Indian Polity
Governor’s Power to Call for Floor Test
Prelims: Floor Test, Constitutional Provisions, Governor’s Discretionary Powers
Mains: Constitutional Provisions related to summoning powers of Governor
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) has said that the Governor cannot call for a Floor Test on the basis of internal differences in the Party Members.
- The SC while hearing a case about a dispute between two factions in a political party, discussed the powers and role of the Governor in calling for a trust vote.
How can the Governor Call for a Floor Test?
- About:
- Article 174 of the Constitution authorizes the Governor to summon, dissolve and prorogue the state legislative assembly.
- Article 174(2)(b) of the Constitution gives powers to the Governor to dissolve the Assembly on the aid and advice of the cabinet. However, the Governor can apply his mind when the advice comes from a Chief Minister whose majority could be in doubt.
- According to Article 175(2), the Governor can summon the House and call for a floor test to prove whether the government has the numbers.
- However, the Governor can exercise the above only as per Article 163 of the Constitution which says that the Governor acts on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers headed by the Chief Minister.
- When the House is in session, it is the Speaker who can call for a floor test. But when the Assembly is not in session, the Governor’s residuary powers under Article 163 allow him to call for a floor test.
- Article 174 of the Constitution authorizes the Governor to summon, dissolve and prorogue the state legislative assembly.
- Governor’s Discretionary Power:
- Article 163 (1) essentially limits any discretionary power of the Governor only to cases where the Constitution expressly specifies that the Governor must act on his own and apply an independent mind.
- The Governor can exercise his discretionary power under Article 174, when the chief minister has lost the support of the House and his strength is debatable.
- Generally, when doubts are cast on the chief minister that he has lost the majority, the opposition and the Governor would rally for a floor test.
- On numerous occasions, the courts have also clarified that when the majority of the ruling party is in question, a floor test must be conducted at the earliest available opportunity.
What are the SC’s Observations on the Governor's Floor Test Call?
- In 2016, the SC in Nabam Rebia and Bamang Felix vs Deputy Speaker case (the Arunachal Pradesh Assembly case) said that the power to summon the House is not solely vested in the Governor and should be exercised with aid and advice of the Council of Ministers and not at his own.
- The Court highlighted the facts that the Governor is not an elected authority and is a mere nominee of the President, such a nominee cannot have an overriding authority over the representatives of the people, who constitute the House or Houses of the State Legislature.
- In 2020, the Supreme Court, in Shivraj Singh Chouhan & Ors versus Speaker, Madhya Pradesh Legislative Assembly & Ors, upheld the powers of the Speaker to call for a floor test if there is a prima facie view that the government has lost its majority.
- The Governor is not denied the power to order a floor test where on the basis of the material available to the Governor it becomes evident that the issue as to whether the government commands the confidence of the House requires it to be assessed on the basis of a floor test.
What is a Floor Test?
- It is a term used for the test of the majority. If there are doubts against the Chief Minister (CM) of a State, he/she can be asked to prove the majority in the House.
- In the case of a coalition government, the CM may be asked to move a vote of confidence and win a majority.
- In the absence of a clear majority, when there is more than one individual stake to form the government, the Governor may call for a special session to see who has the majority to form the government.
- Some legislators may be absent or choose not to vote. The numbers are then considered based only on those MLAs who were present to vote.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Which of the following are the discretionary powers given to the Governor of a State? (2014)
- Sending a report to the President of India for imposing the President’s rule
- Appointing the Ministers
- Reserving certain bills passed by the State Legislature for consideration of the President of India
- Making the rules to conduct the business of the State Government
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.1 Discuss the essential conditions for exercise of the legislative powers by the Governor. Discuss the legality of re-promulgation of ordinances by the Governor without placing them before the Legislature. (2022)
Indian Polity
BCI Allows Foreign Lawyers to Practice in India
Prelims: BCI, Supreme Court, International Commercial Arbitration, Advocate Act 1961.
Mains: BCI Allows Foreign Lawyers to Practice in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Bar Council of India (BCI) has notified Rules for Registration and Regulation of Foreign Lawyers and Foreign Law Firms in India, 2022, allowing foreign lawyers and law firms to practice in India.
