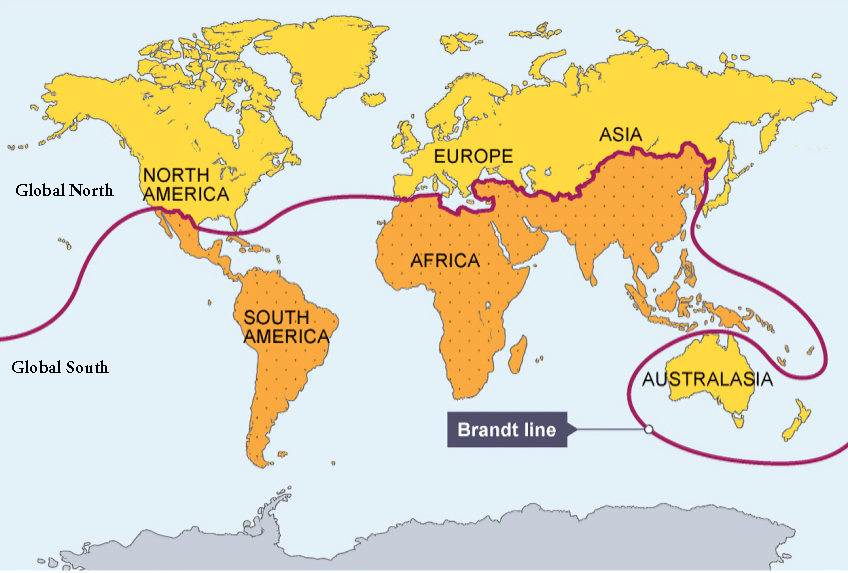
What is Global South?
- About: Global South refers to a group of countries generally characterised as developing, less developed, or underdeveloped.
- The term Global South is not geographical. Rather, its usage denotes a mix of political, geopolitical and economic commonalities between nations.
- It encompasses countries with lower GDPs, higher poverty rates, and less developed infrastructure than the "Global North."
- These nations are typically located in Africa, Latin America, the Caribbean, and Asia (excluding high-income countries like Japan, South Korea and Australia).
- History:
- The term Global South appears to have been first used in 1969 by political activist Carl Oglesby.
- The Brandt Line, introduced by former German Chancellor Willy Brandt in the 1980s, visually represents the global north-south economic divide using per-capita GDP as a measure.
- The Group of 77 (G-77) was established in 1964 during the first UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) session in Geneva, making it the largest intergovernmental organisation of developing nations at that time.
How can India Benefit from Prioritising Africa in its Global South Vision?
- Economic Potential: Africa represents a vast economic opportunity for India. With Indian investments in Africa reaching USD 98 billion in 2023 and trade totaling USD 100 billion, the continent serves as a crucial market for Indian businesses.
- Enhanced Strategic Ties: Africa's influence in global forums is rising, making it a strategic partner for India's global aspirations.
- India's advocacy for African representation in forums like the G20 and UNSC reflects the shared vision for inclusive global governance.
- In this regard, India has achieved several diplomatic victories, such as the African Union’s (AU) inclusion in the G20 in September 2023.
- Tapping Youthful Demographics: Africa's young population, with 60% under the age of 25 years, presents immense potential for collaboration in education, technology, and innovation.
- India's experience in skill development and education initiatives can be leveraged to empower African youth and foster sustainable development.
- Potential Resource Collaboration: Africa's rich reserves of critical minerals essential for industries like renewable energy and technology offer a significant opportunity for collaboration.
- India's expertise in sectors like renewable energy can be combined with Africa's resources to drive innovation and sustainable development.
- Stronger Geopolitical Influence: A strong partnership with Africa enhances India's strategic standing on the world stage.
- It allows India to play a more influential role in shaping global governance and addressing issues critical to the Global South.
- India's growing ties with Africa can help counterbalance China's rising influence on the continent (especially in the Horn of Africa).
What are the Challenges for India as a Leader in the Global South?
- Internal Development Issues: Critics argue India should prioritise its domestic development issues like unequal wealth distribution, unemployment, and inadequate infrastructure, before leading others.
- India's vast rural population lacks access to quality healthcare and education, raising questions about its capacity to address similar issues in other developing nations.
- Diverse Needs and Priorities: The Global South is not a homogenous group. Different countries have varying needs and priorities. Balancing these diverse demands can be difficult.
- African nations might prioritise debt relief, while Southeast Asian nations might focus on technology transfer.
- India needs to find ways to address these distinct needs while promoting a unified front.
- Balancing Global Partnerships: India enjoys strong economic ties with developed nations like the US and Japan. This can create a conflict between advocating for the Global South and maintaining these vital relationships.
- India might shy away from pushing for stricter trade regulations that could potentially harm its exports to developed countries.
- Credibility on Climate Change: India is the world's third-largest emitter of CO2, despite low per capita CO2 emissions. This weakens its position when advocating for stricter climate action within the Global South.
Way Forward
- Frugal Tech Innovation: India can leverage its expertise in frugal innovation by establishing labs focused on developing low-cost, scalable tech solutions for common challenges in the Global South, like mobile health diagnostics or remote learning platforms.
- Rotating Leadership: Instead of a single leader, India could champion a rotating leadership council with representation from different regions within the Global South. This fosters a more collaborative and inclusive approach.
- Global South Satellite Network: India can lead the development of a network of low-cost satellites launched by and operated by a consortium of developing nations. This network can provide essential data and services for areas lacking traditional infrastructure and internet facilities.
- India can also utilise advanced satellite technology like RISAT to develop a quick disaster response network within the Global South.
- South-South Vocational Training Centers: Setting up vocational training centres in strategic locations across the Global South, offering skill development programs relevant to local needs.
