Biodiversity & Environment
River-Cities Alliance Global Seminar
For Prelims: Namami Gange Program, NMCG, NIUA, RCA, Societies Registration Act,1860, Ganga Action Pan.
For Mains: Significance of National Mission for Clean Ganga in the Rejuvenation of River Ganga. Conservation.
Why in News?
National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) in association with the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) organized the ‘River-Cities Alliance (RCA) Global Seminar: Partnership for Building International River-Sensitive Cities’.
- The purpose of the RCA Global Seminar was to provide a platform to discuss and learn good practices for managing urban rivers.
- Previously, a meeting of RCA - DHARA 2023 (Driving Holistic Action for Urban Rivers) was held in February 2023, featuring sessions on International best practices and examples for urban River Management.
National Institute of Urban Affairs
- NIUA is an institute for research, training and information dissemination in urban development and management. It is located in New Delhi, India.
- It was established in 1976 as an autonomous body under the Societies Registration Act 1860.
- The Institute is supported by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, State Governments, urban and regional development authorities and other agencies concerned with urban issues.
What is RCA?
- About:
- The RCA is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Jal Shakti (MoJS) & the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), with a vision to connect river cities and focus on sustainable river centric development.
- The Alliance focuses on three broad themes- Networking, Capacity Building and Technical Support.
- Beginning with 30 member cities in November 2021, the Alliance has expanded to 110 river cities across India and one international member city from Denmark.
- Objective:
- The RCA intends to facilitate knowledge exchange (online) for Indian cities to learn new practices and approaches for urban river management.
- It will also be an opportunity for international cities to learn about experiences in Indian cities, which may be relevant to their contexts.
What is the National Mission for Clean Ganga?
- About:
- It is being implemented by the National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of River Ganga also known as the National Ganga Council.
- This mission was established on 12th August 2011 under the Societies Registration Act,1860 as a registered society.
- It acted as the implementation arm of National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) which was constituted under the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act (EPA),1986.
- NGRBA has since been dissolved with effect from the 7th of October 2016, consequent to constitution of National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of River Ganga (referred as National Ganga Council).
- Objectives:
- The objective of the NMCG is to reduce pollution and ensure rejuvenation of the Ganga River.
- The mission incorporates rehabilitating and boosting the existing STPs (Sewage Treatment Plants) and instant short-term steps to curb pollution at exit points on the riverfront in order to check the inflow of sewage.
- Organizational Structure:
- The Act envisages five tier structure at national, state and district level to take measures for prevention, control and abatement of environmental pollution in river Ganga as below:
- National Ganga Council under chairmanship of Hon’ble Prime Minister of India.
- Empowered Task Force (ETF) on river Ganga under chairmanship of Hon’ble Union Minister of Jal Shakti (Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation).
- National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG).
- State Ganga Committees
- District Ganga Committees in every specified district abutting river Ganga and its tributaries in the states.
- The Act envisages five tier structure at national, state and district level to take measures for prevention, control and abatement of environmental pollution in river Ganga as below:
What are the Other Initiatives for River Rejuvenation in India?
- Namami Gange Programme: It is an Integrated Conservation Mission, approved as a ‘Flagship Programme’ by the Union Government in June 2014 to accomplish the twin objectives of effective abatement of pollution and conservation and rejuvenation of National River Ganga.
- Ganga Action Plan: It was the first River Action Plan that was taken up by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in 1985, to improve the water quality by the interception, diversion, and treatment of domestic sewage.
- The National River Conservation Plan is an extension to the Ganga Action Plan. It aims at cleaning the Ganga River under Ganga Action Plan phase-2.
- National Water Mission (2010): It ensures integrated water resource management leading to water conservation, less wastage, equitable distribution forming better policies.
- National River Ganga Basin Authority (NRGBA): It was formed by the Government of India in the year 2009 under Section-3 of the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
- Ganga was declared as the ‘National River’ of India in 2008.
- Clean Ganga Fund: In 2014, it was formed for cleaning up of the Ganga, setting up of waste treatment plants, and conservation of biotic diversity of the river.