- However, it did not allow them to appear before courts, tribunals or other statutory or regulatory authorities.
What is the BCI Decision?
- For over a decade, BCI was opposed to allowing foreign law firms in India.
- Now, the BCI has reasoned that its move will address concerns about the flow of Foreign Direct Investment in the country and make India a hub of International Commercial Arbitration.
- The rules bring legal clarity to foreign law firms that currently operate in a very limited way in India.
- The BCI said it “resolves to implement these Rules enabling the foreign lawyers and Foreign Law Firms to practice foreign law and diverse international law and international arbitration matters in India on the principle of reciprocity in a well-defined, regulated and controlled manner.
What are the New Rules?
- The notification allows foreign lawyers and law firms to register with BCI to practice in India if they are entitled to practice law in their home countries. However, they cannot practice Indian law.
- According to the Advocates Act 1961, advocates enrolled with the Bar Council alone are entitled to practise law in India. All others, such as a litigant, can appear only with the permission of the court, authority or person before whom the proceedings are pending.
- They shall be allowed to practice transactional work /corporate work (Non-Litigious Practice) such as joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions, Intellectual Property matters, drafting of contracts and other related matters on a reciprocal basis.
- They shall not be involved or permitted to do any work pertaining to the conveyancing of property, title investigation or other similar works.
- Indian lawyers working with foreign law firms will also be subject to the same restriction of engaging only in “Non-Litigious Practice.”
What is the Significance of the New Move?
- It is likely to pave the way for potential consolidation, especially for firms dealing in the cross-border mergers and acquisitions (M&A) practice in particular.
- Entry of foreign law firms will support in a big way the ambition of India to be more visible and valuable in a global context, especially on international trade and commerce.
- This will be a game changer for the mid-size firms and will also help the law firms in India to achieve more efficiency in talent management, IA, technology, domain knowledge in a global context, and management.
What is the Bar Council of India?
- The Bar Council of India is a statutory body created by Parliament under the Advocates Act, 1961 to regulate and represent the Indian bar.
- It performs the regulatory function by prescribing standards of professional conduct and etiquette and by exercising disciplinary jurisdiction over the bar.
- It also sets standards for legal education and grants recognition to universities whose degree in law will serve as qualification for enrolment as an advocate.
- In addition, it performs certain representative functions by protecting the rights, privileges and interests of advocates and through the creation of funds for providing financial assistance to organize welfare schemes for them.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. With reference to India, consider the following statements:
1. Government law officers and legal firms are recognised as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
2. Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
International Relations
India - Australia Critical Minerals Investment Partnership
For Prelims: Critical Minerals, QUAD, Indo-Pacific Region
For Mains: India and Australia Relations, India-Australia Critical Minerals Investment Partnership, Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, India and Australia have reached a significant milestone in working towards investment in critical minerals projects to develop supply chains between the two countries.
What are Critical Minerals?
- About: Critical minerals are elements that are the building blocks of essential modern-day technologies and are at risk of supply chain disruptions.
- Examples: Copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements are critical components in many of today's rapidly expanding clean energy technologies, ranging from wind turbines and power grids to electric vehicles. As the transition to clean energy accelerates, demand for these minerals will skyrocket.
- Indian Policy: India’s Department of Science and Technology, in collaboration with the Council on Energy, Environment and Water, drafted the Critical Minerals Strategy for India in 2016, with a focus on India’s resource requirements till 2030.
- The Indian Critical Minerals Strategy has identified 49 minerals that will be vital for India’s future economic growth.
What are the Key Highlights of the Critical Minerals Investment Partnership (CMIP)?
- Two lithium and three cobalt projects are among the five target projects that CMIP has chosen for thorough due diligence.
- Australia produces almost half of the world’s lithium and is the second-largest producer of cobalt and the fourth-largest producer of rare earths.
- The Partnership's investments will aim to create new supply chains supported by essential minerals processed in Australia, which will support India's efforts to reduce emissions from its energy network and establish itself as a hub of manufacturing, including for electric vehicles.