- This equips individuals with the skills necessary to thrive in the job market and contribute to their economies.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. What strategies and initiatives can India prioritise as a leader of the Global South to address common development challenges, promote regional cooperation, and enhance South-South partnerships? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘The long-sustained image of India as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised nations has disappeared on account of its new found role in the emerging global order.’ Elaborate. (2019)
Agriculture
Accelerating Crop Diversification in India
For Prelims: Crop diversification, Wheat cultivation, Wheat blast disease, Bananas, Green Revolution in India, Leguminous crops, Biofuel, MSP.
For Mains: Needs For Crop Diversification in India, Concerns Related to Crop Diversification.
Why in News?
In recent years, West Bengal has been witnessing a significant transformation in its agricultural landscape through crop diversification, particularly in districts bordering Bangladesh.
- This shift is characterised by farmers moving away from traditional wheat cultivation towards alternatives like bananas, lentils, maize, and other crops.
What are the Reasons Behind the Shift from Wheat Production?
- Wheat Blast Disease: The emergence of wheat blast disease in Bangladesh in 2016 led to a two-year ban on wheat cultivation in border areas of West Bengal, including Murshidabad and Nadia districts, prompting farmers to explore alternative crops.
- Wheat blast disease is a fungal infection caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum (MoT) that primarily affects wheat crops.
- It manifests as dark lesions on wheat spikes, leaves, and stems, leading to severe yield losses.
- Wheat blast disease is a fungal infection caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum (MoT) that primarily affects wheat crops.
- Economic Viability: Farmers have highlighted the economic advantages of cultivating alternative crops such as bananas.
- The profitability of crops like bananas during peak seasons, coupled with stagnant wheat prices and concerns over water consumption, has contributed to the shift.
- Shift to Higher Output Crops: Maize cultivation has seen a significant uptick in the area as well, with production increasing eightfold from 2011 to 2023.
Why India Needs to Focus on Crop Diversification?
- About: Crop diversification refers to the practice of growing a variety of crops on a farm instead of focusing on a single crop.
- The Green Revolution in India, through the introduction of high-yielding rice and wheat varieties, resulted in a substantial increase in food output, effectively reducing hunger and malnutrition.
- However, the monoculture of these crops led to a decrease in crop variety, causing the decline of traditional, region-specific strains and a loss of genetic diversity.
- For instance, India has lost over 100,000 traditional rice varieties since the 1970s due to the Green Revolution's impact.
- Therefore, there is a need to shift towards crop diversification to promote sustainable agriculture.
- The Green Revolution in India, through the introduction of high-yielding rice and wheat varieties, resulted in a substantial increase in food output, effectively reducing hunger and malnutrition.
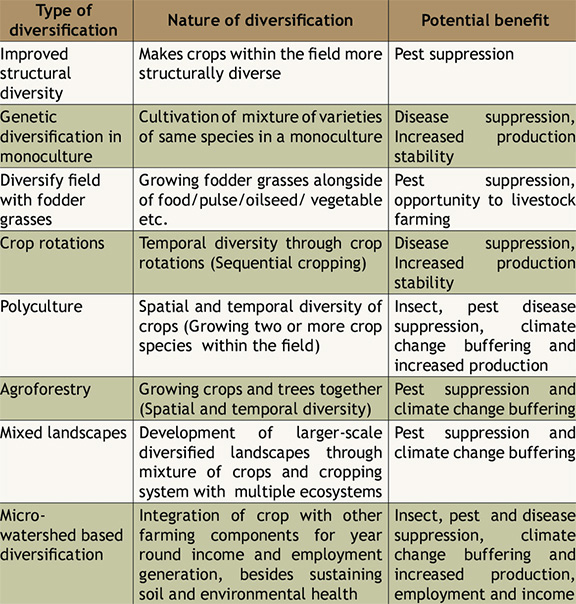
- Benefits of Crop Diversification:
- Risk Reduction: In regions prone to drought, farmers can diversify their crops by growing both drought-tolerant varieties (like millets or sorghum) and water-intensive crops (like rice or vegetables).
- If there's a water shortage, the drought-tolerant crops can still thrive, ensuring some level of harvest despite adverse conditions.
- Soil Health Improvement: Planting leguminous crops like soybeans or peanuts can fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting subsequent crops such as maize or wheat that require nitrogen-rich soil for optimal growth.
- Market Opportunities: Diversifying crops can help farmers tap into niche markets or emerging trends.
- For example, the rising demand for organic produce presents an opportunity for farmers to diversify into organic farming, which often commands higher prices in the market compared to conventionally grown crops.
- Pest and Disease Management: Intercropping or mixed cropping, a form of crop diversification, can help manage pests and diseases.
- For instance, planting marigold flowers alongside vegetable crops can deter pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and promoting natural pest control mechanisms.
- Source of Biofuels: Crops like Jatropha and Pongamia are potential sources for biofuel production. This can offer farmers additional income opportunities and contribute to India's energy security.
- Risk Reduction: In regions prone to drought, farmers can diversify their crops by growing both drought-tolerant varieties (like millets or sorghum) and water-intensive crops (like rice or vegetables).
- Concerns:
- Market Risks and Limited Opportunities: Farmers are often hesitant to switch from established crops like rice and wheat (which have assured government support through MSP) to lesser-known crops.
- These alternatives may have fluctuating market prices or limited demand, leading to potential income loss.
- Financial Constraints: Diversifying crops can require additional investment in seeds, equipment, and even acquiring new knowledge about cultivation practices.
- Smallholder farmers, who make up a significant portion of India's agricultural sector, may not have the financial resources to readily adopt these changes.
- Also, Millets like Jowar, Ragi, and Bajra are gaining traction due to their high nutritional value and ability to thrive in marginal lands.
