Infographics
Electoral Reforms in India
Read More: Free and Fair Elections, Election Commission of India, Empowering Election Commission of India


Economy
Reforms in Multilateral Development Banks
For Prelims: Multilateral Development Banks, World War II, World Bank Group, Asian Development Bank, African Development Bank, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
For Mains: Key Challenges Related to MDBs and Reforms.
Why in News?
Recently, the UN Secretary-General, highlighted that reforming multilateral development banks (MDBs) will be a major focus at this year's Summit of the Future, occurring during the UN General Assembly in September 2024.
What are Multilateral Development Banks?
- About: MDBs are international financial institutions that provide financing and professional advice for economic and social development projects in developing countries.
- They are formed and capitalised by multiple countries through pooled resources and shared representation on their boards.
- They originated in the aftermath of World War II to rebuild war-ravaged nations and stabilise the global financial system.
- Objective: Unlike commercial banks, MDBs do not seek to maximise profits for their shareholders.
- Instead, they prioritise development goals, such as ending extreme poverty and reducing economic inequality.
- They often lend at low or no interest or provide grants to fund projects in infrastructure, energy, education, environmental sustainability, and other areas that promote development.
- Major MDBs: World Bank Group, Asian Development Bank, African Development Bank, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, and the Inter-American Development Bank.
What are the Key Challenges Related to MDBs?
- Resource Constraints: MDBs are often constrained by the amount of capital they have available to lend. This can limit their ability to finance large-scale development projects, especially in the face of growing needs.
- Keeping Pace with Global Challenges: The world faces new and complex challenges like climate change, pandemics, and technological disruption.
- MDBs have not fully adapted these growing challenges in their strategies and approaches to effectively address these issues.
- Decision-Making: The current voting structure in some MDBs gives more power to developed countries.
- Developing nations are pushing for a greater say in decision-making to reflect their needs and priorities.
- Concerns exist about the transparency of MDB decision-making processes and the need for stronger accountability mechanisms to prevent corruption and mismanagement.
- For example, the United States holds a considerable 15.85% of the voting power in the World Bank, granting it substantial influence over the institution's decisions.
- One-SIze FIts All Approach: One-size-fits-all lending conditions from MDBs, such as uniform interest rates or repayment schedules, are challenging for countries of the global south due to their diverse economic structures and financial capabilities.
What Reforms are Necessary in Multilateral Development Banks?
- Financing Climate Action: MDBs can play a crucial role in mobilising resources for climate change mitigation and adaptation projects in developing countries.
- This could involve creating dedicated climate finance facilities, offering green bonds, and developing innovative risk-sharing instruments for renewable energy projects.
- Knowledge Sharing & South-South Cooperation: Encouraging MDBs to facilitate knowledge exchange between developing countries.
- This could involve connecting countries facing similar challenges and fostering collaboration on successful development strategies.
- Graduation Strategies: As middle-income countries develop, creating clear pathways for them to "graduate" from concessional loans to market-rate financing from private sources.
- This frees up MDB resources for low-income countries that still need significant support.
- Social and Environmental Safeguards: Strengthening safeguards to ensure MDB-funded projects avoid negative social or environmental impacts and promote inclusive sustainable development.
Which are the Key MDBs India is Affiliated With?
- World Bank Group: India is a member of four of the five constituents of the World Bank Group viz., International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), International Development Association (IDA), International Finance Corporation (IFC) and Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA).
- India is not a member of ICSID (International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes).
- World Bank assistance in India started in 1948 when funding for the Agricultural Machinery Project was approved.
- Asian Development Bank (ADB): India is a founding member of ADB and the bank’s fourth-largest shareholder.
- Since commencing operations in 1986, ADB has aligned its operations in the country to the government’s developing priorities.
- This approach will be pursued through the forthcoming country partnership strategy, 2023–2027.
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB): India is a founding member of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) with the second-highest voting share after China.
- It is headquartered in Beijing.
- New Development Bank (NDB): India, the founding member of NDB, is the second-largest recipient of NDB's financial support at USD 7.5 billion after China.
- It was established in 2015 by the BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa).
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the role of Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) in promoting sustainable development and inclusive growth globally. How can MDBs effectively address the growing climate challenges? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), consider the following statements: (2019)
- AIIB has more than 80 member nations.
- India is the largest shareholder in AIIB.
- AIIB does not have any members from outside Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. India has recently signed to become a founding member of New Development Bank (NDB) and also the Asian Infrastructure Bank (AIIB). How will the role of the two Banks be different? Discuss the strategic significance of these two Banks for India. (2012)


Indian Polity
Engaging India's Youth in Voting
For Prelims: Elections, NOTA, Representation of the People Act, 1951, Election Commission of India, Voter Rights, Electronic Voting Machine, Rule 49P
For Mains: Youth participation in the electoral process, Implications of low voter turnout
Why in News?
As India gears up for the 18th Lok Sabha elections, a concerning trend emerges, the reluctance of the country's youngest eligible voters to participate.
Why are India's Youngest Voters Hesitant to Participate?
- Historical Trends:
- Less than 40% of voters between 18 and 19 have registered for the 2024 elections, raising concerns about youth engagement in the electoral process.
- Lowest enrollment rates in Delhi, Bihar, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Despite exposure to political voices via social media, many young people seem hesitant to participate actively in voting, despite their passion for social action and protests.
