Indian Economy
Advisory Committee Suggests Ban on Diesel 4-Wheelers
For Prelims: National Hydrogen Energy Mission, FAME scheme, net-zero goals for 2070, electric vehicles
For Mains: India's transition to renewable energy and electric vehicles, Impacts of diesel-powered vehicles, Strategies for achieving India's net-zero goal for 2070.
Why in News?
Recently, the Energy Transition Advisory Committee formed by Union Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has recommended that India should ban diesel-powered 4-wheeler vehicles by 2027 and switch to electric and gas-fuelled vehicles in cities with more than a million people and polluted towns to reduce emissions.
- The Committee, headed by former petroleum secretary Tarun Kapoor, also suggested phasing out motorcycles, scooters, and three-wheelers with internal combustion engines by 2035.
What are the Recommendations of the Committee?
- Move Towards Renewable Energy:
- India is one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases globally, and to achieve its net-zero goal for 2070, it wants to produce 40% of its electricity from renewables.
- In line with this, the panel report suggests that no city buses should be added that are not electric by 2030, with diesel buses for city transport not to be added from 2024 onwards.
- It called to partially shift to electric and partially to ethanol-blended petrol with almost 50% share in each category.
- India is one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases globally, and to achieve its net-zero goal for 2070, it wants to produce 40% of its electricity from renewables.
- Incentives to Boost EV Use:
- To boost electric vehicle (EV) use in the country, the report calls for the targeted extension of incentives under the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles scheme (FAME).
- Transition to Gas-Powered Trucks and Railways:
- The panels also recommended that new registrations of only electric-powered city delivery vehicles should be allowed from 2024, with higher use of railways and gas-powered trucks for the movement of cargo.
- The railway network is anticipated to be fully electric in two to three years. The panel recommended that long-distance buses in India be powered by electricity in the long term, with gas used as a transition fuel for 10-15 years.
- Increase in Share of Gas in its Energy Mix:
- India aims to raise the share of gas in its energy mix to 15% by 2030 from the current 6.2%.
- To achieve this goal, the panel suggests building underground gas storage equivalent to two months' demand.
- The panel also recommends the use of depleted oil and gas fields, salt caverns, and aquifers for building gas storage with the participation of foreign gas-producing companies.
- India aims to raise the share of gas in its energy mix to 15% by 2030 from the current 6.2%.
What about Diesel Consumption in India?
- Consumption Trends:
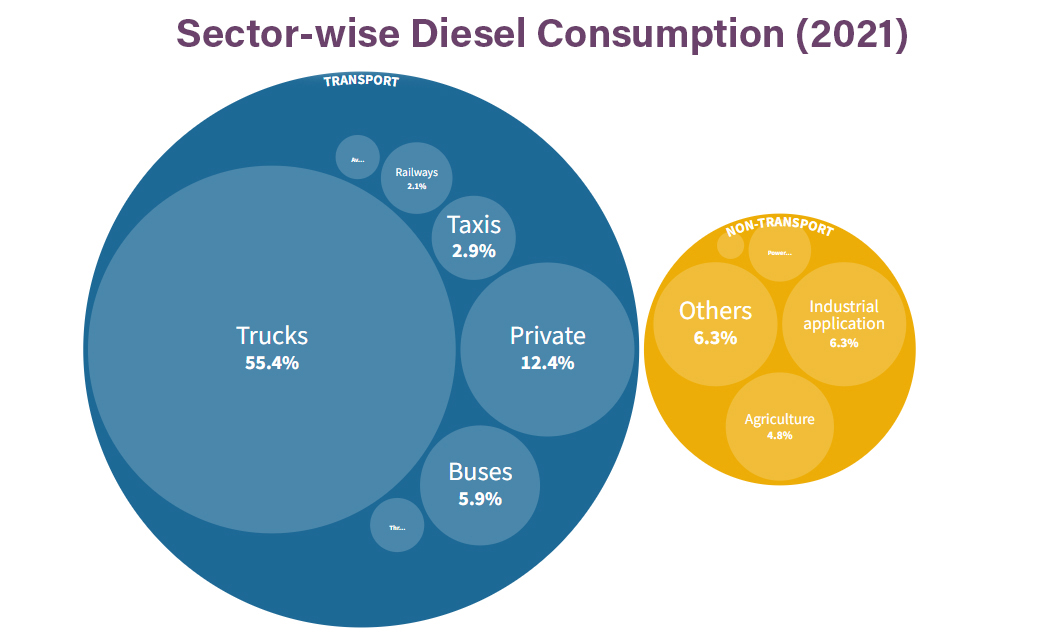
- Diesel currently accounts for about 40% of India’s petroleum products consumption with 80% of that being used in the transport sector.
- Petrol and diesel demand in India is expected to peak in 2040 and decline post that due to electrification of vehicles.