- However, creating a robust market for these requires investment in processing facilities to convert them into consumer-friendly products like ready-to-eat mixes or breakfast cereals.
- Lack of Infrastructure and Storage: Perishable, diversified crops often require specialised storage and transportation facilities that may not be readily available in rural areas.
- Without proper infrastructure, these crops can spoil quickly, leading to wasted produce and lost income.
- Clash With Dietary Habits: Crop diversification in India, particularly in regions where rice and wheat are staples for a significant portion of the population, could potentially disrupt the established market dynamics and consumption patterns prevalent in these areas.
- Market Risks and Limited Opportunities: Farmers are often hesitant to switch from established crops like rice and wheat (which have assured government support through MSP) to lesser-known crops.
What are the Steps Taken by the Government Regarding Crop Diversification?
- Crop Diversification Programme: The Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) has been implementing the Crop Diversification Programme (CDP) since 2013-14, as part of the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY), specifically targeting the Original Green Revolution States- Haryana, Punjab, and Western Uttar Pradesh.
- This initiative aims to shift focus from water-intensive paddy cultivation to alternative crops such as pulses, oilseeds, coarse cereals, nutri cereals, and cotton.
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH): It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root & tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa and bamboo.
- Increase in MSP for Kharif Crops: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved an increase in the Minimum Support Prices (MSP) for all mandated Kharif crops for the Marketing Season 2023-24.
- Mera Pani-Meri Virasat Scheme (Haryana): It offers financial aid to farmers transitioning from paddy cultivation to water-saving alternatives like pulses, oilseeds, millets, and vegetables.
Way Forward
- Agri-Tourism and 'U-Pick' Farms: Experiential tourism is gaining popularity. Creating 'U-Pick' farms where tourists can harvest their fruits and vegetables directly from the field can be a win-win for India.
- This provides farmers with additional income, fosters a connection between consumers and agriculture, and promotes appreciation for diversified crops.
- Biofortification through Gene Editing: Gene editing techniques like CRISPR can be used to develop crops with enhanced nutritional value.
- This can address malnutrition concerns and create new markets for biofortified crops.
- However, ethical considerations and stringent regulations need to be addressed.
- Regenerative Agriculture for Sustainable Diversification: Regenerative agriculture practices like cover cropping, composting, and no-till farming can be integrated with diversified crop rotations to create a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system.
- This not only benefits long-term crop yields but also sequesters carbon, mitigating climate change.
|
Drushti Mains Question: Q. What are the key innovative strategies that India needs to expedite to accelerate crop diversification, ensuring sustainable agriculture, farmer livelihoods, and food security? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. How did India benefit from the contributions of Sir M. Visvesvaraya and Dr. M.S. Swaminathan in the fields of water engineering and agricultural science respectively? (2019)
Q. Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How have these revolutions helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (2017)
Geography
Magnetic Fossils in Bay of Bengal
For Prelims: Magento Fossils, Magnetotactic bacteria, Earth's magnetic field, Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, Middle Eocene Climatic Optimum, Bay of Bengal, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, National Institute of Oceanography, Electron Microscopy
For Mains: Significance of Study of Magneto Fossils.
Why in News?
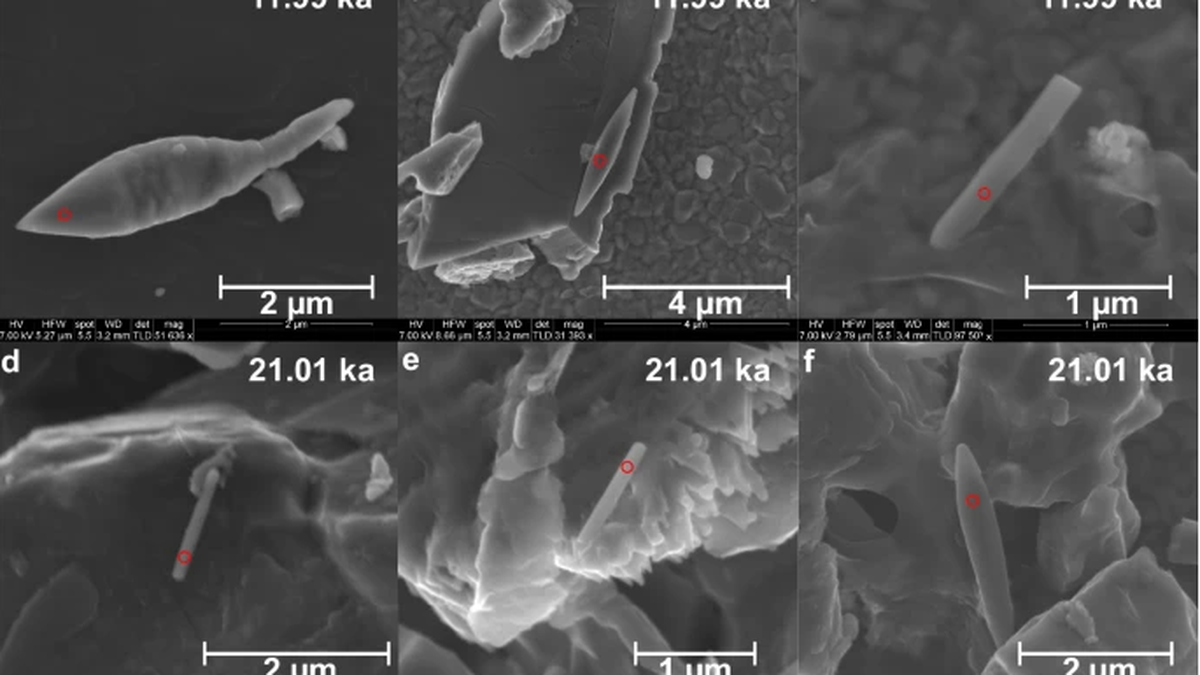
Recently, scientists have unearthed a 50,000-year-old sediment, a massive magneto fossil found deep in the Bay of Bengal, marking one of the youngest discoveries of its kind.
