Indian Economy
States’ Power to Make GST Laws
For Prelims: GST, GST Council, Supreme Court
For Mains: Cooperative Federalism and Competitive Federalism challenges of GST
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court in a judgment championing the importance of “Cooperative Federalism” for the well-being of democracy, held that Union and State legislatures have “equal, simultaneous and unique powers” to make laws on Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the recommendations of the GST Council are not binding on them.
- The apex court’s decision came while confirming a Gujarat High Court ruling that the Centre cannot levy Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) on ocean freight from Indian importers.
- The Supreme Court has held that GST on ocean freight paid in case of import of goods is unconstitutional.
What is the SC Ruling?
- Center and the States are “autonomous, independent and even competing units” while making GST laws. Cooperative federalism is treated like a marble cake federalism due to the integrated approach of the federal units.
- The recommendations of the GST Council are the product of a collaborative dialogue involving the Union and the states. They are recommendatory in nature.
- The recommendations only have a persuasive value. To regard them as binding would disrupt fiscal federalism when both the Union and the states are conferred equal power to legislate on GST.
- Emphasized that Article 246A (which gives the States power to make laws with respect to GST) of the Constitution treats the Union and the States as “equal units”.
- It confers simultaneous power (on Union and States) for enacting laws on GST.
- Article 279A, in constituting the GST Council, envisions that neither the Centre nor the states are actually dependent on the other.
- There are no provisions in the Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017 (GST Act) that deal with situations where there is repugnancy between the laws drawn up by the Centre and states, and it is for the GST Council to advise them suitably whenever such occasions arise.
What is Cooperative and Competitive Federalism?
- Cooperative Federalism:
- The Centre and states share a horizontal relationship, where they “cooperate” in the larger public interest.
- It is an important tool to enable states’ participation in the formulation and implementation of national policies.
- Union and the states are constitutionally obliged to cooperate with each other on the matters specified in Schedule VII of the constitution.
- Competitive Federalism:
- The relationship between the Central and state governments is vertical and between state governments is horizontal.
- This idea of Competitive federalism gained significance in India post 1990s economic reforms.
- In a free-market economy, the endowments of states, available resource base and their comparative advantages all foster a spirit of competition. Increasing globalisation, however, increased the existing inequalities and imbalances between states.
- In Competitive federalism States need to compete among themselves and also with the Centre for benefits.
- States compete with each other to attract funds and investment, which facilitates efficiency in administration and enhances developmental activities.
- Competitive federalism is not part of the basic structure of Indian constitution. It is the decision of the executives.
- The relationship between the Central and state governments is vertical and between state governments is horizontal.
What is Goods and Services Tax?
- GST is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition.
- GST is one indirect tax for the entire country.
- The GST council is the key decision-making body that will take all important decisions regarding GST.
Way Forward
- The judgment may change the landscape of those provisions under GST which are subject to judicial review.
- As the court has gone ahead to categorically hold that the GST Council recommendations have only persuasive value, there will be a pragmatic approach to the provisions which are subject to judicial review by way of challenge to the constitutionality of such provisions based on GST Council recommendations.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Q. Consider the following items: (2018)
- Cereal grains hulled
- Chicken eggs cooked
- Fish processed and canned
- Newspapers containing advertising material
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Good and Services Tax)?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: C
Exp:
- Certain goods are kept under nil or 0% GST rate to benefit the masses. No GST is imposed on items like edible vegetables, roots and tubers, cereals, fish (not frozen or processed, fresh fruits and vegetables (other than frozen or processed), meat (other than in frozen state and put up in unit containers), cane jaggery (gur), tender coconut water, silkworm laying cocoon, raw silk, silk waste, wool, not carded or combed, cotton used in Gandhi Topi, cotton used in Khadi Yarn, coconut, coir fibre, jute fibre raw or processed but not spun, puja samagri, live animals (except horses), all goods of seed quality, coffee beans, not roasted, unprocessed green tea leaves, fresh ginger, fresh turmeric (other than in processed form), human blood and its components, all types of contraceptives, organic manure, other than those bearing brand name, kumkum, bindi, sindhur, alta, firewood or fuel wood, wood charcoal, betel leaves, judicial, nonjudicial stamp papers, court fee stamps when sold by the government treasuries or authorized vendors, postal items like envelope, post card etc. solid by government, rupee notes when sold to the RBI and cheques, printed books, including braille books, newspaper, maps, earthen pot and clay lamps, bangles (except those made from precious metals),
agricultural implements manually operated or animal driven, hand tools, such as spades shovels, handloom, spacecraft, hearing aids. - All the mentioned items in the given question, except processed and canned fish are included in the exemptions under the GST.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.