- Together, the two countries are dedicated to reducing emissions, ensuring energy security, and expanding the global markets for essential minerals and clean technology.
How have the India-Australia Trade Relations been so far?
- Cordial Relations: India and Australia have excellent bilateral relations that have undergone transformational evolution in recent years, developing into a friendly partnership on a positive track.
- This is a unique partnership defined by shared values such as parliamentary democracies, Commonwealth traditions, increased economic engagement, long-standing people-to-people ties, and increased high-level interaction.
- India-Australia Comprehensive Strategic Partnership: It was launched during the India-Australia Leaders' Virtual Summit in June 2020, and it is the foundation of India and Australia's bilateral relations.
- Trading Partners: India-Australia bilateral trade in both goods and services is expected to reach USD 27.5 billion in 2021 consisting largely of raw materials, minerals and intermediate goods.
- Others: India and Australia are partners in the trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) arrangement along with Japan which seeks to enhance the resilience of supply chains in the Indo-Pacific Region.
- Further, India and Australia are also members of the QUAD grouping (India, the US, Australia, and Japan), to enhance cooperation and develop partnerships across several issues of common concern.
What are Countries Around the World doing About Critical Minerals Supply?
- United States: In 2021, the US ordered a review of vulnerabilities in its critical minerals supply chains and found that an over-reliance on foreign sources and adversarial nations for critical minerals and materials posed national and economic security threats.
- India: It has set up KABIL or the Khanij Bidesh India Limited, a joint venture of three public sector companies, to ensure a consistent supply of critical and strategic minerals to the Indian domestic market.
- It ensures the mineral security of the nation; it also helps in realizing the overall objective of import substitution.
- Other Countries: In 2020, the US, Canada, and Australia launched an interactive map of critical mineral deposits intending to help governments to identify options to diversify the sources of their critical minerals. Uk's critical minerals strategy' sets out the government's plans for improving the resilience of critical minerals supply chains and increasing our security of supply. Through this strategy, the UK will: accelerate the growth of UK's domestic capabilities.
Conclusion
- The CMIP between Australia and India represents a significant milestone in bilateral relations.
- The two countries should work together to ensure that the alliance is properly implemented and to investigate opportunities for collaborative research and development. The vital minerals industry may change as a result of the CMIP, which will also help both countries' economies grow and thrive.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1 Recently, there has been a concern over the short supply of a group of elements called ‘rare earth metals’. Why? (2012)
- China, which is the largest producer of these elements, has imposed some restrictions on their export.
- Other than China, Australia, Canada and Chile, these elements are not found in any country.
- Rare earth metals are essential for the manufacture of various kinds of electronic items and there is a growing demand for these elements.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Social Justice
Rising Concerns over Freshwater Shortages
For Prelims: World Wide Fund for Nature, Central Ground Water Board, National Water Policy, 2012, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, Jal Shakti Abhiyan- Catch the Rain Campaign, Atal Bhujal Yojana.
For Mains: Status of Freshwater Shortage in India, Issues Related to Water Resources in India.
Why in News?
Recently, a global study released by Circle of Blue and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) analysed attitudes towards freshwater shortages by surveying almost 30,000 people from 31 countries.
- People in Argentina, South Korea, Vietnam, Colombia, Germany and Peru reported the largest increases in concerns about water shortages over the past few years.
What are the Major Highlights of the Report?
- 30% of people claim to be greatly impacted by freshwater shortages.
- Strong concerns about freshwater shortages have increased from 49% in 2014 to 61% in 2022, among 17 countries consistently tracked.
- People in urban areas (32%) are more likely to be greatly affected by a lack of freshwater than those in rural (28%) or towns and suburban areas (26%).
- 38% of people said they have been “greatly” personally affected by climate change.
- People who claimed to be personally affected by climate change viewed drought as the most concerning impact of it.
What is the Status of Freshwater Shortage in India?
- About:
- India’s freshwater crisis is constant. Although India has 16% of the world’s population, the country possesses only 4% of the world’s freshwater resources.
- According to NITI Aayog, a large number of Indians face high to extreme water stress.