- Scientists at CSIR-National Institute of Oceanography, used magnetic analyses and electron microscopy to study a sediment sample from the southwestern Bay of Bengal.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Monsoon Fluctuations: Analysis of sediment samples indicated fluctuations in monsoon strength during the last Glacial Maximum-Holocene period, impacting weathering and sedimentation.
- Optimal Conditions for Magnetic Fossil Growth: The study suggests that warming events are not necessary for giant magneto fossil formation; instead, an optimal balance of iron, organic carbon, and suboxic conditions is crucial.
- Information Encoded by Magnetofossils: Magnetofossils encode information about past environmental conditions, including nutrient availability, oxygen levels, and water stratification in ancient aquatic environments.
- Rivers like Godavari, Mahanadi, Ganga-Brahmaputra, Cauvery, and Penner, discharging into the Bay of Bengal, contributed to magneto fossil formation by providing nutrient-rich sediment and reactive iron.
What are Magento Fossils?
- About:
- "Magneto Fossils" refer to fossilised remains of magnetotactic bacteria that contain magnetic minerals.
- Magnetotactic bacteria leave fossilised magnetic particles in geological records.
- Magnetotactic Bacteria:
- Magnetotactic bacteria are mostly prokaryotic organisms that arrange themselves along the earth’s magnetic field. It was discovered by Salvatore Bellini in 1963.
- These organisms follow the magnetic field to reach places that had optimal oxygen concentration. This process is facilitated by the presence of iron-rich crystals within their cells.
- Magnetotactic bacteria create tiny crystals of magnetite or greigite within their cells to navigate changing oxygen levels and sediment saturation in water bodies.
- Crystals within magnetotactic bacteria are arranged in a chain configuration through magnetotaxis.
- Rare giant magneto fossils are less common than conventional magnetic fossils, these are likely produced by eukaryotes rather than bacteria.
- Origin of Magnetofossils:
- Most giant magnetofossils have been found in sediments dating to two geological time periods — Paleocen-Eocene Thermal Maximum (roughly 56,000 million years ago) and Middle Eocene Climatic Optimum (about 40 million years ago) — both of which were known for a rise in global temperature.
- It suggested that the magnetofossils formed only during periods of extreme warming.
- Discovery of giant magneto fossils from the Bay of Bengal were determined to be from the late Quaternary period, approximately 50,000 years ago, making them the youngest giant magneto fossils discovered to date.
- The present study challenges the assumption that the magnetofossils formed only during periods of extreme warming.
- Most giant magnetofossils have been found in sediments dating to two geological time periods — Paleocen-Eocene Thermal Maximum (roughly 56,000 million years ago) and Middle Eocene Climatic Optimum (about 40 million years ago) — both of which were known for a rise in global temperature.
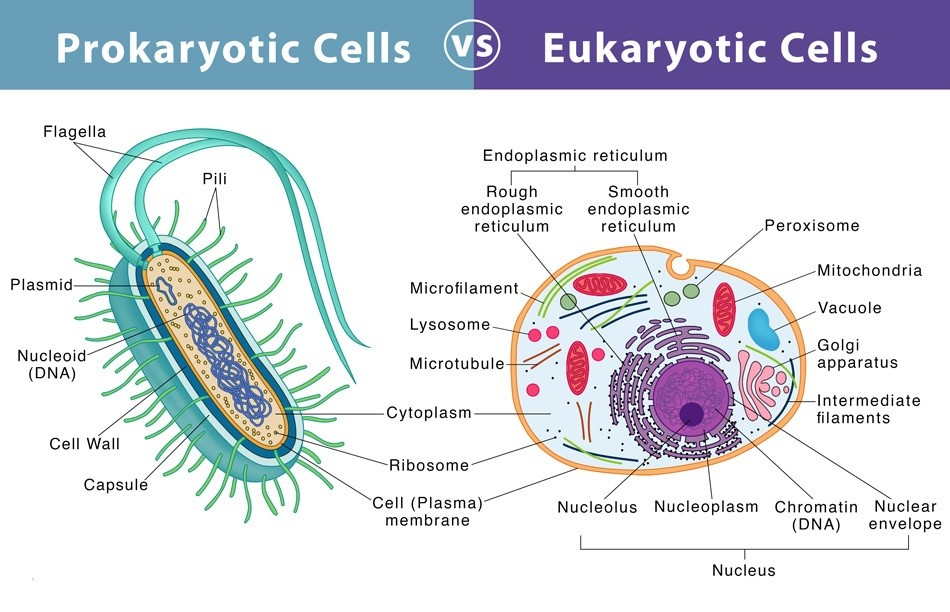
| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
|
|
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the Magento Fossils and the role of magnetotactic bacteria in their formation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The word ‘Denisovan’ is sometimes mentioned in media in reference to (2019)
(a) fossils of a kind of dinosaurs
(b) an early human species
(c) a cave system found in North-East India
(d) a geological period in the history of Indian subcontinent
Ans: (b)
Important Facts For Prelims
Green Steel Policy
Why in News?
The Steel Ministry is developing a comprehensive green steel policy, encompassing the manufacturing process, required skill set, and funding support, as part of a complete decarbonization strategy.
What is Green Steel?
- About:
- Green steel is the eco-friendly production of steel with lower greenhouse gas emissions, possibly reducing costs and enhancing quality compared to traditional methods.