Economy
Fostering Effective Energy Transition 2022
For Prelims: World Economic Forum, Energy Transition
For Mains: Way forward for smooth energy transition
Why in News?
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has released a report named Fostering Effective Energy Transition 2022, which calls for urgent action by both private and public sectors to ensure a resilient energy transition to address the challenges to environmental sustainability, energy security and energy justice and affordability.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- The energy transition is not keeping pace with the growing climate urgency, and recent compounded disruptions from a post-pandemic surge in energy demand, fuel supply bottlenecks, inflationary pressures and reconfigured energy supply chains as a result of the war in Ukraine have made the transition even more difficult.
- High energy prices, risks of energy supply shortages, and soaring demand for fossil fuels are simultaneously challenging energy affordability, energy security and access, and sustainability.
- The lack of access to an affordable energy supply has emerged as a key threat to a just transition.
- Industrial activity generates more than 30% of anthropogenic emissions, yet many industries face considerable challenges to decarbonize.
- Skewed Fuel Imports: Of the 34 countries with advanced economies, 11 rely on only three trade partners for over 70 % of their fuel imports.
What are the Recommendations?
- Climate Commitments and Long-Term Visions:
- More countries need to make binding climate commitments, create long-term visions for domestic and regional energy systems, attract private sector investors for decarbonisation projects and help consumers and the workforce adjust.
- Holistic Approach on Transition Imperatives:
- It is crucial to develop adequate enablers and support mechanisms to keep the momentum of the transition through this turbulent phase.
- What is needed now, more than ever, is a holistic approach that delivers concurrently on the three transition imperatives – energy affordability, availability, and sustainability – at an accelerated pace.
- Incentivize Efficient Consumption and Behavioral Intervention:
- Actions are necessary to protect those most vulnerable through appropriate support measures, in a way that incentivizes efficient consumption.
- Behavioral interventions and fourth industrial revolution technologies can help households and businesses alike.
- Energy Diversity and Security:
- Dual diversification (of supply source and supply mix) is key to strengthening countries’ energy security.
- Diversifying the ecosystem of import partners in the short-term and diversifying the portfolio of domestic energy with low-carbon alternatives in the long-term can yield significant benefits.
- Supply-side Interventions and Demand-Side Efficiencies:
- Supply-side interventions will need to be augmented with demand-side efficiencies.
- Current energy market volatility and security constraints provide an opportunity to supercharge the transition by boosting demand for clean energy and fostering more efficient energy consumption from both industrial and end consumers.
- Regulatory frameworks:
- Regulatory frameworks need to be strengthened to drive the necessary actions and investments.
- Anchoring climate commitments into legally binding frameworks would not only ensure that those commitments endure political cycles, but also provide enforcement mechanisms to keep the long-term implementation efforts on track.
- Clean Demand:
- Clean demand signals could be the necessary turning point to scale the projects and investments required for the development of low-emission industries.
What is World Economic Forum?
- About:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) is a Swiss nonprofit foundation established in 1971, based in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Recognized by the Swiss authorities as the international institution for public-private cooperation.
- Mission:
- Committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas.
- Founder and Executive Chairman: Klaus Schwab.
- Some major reports published by WEF are:
- Energy Transition Index.
- Global Competitiveness Report.
- Global IT Report
- WEF along with INSEAD, and Cornell University publishes this report.