- Reasons for High Preference of Diesel:
- The higher fuel economy of diesel engines over petrol powertrains is one factor. This stems from the greater energy content per litre of diesel, and the inherent efficiency of the diesel engine.
- Diesel engines do not use high-voltage spark ignition (spark plugs), and thus use less fuel per kilometre, as they have higher compression ratios, making it the fuel of choice for heavy vehicles.
- Also, diesel engines offer more torque (rotational or turning force) and are less likely to stall as they are controlled by a mechanical or electronic governor, thereby proving to be better for haulage.
- Impact of Diesel-Powered Vehicle:
- Air Pollution:
- Diesel engines emit higher levels of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which contribute to air pollution and can have negative health impacts on humans and wildlife.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
- While diesel engines are more fuel-efficient, they also emit higher levels of carbon dioxide, which contributes to climate change.
- Noise Pollution:
- Diesel engines are typically louder than gasoline engines, which can contribute to noise pollution and negatively impact quality of life in urban areas.
- Environmental Damage:
- Diesel spills can cause significant environmental damage, especially if they occur near water sources or sensitive ecosystems.
- Air Pollution:
Why is Implementing a Diesel Ban for Commercial Vehicles Challenging?
- Practicality and Implementation:
- Uncertainty about the practicality of the proposed ban vis-a-vis medium and heavy commercial vehicles.
- It may result in disruption in the transport of goods and public transportation services.
- Dominance of Diesel in Transport Segment:
- High dependency on diesel for long-haul transportation and city bus services.
- Diesel sales account for around 87% in the transport sector; trucks and buses contribute to approximately 68% of diesel fuel sales.
- Conversion Challenges:
- Transitioning diesel trucks to compressed natural gas (CNG) poses limitations.
- CNG usage is primarily suited for shorter distances and has lower tonnage carrying capacity.
- Transitioning diesel trucks to compressed natural gas (CNG) poses limitations.
- Compliance with Current Emission Norms:
- Automakers argue that diesel vehicles comply with existing emission norms.
- Significant investments made by car manufacturers to transition diesel fleets to BS-VI emission norms; diesel ban might imply that all the time, money and efforts were in vain.
What are India’s Initiatives for a Renewable Energy based Transport Sector?
- FAME Scheme:
- Provides fiscal incentives for EV manufacturing and adoption.
- Aims to achieve 30% EV penetration by 2030.
- Supports deployment of charging technologies and stations in urban centers.
- National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage:
- Aims to improve air quality, reduce oil import dependence, and enhance uptake of renewable energy and storage solutions.
- Drives strategies for transformative mobility and phased manufacturing programs for EVs, EV components and batteries.
- Customs Duty Exemption for Lithium-ion Cell Batteries:
- The government has exempted the import of lithium-ion cell batteries from customs duties to bring down their cost and scale up their production in India.
- National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- This mission aims to develop green hydrogen as a clean and affordable energy source for various sectors such as industry, transport, and power.
- It envisages setting up of green hydrogen production plants, storage and distribution infrastructure, and end-use applications.
- This mission aims to develop green hydrogen as a clean and affordable energy source for various sectors such as industry, transport, and power.
- Ethanol blending
- It involves mixing ethanol with petrol to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
- The level of ethanol blending in petrol in India has reached 9.99%. The target for 20% ethanol blending in petrol (also called E20) has been advanced to 2025 from 2030.
- Incentives under PLI Scheme:
- It has been rolled out for various industries including the automobile and auto-component industry.
- Around Rs.18,000 crore was approved for development of advanced cell chemistry battery storage manufacturing.
- These incentives further aim to encourage indigenous development of Electric Vehicles (EVs) so as to bring down their upfront cost.
- SATAT Scheme:
- Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) initiative aims to promote Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG) as an alternative, green transport fuel.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”.Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)


Indian Economy
RBI's Gold Reserves
For Prelims: Forex and Gold reserve with RBI, Bank of International Settlements (BIS), SDR, IMF.
For Mains: India’s forex reserve and role of central bank in its management.
Why in News?
As per RBI’s Half Yearly Report on Management of Foreign Exchange Reserves: October 2022 - March 2023, its gold reserves touched 794.64 metric tonnes in FY 22-23, an increase of nearly 5% over FY 21-22(760.42 metric tonnes)
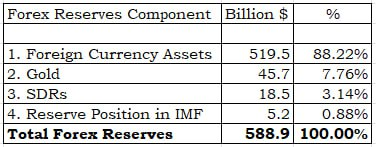
- Gold reserves along with foreign currency assets, special drawing rights and reserve tranche position in the International Monetary Fund make up India’s forex reserves.
How Much Gold has RBI Bought?
- Total Reserves:
- As per RBI, 437.22 tonnes of gold are held overseas are held with the Bank of England and the Bank of International Settlements (BIS), and 301.10 tonnes of gold is held domestically.
- As on March 31, 2023, the country’s total forex reserves stood at $578.449 billion, and gold reserves were pegged at $45.2 billion.