- Bihar reports only 9.3 lakh enrolled out of a potential 54 lakh (17%), despite being known for its youthful population.
- Similar trends are observed in other states like Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, and Maharashtra, where enrollment rates remain notably low.
- Less than 40% of voters between 18 and 19 have registered for the 2024 elections, raising concerns about youth engagement in the electoral process.
- Lack of Political Education: Many young people feel that the education system does not adequately prepare them to understand the political process and its significance.
- Insufficient education on the importance of civic engagement and voting.
- Lack of critical thinking skills and political awareness in school curriculum.
- Insufficient education on the importance of civic engagement and voting.
- Absence of Youth-Centric Agendas: Political parties often fail to advocate agendas that resonate with the younger demographic, leading to a disconnection.
- Political parties may often overlook key issues that are of significant concern to the younger demographic, such as job opportunities , and affordable higher education.
- Inadequate Representation: Despite forming a significant portion of the population, youth are often underrepresented in political decision-making bodies.
- This lack of representation can lead to policies that do not adequately address the needs and concerns of young people.
- Lack of Engagement: Limited opportunities for meaningful participation in the political process.
- Disillusionment with top-down decision-making and governance structures.
- Social Pressures:
- Social pressures, including stereotypes and negative perceptions, can discourage youth from engaging in politics.
- Instead of focusing on meaningful agendas, there's often an emphasis on money and muscle power in politics.
- This can divert attention from genuine political activism and hinder youth participation in bringing about meaningful change.
- Disconnect from Issues:
- Feeling disconnected from political issues that directly affect their lives and communities.
- Perceived irrelevance of political decisions to their immediate concerns and priorities.
- Technological Influence:
- Over Reliance on social media for information, leading to misinformation and superficial engagement with political issues.
How Voter Disinterest Puts Democracy at Risk?
- Disenfranchisement:
- Disenfranchisement refers to the deprivation of voting rights, often resulting from legal barriers, thereby impeding citizens' ability to participate in the democratic process.
- Many migrants face disenfranchisement due to their inability to travel to polling stations where they are registered as voters, as required by law. While it is possible to register to vote at a new location, doing so requires proof of a fixed address, which many of the poor do not have.
- Social disenfranchisement during elections persists despite constitutional guarantees (article 326) that hinder equitable participation in the electoral process.
- Disenfranchisement refers to the deprivation of voting rights, often resulting from legal barriers, thereby impeding citizens' ability to participate in the democratic process.
- Undermining Democratic Principles:
- Voter disinterest challenges the core principle of democracy, which thrives on active citizen participation in the electoral process.
- When citizens disengage from voting, they relinquish their role in collective decision-making, eroding the foundation of democratic governance.
- Perpetuating Exclusion:
- Disinterested voters allow a minority to dictate the course of governance, leading to a cycle of exclusion for marginalised communities.
- Lack of voter participation perpetuates inequality and injustice, as the voices of underrepresented groups go unheard in policymaking.
- Questioning Legitimacy:
- Low voter turnout raises questions about the legitimacy of electoral outcomes, undermining public trust in the democratic process.
- When a significant portion of the population abstains from voting, the mandate of elected representatives may be called into question, casting doubt on the credibility of democratic institutions.
What are the Voter Rights and Responsibilities in Elections?
- Voter Enrollment and Rights:
- Eligibility:
- In India, the Electoral Roll updates quarterly, allowing registration in the quarter they come of age of 18. Eligible youth receive an Electors Photo Identity Card(EPIC) upon registration.
- This applies to those reaching 18 by 1st January, 1st April,1st July, or 1st October.
- In India, the Electoral Roll updates quarterly, allowing registration in the quarter they come of age of 18. Eligible youth receive an Electors Photo Identity Card(EPIC) upon registration.
- One Place Registration: Voters can be enrolled only at one place, multiple registrations are an offence.
- Alternative ID:
- Having a voter ID or Election Commission of India prescribed document doesn't guarantee voting. The name must be on the electoral rolls and a valid ID is required to cast a vote.
- Voters can use their Electors Photo Identity Card (EPIC) or other documents specified by the Commission at polling station.
- A ration card is not a valid identification for voting.
- Alternative documents include an Aadhaar card, MNREGA job card, driving licence, PAN card, a smart card from Registrar General and Census Commissioner, passport, pension document with photo, identity card from the government agency, or an MLA/MP identity card.
- Eligibility:
- Disqualification from Voting Process:
- Individuals who are convicted of offences committed under Section 171E (which deals with bribery) and Section 171F (which deals with personation or undue influence at an election) of the Indian Penal Code are disqualified from participating in elections.
- Those convicted of offences under Section 125 (which deals with various electoral offences), Section 135 and Section 136 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 face disqualification from elections.
- If an individual votes in more than one constituency, his vote is disqualified.
- Voting Process:
- Wrong Button:
- If a wrong button is pressed on an Electronic Voting Machine (EVM), approach the polling officer for a reset and let you vote again.
- Refusal to Vote:
- Electors can refuse to vote even after registering their identities before the presiding officer and reaching the polling booth.
- The NOTA (None Of The Above) option allows voters to express a lack of confidence in any candidate, while the ‘refusal to vote’ option allows an elector to shun the entire poll process.