- Global Gender Gap Report.
- Global Risk Report.
- Global Travel and Tourism Report.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: A
Exp:
- The Global Gender Gap Report is published by the World Economic Forum. The report’s Gender Gap Index, which is designed to measure gender equality ranks countries, according to the calculated gender gap between women and men in four key areas: health, education, economy and politics to gauge the state of gender equality in a country.
- The Global Gender Gap Report 2021 benchmarks 156 countries on their progress towards gender parity across four thematic dimensions: Economic Participation and Opportunity; Educational Attainment, Health and Survival, and Political Empowerment. In addition, this year’s edition studied skills gender gaps related to Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- India ranks 140th in WEF Gender Gap Index-2021. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q. India’s ranking in the ‘Ease of Doing Business Index’ is sometimes seen in the news. Which of the following has declared that ranking? (2016)
(a) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
(b) World Economic Forum
(c) World Bank
(d) World Trade Organization (WTO)
Ans: C
Exp:
- Ease of Doing Business Index provides objective measures of business regulations and their enforcement across 190 economies and selected cities at the sub-national and regional level. It is prepared and released by the World Bank.
- The Doing Business Project, launched in 2002 looks at domestic small and medium-size companies and measures the regulations applying to them through their life cycle.
- India was ranked 63rd in the latest Doing Business Report (DBR 2020).
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer
Agriculture
Guidelines for Safety Assessment of Genome Edited Plants, 2022
For Prelims: Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee, GMO, Genome Editing, DBT, Genetically Modified crops
For Mains: Genetic Engineering
Why in News?
Recently, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has issued guidelines easing norms for research into Genetically Modified (GM) crops and circumventing challenges of using foreign genes to change crops profile.
- Earlier, the Government has allowed genome-edited plants without the cumbersome GMO (Genetically Modified Organisms) regulation at the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
What are the Highlights of the Guidelines?
- Exempts Researchers from Seeking Approvals:
- It exempts researchers who use gene-editing technology to modify the genome of the plant from seeking approvals from the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
- The GEAC evaluates research into GM plants and recommends, or disapproves, their release into farmer fields.
- The final call, however, is taken by the Environment Minister as well as States where such plants could be cultivated. The Environment Ministry too has sanctioned this exemption.
- The guidelines provide a road map for the sustainable use of genome editing technologies and applicable to public and private sector research institutions engaged in research and development and handling of genome edited plants.
- It exempts researchers who use gene-editing technology to modify the genome of the plant from seeking approvals from the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
- Issues Guidelines Address:
- Most often, GM plants that have drawn such scrutiny are those that use transgenic technology or introduce a gene from another species into a plant, such as BT-cotton, which uses a soil bacterium gene to protect against pest attack.
- The worry around this method is that these genes may spread to neighbouring plants, where such effects are not intended and so their applications have been controversial.
What is Genome Editing?