- Bhuvan-Ganga Web App: It ensures involvement of the public in monitoring of pollution entering into the river Ganga.
- Ban on Waste Disposal: In 2017, the National Green Tribunal banned the disposal of any waste in the Ganga.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2014)
- Animal Welfare Board of India is established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body.
- National Ganga River Basin Authority is chaired by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
- The Animal Welfare Board of India was established in 1962 under Section 4 of the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change constituted under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) was established in 2009 under the Environment Protection Act, 1986, which declared Ganges as the “National River” of India. It is a financing, planning, implementing, monitoring and coordinating authority for the river Ganges. It functions under the erstwhile Ministry of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation (now Ministry of Jal Shakti). It is chaired by the Prime Minister of India. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Discuss the Namami Gange and National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) programmes and causes of mixed results from the previous schemes. What quantum leaps can help preserve the river Ganga better than incremental inputs? (2015)


International Relations
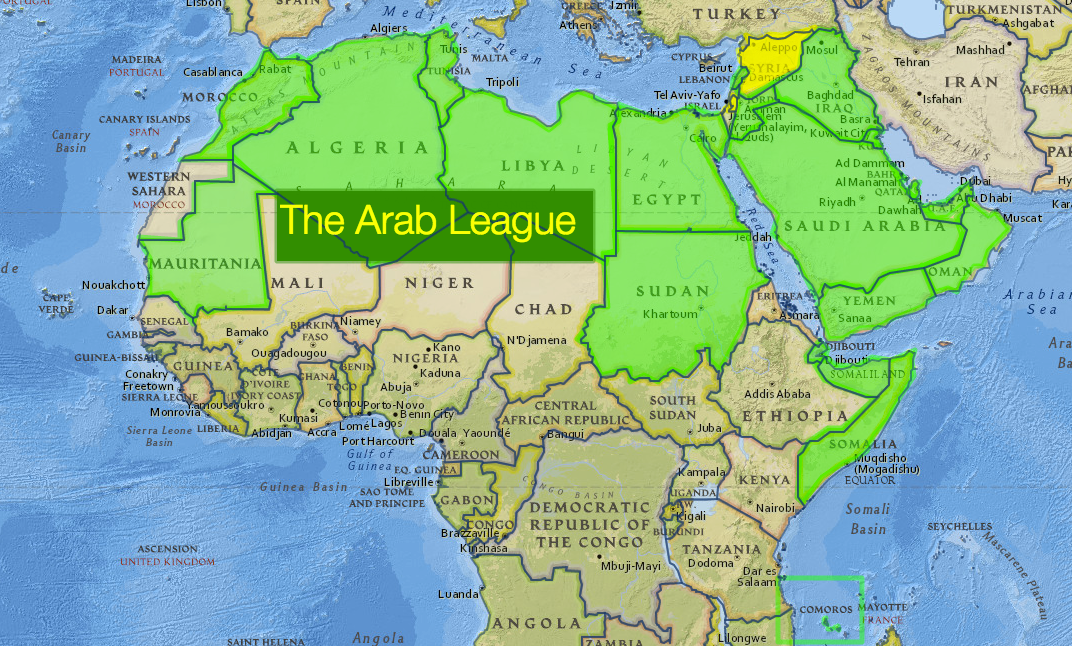
Arab League
For Prelims: Arab League, Middle East, Gulf Countries, Oil, Remittance, Syria Crisis.
For Mains: Arab League-Significance of India in Middle East.
Why in News?
Recently, the Arab League has re-admitted Syria into the organization, after a suspension over a decade.
Why has Syria Readmitted to the Arab League?
- Suspension:
- Syria was suspended from the Arab League in 2011 after it violently cracked down on anti-government protests.
- The Arab League accused Syria of not complying with a peace plan that called for a withdrawal of military forces, the release of political prisoners, and the start of a dialogue with opposition groups.
- Despite attempts at peace negotiations and ceasefire agreements, the violence continued, leading to Syria's suspension.
- This had economic and diplomatic consequences for Syria.
- Readmission:
- The move signifies softness in relations between Syria and other Arab governments and is seen as the start of a gradual process to resolve the crisis in Syria.