- Unauthorised Voting:
- Voters can still vote if someone else has already voted in their name by using a "Tendered Ballot Paper" according to Rule 49P of the Conduct of Elections Rules.
- The Presiding Officer will collect and keep the tendered ballot paper separate.
- Proxy Voting:
- Service voters with service qualifications, such as members of the armed forces, Government employees posted outside the country, and members of the armed police force of a State, can use the proxy voting facility.
- They can appoint a proxy, who must be a resident of the same constituency, to vote on their behalf.
- Vote from Home:
- The ECI introduced home voting for the elderly and Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) in the 2024 Lok Sabha elections, allowing those above 85 years of age and PwDs with 40% benchmark disability to avail of this facility.
- Wrong Button:
- Reporting Malpractices:
- Report violations anonymously using the cVIGIL citizen mobile app to capture images or videos of malpractices you witness.
- The ECI guarantees a response within 100 minutes, specifying the action taken.
- The app allows users to report violations, track location via GPS, capture live incidents, monitor complaint status, and report violations anonymously.
- Report violations anonymously using the cVIGIL citizen mobile app to capture images or videos of malpractices you witness.
Way Forward
- Engage young voters through appealing political agendas and increased understanding of the political system.
- Advocate for increased representation of youth in political decision-making processes.
- Provide platforms for young voices to be heard and valued in societal and political discussions.
- Recognising the power of every vote is essential to breaking free from the cycle of disenfranchisement.
- Encouraging active participation in the democratic process is crucial for safeguarding the principles of democracy and ensuring inclusive governance
- Focus on states with large youth populations, addressing issues affecting young adults during political campaigns, and dispelling stereotypes about Gen Z's (generation of people born between 1997 and 2012) social awareness and engagement.
- Empower India's youth by orienting them towards the impact of their decisions, sensitising them towards local and national issues, encouraging informed choices and emphasising the consequences of not participating in the democratic process.
- Harness the potential of digitally connected and socially aware youth, and encourage activism, social responsibility, and empowerment among young voters.
- Explore the possibility of implementing secure online voting to accommodate the digital generation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. How does voter disinterest impact democracy? Evaluate its implications on democratic principles, electoral legitimacy, and inclusive governance, with relevant examples from the Indian electoral context. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The Election Commission of India is a five-member body.
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs decides the election schedule for the conduct of both general elections and bye-elections.
- Election Commission resolves the disputes relating to splits/mergers of recognised political parties.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- According to the Constitution of India a person who is eligible to vote can be made a minister in a State for six months even if he/she is not a member of the Legislature of that State.