- In value terms (USD), the share of gold in the total forex Eserves increased to about 7.81% at the end of March 2023.
- Recent Purchase:
- The RBI bought 34.22 tonnes of gold in FY 23 (65.11 tonnes of gold in fiscal 2022).
- Between FY 2019 – FY 2021, RBI’s gold reserves were 228.41 tonnes.
- According to the World Gold Council's regional CEO (India), the RBI is among the top five central banks that are buying gold.
- The RBI bought 34.22 tonnes of gold in FY 23 (65.11 tonnes of gold in fiscal 2022).
Which Other Banks are Buying Gold?
- According to the World Gold Council (WGC), gold is being bought mainly by central banks of emerging market economies.
- The WGC report said that in 2022, the People’s Bank of China reported the first increase in its gold reserves since September 2019.
- China has been historically a large buyer of gold.
- During 2022, the central banks from the Middle East, including Egypt, Qatar, Iraq, the UAE, and Oman significantly boosted their gold reserves.
- By the end of 2022, the Central Bank of Uzbekistan became a net purchaser of gold, with its gold reserves rising by 34 tonnes.
- In January-March 2023, the Monetary Authority of Singapore was the largest single buyer of gold after it added 69 tonnes to its gold reserves
Why is RBI Hoarding the Gold?
- Counter Strategy against Negative Interest Rate:
- When the RBI has foreign currency (USD) in its reserves then it invests these dollars to purchase US Govt. bonds on which it earns interest.
- The real interest, however, on these bonds has turned negative due to the rise in inflation in the US.
- The real interest rate is the rate of interest an investor, saver or lender receives (or expects to receive) after allowing for inflation (real interest = nominal interest minus inflation rate).
- The real interest, however, on these bonds has turned negative due to the rise in inflation in the US.
- At the time of such inflation, the demand for gold has increased and RBI being its holder can earn a good return even in stressed economic situations.
- When the RBI has foreign currency (USD) in its reserves then it invests these dollars to purchase US Govt. bonds on which it earns interest.
- Good Hedge in Geopolitical Uncertainty: Due to the uncertainties arising amid the Russia-Ukraine war and US’ conflicts with China, there has been a decline in the acceptance of Dollar by some of the prominent global supplier of Goods like Russia and China.
- If RBI holds dollars and it depreciates/weakens with respect to other currencies, then it's a loss for RBI.
- However, due to the intrinsic value of gold and its limited supply, gold is able to retain its value much longer than other forms of currency.
- Diversify Forex Reserves: Gold is a safer, more secure and more liquid asset and it performs better during times of crisis, and as a long-term store of value.
- Gold has an international price which is transparent, and it can be traded anytime.
How is Gold Significant in the Economy?
- Gold as a Reserve Currency: For most of the 20th century, gold served as the world's reserve currency. The US used the gold standard until 1971 where it was required to have equivalent reserves of gold to back up the paper money.
- Due to the volatility of the US dollar and other currencies, some economists advocate returning to the gold standard since it has been discontinued.
- Intrinsic Value: Due to its inherent value and limited supply, inflationary periods see an increase in demand for gold. Gold is able to keep its value much longer than other forms of currency because it cannot be diluted.
- Gold to Boost Value of Currency: The value of a nation's currency starts depreciating when its imports exceed its exports. A country that is a net exporter, on the other hand, will see an increase in the value of its currency.
- As this raises the value of the country's total exports, a nation that exports gold or has access to gold reserves will see an increase in the strength of its currency when gold prices rise.
- Gold as a Substitute to G-Sec: The central bank of a country can use Gold as a medium to sterilize the market from the influence of foreign currency (in case of FDI) or use as a medium for open market operations (OMO).
- In both of these operations Gold can be used in place of G-Sec.
Note:
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 provides the overarching legal framework for deployment of reserves in different foreign currency assets and gold within the broad parameters of currencies, instruments, issuers and counterparties.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. What is/are the purpose/purposes of Government’s ‘Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme’ and ‘Gold Monetization Scheme’? (2016)
- To bring the idle gold lying with Indian households into the economy.
- To promote FDI in the gold and jewellery sector.
- To reduce India’s dependence on gold imports.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. Which one of the following groups of items is included in India’s foreign-exchange reserves? (2013)
(a) Foreign-currency assets, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and loans from foreign countries
(b) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and SDRs
(c) Foreign-currency assets, loans from the World Bank and SDRs
(d) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and loans from the World Bank
Ans: (b)


Biodiversity & Environment
Forest Fires in Goa
For Prelims: Forest Fires: Types, Causes, advantages and disadvantages, National Action Plan for Forest Fires (NAPFF), National Afforestation Programme (NAP)
For Mains: Forest Fires and its mitigation
Why in News?
The inquiry of bushfires that broke down in March 2023 by Goa Forest department has found that the fires were largely triggered by natural causes.