- North India, the most populated belt of the nation is going to face grievous irreversible fresh water scarcity by 2060 since the availability of the vital resource will decline on account of climate change.
- Issues:
- Rising Water Pollution: There is a large amount of domestic, industrial, and mining waste that is discharged into water bodies, which can lead to waterborne illnesses.
- Moreover, water pollution can lead to eutrophication, which can significantly impact aquatic ecosystems.
- Overexploitation of Groundwater: 256 of 700 districts in India have reported critical or overexploited groundwater levels, according to the Central Ground Water Board (2017).
- Wells, ponds and tanks are drying up as groundwater resources come under increasing pressure due to over-reliance and unsustainable consumption. This has escalated the water crisis.
- Potential Rural-Urban Conflict: Cities are rapidly expanding as a result of rapid urbanisation, and a large influx of migrants from rural areas has increased the per capita use of water in cities, which is causing water to be transferred from rural reservoirs to urban areas to meet the deficit.
- Considering the downward trend of water level in urban areas, it is likely that cities will rely heavily on rural areas for raw water supply in the future, which may spark the rural-urban conflict.
- Rising Water Pollution: There is a large amount of domestic, industrial, and mining waste that is discharged into water bodies, which can lead to waterborne illnesses.
What are the Current Government Initiatives Related to Water Management?
Way Forward
- Sustainable Groundwater Management: There is a need to devise a proper mechanism and rural-urban integrated projects for artificial recharge to groundwater and rainwater harvesting at household level, conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater, and regulation of water reservoirs.
- Water Conservation Zone: There is a need to shift focus towards efficient water governance and increased data discipline regarding the status of water bodies at regional, state and national level, and setting up water conservation zones.
- Leveraging Modern Water Management Techniques: Information Technology can be linked with water-related data systems. Also, in recent years, breakthroughs in research and technology have made it possible to make water that was considered unfit for consumption, clean and safe for consumption.
- Some of the most frequently used techniques include Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR), Desalinization, Nanofiltration, and Solar and UV Filtration.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Which one of the following ancient towns is well known for its elaborate system of water harvesting and management by building a series of dams and channelizing water into connected reservoirs? (2021)