- According to the Representation of People Act, 1951, a person convicted of a criminal offense and sentenced to imprisonment for five years is permanently disqualified from contesting an election even after his release from prison.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss the role of the Election Commission of India in the light of the evolution of the Model Code of Conduct. (2022)


Geography
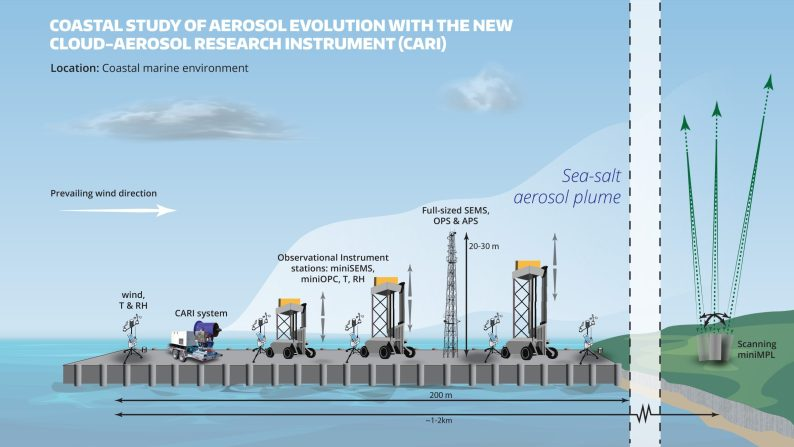
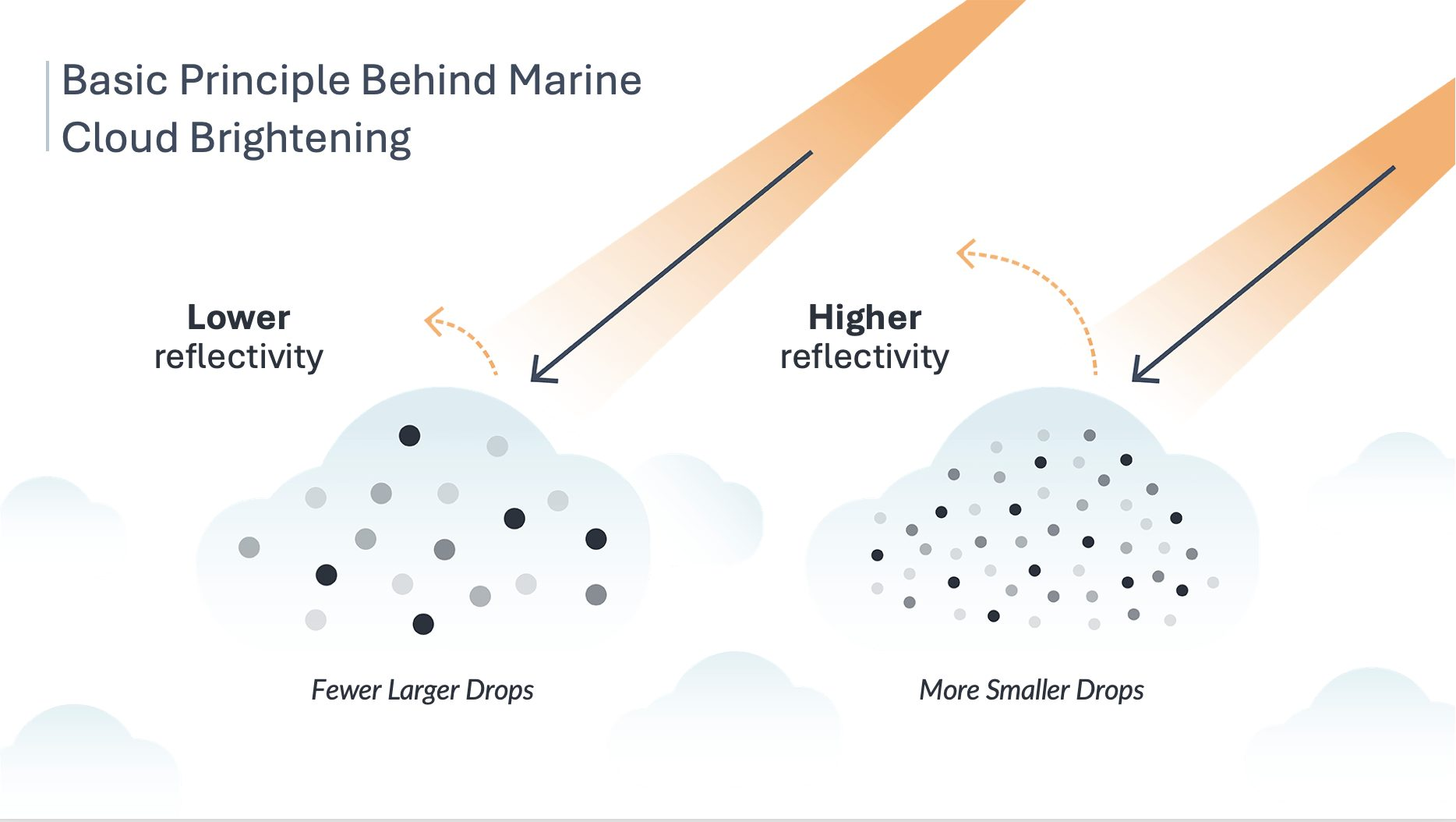
Marine Cloud Brightening
For Prelims: Marine cloud brightening, Coral bleaching, Global warming, Great Barrier Reef, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
For Mains: Mechanism of Marine Cloud Brightening and Related Challenges and Risks, Environmental Pollution & Degradation, Conservation
Why in News?
Recently, scientists are testing a geoengineering technique called marine cloud brightening.
- This method involves using machines to inject tiny saltwater particles into marine stratocumulus clouds, aiming to increase their reflectivity and cool the Earth.
What is Marine Cloud Brightening?
- About:
- Marine cloud brightening is a scientific initiative that explores how altering atmospheric particles (aerosols) can impact cloud reflectivity.
- By releasing tiny aerosol particles into the atmosphere, researchers aim to enhance cloud brightness, leading to increased sunlight reflection.
- Aerosols of the right size and concentration could significantly increase the reflectivity of specific types of clouds.
- This phenomenon is visible in satellite images of clouds brightened by ship emissions (known as “ship tracks”).
- Goals of the Marine Cloud Brightening Program:
- Better understanding of the present-day effects of pollution aerosols on clouds.
- Investigate whether aerosol particles made from sea salt could be used to intentionally reduce near-term climate warming while greenhouse gas concentrations are brought down to safer levels.
- Understand the benefits, risks, and efficacy of the intentional use of aerosols to reduce warming through different implementations of marine cloud brightening.
Aerosol and Climate Effect:
- Aerosol concentration is declining due to expanding air quality regulations, leading to fewer particles in the atmosphere.
- Most aerosol particles have a cooling effect on climate, so their reduction adds to global warming.
- Scientists estimate that aerosols from human emissions are offsetting 0.5°C of global warming, but the actual cooling effect could range from 0.2°C to 1.0°C.
- Uncertainty about aerosol effects on clouds contributes to uncertainty in future warming projections.
What are the Challenges and Risks Associated with MCB?
- Technical Feasibility: MCB involves the large-scale spraying of seawater into the atmosphere at significant altitudes, which presents engineering complexities in terms of design, cost, maintenance, and operation of the spraying devices.
- Environmental Impacts: Alterations in cloud patterns and precipitation due to MCB could affect regional climate and hydrological cycles, potentially causing unintended consequences like droughts or floods.
- Changes in clouds over broad regions affect the circulation of the atmosphere, weather, and precipitation.
- Both marine cloud brightening (MCB) and pollution aerosols can change clouds, which in turn affects regions both nearby and far from where the brightening occurs.
- Ethical Issues: MCB raises ethical dilemmas about human intervention in natural processes and the governance and decision-making processes surrounding its implementation.
- Moral Hazard: MCB might lead to complacency among policymakers and the public, diminishing their commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to climate change.