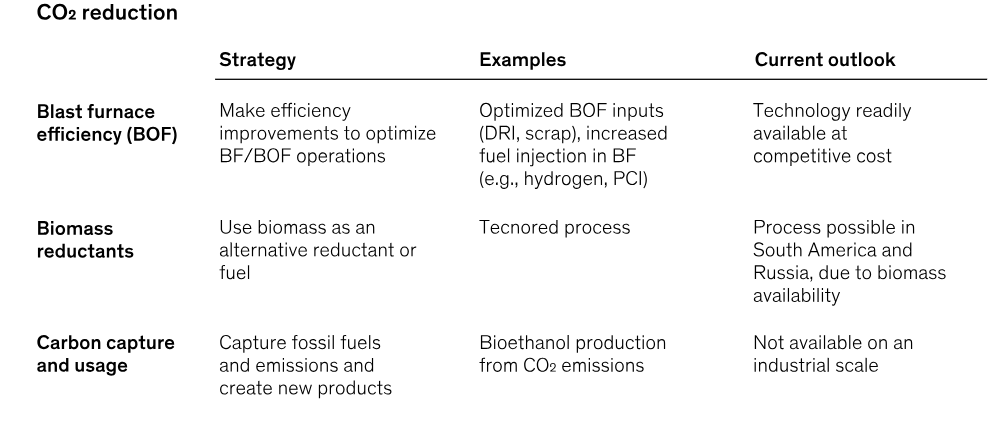
- Need:
- High Coal Consumption in Blast Furnace: The steel manufacturing process, involving blast furnaces, basic oxygen furnaces, and electric arc furnaces, is a major global source of carbon emissions, primarily due to the high coal and coke consumption in blast furnace operations.
- A study suggests that with steel demand projected to rise through the 21st century, there is a strong incentive to seek low greenhouse gas (GHG) emission alternatives for steel production.
- India's domestic steel sector contributes 12% of the country's greenhouse gas emissions, with an emission intensity of 2.55 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of crude steel, higher than the global average of 1.9 tonnes of CO2.
- High Coal Consumption in Blast Furnace: The steel manufacturing process, involving blast furnaces, basic oxygen furnaces, and electric arc furnaces, is a major global source of carbon emissions, primarily due to the high coal and coke consumption in blast furnace operations.
- As a Low-Grade Carbon Production Method:
- It Includes carbon capture and storage (CCS), using Green/Blue hydrogen, high biomass utilization, and artificial iron units (AIUs) for reducing carbon emissions and producing high-grade steel.
- Global Initiatives:
- First Movers Coalition:
- It is an initiative of the World Economic Forum to decarbonize industrial sectors like steel.
- The Coalition announced it had expanded, with 55 companies and nine countries now committed to purchasing a proportion of the industrial materials and transport they need from suppliers using near-zero or zero-carbon solutions.
- The Industrial Deep Decarbonization Initiative (IDDI):
- It encourages governments to report environmental data and use low-emission and near-zero emissions cement/concrete and steel in construction projects, with nine countries, including the U.S., having joined and set to declare their pledges.
- SteelZero and ConcreteZero:
- The Climate Group’s SteelZero and ConcreteZero initiatives are corporate partnerships with 25 and 22 companies respectively committed to using net-zero steel and low- and net-zero emission concrete — and effectively cement, as its key ingredient.
- European Union:
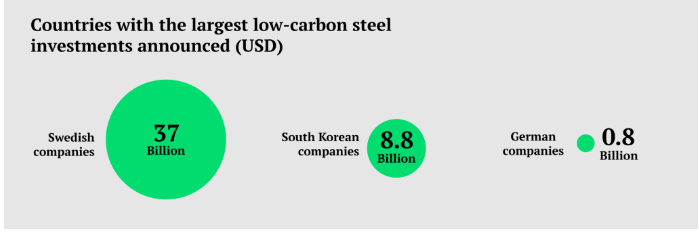
- By 2030, the European Union is projected to host nearly 50 green and low-carbon steel projects, driven in part by policies like the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism.
- Sweden:
- Hybrit supplied Volvo with the first coal-free "green steel," while H2 Green Steel is constructing a fossil fuel-free steel plant in Sweden with a sustainable hydrogen facility, both striving for environmentally friendly steel production.
- First Movers Coalition:
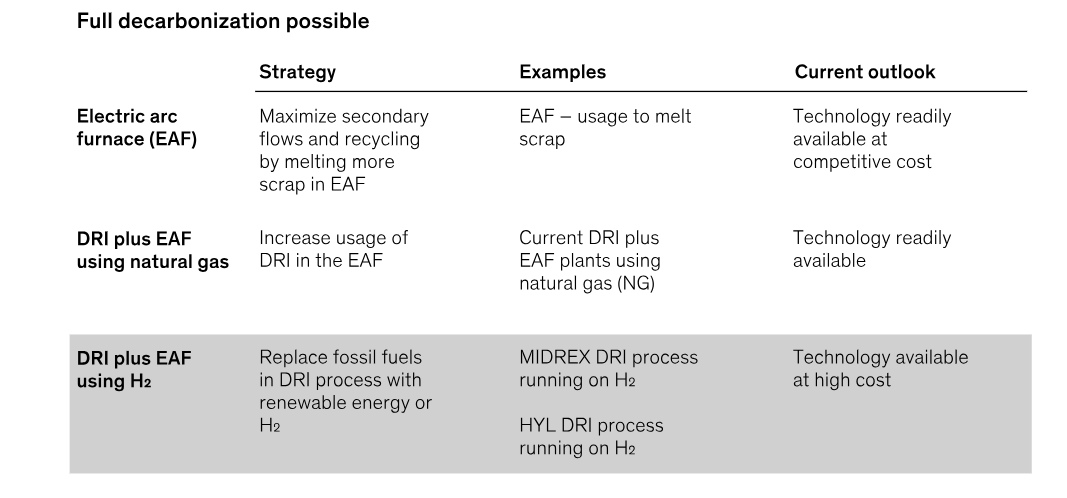
- India’s Initiative:
- The Steel Ministry is developing a green steel policy, including process definition, required skills, and funding, with a focus on complete decarbonization.