(a) Dholavira
(b) Kalibangan
(c) Rakhigarhi
(d) Ropar
Ans: (a)
Q.2 With reference to ‘Water Credit’, consider the following statements: (2021)
- It puts microfinance tools to work in the water and sanitation sector.
- It is a global initiative launched under the aegis of the World Health Organization and the World Bank.
- It aims to enable the poor people to meet their water needs without depending on subsidies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What are the salient features of the Jal Shakti Abhiyan launched by the Government of India for water conservation and water security? (2020)
Q.2 Suggest measures to improve water storage and irrigation system to make its judicious use under the depleting scenario. (2020)
Important Facts For Prelims
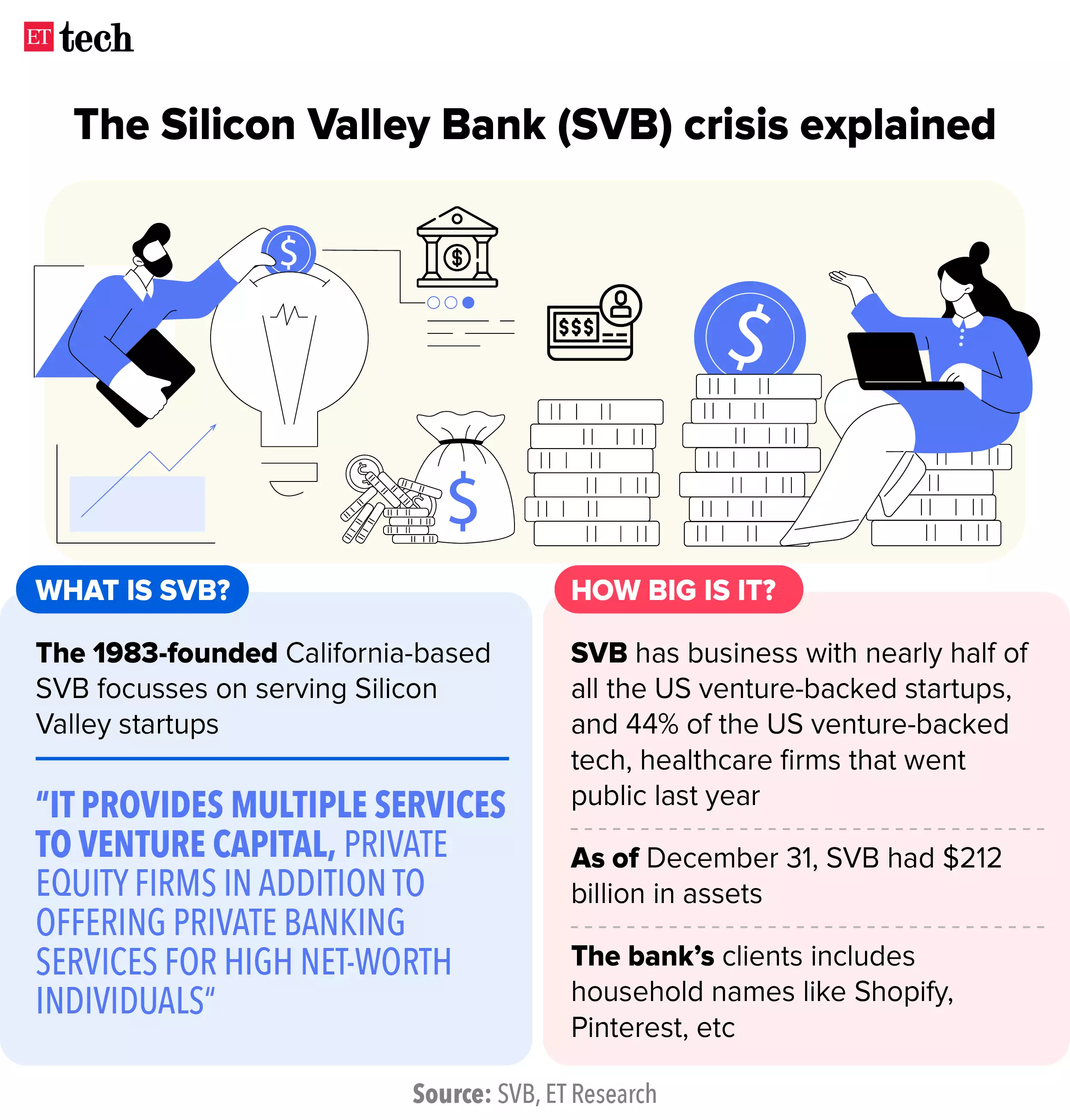
SVB Financial Group Collapse
Why in News?
Recently, the U.S. banking regulators shut down the Silicon Valley Bank (SVP) Financial Group, causing shockwaves in the startup community.
- The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank was caused by the US Federal Reserve's decision to raise interest rates, leading to less appetite for risk and resulting in investors pulling out their money to meet their liquidity needs.
What led to the Decline of SVP Financial Group?
- Sequence of Event of Failure:
- Federal Reserve raises rates;
- Some SVB clients face cash crunch;
- SVB sells Bond portfolio at a loss;
- SVB Announces Stock Sale;
- Stock Sale Collapses;
- SVB goes into Receivership.
- Causes of SVB's Failure:
- SVB sold substantially all of its available-for-sale securities at a USD 1.8-billion loss, mostly in the form of US Treasury securities.
- It received a massive volume of deposits during the tech boom of 2020-2021, and invested the proceeds into long-term Treasury bonds while interest rates were low.
- However, with interest rates rising, the market value of these Treasuries became substantially lower than SVB paid, triggering withdrawal requests from depositors.
What are the Effects of SVB Failure?
- Bank Runs:
- The bank’s failure is raising concerns about other banks. Bank runs can happen when customers or investors panic and start pulling their deposits. Perhaps the most immediate concern is that the failure of Silicon Valley Bank would scare off customers of other banks.
- Indian Startup:
- SVB was an important lender to several Indian start-ups, and its failure will affect the withdrawal of money from their accounts.