Conclusion:
- Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB), a cutting-edge climate intervention, remains in its early research and development stages. Scientists are diligently exploring its feasibility, efficacy, and potential impacts.
- Sustainable human adaptation is considered the sole novel approach among various geoengineering methods to mitigate global warming and address climate change, with acknowledgment of associated risks and uncertainties
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the various geoengineering techniques proposed to mitigate climate change and their potential impacts on global climate systems. How does sustainable human adaptation stand out as a unique approach in this context? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2012) Chlorofluorocarbons, known as ozone-depleting substances, are used
- in the production of plastic foams
- in the production of tubeless tyres
- in cleaning certain electronic components
- as pressurizing agents in aerosol cans
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. Bring out the relationship between the shrinking Himalayan glaciers and the symptoms of climate change in the Indian subcontinent. (2014)


Important Facts For Prelims
Israel's GPS Spoofing Against Iran
Why in News?
Recent reports suggest that Israel employed Global Positioning System (GPS) spoofing techniques to protect against Iranian missile attacks, reminiscent of past instances like United States (US) actions during the Kargil war in India.
What is GPS Spoofing?
- About:
- GPS spoofing is a technique used to manipulate the GPS signals to deceive receivers, making them believe they are at a different location than they are.
- This can involve broadcasting false GPS signals or altering genuine ones to mislead navigation systems, leading to inaccurate positioning information.
- Spoofing can be used for various purposes, including deceiving enemy navigation systems, protecting against unauthorised tracking, or creating false location data for malicious intents.
- Implications:
- Military Disruption: Misleading enemy navigation systems, leading to inaccurate targeting.
- Navigation Safety Risks: Potential accidents or collisions in maritime and aviation sectors.
- Critical Infrastructure Disruption: Disruption of essential services like power grids or transportation systems.
- Financial Fraud: Manipulation of location-based services for fraudulent transactions.
- National Security Threats: Deception of military or government agencies, espionage, and infiltration risks.
Did the US Engage in GPS Spoofing During the Kargil War?
- According to the reports, about 25 years ago, Pakistani soldiers crossed into India and took positions in Kargil in 1999. The Indian military requested GPS data for the region but was denied by the US.
- The US initially employed a technology called "selective availability" to intentionally introduce errors into civilian GPS receivers, reserving the best accuracy for military use.
- This technology was used to "degrade" GPS accuracy for the Indian military during the Kargil war, hindering their operations.
- India's Response:
- India developed NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation), which was erstwhile known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- NavIC provides precise and secure positioning, navigation, and timing services anywhere in India and 1500 kilometres beyond India's territorial boundary.
- NavIC offers two services:
- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- NavIC SPS signals are interoperable with the other global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals namely GPS, Glonass (Russia), Galileo (European Union) and BeiDou (China).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q.1 Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
a. Australia
b. Canada
c. Israel
d. Japan
Ans: d
Exp:
- Navigation Systems Operational in the World:
- GPS from the U.S.
- GLONASS from Russia.
- Galileo from European Union
- BeiDou from China.
- NavIC from India
- QZSS from Japan. Hence, option D is correct.
Q.2 With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements: (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. Km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) None
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Padma Awards 2024
Why in News?
Recently, President Droupadi Murmu presented the prestigious Padma Awards of 2024 to a distinguished group of people.
Who were the Recipients of the Padma Awards in 2024?
- The group included former Vice-President M. Venkaiah Naidu, actor and politician Mithun Chakraborty, singer Usha Uthup, and tennis player Rohan Bopanna and others.
- The founder of Sulabh International Bindeshwar Pathak and Bharatanatyam dancer Padma Subrahmanyam were conferred with Padma Vibhushan.
- For 2024, the President had approved the conferment of 132 Padma awards, including two duo cases (in a duo case, the Award is counted as one).
- The list comprises 5 Padma Vibhushan, 17 Padma Bhushan and 110 Padma Shri Awards.
- 30 of the awardees are women, 8 persons from the category of Foreigners/NRI/PIO/OCI and 9 Posthumous awardees.
What are the Key Points About the Padma Awards?
- Background:
- The Padma Awards are announced annually on Republic Day (26th January).
- Instituted in 1954, it is one of the highest civilian honours of India.
- Objective:
- To recognise achievements in all fields of activities or disciplines where an element of public service is involved.
- Categories:
- The Awards are given in three categories:
- Padma Vibhushan (for exceptional and distinguished service),
- Padma Bhushan (distinguished service of higher order) and
- Padma Shri (distinguished service).
- Padma Vibhushan is highest in the hierarchy of Padma Awards followed by Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri.
- The Awards are given in three categories:
- Disciplines:
- The awards are given in various disciplines/ fields of activities like art, social work, public affairs, science and engineering, trade and industry, medicine, literature and education, sports, civil service, etc.
- Eligibility:
- All persons without distinction of race, occupation, position or sex are eligible for these Awards.
- Selection Process:
- Padma Awards Committee:
- The Awards are conferred on the recommendations made by the Padma Awards Committee, which is constituted by the Prime Minister every year.
- Awarded by President:
- The awards are presented by the President of India usually in March/April every year.
- Padma Awards Committee:
Bharat Ratna
- It is the highest civilian award in the country. It is awarded in recognition of exceptional service/performance of the highest order in any field of human endeavour.
- It is treated on a different footing from the Padma Award. The recommendations for Bharat Ratna are made by the Prime Minister to the President of India.