- Already 13-odd task forces had been formed to determine the various modalities around green steel-making, including a definition of the offering.
- Recently, the 14th task force was set up to explore the option of using biochar or biomass (as an alternative in blast furnaces) in steel-making, thereby bringing down carbon emissions during the manufacturing process.
- India is exploring its own pure-hydrogen-based DRI (direct reduction of iron) technology, with the project report currently under scrutiny, and also considering a consortium-based pilot for a hydrogen-based DRI facility.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has allocated ₹455 crore for piloting the use of hydrogen in steel making.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the ‘Index of Eight Core Industries’, which one of the following is given the highest weight? (2015)
(a) Coal production
(b) Electricity generation
(c) Fertilizer production
(d) Steel production
Ans: B
Q. Consider the following statements: (2009)
- MMTC Limited is India’s largest international trading organization.
- Neelachal Ispat Nigam Limited has been set up by MMTC jointly with the Government of Orissa.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: C
Important Facts For Prelims
Unite Aware Platform
Why in News?
Recently, India launched a new database (Unite Aware platform) to record crimes against UN peacekeepers and monitor progress in holding perpetrators accountable.
- It was launched by the India-led Group of Friends (GOF) initiative in its second meeting to promote accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
What is the Use of the Database?
- The database will serve as an online repository to monitor and address cases of malicious acts against Peacekeepers.
- It will facilitate comprehensive analysis and drive effective strategies for promoting accountability.
- It is hosted on the Unite Aware platform.
- It implements the provisions of UN Security Council resolution 2589 (adopted in August 2021) which called upon troops hosting member states to bring to justice perpetrators of all acts of violence against United Nations personnel.
What is GOF?
- About: On 16th December 2022, India launched a ‘Group of Friends’ to promote accountability for crimes against peacekeepers. It comprises 40 member states.
- It calls on member states to investigate, arrest, and prosecute perpetrators of crimes against peacekeepers (Blue Helmets) in line with international obligations, and to promote accountability both within and outside the UNSC in practical terms.
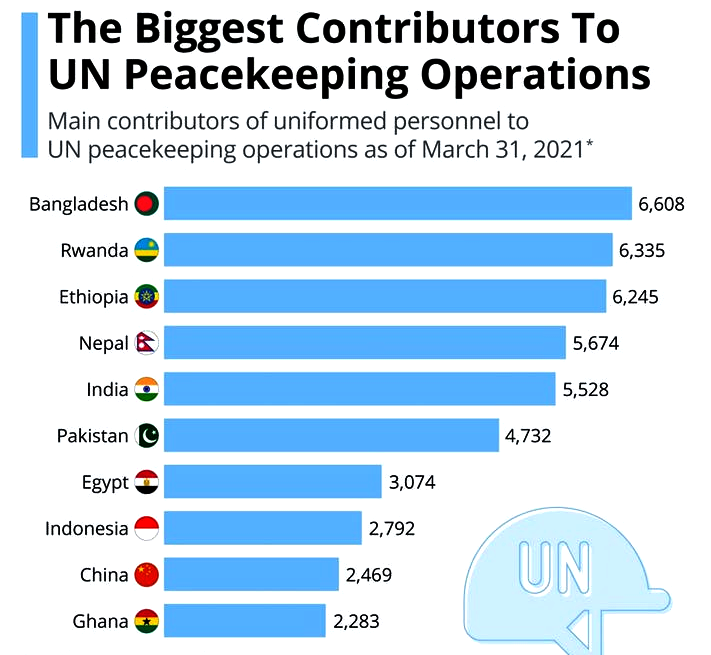
- India has lost 177 of its peacekeepers in the line of duty, the largest by far from any troop-contributing country.
- It calls on member states to investigate, arrest, and prosecute perpetrators of crimes against peacekeepers (Blue Helmets) in line with international obligations, and to promote accountability both within and outside the UNSC in practical terms.
- Co-chairs: India, Bangladesh, Egypt, France, Morocco and Nepal.