- About:
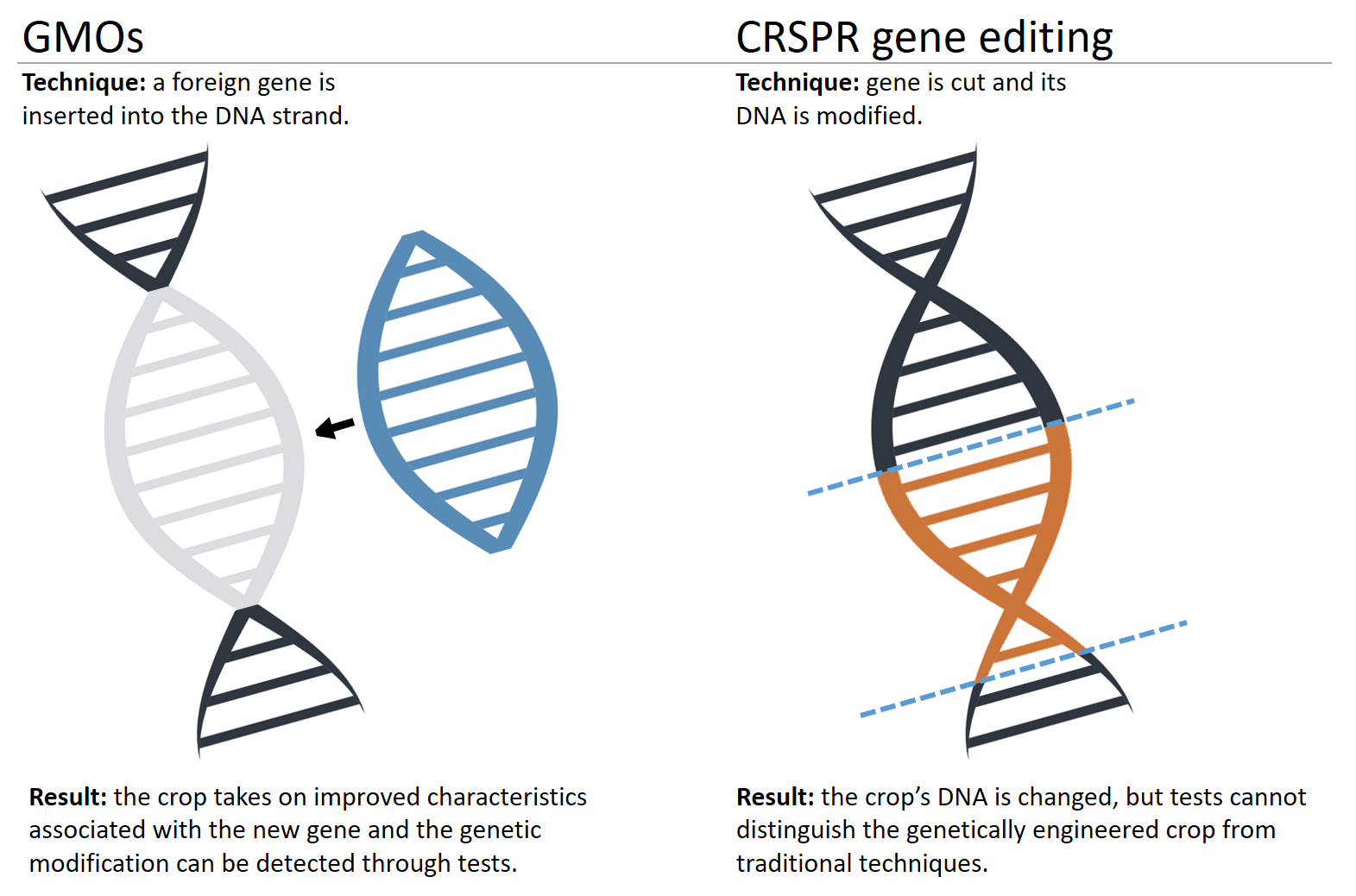
- Genome editing enables modification of plants’ owned genes, without insertion of external genes, as with GM crops.
- Genome-edited varieties possess no foreign DNA and are indistinguishable from crops developed through conventional plant-breeding methods, or using naturally occurring mutations.
- Approaches to Genome Editing:
- Several approaches to genome editing have been developed. A well-known one is called CRISPR-Cas9.
- CRISPR-Cas9 is short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9.
- This tool has opened up various possibilities in plant breeding. Using this tool, agricultural scientists can now edit the genome to insert specific traits in the gene sequence.
- Depending on the nature of the edit that is carried out, the process is divided into three categories — SDN 1, SDN 2 and SDN 3.
- Site Directed Nuclease (SDN) 1 introduces changes in the host genome’s DNA through small insertions/deletions without introduction of foreign genetic material.
- In SDN 2, the edit involves using a small DNA template to generate specific changes. Both these processes do not involve alien genetic material and the end result is indistinguishable from conventionally bred crop varieties.
- The SDN3 process involves larger DNA elements or full-length genes of foreign origin which makes it similar to Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) development.
- Several approaches to genome editing have been developed. A well-known one is called CRISPR-Cas9.