- The Crisis in Syria has resulted in the displacement of roughly half of the pre-war population of 21 million and the deaths of over 300,000 civilians.
- A committee involving Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Jordan, and Iraq will be established to help Syria achieve these goals.
- But the decision does not mean a resumption of relationships between Arab states and Syria as it is up to each country to decide this individually.
- It calls for a resolution of the crisis resulting from Syria's civil war, including the flight of refugees to neighboring countries and drug smuggling across the region.
- The move signifies softness in relations between Syria and other Arab governments and is seen as the start of a gradual process to resolve the crisis in Syria.
What is the Arab League?
- About:
- Arab League, also called League of Arab States (LAS), is an intergovernmental pan-Arab organisation of all Arab states in the Middle East and North Africa.
- It was formed in Cairo, Egypt on 22nd March 1945, following the adoption of the Alexandria Protocol in 1944.
- Members:
- Currently, there are 22 Arab countries: Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.
- Objective:
- It aims to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural, economic, and social programs of its members and to mediate disputes among them or between them and third parties.
- The signing on 13th April 1950, of an agreement on joint defense and economic cooperation also committed the signatories to coordination of military defense measures.
- It aims to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural, economic, and social programs of its members and to mediate disputes among them or between them and third parties.
- Concerns:
- The Arab League has been criticized for its inability to effectively address the issues it was created to handle. Many question the relevance of the institution, with its slogan of “one Arab nation with an eternal mission” being seen as outdated.
- This has led to instances where important events, like the annual leaders' summit, have been postponed or canceled.
- The League has also been criticized for its lack of effectiveness in enforcing decisions and resolving conflicts among its members. It has been accused of disunity, poor governance, and being more representative of autocratic regimes than of the Arab people.
- The Arab League has been criticized for its inability to effectively address the issues it was created to handle. Many question the relevance of the institution, with its slogan of “one Arab nation with an eternal mission” being seen as outdated.
What is the Significance of the Middle East/North Africa (MENA) for India?
- Middle East:
- India has enjoyed centuries of good relations with countries like Iran, while smaller gas-rich nation Qatar is one of India’s closest allies in the region.
- India shares good relations with most of the countries in the Gulf.
- The two most important reasons for the relationship are Oil and gas, and trade.
- Two additional reasons are the huge number of Indians who work in the Gulf countries, and the Remittance they send back home.
- North Africa:
- North African nations like Morocco and Algeria are important as they serve as gateways to other parts of Africa, which is relevant for India, given its desire to penetrate Francophone Africa (French Speaking African Nations).
- North Africa is significant for India because of its potential as a source of clean energy. The region has abundant solar and wind resources, which can be harnessed to generate electricity.
- India has set ambitious renewable energy targets, and North Africa could provide an opportunity for India to meet its renewable energy goals.
- North Africa is also strategically located, making it an important region for trade and commerce.
- The Suez Canal puts North Africa at the crossroads of global trade. With more than 22000 ship transits in 2022, the canal is one of the world's most important maritime routes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
| Towns sometimes mentioned in news | Country | |
| 1. | Aleppo | Syria |
| 2. | Kirkuk | Yemen |
| 3. | Mosul | Palestine |
| 4. | Mazar-i-sharif | Afghanistan |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 4
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q2. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Q3. The area known as ‘Golan Heights’ sometimes appears in the news in the context of the events related to (2015)
(a) Central Asia
(b) Middle East
(c) South-East Asia
(d) Central Africa
Ans: (b)
Q4. Yom Kippur War was fought between which sides/ countries? (2008)
(a) Turkey and Greece
(b) Serbs and Croats
(c) Israel, and Arab countries led by Egypt and Syria
(d) Iran and Iraq
Ans: (c)


Indian Economy
US Fed Rate Hike
For Prelims: US Fed Rate Hike’s impact on Indian Economy, Inflation, RBI, Exchange Rate
For Mains: US Fed Hike’s impact on Indian Economy and options available
Why in News?