- The GoF will convene two meetings of its members per year, organise and host one event per year to inform and galvanise support for promoting accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
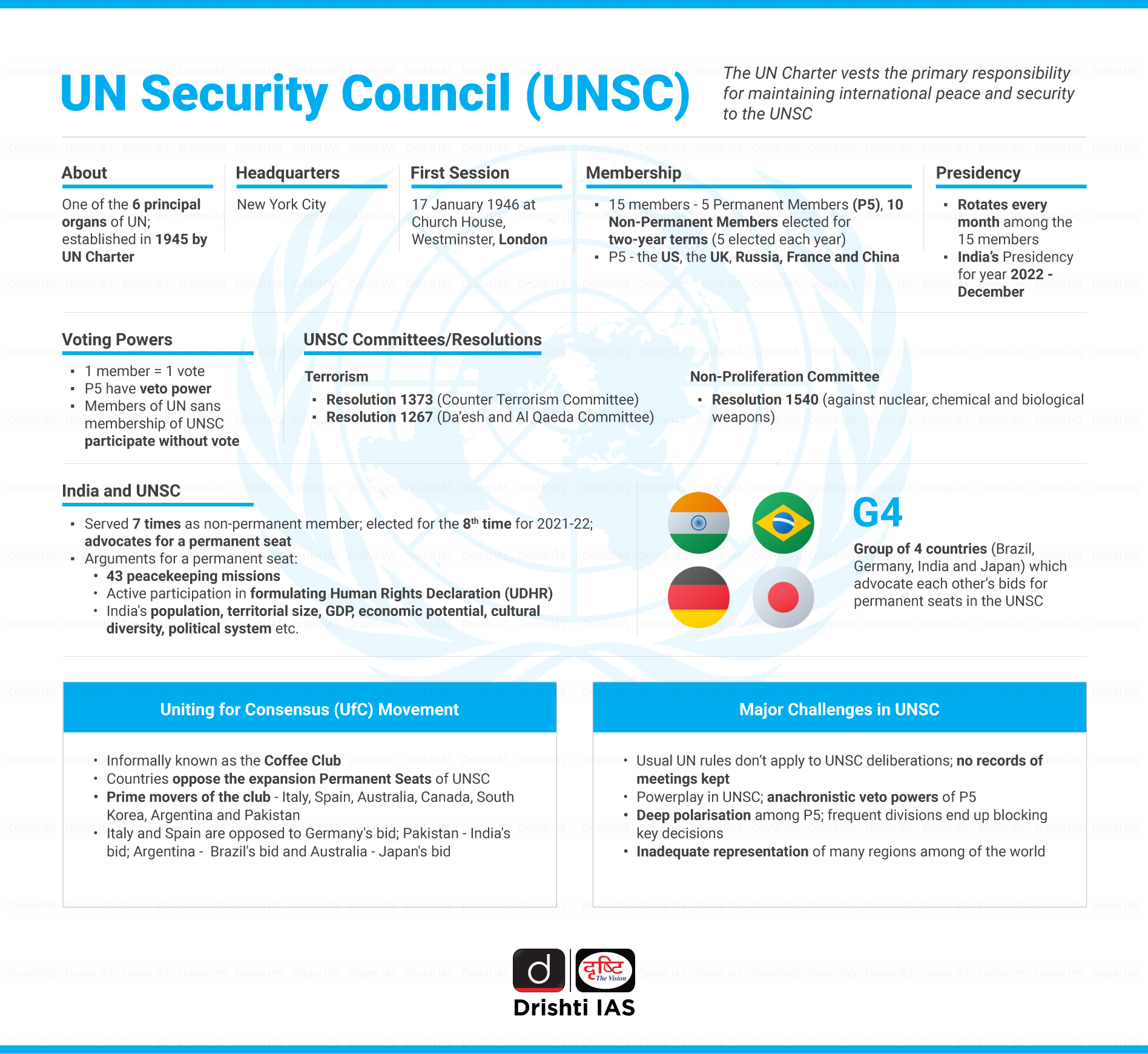
Q. The Security Council of UN consists of 5 permanent members, and the remaining 10 members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of (2009)
(a) 1 year
(b) 2 years
(c) 3 years
(d) 5 years
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to the “United Nations Credentials Committee”, consider the following statements:
- It is a committee set up by the UN Security Council and works under its supervision.
- It traditionally meets in March, June and September every year
- It assesses the credentials of all UN members before submitting a report to the General Assembly for approval.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
(a) 3 only
(b) 1 and 3
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 2
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. Discuss the impediments India is facing in its pursuit of a permanent seat in UN Security Council. (2015)
Important Facts For Prelims
Ozone Found on Jupiter's Moon Callisto
Why in News?
Recently, a team of scientists from various countries, including India, has uncovered compelling evidence suggesting the existence of ozone on Callisto, one of Jupiter's moons.
- Previously thought of as a barren celestial body, scientists now consider that this icy moon could harbour conditions conducive to supporting life.
Note
Researchers recreated Callisto's surface conditions in the laboratory and exposed this setup to vacuum-ultraviolet photons and observed an absorption spectrum showing ozone formation, similar to what Hubble observed on Callisto in 1997.
- Ozone presence suggests the presence of oxygen, essential for life.
What are the Key Features of Callisto?
- About: Callisto ranks as one of Jupiter’s largest moons and is the third-largest moon in the Solar System, following Ganymede (Jupiter) and Titan (Saturn).
- It was discovered in 1610, by Italian scientist Galileo Galilei along with Jupiter’s three other largest moons: Ganymede, Europa and Io.
- As per NASA, after Saturn (146), Jupiter (95) boasts the highest number of moons in the Solar System.
- Features: It is primarily composed of water ice, rocky materials, sulfur dioxide, and organic compounds.
- Its surface is heavily cratered, indicating a long history of being struck by asteroids and comets.
- It also lacks the extensive seismic activity seen on some of Jupiter’s other moons, such as Io and Europa.
What are Some Other Potentially Habitable Celestial Bodies?
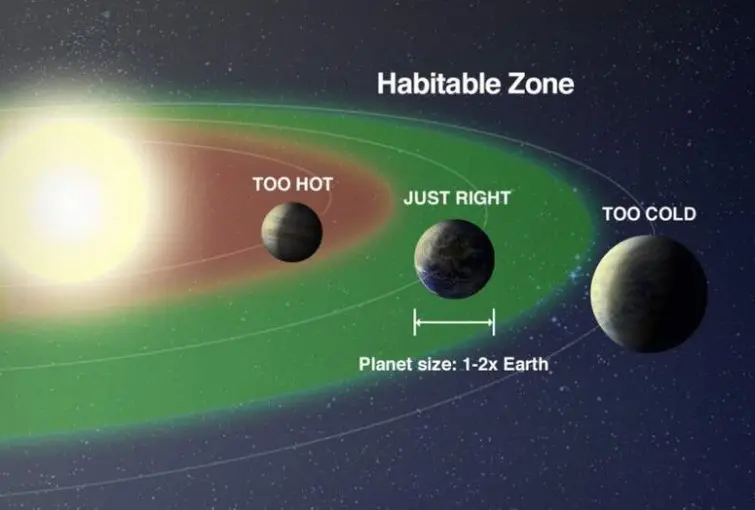
- Habitable Zone: Habitable zone is the distance from a star at which liquid water could exist on orbiting planets’ surfaces.