What did the Forest Department Inquiry Find?
- Cause behind Forest Fire: The report suggests that a conducive environment and extreme weather conditions — deficient rainfall in the preceding season, unusually high temperatures, low moisture and humidity — led to the fires.
- Very little rain in Goa since October 2022, along with heat-wave-like conditions and low humidity, created conditions that were ripe for forest fires.
- Goa's Forest Fire:
- The India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021 published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) classifies 100% of Goa’s forest cover as “less fire prone”.
- Also, Goa does not experience crown fires (caused by friction of trees) which mostly occur abroad.
- Surface fires are common in moist deciduous forests of Goa.
- Minor surface fires that burn undergrowth and dead organic matter on the forest floor are common due to the slash-and-burn techniques used by villagers to clear grazing land for cattle.
- Cashew farmers often start minor constrained fires to clear weeds and reduce undergrowth.
What are Forest Fires?
- About:
- Forest fires are uncontrolled fires that occur in areas with a significant amount of combustible vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, or shrublands.
- Causes of Forest Fire:
- Natural: Lightning is the most prominent cause which set trees on fire. However, rain extinguishes such fires without causing much damage.
- Spontaneous combustion of dry vegetation and volcanic activities also cause forest fires.
- High atmospheric temperatures and dryness (low humidity) offer favorable circumstance for a fire to start.
- Man-Made: Fire is caused when a source of fire like naked flame, cigarette or bidi, electric spark or any source of ignition encounters inflammable material.
- Natural: Lightning is the most prominent cause which set trees on fire. However, rain extinguishes such fires without causing much damage.
- Types:
- Crown fires burn trees up their entire length to the top. These are the most intense and dangerous wildland fires.
- Surface fires burn only surface litter and duff. These are the easiest fires to put out and cause the least damage to the forest.
- Ground fires (sometimes called underground/subsurface fires) occur in deep accumulations of humus, peat and similar dead vegetation that become dry enough to burn.
- Advantages:
- Cleaning the Forest Floor
- Providing Habitat
- Killing Disease
- Nutrient Recycling
- Disadvantages:
- Kill or Injure unintended Plants/Trees
- Can Lead to Erosion and Sedimentation
- Can Devastate the Ecosystem
- Threat to Human Life
- Vulnerability in India:
- The forest fire season normally extends from November to June in India.
- A report by the Council of Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) has noted:
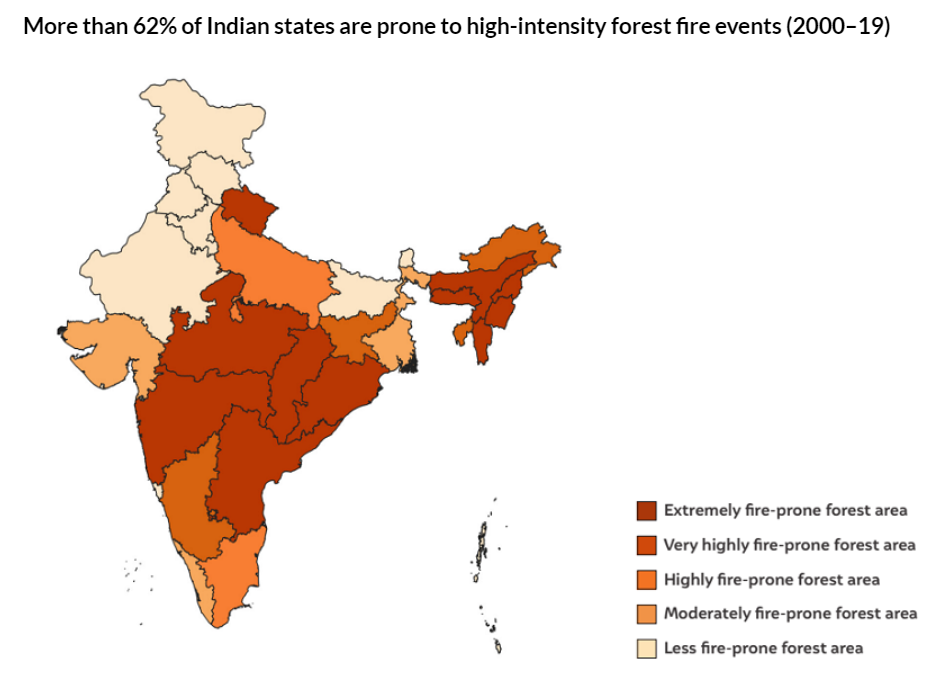
- A tenfold increase in forest fires over the past two decades and says more than 62% of Indian states are prone to high-intensity forest fires.
- Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Telangana, and the Northeastern states are most prone to forest fires.
- Mizoram has seen the highest incidence of forest fires over the last two decades, and 95% of its districts are forest fire hotspots.
- The ISFR 2021 estimates that more than 36% of the country’s forest cover is prone to frequent forest fires, 6% is ‘very highly’ fire-prone, and almost 4% is ‘extremely’ prone.