- Global Developments:
- Genome editing is being used in most crop plants for which partial or complete genome sequence is available and is being applied in around 40 crops across 25 countries.
- The US and China are leaders in usage of this technology for developing crop varieties like rice, maize, soybean, canola and tomato which withstand biotic and abiotic stresses arising out of climate change.
What is the Difference between Gene Editing and Genetically Modifying?
- To create genetically modified crops and animals, scientists will typically remove the preferred gene from one organism and randomly introduce it into another organism.
- A well-known genetically modified type of crop is Bt corn and cotton, where a bacterial gene was introduced that produces insecticidal toxins into the part of the plant where the insect eats, causing death to the insect.
- In simple terms, gene editing is a small, controlled tweak to a living organism’s existing DNA versus the introduction of a new, foreign gene.
- It is nearly impossible to detect whether an organism’s DNA has been edited or not because the changes are indistinguishable from naturally occurring mutations.
What is the Significance of the Genome Technique?
- Improve Resistant to Diseases:
- The technology has great promise and emphasis is needed on improving oilseed and pulse crop varieties’ resistant to diseases, insects or pests, and tolerant to drought, salinity and heat stresses.
- Faster Development of Crop Varieties:
- Conventional breeding technique takes 8 to 10 years to develop agricultural crop varieties, while through genome editing, it can be done in two to three years.
What are the Issues with Genome Editing Technique?
- Across the world, GM crops have been a topic of debate, with many environmentalists opposing it on the grounds of bio safety and incomplete data. In India, the introduction of GM crops is a laborious process which involves multiple levels of checks.
- Till date the only crop which has crossed the regulatory red tape is Bt cotton.
- Scientists both in India and across the world have been quick to draw the line between GM crops and genome edited crops. The latter, they have pointed out, has no foreign genetic material in them which makes them indistinguishable from traditional hybrids.
- Globally, European Union countries have bracketed genome edited crops with GM crops. Countries like Argentina, Israel, US, Canada, etc have liberal regulations for genome edited crops.
- Gene editing techniques which involve altering the function of genes and can cause “large and unintended consequences” that can change the “toxicity and allergenicity” of plants.
Way Forward
- In the face of such new advances regarding Genome Technology, the regulatory regime needs to be strengthened as well as rationalised, for the sake of domestic as well as export consumers.
- Technology approvals must be streamlined, and science-based decisions implemented.
- Rigorous monitoring is needed to ensure that safety protocols are followed strictly, and enforcement must be taken seriously to prevent the spread of illegal GM crops.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Q. With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017)
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only,
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: D
Exp:
- Chinese scientists decoded rice genome in 2002. The Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) scientists used the genome sequencing to develop better varieties of rice such as Pusa Basmati-1 and Pusa Basmati-1121, which currently makes up substantially in India’s rice export. Several transgenic varieties have also been developed, including insect resistant cotton, herbicide tolerant soybean, and virus resistant papaya. Hence, 1 is correct.
- In conventional breeding, plant breeders scrutinize their fields and search for individual plants that exhibit desirable traits. These traits arise spontaneously through a process called mutation, but the natural rate of mutation is very slow and unreliable to produce all the plant traits that breeders would like to see. However, in genome sequencing it takes less time, thus it is more preferable. Hence, 2 is correct.
- The host-pathogen interaction is defined as how microbes or viruses sustain themselves within host organisms on a molecular, cellular, organism or population level. The genome sequencing enables the study of the entire DNA sequence of a crop, thus it aids in understanding of pathogens’ survival or breeding zone. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer


International Relations
BRICS High Level Meeting on Climate Change
For Prelims: Climate Change, BRICS, COP 26, UNFCCC, Paris Agreement
For Mains: Issues of climate change and various international conventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change participated in the BRICS high-level meeting on Climate Change where he highlighted the relevance of the forum to jointly address climate change, to explore approaches to accelerate low-carbon and resilient transition, and to achieve sustainable recovery and development.