- Usually, three Bharat Ratna awards are given in a year. However, this year in 2024, the government has named five people for Bharat Ratna.
Abolition of Titles Under Article 18 of the Constitution:
- Article 18(1) of the Indian Constitution abolishes all titles and prohibits the state from conferring titles on any individual, whether they are a citizen or a non-citizen.
- However, military and academic distinctions are exceptions to this prohibition.
- This means that universities, for instance, can grant titles or honours to individuals based on their merit.
- A "title" refers to an attachment to one's name, such as a prefix or suffix (e.g., Sir, Nawab, Maharaja).
- In a democracy, the creation of titles and titular glories is discouraged as it goes against the principles of social equality.
- Awards like "Bharat Ratna," "Padma Vibhushan," and "Padma Shri" are not prohibited under Article 18 because they signify state recognition of exceptional work by citizens in various fields.
- In the landmark judgment Balaji Raghavan v. Union of India, 1996, the court held that National awards aren’t titles under clause 1 of Article 18.
Note:
- In the case of Indira Jaising v. Supreme Court of India, 2017, a complaint was lodged to question the usage of the term ‘senior advocate’ before the names of the advocates.
- The Supreme Court ruled that this is not the title, but rather a demarcation, and therefore does not violate Article 18 of the Indian Constitution.
Read more: Republic Day
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards: (2021)
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are titles under the Article 18(1) of the Constitution of India.
- Padma Awards, which were instituted in the year 1954, were suspended only once.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of five in a particular year.
Which of the above statements are not correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Sustainable Finance for Tiger Landscapes Conference
Why in News?
The Bhutanese government hosted the Sustainable Finance for Tiger Landscapes Conference on Earth Day 2024 to mobilise USD 1 billion over the next decade for conserving tigers and their habitats across Asia.
What is the Sustainable Finance for Tiger Landscapes Conference?
- About:
- The two-day conference will be hosted by Bhutan under the patronage of the country’s queen, Jetsun Pema Wangchuck.
- It seeks to mobilise the amount of USD 1 billion over 10 years for the preservation of tiger landscapes.
- The conservation of tiger landscapes is vital to maintaining biodiversity, sequestering carbon, supplying resources to over 100 million people, and ensuring the overall health of the planet.
- The conference convened tiger range countries, visionary private and public sector donors, international development agencies, the Tiger Conservation Coalition, and other conservation organisations.
- Key Highlights from the Conference:
- High-level representatives from ten tiger range countries delivered statements on the progress and ambitions for conserving their tiger landscapes.
- The conference culminated with the Paro Statement by the Royal Government of Bhutan reiterating it’s objective.
- Other Sources of Funding:
- Since 2010, the Global Environment Facility has provided more than USD 197 million in financing and mobilized another USD 880 million, in co-finance, for tiger conservation.
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA):
- About:
- India has proposed to launch a mega global alliance under its leadership to protect big cats and assured support over five years with guaranteed funding of USD 100 million.
- The proposed International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) will work towards the protection and conservation of the seven major big cats — tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, puma, jaguar and cheetah.
- Membership to the alliance will be open to 97 “range” countries, which contain the natural habitat of these big cats, as well as other interested nations, international organisations, etc.
- The alliance was inspired by the arrival of cheetahs in 2022 from Namibia.
- India is the only country in the world to have tigers, lions, leopards, snow leopards and cheetahs in the wild except for the pumas and jaguars.
- So, it is only befitting that India takes the lead to bring together all big cat range countries under an United Nations(UN)-like organisation.
- Structure of IBCA:
- A General Assembly consisting of all member countries.
- A council of at least seven but not more than 15 member countries elected by the General Assembly for a term of 5 years, and a Secretariat.
- General Assembly will appoint the IBCA Secretary General for a specific term.
What are Global Initiatives for Tiger Conservation?
- Integrated Tiger Habitat Conservation Programme (ITHCP)
- St. Petersburg Declaration on Tiger Conservation
- Global Tiger Forum
- Global Tiger Initiative (GTI)
- Tiger Conservation Coalition:
- It is an independent group of organizations that have worked extensively together on major tiger assessments.