- Also, An FSI study has found that nearly 10.66% area under forests in India is ‘extremely’ to ‘very highly’ fire prone.
What are the India’s Initiatives Related to Managing Forest Fires?
- National Action Plan for Forest Fires (NAPFF): It was started in 2018 with the goal of reducing forest fires by informing, enabling, and empowering forest fringe communities and incentivizing them to collaborate with state forest departments.
- National Mission for Green India (GIM): Launched under the National Action Plan on Climate Change, the GIM aims to increase forest cover and restore degraded forests.
- It promotes the use of community-based forest management, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable forest practices, which contribute to preventing forest fires.
- Forest Fire Prevention and Management Scheme (FFPM): FFPM is implemented by the FSI under the MoEF&CC. It aims to strengthen the forest fire management system by utilizing advanced technologies such as remote sensing.
- It is the only government-sponsored programme dedicated to assisting states in dealing with forest fires.
What should be done to Mitigate Forest Fires?
- Create Fire Breaks: Fire breaks are areas where vegetation has been removed, creating a gap that can slow or stop the spread of a fire.
- Monitor and Manage Forests: Monitoring forests and managing them appropriately can help prevent fires from starting or spreading.
- Early Detection and Rapid Response: Early detection of a forest fire is critical for effective mitigation.
- The Forest Survey of India (FSI) is using satellite imaging technology (like MODIS) to analyse forest fire affected areas and boost prevention.
- Fuel Management: Reducing the accumulation of dead trees, dry vegetation, and other combustible materials through activities such as thinning and selective logging.
- Firewise Practices: Safe practices must be adopted in areas near forests viz. factories, coal mines, oil stores, chemical plants and even in household kitchens.
- Practice Controlled Burning: Controlled burning involves setting small fires in a controlled environment.


Internal Security
Common Uniform in Indian Army
For Prelims: Indian Army, Uniform Accouterments, Regimental Parochialism.
For Mains: Significance of Common Uniform in Indian Army.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Army has decided that from 1st August 2023, all officers of the rank of Brigadier and above will wear Common Uniform items irrespective of their cadre and appointment, in order to promote and strengthen common identity and approach.
What is the Uniform of Senior Indian Army Officers?
- Current Position:
- Different branches of the Indian Army wear different uniform accouterments, such as berets, lanyards, and badges of rank, based on their regimental or corps affiliation.
- Accouterments are additional items of dress or equipment that are worn or carried, especially by military personnel, to complete a uniform or outfit.
- Infantry officers and Military Intelligence officers wear dark green berets, armored corps officers wear black berets, and other corps officers wear dark blue berets. Officers from the Corps of Military Police wear red berets.
- As of now, all officers from the rank of Lieutenant to General wear uniform accoutrements as per their regimental or corps affiliation.
- Different branches of the Indian Army wear different uniform accouterments, such as berets, lanyards, and badges of rank, based on their regimental or corps affiliation.
- New Uniform:
- All officers of the rank of Brigadier, Major General, Lt. General, and General will now wear berets (caps) of the same colour, common badges of rank, a common belt buckle, and a common pattern of shoes.
- The shoulder rank badges will be golden for all senior officers.
- As of now, officers from the rifle regiments such as Gorkha Rifles, Garhwal Rifles and Rajputana Rifles wear black rank badges.
- The shoulder rank badges will be golden for all senior officers.
- The headgear, shoulder rank badges, gorget patches, belts and shoes of senior officers of Brigadier and above ranks will now be standardised and common.
- There is no change to the uniform worn by Colonels and below-rank officers.
- They will no longer wear regimental lanyards (cords) on their shoulders. They will also not wear any shoulder flashes like ‘Special Forces’, ‘Arunachal Scouts’, ‘Dogra Scouts’, etc.
- Thus, there will be no item of uniform that will identify them as belonging to a particular Regiment or Corps. All officers of these higher ranks will dress alike in the same pattern of uniform.
- All officers of the rank of Brigadier, Major General, Lt. General, and General will now wear berets (caps) of the same colour, common badges of rank, a common belt buckle, and a common pattern of shoes.
What is the Significance of this Decision?
- This decision will help to promote a more cohesive and integrated organizational culture within the Indian Army.
- A standard uniform will ensure a common identity for all senior-rank officers, while reflecting the true ethos of the Indian Army.
- By eliminating regimental parochialism and promoting a sense of common identity and purpose among senior officers, the Army may be better able to meet the challenges of modern warfare and adapt to changing strategic circumstances.
- Regimental Parochialism refers to loyalty towards one's regiment or corps. It is a sense of pride and attachment to one's unit that can sometimes lead to a lack of cooperation or competition with other units within the same organization.
- It may also improve the ability of senior officers to command troops of mixed regimental lineage.