- The Meeting was chaired by People's Republic of China and was attended by Environment Ministers of BRICS nations including Brazil, Russia, India and South Africa.
What are the Highlights of the Meeting?
- India underscored its commitment to strong climate action including the promotion of sustainable lifestyles based on mindful consumption and reduction of waste.
- India is today leading by example by taking several robust steps in the field of renewable energy, sustainable habitats, creation of carbon sinks through additional forest and tree cover, transition to sustainable transport, E-mobility, mobilizing the private sector to make climate commitments, etc.
- India has progressively continued decoupling economic growth from greenhouse gas emissions.
- Ambitious implementation of climate actions by developing countries is contingent on the ambitious and adequate delivery of climate finance, technology transfer, and other implementation support, as mandated by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement.
- BRICS nations expressed optimism towards the delivery of climate finance as per the Glasgow decision and the Climate Finance Delivery Plan released by the COP 26 Presidency.
- BRICS Environment Ministers expressed commitment to strengthen collaboration on climate change and broaden and deepen the contents of cooperation.
- Further, the countries agreed to carry out policy exchanges and cooperation in areas of environment and climate change.
What is BRICS?
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies, namely Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- In 2001, the British Economist Jim O’Neill coined the term BRIC to describe the four emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, and China.
- The grouping was formalised during the first meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers’ in 2006.
- South Africa was invited to join BRIC in December 2010, after which the group adopted the acronym BRICS.
- The BRICS brings together five of the largest developing countries of the world, representing 41% of the global population, 24% of the global GDP and 16% of the global trade.
- The chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members, in accordance with the acronym B-R-I-C-S.
- India was the chair for 2021.
- During the Sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (Brazil) in 2014, the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB - Shanghai, China). They also signed the BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement to provide short-term liquidity support to the members.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- New Development Bank has been set up by APEC.
- The headquarters of New Development Bank is in Shanghai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: B
Exp:
- The New Development Bank (NDB) was formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank.
- It is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The bank is headquartered in Shanghai, China. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- During the sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (2014), the New Development Bank (NDB) was established by the Fortaleza Declaration to strengthen cooperation among BRICS and supplement the efforts of multilateral and regional financial institutions for global development.
- It had an initial authorized capital of US$ 100 billion, with an initial subscribed capital of US$ 50 billion, equally shared among founding members.
Q. The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’, recently in the news, is related to the affairs of (2015)
(a) ASEAN
(b) BRICS
(c) OECD
(d) WTO
Ans: B
Exp:
- Fortaleza Declaration was proclaimed in the 6th BRICS summit in 2014. It included:
- Agreement for setting up the New Development Bank (NDB) with $100 billion corpus, which will distribute the funds equally among all the BRICS nations for mobilizing resources for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in BRICS.
- BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) with an initial size of $100 billion to tackle short-term liquidity demands.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer
Governance
Amendments to the Companies Act
For Prelims: Companies Act, 2013, Company Law Committee
For Mains: Proposed Amendments to Companies Act
Why in News?
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs is set to introduce amendments to the Companies Act in the winter session of Parliament.
- The ministry has received feedback from experts and professionals on these recommendations made by the Company Law Committee that gave its Report in April 2022 to the finance and corporate affairs minister.
What are the Key Proposals?
- It is expected to raise the bar on corporate governance, especially in hiring for board positions and handling resignations of auditors and top executives.
- The key proposals seek to ensure that independent directors are truly independent, and companies are more open about instances of statutory auditors making adverse remarks or qualifications on the financial statements or even quitting their audit assignment.
- It seeks to protect the independence of the statutory auditors by making several changes to the law, including mandatory joint audits for certain types of companies.
- The idea of the proposed changes to the Companies Act is to strengthen the gatekeepers of good governance(Corporate governance)—independent directors and auditors—infuse more transparency into company affairs and allow companies to issue fractional shares and discounted shares as part of efforts to improve ease of doing business.
- The issue of fractional shares, a practice currently prohibited under the Companies Act, will help retail investors access high-value shares, while discounted shares will allow a company in distress to convert debt to equity.