- Habitable zones are also known as Goldilocks’ zones, where conditions might be just right (neither too hot nor too cold) for life.
- Potential Habitable Celestial Bodies
- Kepler 22b: It is the first planet confirmed by NASA's Kepler mission to orbit within the habitable zone of a sun-like star.
- The planet, 2.4 times the size of Earth, resides in a region where liquid water could potentially exist, vital for sustaining life.
- Proxima Centauri b: Proxima Centauri b is an exoplanet, which is a planet that orbits a star other than our sun.
- It is located in the habitable zone of its star, which means that it is the right distance from the star to potentially have liquid water on its surface.
- Proxima Centauri b is also very close to Earth, at only 4.2 light-years away.
- TRAPPIST-1 System (Star System): The TRAPPIST-1 system is a group of seven Earth-sized planets orbiting an ultra-cool dwarf star about 39 light-years away.
- Several of the planets within the TRAPPIST-1 system are located within the habitable zone, and some may have liquid water on their surfaces.
- Kepler 22b: It is the first planet confirmed by NASA's Kepler mission to orbit within the habitable zone of a sun-like star.
Significance of Ozone
- Ozone, composed of three oxygen atoms (O3) bonded together, plays a vital role in shielding planets from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- The ozone layer is found in the lower part of the earth’s stratosphere, around 15-35 km above ground.
- It acts as a protective layer in Earth's atmosphere, absorbing most of the sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation and preventing it from reaching the surface.
- Ultraviolet radiation in particular is harmful to many species (but also useful to some others).
- Two of its components, called ultraviolet-B and ultraviolet-C can damage DNA, trigger mutations, and increase the risk of skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Which one of the following is associated with the issue of control and phasing out of the use of ozone-depleting substances? (2015)
(a) Bretton Woods Conference
(b) Montreal Protocol
(c) Kyoto Protocol
(d) Nagoya Protocol
Ans: (b)
Q.2 Which one of the following planets has largest number of natural satellites or moons? (2009)
(a) Jupiter
(b) Mars
(c) Saturn
(d) Venus
Ans: (a)
Rapid Fire
Resourcefulness of Konda Reddi’s Tribe's Knowledge
Recently, forest officials learnt that the bark of an Indian laurel tree or Indian Silver Oak (Ficus microcarpa) stores water, particularly in the summer, as claimed by the Konda Reddi tribe.
- The Indian laurel tree is native to Southeast Asia and regions of India, it thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. A glossy, dark green-leaved evergreen tree, its latex sap is used in making rubber products.
- Konda Reddi tribe is a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group inhabiting the Papikonda hill range (Andhra Pradesh) in the Godavari region. Their mother tongue is Telugu with a unique accent.
- Papikonda National Park (PNP) was declared a reserved forest in 1882, a wildlife sanctuary in 1978, and a national park in 2008.
- PNP has moist deciduous forests and includes animal species such as tigers, mouse deer, gaur etc.
Read more: Bills to Include PVTGs to ST List in Odisha and AP, Empowering the Tribal Society.
Rapid Fire
FSSAI Directives to E-commerce Food Business Operators
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has directed e-commerce food business operators (FBOs) to correctly categorise food products on their websites.
- The Authority observed cases where licensed "proprietary foods," such as dairy-based, cereal-based, and malt-based beverage mixes, were incorrectly labelled and sold on e-commerce platforms as health or energy drinks.
- The food products are considered proprietary food if there are no existence of standards for them in FSSAI regulations.
- FSSAI clarified that "Health Drink" is not defined or standardised anywhere under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 and advised FBOs to rectify this misclassification by placing such products in the appropriate category as per the law.
- Also, FSSAI further said that the term ‘energy drinks’ is permitted to be used only for products which have been licensed under that specific food category system.
Read more: FSSAI to Streamline Food Safety Regulations
Rapid Fire
Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index
According to a survey released by Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited (HSBC), India's Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) reached a 16-year peak of 59.1 in March 2024.
- PMI is an economic indicator, which is derived after monthly surveys of different companies. It shows trends in both the manufacturing and services sector.
- A PMI above 50 represents an expansion when compared with the previous month.
- It helps in determining whether the market conditions, as seen by purchasing managers, is expanding, contracting or staying the same.
- It is used to provide information regarding the current and future business conditions.
- The HSBC India Manufacturing PMI is compiled by S&P Global.
Read more: Purchasing Managers’ Index, The Making of A Manufacturing Hub
Rapid Fire
Raising Day of Army Medical Corps
The Army Medical Corps (AMC) commemorated its 260th Raising Day (3rd April 2024) reflecting on centuries of dedication and sacrifice in serving the nation.
- The AMC, originally known as the Indian Medical Service, was founded in India in 1764 during the British colonial era. With the motto of 'Sarve Santu Niramaya' (let all be free from disease) through selfless service.
- The Indian Army Medical Corps (IAMC) was established on 3rd April 1943, following the Royal Army Medical Corps model (United Kingdom). It was created by merging the Indian Medical Service (IMS), Indian Medical Department (IMD), and Indian Hospital Corps (IHC) into a unified corps of officers and men.
- The IAMC was re-designated as the Army Medical Corps (AMC) effective from 26th Jan 1950.
- The AMC has excelled in UN Peacekeeping Missions and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) activities, contributing to national progress and development.
- The AMC Raising Day recognises the contributions of Officers, and other ranks of the Army Medical Corps who have positively impacted the lives of personnel, families, and veterans of the Armed Forces.
Read more: Indian Army's Proactive Measures for Mental Health