- By presenting a neutral uniform rather than a regimental one, senior officers may be able to establish a more inclusive and collaborative leadership style that transcends traditional loyalties and affiliations.
What is the Tradition in Other Armies?
- In the British army, from where the Indian Army derives its uniform pattern and associated heraldry, the uniform worn by officers of the rank of Colonel and above is referred to as the Staff uniform, to distinguish it from the Regimental uniform.
- The wearing of any item of Regimental uniform, particularly headdress, with the Staff uniform is not authorised.
- Among neighbouring countries, the Pakistan and Bangladesh armies follow the same pattern as the British army.
- All regimental uniform items are discarded beyond the rank of Lt Colonel. All officers of the rank of Brigadier and above wear similar pattern uniform.


Important Facts For Prelims
Laureus World Sports Awards 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the winners of the 2023 Laureus World Sports Awards were announced. The Awards were held in person in Paris for the first time since 2020.
What are the Key Points?
- About:
- The awards are conferred annually to honour the greatest and most inspirational sporting triumphs of the year and showcases the work of Laureus Sport for Good.
- The first Laureus World Sports Award ceremony took place on May 25, 2000.
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- It is often referred to as the sporting equivalent of the Oscars.
- Award Categories:
- Laureus World Sportsman of the Year
- Winner of 2023: Lionel Messi (Argentina)
- Lionel Messi became the first footballer to be awarded the Sportsman of the Year (in 2020)
- Laureus World Sportswoman of the Year
- Winner of 2023: Shelly-Ann Fraser-Pryce (Jamaica)
- Laureus World Team of the Year
- Winner of 2023: Argentina Men's Football Team
- Laureus World Breakthrough of the Year
- Winner of 2023: Carlos Alcaraz (Spain)
- Laureus World Comeback of the Year
- Winner of 2023: Christian Eriksen (Denmark)
- Laureus World Action Sportsperson of the Year
- Winner of 2023: Eileen Gu (China)
- Laureus Sport for Good
- Winner of 2023: TEAMUP (Global)
- TeamUp is a psycho-social support intervention developed by War Child, Save the Children and UNICEF Netherlands, which helps children in difficult situations to relieve stress and tension.
- Winner of 2023: TEAMUP (Global)
- Laureus World Sportsperson of the Year With a Disability
- Winner of 2023: Catherine Debrunner (Switzerland)
- The shortlist for World Athlete of the Year with a Disability is provided by the International Paralympic Committee.
- Laureus World Sportsman of the Year
- Important Awardees:
- Roger Federer holds the record for winning the most awards. The Swiss tennis player has won six awards, five for Sportsman of the Year and one for Comeback of the Year.
- Serena Williams holds the record for winning the most award by a female.
- Lionel Messi – who led Argentina to the World Cup in 2022 – became the first athlete to win the Laureus World Sportsman of the Year and also pick up the Laureus World Team of the Year Award in the same year i.e, 2023.
- Other Categories of Awards:
- Apart from these regular seven awards, there are some more awards that were awarded which are discretionary awards. These include:
- Lifetime Achievement Award
- Sport for Good Award
- Spirit of Sport Award
- Exceptional Achievement Award
- Sporting Inspiration Award
- Apart from these regular seven awards, there are some more awards that were awarded which are discretionary awards. These include:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000:
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far.
- Roger Federer received this award maximum number of times compared to others.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
- The Laureus World Sports Awards is the premier global sporting awards. First held in 2000, the annual event honours the greatest and most inspirational sporting triumphs of the year and showcases the work of Laureus Sport for Good.
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The award has been received mostly by Men’s Football Team (6 times) players so far. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Roger Federer (5 times) has received this award, the maximum number of times compared to others followed by Usain Bolt (4 times) and Novak Djokovic (4 times). Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Auroras
Why in News?
A significant geomagnetic storm is anticipated, triggered by strong solar storm. This occurrence has the potential to "supercharge" auroras, creating a spectacular visual display in the night sky.
What are Auroras?
- About:
- Auroras are luminous phenomena that occur near the North (Aurora Borealis) and South Poles (Aurora Australis).
- They are caused by the interaction of charged particles from the Sun with the Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere.
- Composition and Colors:
- Auroras consist of gases and particles, including oxygen and nitrogen.
- The collisions of these particles with the atmosphere release energy in the form of light.
- The colors observed in auroras depend on the type of gas and altitude of the collisions.
- Geomagnetic Storms and Auroras:
- Geomagnetic storms, triggered by solar events like coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and solar flares, enhance auroral activity.
- CMEs are eruptions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun, while solar flares are bursts of energy.
- CMEs often occur alongside solar flares, which are explosions on the Sun's surface, but they are also known to occur independently.
- Geomagnetic storms, triggered by solar events like coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and solar flares, enhance auroral activity.
- Solar Storms and Aurora Intensity:
- Strong solar storms result in increased solar activity, leading to more pronounced auroral displays.