- Some of the past bankruptcies in the corporate sector, particularly those involving large non-bank financial companies facing serious financial difficulties, have prompted the government to consider some of these changes.
What is the Indian Companies Act?
- Indian Companies Act is an Act of the Parliament which was enacted in 1956. It enables the companies to be formed by registration, sets out the responsibilities of companies, their executive director and secretaries.
- In 2013, the Government amended the Indian Companies Act 1956 and added a new Act called as Indian Companies Act 2013.
- The Companies Act, 1956 was replaced partially by the Indian Companies Act 2013.
- It became an act and finally it came into force in September 2013.
- In 2020, the Parliament of India passed the Companies (Amendment) Bill, 2020 to further amend the Companies Act and decriminalise various compoundable offences as well as promote ease of doing business in the country.
- Reduction in penalties for certain offences as well as in timeline for rights issues, relaxation in corporate social responsibility (CSR) compliance requirements and creation of separate benches at the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) are among the proposed changes too.
What are the Features of the Companies Act of 2013
- It regulates incorporation of a company, responsibilities of a company, directors, and dissolution of a company.
- It is divided into 29 chapters which containing 470 sections as against 658 Sections in the former Companies Act, 1956 and has 7 schedules.
- It provides a maximum of 200 members, earlier the private companies the maximum number of members were 50.
- A new term of ‘one-person company’ is included in this act.


International Relations
SCO ‘Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS)’ Meeting
For Prelims: SCO, RATS, Council of RATS-SCO
For Mains: Diplomatic and Economic relations of India with SCO, Bilateral relations of India with SCO member nations
Why in News?
Recently, a meeting held between the member nations of the SCO under the framework of the SCO’s Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS). It is the first such meeting in India since Russia’s evasion of Ukraine and China’s transgression along the Line of actual control.
- SCO-RATS meeting agenda is to boost cooperation in fighting different global and regional security challenges.
- India has chaired the Council of Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure of SCO (RATS SCO).
What is the Agenda Discussed in the Meeting?
- Situation of Afghanistan and security concerns raised due to the fall of Afghanistan in the hands of the Taliban was the main agenda of the meeting.
- India has expressed a strong desire to strengthen its security cooperation with the SCO and its Regional Anti-Terrorism Structure, which focus on security and defence matters.
What is Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure-SCO?
- SCO-RATS is a permanent body of the Sanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
- It is promoting coordination and interaction between the SCO member states as per as fight against terrorism, extremism and separatism are concern.
- The main functions of SCO-RATS are information sharing.
- As a member, India has actively participated in the activities of SCO-RATS.
- India’s permanent membership would enable it to generate greater understanding among members for its perspective.
What is the Shanghai Cooperation Organization?
- About:
- SCO was created in 2001.
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) was established as a multilateral association to ensure security and maintain stability across the vast Eurasian region.
- It envisages joining forces to counteract emerging challenges and threats, and enhance trade, as well as cultural and humanitarian cooperation.
- Prior to the creation of SCO in 2001, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan were members of the Shanghai Five.
- Shanghai Five (1996) emerged from a series of border demarcation and demilitarization talks which the four former Soviet republics held with China to ensure stability along the borders.
- Following the accession of Uzbekistan to the organization in 2001, the Shanghai Five was renamed the SCO.
- The SCO Charter was signed in 2002 and entered into force in 2003. The SCO's official languages are Russian and Chinese.
- SCO has two Permanent Bodies:
- SCO Secretariat in Beijing,
- Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) in Tashkent.
- Member Nations: Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan.
- Recently, Iran’s bid to become a full member of the SCO has been approved.
Important Facts For Prelims
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Why in News?
Recently, in a study it was found that the lower respiratory infections caused by the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) are more frequent in children under the age of five.
- According to a report published by the Lancet, it is responsible for the death of 1,00,000 children in the world during the year 2019.
What is the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)?
