International Relations
Changing Dynamics of Global South
- 18 Sep 2023
- 12 min read
For Prelims: Global South, Group of 77 (G-77), Global North, Green Energy Fund, G20 summit, UN Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC), European Union (EU), Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), Quad, Indo-Pacific Economic Forum, BRICS summit, G7 summit, Brandt Line.
For Mains: History of the Global South, Scenario of Global South's Increasing Influence, Influence of the Global South in Global Politics
Why in News?
Earlier in 2023, the Prime Minister of India organised a virtual summit on the "Voice of the Global South", involving approximately 125 countries. The objective of this summit was to solicit the opinions and input of countries from the Global South in order to determine the priorities for the region.
What is the History of the Global South?
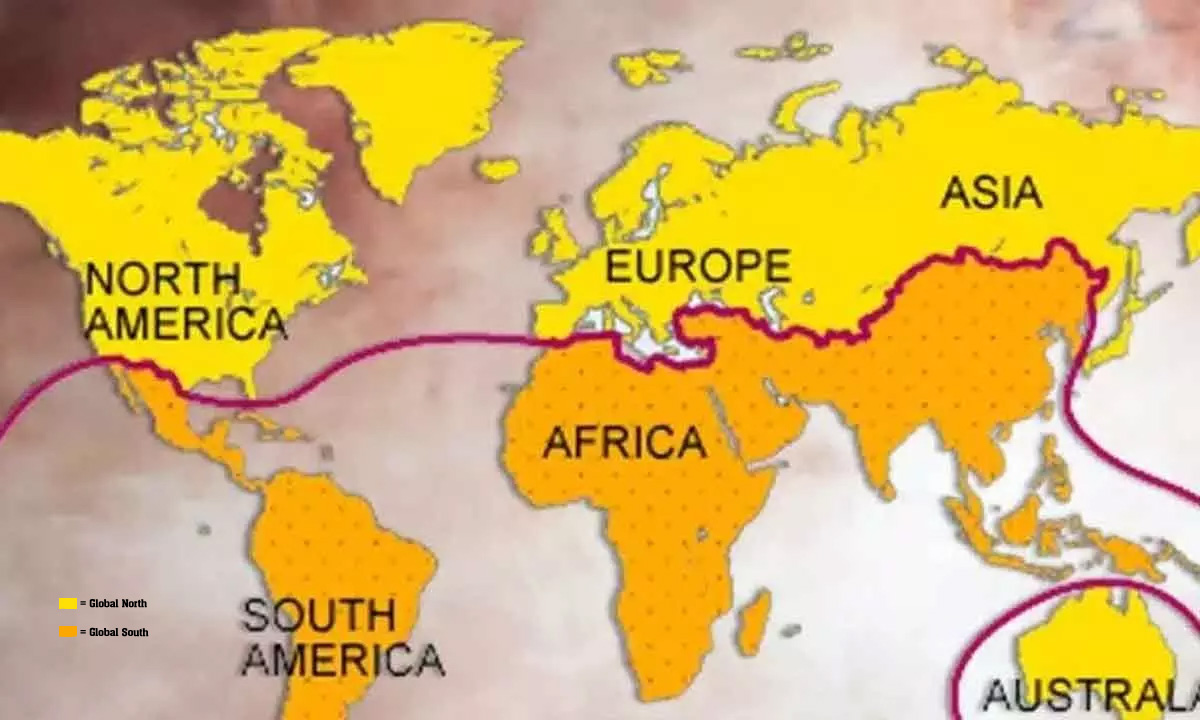
- Historical Context: The term "Global South" is often used to highlight the historical legacy of colonialism and the economic disparities between the formerly colonised nations and the developed Western nations.
- It underscores the challenges faced by these countries in achieving economic growth and development.
- Formation of the G-77: In 1964, the Group of 77 (G-77) countries came into existence when they signed a Joint Declaration during the first session of the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) in Geneva.
- The G-77 became the largest intergovernmental organisation of developing countries at the time.
- Purpose of G-77: It was created to promote the economic interests of developing countries and improve their ability to negotiate on international economic issues within the UN system.
- It now includes 134 countries across Asia, Africa, South America, the Caribbean and Oceania. China is not technically part of the group, hence, the grouping is often referred to as "G-77+China" in multilateral forums.
- UNOSSC: The UN Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC) was established in 1974. Its role is to coordinate cooperation between countries in the Global South and with developed countries or multilateral agencies, in collaboration with the G-77.
What led to the Revival of Global South?
- In the early decades of the 21st century, there was a noticeable decline in interest and attention towards the Global South.
- This trend was particularly evident in countries like India and Indonesia, which were perceived as moving away from their ‘Third World’ origins and seeking a more prominent role on the global stage as they reformed and expanded their economies.
- However, in recent times, the Global South has regained its importance and relevance, signifying a growing recognition of the region's significance in shaping the emerging global order. Several key factors are cited as contributing to this resurgence:
- Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic: The Covid-19 pandemic had a severe impact on many countries in the Global South, both in terms of public health and economic challenges. This crisis refocused attention on the vulnerabilities and needs of these nations.
- Economic Downturn: The economic downturn resulting from the pandemic disproportionately affected countries in the Global South, highlighting the need for international cooperation and support.
- Repercussions of Russia-Ukraine Conflict: The Russia-Ukraine conflict had a global economic impact. This had ripple effects on the developing world, further underscoring the interconnectedness of global affairs and the importance of the Global South in international diplomacy.