- The number of charged particles reaching the Earth's atmosphere during these storms intensifies the auroras.
- The strength of the solar storm and the alignment of the Earth's magnetic field affect the visibility and vibrancy of the auroras.
- Cultural and Scientific Significance:
- Auroras hold cultural and spiritual significance in various indigenous communities around the world.
- Scientific research on auroras helps us understand the Earth's magnetosphere, solar-terrestrial interactions, and space weather.
What is a Geomagnetic Storm?
- About:
- A geomagnetic storm refers to the disruptions to the Earth’s magnetic field caused by solar emissions.
- Cause:
- The largest storms that result from these conditions are associated with solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs). When a CME or a high-speed solar stream reaches our planet, it slams into the magnetosphere.
- The Earth’s magnetosphere is created by its magnetic fields and it usually protects us from the particles emitted by the Sun.
- When a CME or a high-speed stream arrives at Earth, it peels open the planet’s magnetosphere, kind of like an onion. This allows energetic solar wind particles to stream down and hit our atmosphere over the poles.
- The largest storms that result from these conditions are associated with solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs). When a CME or a high-speed solar stream reaches our planet, it slams into the magnetosphere.
- Conditions: The solar wind conditions that are effective for creating geomagnetic storms are:
- Sustained (for several to many hours) periods of high-speed solar wind
- A southward directed solar wind magnetic field (opposite the direction of Earth’s field) at the dayside of the magnetosphere.
- Impact:
- Solar weather events like this can supercharge auroras, sometimes making them visible in places where they wouldn’t have been otherwise.
- They can also disrupt navigation systems and create harmful geomagnetic induced currents (GICs) in the power grid and pipelines.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth?
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
(b) 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
(c) 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
36th CISO Deep-Dive Training Programme
Why in News?
The National e-Governance Division (NeGD), under its Capacity Building scheme, organised 36th CISO Deep-Dive training programme with 24 participants from Central Line Ministries and States/UTs at Indian Institute of Public Administration, New Delhi.
- The training program is a part of a series of workshops organised under the Cyber Surakshit Bharat initiative.
What is Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative?
- The Cyber Surakshit Bharat initiative was conceptualised with the mission to spread awareness about cyber-crime and build capacities of Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT officials, across all government departments.
- It was launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in 2018 in cooperation with National e-Governance Division (NeGD) and various industry partners in India.
What is CISOs Deep Dive Training?
- About:
- It is the first-of-its-kind partnership between the Government and industry consortium under Public Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- Objectives:
- Create awareness on the emerging landscape of cyber threats.
- Provide in-depth understanding of related solutions.
- Applicable frameworks, guidelines & policies related to cyber security.
- Share best practices to learn from success & failures.
- Provide key inputs to take informed decisions on Cyber Security related issues in their respective functional area.
- Participants:
- The programme is organised for chief information security officers (CISOs) and frontline IT officials from various ministries and departments, government and semi-government organisations from central and state governments, PSUs, and banks among others.
- Training:
- NeGD provides logistic support in arranging the training programmes, whereas the industry consortium provides technical support for the training.
- The training partners from the industry are Microsoft, IBM, Intel, Palo Alto Networks, E&Y, and Dell-EMC, NIC, CERT-In, and CDAC are knowledge partners from the Government side.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Enhancing Cyber Security?
- Global:
- India-Specific:
- National Cyber Security Strategy 2020
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal
- Computer Emergency Response Team - India (CERT-In)
- Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2022
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA)
- Digital India Bill, 2023
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: In 2017, this platform was introduced for internet users to clean their computers and devices by wiping out viruses and malware.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The terms ‘WannaCry, Petya and EternalBlue’ sometimes mentioned in the news recently are related to (2018)
(a) Exoplanets
(b) Cryptocurrency
(c) Cyber-attacks
(d) Mini satellites
Ans: (c)
- Ransomware is a form of malicious software (or malware). Once it takes over the computer, it threatens to harm the user, usually by denying access to data. The attacker demands a ransom from the victim, promising to restore access to the data upon payment. WannaCry, Petya and EternalBlue are few of the ransom ware, which created havoc by demanding the victim ransom payment in bit coin (crypto currency).
- Cryptocurrency is a digital currency in which encryption techniques are used to regulate the generation of units of currency and verify the transfer of funds, operating independently of a central bank. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Rabindranath Tagore, Maharana Pratap, and Gopal Krishna Gokhale
On 9th May, the Prime Minister paid tribute to Rabindranath Tagore, Maharana Pratap, and Gopal Krishna Gokhale on their birth anniversaries.
Rabindranath Tagore, also known as Gurudev, was a prolific literary figure and polymath, known for his contributions to Bengali literature and music. As per Bengali Calendar, 'Rabindranath Tagore Jayanti' is observed on the 25th day of the Bengali month of Baishakh, and this day is being celebrated today, May 9th, 2023. Tagore's compositions of over 2000 songs, called "Rabindra Sangeet," and his renowned works like Gitanjali have left a lasting impact. As the first non-European Nobel Prize laureate in Literature in 1913, he became a symbol of artistic excellence. Tagore's philosophies and the establishment of Vishwa-Bharati University continue to inspire generations.