- Its member organizations include the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC), the United Nations Development Programme and the World Wildlife Fund.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC): (2017)
- TRAFFIC is a bureau under United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- The mission of TRAFFIC is to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans:(b)
Q. Consider the following protected areas: (2012)
- Bandipur
- Bhitarkanika
- Manas
- Sunderbans
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)


Rapid Fire
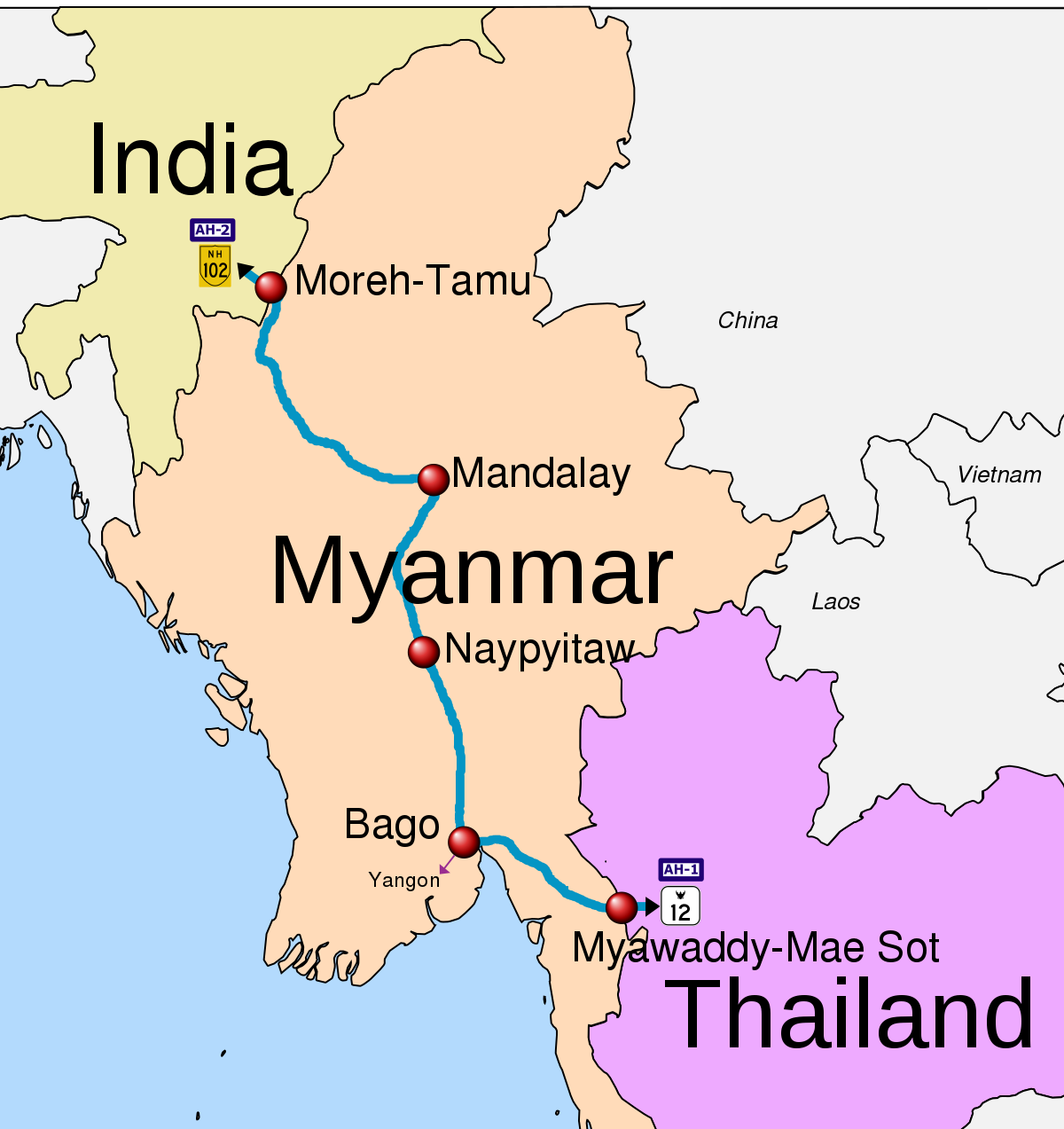
Myanmar’s Karen Ethnic Minority
Recently, Myanmar’s Karen ethnic minority asserted their proximity to capturing a significant Myawaddy trading town adjacent to the Thailand border.
- The Karen ethnic minority, indigenous to the Thailand-Burma border region in Southeast Asia, predominantly resides in the Karen State of Myanmar.
- Their origin is believed to have roots tracing back to the Gobi Desert in Mongolia.
- Myawaddy is Myanmar’s most active trading post with Thailand and its fall would have significant economic implications.
- The Karen National Union (KNU) is the political organisation representing the Karen people and has an armed wing, the Karen National Liberation Army.
- The conflict in Myanmar began after the army ousted the elected government of Aung San Suu Kyi in 2021 and suppressed widespread nonviolent protests.
- Myawaddyy is a trading town in Myanmar that connects with Mae Sot in Thailand. These are the endpoints of the India- Myanmar- Trilateral Highway.


Rapid Fire
Verification Mechanism in RoDTEP Scheme
The government is setting up a system to verify that only taxes paid on materials used (input duties) are refunded under the RoDTEP scheme.
- The US and EU imposed anti-subsidy duties on some Indian exports even though the Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) scheme aims to reimburse input taxes.
- This happened because Indian exporters couldn't demonstrate the connection between the RoDTEP benefits received and the input taxes clearly during inspections by the US and EU.
- According to the government, the new verification process is through a team consisting of officials from the Department of Revenue and the Directorate General of Foreign Trade.
- It will address this issue by randomly checking manufacturers and ensuring proper documentation to prove RoDTEP payments are legitimate tax refunds, not subsidies.
- In January 2021, India switched from the Merchandise Export from India Scheme (MEIS) to the RoDTEP scheme. This change came about because MEIS faced criticism from other World Trade Organisation (WTO) member countries.
- They argued that MEIS didn't clearly show how the amount of money paid to exporters was connected to the taxes they paid on materials used in production.


Rapid Fire
Star Campaigners of Political Parties
A political party recently designated a prominent figure closely associated with a Chief Minister as a 'star campaigner' for its electoral activities in a different state.
- Section 77 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 (RP Act) provides for law relating to expenditure incurred by ‘leaders of a political party’.