Why is the Term Global South Criticised?
- Inaccuracy of the Term: The term "Global South" is criticised for its inaccuracy in representing the countries it was intended to describe.
- It is pointed out that some countries typically considered part of the Global South, like India, are actually located in the Northern Hemisphere, while others, such as Australia, are in the Southern Hemisphere but often categorised as part of the Global North.
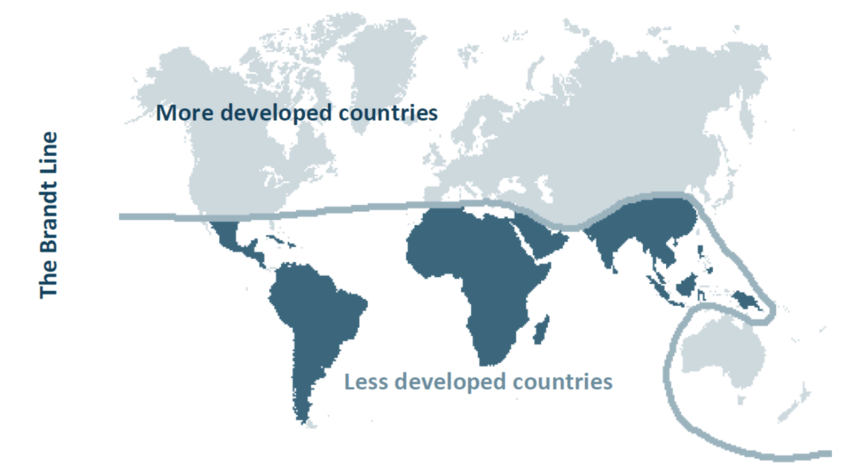
- Need for a More Precise Classification: In the 1980s, the recognition of this inaccuracy led to the development of the "Brandt Line" - a curve that more accurately divided the world into the economic North and South based on factors like economic development and wealth distribution, rather than simply by geographical location.
What are the Demands of the Global South?
- Proportionate Voice at Global Level: The Global South, comprising countries with significant populations, recognises that they have the most at stake in shaping the future of the world.
- With three-fourths of the global population residing in these countries, they argue that they should have a proportionate and meaningful voice in global decision-making processes.
- Equitable Representation: Global South demands an equitable representation in global governance. The current model of global governance may not adequately reflect the demographic and economic realities of the world, and there is a call for change to ensure that the voices of the Global South are heard and considered.
What Signifies the Influence of the Global South in Global Politics?
- Prioritising Global South: India's Presidency of the G20 was driven by the priorities of the Global South. This suggests a growing awareness of the need to address issues and concerns that are particularly relevant to developing countries in the Global South.
- Global South Leadership: The fact that developing countries like Indonesia, India, Brazil, and South Africa are consecutively hosting the G20 summit indicates a desire for greater leadership and influence from the Global South in global decision-making processes.
- These countries represent a significant portion of the world's population and economies.
- Inclusivity: The "Voice of the Global South" summit demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity and consultation with a wide range of nations from the Global South.
- This indicates a shift away from traditional power structures dominated by Western countries.
- Multilateralism: The emphasis on the Global South's priorities and the involvement of these countries in hosting and shaping the G20 agenda reflects a commitment to multilateralism, where decisions are made collectively by a diverse group of nations.
- Rising Influence of Developing World: This is evident through the participation of various organisations such as G20, BRICS, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), Quad, the Indo-Pacific Economic Forum, and other global players who are actively seeking involvement from countries in the Global South in decision-making processes.
What is the Evidence of the Global South's Increasing Influence?
- Establishment of the 'Loss and Damage Fund': At the COP27 Climate Change conference in Egypt, the establishment of the 'Loss and Damage fund' was celebrated as a significant win for the Global South.
- It signifies a recognition of the disproportionate burden borne by countries in the Global South.
- Global South in COP28: In the upcoming UNFCCC COP 28 in the UAE, it is anticipated that countries from the Global South will take a leading role in driving discussions on mitigating climate change.
- G7 Inclusivity: Japan, as the host of the G7 summit, made a notable effort to involve developing countries such as India, Brazil, Vietnam, Indonesia, Comoros, and the Cook Islands in the discussions.
- This was seen as an outreach to the Global South, indicating a desire for a more inclusive dialogue among the world's wealthiest nations.
- BRICS Summit Expansion: The BRICS summit, held in South Africa, expanded its membership from five to 11 members. This expansion was attributed to a concerted effort to engage with and incorporate more countries from the Global South into the BRICS grouping, underscoring its growing importance.
- G-77 Summit in Cuba: The G-77 summit held recently in Havana, Cuba showcased the significance of the Global South on the global stage, as it brought together a substantial number of developing countries to discuss key issues.
- African Union's Inclusion into G20: The inclusion of the 55-nation African Union into the G20 is seen as a significant outcome of the conference indicating a growing recognition of the African nations in global affairs and the need to include their perspectives and contributions in shaping the emerging global order.
Conclusion
As the world navigates through complex challenges and opportunities, the Global South's influence continues to evolve, and its demands for equitable representation and a meaningful voice in global governance remain at the forefront. The global community is witnessing a rebalancing of power dynamics, with the Global South playing an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of international politics and cooperation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘The long-sustained image of India as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised nations has disappeared on account of its new found role in the emerging global order.’ Elaborate. (2019)