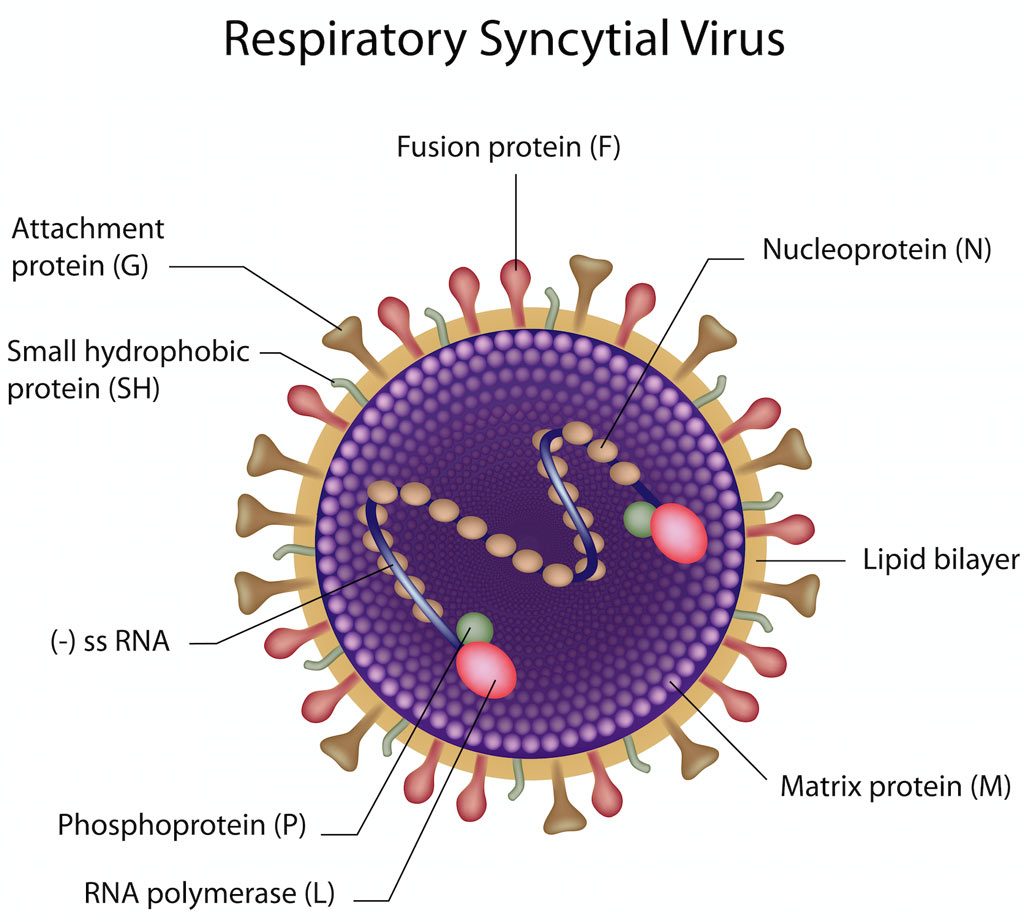
- About:
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus is a common respiratory virus.
- It is characterized by its highly contagious nature i.e., it has a high potential to infect people.
- It exacerbated the seasonal lung infection.
- It commonly infects children especially under 2 to 6 years of age.
- In most of the cases it has symptoms like the common cold but in advanced stages it converts into phenumonia and bronchiolitis.
- Key Findings:
- In the year 2019, over 45000 infant fatalities under the age of six were reported.
- One child out of every five RSV infected children died in the entire world.
- Children six months and younger are most vulnerable to this virus.
- According to the research, the annual incidence rate in India is 53 per 1,000 children (5.3%), with an estimated 61,86,500 cases of RSV associated with acute lower respiratory infection in children under the age of five.
- RSV killed 97 percent of children under the age of five in low- and middle-income nations.
What is the Cure for Respiratory Syncytial Virus?
- There is no reliable cure available for RSV infection.
- Scientists, Government and concerning authority are promoting research and development in this domain to find out appropriate medicine and vaccination to save the life of infants and children.