- SVB offered an easy way for start-ups in India to park their cash as firms could set up their bank accounts without needing a United States Social Security Number or Income Tax Identification Number.
Important Facts For Prelims
International Day of Action for Rivers 2023
Why in News?
Every year on March 14, the International Day of Action for Rivers (IDAR) is observed to promote awareness of the importance of the river systems on the planet earth.
- This year, the 25th anniversary of the day was observed. The day was earlier known as International Day against Dams, for Rivers, Water, and Life.
What are the Key Points Related to IDAR?
- Theme: Rights of Rivers.
- It calls for the designation of rivers as a national treasure.
- History:
- The participants of the First International Meeting of People Affected by Dams held in March 1997 in Curitiba Brazil adopted the International Day of Action Against Dams and For Rivers, Water, and Life.
- 20 countries' representatives had decided that the International Day of Action would take place on 14 March Brazil's Day of Action Against Large Dams.
- Significance:
- It demonstrates how crucial rivers are to sustaining human life.
- Rivers and other freshwater environments are crucial sources of clean water for agriculture and drinking but are sadly being subjected to significant quantities of pollution and contamination by both the general people and industries.
- The day tries to focus on the uneven access to clean water and the pollution occurring due to human activities. This is the reason behind the increase in the pollution of freshwater.
- It demonstrates how crucial rivers are to sustaining human life.
What are the Related Indian Initiatives?
- Namami Gange Programme: It is an Integrated Conservation Mission, approved as a ‘Flagship Programme’ by the Union Government in June 2014 to accomplish the twin objectives of effective abatement of pollution and conservation and rejuvenation of National River Ganga.
- Ganga was declared as the ‘National River’ of India in 2008.
- Ganga Action Plan: It was the first River Action Plan that was taken up by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in 1985, to improve the water quality by the interception, diversion, and treatment of domestic sewage.
- The National River Conservation Plan is an extension to the Ganga Action Plan.
- National River Conservation Plan (NRCP):
- NRCP is the Centrally Sponsored Scheme implemented for abatement of pollution in identified stretches of rivers in the country, excluding those in Ganga basin, by providing financial and technical assistance to the States/Union Territories (UTs) on cost sharing basis.
- National River Rejuvenation Mechanism:
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) directed the Ministry of Jal Shakti to devise an appropriate National River Rejuvenation Mechanism for effective monitoring of steps to curb pollution and for rejuvenation of all polluted river stretches across the country.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Discuss the Namami Gange and National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) programmes and causes of mixed results from the previous schemes. What quantum leaps can help preserve the river Ganga better than incremental inputs? (2015)
Important Facts For Prelims
National Policy on Older Persons in India
Why in News?
The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment implements a Central Sector Scheme of Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC).
What are the Initiatives Related to Welfare of Senior Citizens in India?
- National Policy on Older Persons (NPOP):
- The National Policy on Older Persons (NPOP) was announced in 1999 to reaffirm the commitment to ensure the well-being of older persons.
- The Policy envisages State support to ensure financial and food security, health care, shelter and other needs of older persons, equitable share in development, protection against abuse and exploitation, and availability of services to improve the quality of their lives.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme funded by the Senior Citizens’ Welfare Fund.
- The scheme provides aids and assistive living devices to senior citizens belonging to BPL category or those who earn less than 15000/- per month and suffer from age-related disabilities such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth, and loco-motor disabilities.
- Elderline:
- The National Helpline for Senior Citizen (14567)-Elderline has been set up by the Ministry to address the grievances of elders in 2021.
- The helpline has been launched across the country and offers services to senior citizens through a toll-free number.
- The National Helpline for Senior Citizen (14567)-Elderline has been set up by the Ministry to address the grievances of elders in 2021.
- Seniorcare Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE):
- It is an initiative launched in 2021 to encourage innovative start-ups to develop products, processes, and services for the welfare of the elderly.
- Under this initiative, innovative start-ups are identified and provided with equity support of up to Rs.1 crore per project while ensuring that the total Government equity in the start-up does not exceed 49%.