- These ‘leaders of a political party’ are popularly known as ‘star campaigners’.
- The only requirement is that these persons have to be members of the political party that appoints them.
- The RP Act provides that a recognised political party (national or State) can appoint a maximum of 40 star campaigners while a registered unrecognised political party can appoint up to 20.
- The names of the star campaigners are to be communicated to the Election Commission (EC) and Chief Electoral Officer (CEO) of the States as applicable within 7 days from the date of notification of such election.
- The expenses for travel by them during campaigning are not counted towards a candidate's election expenditure limit.
- However, this exemption applies only if the star campaigners engage in general campaigning for the party.
- If they specifically campaign for candidates or share platforms with them, the expenses are attributed to the candidate's expenditure.


Rapid Fire
Neptis Philyra
A rare butterfly species named Neptis philyra (Nymphalidae family), also known as the long-streak sailor, has been discovered for the first time in India at the Tale Valley Wildlife Sanctuary (TWS), Arunachal Pradesh by a team of butterfly enthusiasts.
- Previously known to be found across various regions of East Asia, including eastern Siberia, Korea, Japan, and central and southwest China.
- It has serrated wings with rich brownish-black on the upper side and yellow-brown on the underside.
- It has a white cell streak on the forewing that forms a “hockey stick” pattern.
- The TWS is named after the Tale Valley, where the wild onion "Tale" is abundant. located in the Lower Subansiri District. The sanctuary is home to a variety of wildlife including the elusive clouded leopard, Indian elephant, and rare orchid species.
- The area is popular for bird and butterfly watching, and there is potential for ecotourism, especially focusing on cultural and scientific planning.
Read more: White Tufted Royal Butterfly, Clouded Leopards and Their Habitats


Rapid Fire
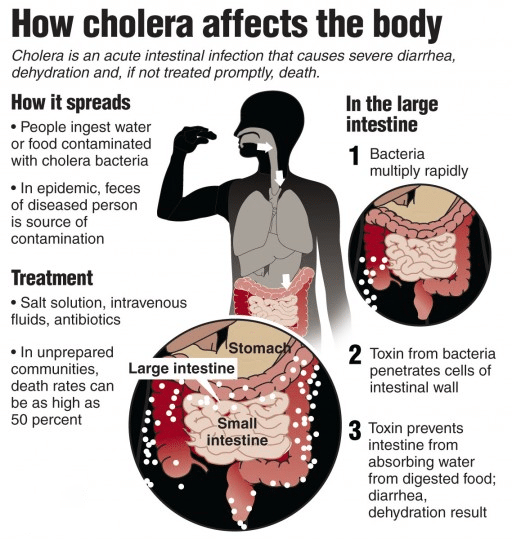
Euvichol-S
Recently, the new oral vaccine for cholera Euvichol-S, received prequalification by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- It is third inactivated oral vaccine to treat Cholera. The other two vaccines are Euvichol and Euvichol-Plus.
- Currently, 23 countries are reporting cholera outbreaks with severe impacts seen in specific regions such as the Comoros, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Mozambique, Somalia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
- Cholera, a water-borne disease primarily caused by the bacteria Vibrio cholerae.
- Symptoms includes profuse watery diarrhoea, Vomiting, Leg cramps.
- Person may get cholera by drinking water or eating food contaminated with the cholera bacterium.
Read more : Cholera


Rapid Fire
Dragonfly Rotorcraft Mission
Recently, NASA has confirmed the Dragonfly rotorcraft mission to Saturn’s moon, Titan.
- Dragonfly is a dual quadcopter, resembling a car-sized rotorcraft that can cover tens of kilometres on Titan in under an hour.
- Due to Titan's hazy atmosphere, Dragonfly will use a radioisotope power system, similar to the Curiosity rover on Mars.
- Dragonfly will fly to dozens of promising locations on Titan looking for prebiotic chemical processes common on both Titan and Earth.
- This will be the first time NASA will fly a multi-rotor vehicle for science on other planets.
- The craft will land first at the equatorial “Shangri-La” dune, exploring the region in short trips before building up to longer “leapfrog” flights of 8 kilometres.
- Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest planet in the Solar System, known for its distinctive ring system.
- Titan is Saturn’s largest moon, has an earthlike cycle of liquids flowing across its surface.
- It is the only moon with a thick atmosphere.
Read More: Dragonfly Mission


Rapid Fire
Youngest World Chess Champion
Recently, D Gukesh won the International Chess Federation (FIDE) Candidates Chess Tournament 2024 in Toronto, Canada.
- He became the youngest-ever challenger to the world title and secured his place in chess history.
- Currently, India has got 7 players in the top 20 junior rankings and a third of the top 30 juniors globally.
- The current world champion is Ding Liren, who defeated his opponent Ian Nepomniachtchi in the 2023 World Chess Championship.
- Magnus Carlsen, the previous world champion, had declined to defend his title.
- International Chess Federation (FIDE), has held the Candidates Tournament since 1950.
- This prestigious event determines who gets to challenge the reigning World Chess Champion.
- It used to be held every three years until 1992, but since 2013, it follows a two-year cycle.
- FIDE is the governing body of the sport of chess, and it regulates all international chess competitions.
- It's constituted as a non-governmental institution. It organizes the World Chess Championship.
Read more: FIDE Grand Swiss Open 2023