Maharana Pratap, born on 9th May 1540 in Kumbhalgarh, Rajasthan, was the 13th King of Mewar. He is known for his valiant efforts in the Battle of Haldighati fought against the Mughal forces in 1576. Although he was defeated in the battle, his bravery and resilience are celebrated. Maharana Pratap's loyal horse, Chetak, is remembered for sacrificing its life during the war. Despite the defeat, Maharana Pratap later reclaimed parts of Mewar and made significant contributions to the region. He passed away on 19th January 1597, leaving behind a legacy of courage.
Gopal Krishna Gokhale, a prominent social reformer and educationist, was born on 9th May 1866 in present-day Maharashtra. Gokhale played a crucial role in India's freedom movement. He advocated for social empowerment, education, and peaceful methods to achieve independence. Gokhale was associated with the Moderate Group of the Indian National Congress and played a key role in framing the Morley-Minto reforms of 1909. He established the Servants of India Society, worked on various publications, and mentored Mahatma Gandhi, who considered him his political guru.
Read more: Rabindranath Tagore, Gopal Krishna Gokhale, Birth Anniversary of Maharana Pratap
Sittwe Port
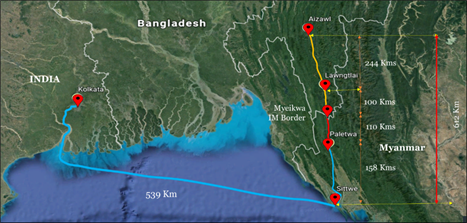
Recently, India and Myanmar jointly inaugurated the Sittwe Port in Myanmar's Rakhine State, marking an important milestone in enhancing bilateral and regional trade while also contributing to the local economy of the state.
The port's operationalization is expected to provide greater connectivity and leads to employment opportunities, as well as enhance growth prospects in the region. The project aims to provide an alternative connectivity route for Mizoram with Indian ports through the Kaladan River in Myanmar.
It includes segments such as shipping from Haldia to Sittwe port, inland water transport from Sittwe to Paletwa via the Kaladan River, road transport from Paletwa to the Indo-Myanmar border, and further road transport to NH.54 in India.
The Sittwe Port is part of the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project, funded by the Indian government, and will play a crucial role in linking India's East Coast to the North-eastern states through waterways and roads.
Read more: India-Myanmar Relations, Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project
Fertilizer Flying Squads
The Department of Fertilizers (DoF), under Union Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, has implemented a range of measures to combat malpractices and ensure the availability of quality fertilizers for farmers in India. These initiatives have successfully prevented the diversion and black marketing of fertilizers across the country.
Specialized teams called Fertilizer Flying Squads (FFS) have been formed to keep a strict vigil and crack down on activities such as diversion, black marketing, hoarding, and the supply of sub-standard fertilizers. Stringent actions – surprise inspections conducted across states/UTs and seizure of suspected urea bags – have been taken. Additionally, sample testing has been intensified to address the misuse of urea for non-agricultural purposes.
For the first time, 11 persons have been jailed under Prevention of Blackmarketing and Maintenance of Supplies (PBM) Act 1980 for diversion and black marketing of urea in the last one year. Several other legal and administrative proceedings have also been exercised under Fertilizer Control Order-1985.
The measures have not only benefitted the farmers but have also generated cross-country demand for Indian fertilizers. By preventing the smuggling of urea across borders, neighboring countries have approached India for urea imports. DoF has also encouraged innovative practices such as the Integrated Fertilizer Management System (iFMS) to raise awareness among farmers about fertilizer quality.
Read more: Fertiliser Consumption in India
IBM and NASA Create Geospatial Model
Recently, NASA and IBM, an American MNC, have introduced a new geospatial model to convert satellite data into high-resolution maps of floods, fires, and other landscape changes, providing insights into the planet's history and future. This collaboration aims to offer a preview of the geospatial platform in the second half of this year, with potential applications including assessing climate-related risks, monitoring forests for carbon-offset initiatives, and developing predictive models to tackle climate change, emphasizing that foundation models like this enhance the scalability, affordability, and efficiency of deploying artificial intelligence.
Geospatial technology, utilizing tools like GIS (Geographic Information System), GPS (Global Positioning System)and Remote Sensing enables geographic mapping and analysis. It captures spatial information about objects, events, and phenomena, either static or dynamic. Static data includes road positions, earthquake events, or regional malnutrition, while dynamic data involves moving vehicles, pedestrians, or the spread of diseases. This technology aids in creating intelligent maps to identify spatial patterns in large datasets and supports decision-making regarding the allocation of scarce resources.
Read more: Geospatial technology