- It is an initiative launched in 2021 to encourage innovative start-ups to develop products, processes, and services for the welfare of the elderly.
- Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana:
- The Ministry has also included awareness generation/sensitization programs with school/college students for strengthening inter-generational bonding under the umbrella scheme of Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana.
- It aims to provide information and educational material to individuals, families, and groups for better understanding of the aging process.
- The Ministry has also included awareness generation/sensitization programs with school/college students for strengthening inter-generational bonding under the umbrella scheme of Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Procedure for Inclusion of Communities in Scheduled Tribes List
The Tribal Affairs Ministry has insisted in Parliament that the criteria set out by the Lokur Committee for inclusion of communities in scheduled tribes list was appropriate and there is no need for revision.
The process to include tribes in the ST list begins with the recommendation from the respective State governments, which are then sent to the Tribal Affairs Ministry, which reviews and sends them to the Registrar General of India for approval. This is followed by the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes’ approval before the list is sent to the Cabinet to bring in the appropriate amendment to Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
The criteria given by Lokur Committee include: primitive traits, distinct culture, geographical isolation, shyness of contact with the community at large, and backwardness.
Previously, a government task force formed in 2014, criticized the inclusion criteria and procedure for being outdated and contradictory to affirmative action stating that it leads to exclusion and delays in inclusion of communities. The proposal to amend it, after being in the pipeline for nearly eight years, was put on hold.
Parliamentary Standing Committee Flags cut in MGNREGS Budget
A Parliamentary Standing Committee has expressed concerns over reduction of Rs 29,400 crore in the budget for the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme(MGNREGS) for financial year 2023-24.
The committee report questions the reasoning behind the reduction in funds for MGNREGA and recommends a reconsideration to ensure effective implementation.
On the issue of mandatory attendance through the National Mobile Monitoring System App, the committee while conceding the need of a real-time attendance capturing app, noted that unavailability of smart-phones, proper internet connectivity and the presence of MGNREGA workers for both ‘in’ and ‘out’ attendance pose challenges for beneficiaries.
The committee has recommended that the government should increase wage rates under MGNREGA by linking it to a suitable pricing index and to increase guaranteed work days from 100 days.
Read More: MGNREGA.
IMD launched 7 Services on UMANG Mobile App
Recently, IMD has launched seven of its services (Current Weather, Nowcast, City Forecast, Rainfall Information, Tourism Forecast, Warnings and Cyclone) with ‘UMANG’ mobile App for use by public. Earlier in 2020, IMD had developed mobile App ‘MAUSAM’ for weather forecasting, ‘Meghdoot’ for Agromet advisory dissemination and ‘Damini’ for lightning alert.
IMD follows a seamless forecasting strategy. The long range forecasts (for the whole season) followed by extended range forecast issued on every Thursday with a validity period of four weeks, followed by short to medium range forecast and warnings daily valid up to next five days with an outlook for subsequent two days, followed by very short range forecast of severe weather up to three hours (nowcast: updated every 3 hours).
Initiatives in recent years include dissemination of information to users by e-mail, WhatsApp groups and social media on regular basis and Nowcast about severe weather to registered users through SMS.
O-SMART Scheme
Government allocated an amount of Rs. 2177 crore for implementation of ‘Ocean Services, Modelling, Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)’ Scheme during a period of 5 years i.e 2021-22 to 2025-26. Further, to achieve the objectives of the scheme, following steps are being taken by the Ministry of Earth Sciences:
Various ocean observational platforms including Argo floats, XBT/XCTDs, Wave Rider Buoys, Automatic Weather Stations, Drifters, Moored Buoys, Tide Gauges, Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers, were deployed.
Operational services on Tsunami Early Warnings, Storm Surges, Potential Fishing Zones, Ocean State Forecast, Harmful Algal Blooms, Coral Reefs, Multi Hazard Vulnerability, Coastal Vulnerability Indices, High Wave Alerts, Oil Spill, Search and Rescue operations etc were generated using the data and models operational in house and was provided on day-to-day basis to various stake holders and end users.
Coastal surveys and deep-sea cruises and Public awareness campaign and related activities are conducted on regular basis to disseminate technology and policies.