After raising interest rates aggressively to tame inflation, the US Federal Reserve has once again raised its benchmark overnight interest rate by a quarter of a percentage point to the 5.00%-5.25% range.
- Overnight rates are the rates at which banks lend funds to each other at the end of the day in the overnight market.
- In many countries, the overnight rate is the interest rate the central bank sets to target monetary policy (Repo Rate in India).
What could be the Possible Impact of this Hike on India?
- The economists have expected that the latest Fed hike may not have a material impact on India as the RBI has paused hikes and there is weakness in the crude oil prices as well.
- Domestic markets are likely to remain resilient and if there is volatility, it would have a limited impact on the economy.
- It is also expected that the strength of the rupee and the continued buying by foreign institutional investors (FIIs) will strengthen the market.
- FIIs have already started investing in India, with inflows in April 2023 rising to Rs 13,545 crore and Rs 8,243 crore in May so far.
- Moreover, this hike is being viewed as last one for this year,2023 and the Fed will start cutting rates from the second half of 2023.
- If the Fed opts for a cut later in the year, capital inflows are expected to pick up.
- If the Fed starts cutting rates from July 2023, markets are expected to rise sharply.
Why do Central Banks resort to a Rate Hike?
- The central bank may increase interest rates to control inflation.
- This is being done to reduce the amount of money available for borrowing, which can help to cool down the economy and prevent prices from rising too quickly.
- With higher borrowing costs, people and companies may be less willing to borrow, which can slow down economic activity and growth.
- Businesses may take fewer loans, hire fewer people, and reduce production in response to the increased costs of borrowing.
What are the Impacts of US Fed Rate Hike on Indian Economy?
- Capital Flows: A US Fed rate hike can lead to a rise in interest rates in the US, which can attract capital flows from other countries. This can lead to a reduction in foreign investment in India, which can affect economic growth.
- Depreciation of rupee: It can also lead to a depreciation of rupee, which can have an impact on India's trade balance and current account deficit.
- Depreciation of Indian rupee may result in costlier imports such as crude oil and other goods. This may bring the imported inflation in Indian Economy.
- Domestic Borrowing Costs: It can lead to an increase in borrowing costs in India, as investors may choose to invest in US securities instead of Indian securities. This can lead to a reduction in domestic investment and higher borrowing costs for businesses and individuals.
- Stock Market: It can also impact the stock market in India. Higher US interest rates can lead to a reduction in demand for risky assets such as equities, which can lead to a decline in stock prices in India.
- External Debt: India’s external debt is mostly denominated in US Dollars, a US Fed rate hike can increase the cost of servicing that debt, as the value of the rupee may fall against the dollar. This can lead to an increase in India's external debt burden and a negative impact on the economy.
- Banks: The banking industry gets benefited by the interest rates rise, as banks re-price their loan portfolio much quicker than their deposit rates, which helps them to increase their net interest margin.
What Options are Available with India to Counter Fed Hikes?
- Adjusting Domestic Interest Rates: The RBI, could raise interest rates in response to the Fed hikes to attract foreign investors to invest in Indian markets, which would increase demand for Indian currency and help maintain its value. However, this could also slow down domestic economic growth.
- Diversifying Reserves: India could diversify its foreign exchange reserves to reduce its dependence on the U.S. dollar and mitigate the impact of Fed rate hikes. For instance, India could increase its holdings of other major currencies such as the Euro, Yen, and Chinese Yuan.
- Enhancing Trade Relations with Other Countries: India could focus on expanding trade ties with other countries to boost its economic growth and reduce the impact of the Fed rate hikes. This could include exploring new export markets, attracting foreign investment, and increasing bilateral trade agreements.
- Encouraging Domestic Consumption: If the Fed rate hikes lead to a slowdown in the Indian economy, the government could boost domestic consumption through measures such as tax cuts, subsidies, or public works programs to stimulate economic activity.
- Reduce Dependence on Crude Oil: One of the major effects of a stronger US dollar is the increase in crude oil prices, which in turn contributes to the overall rise in commodity prices. To address this, it is important to promote the use of alternative sources of energy such as renewable energy and ethanol.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Indian Government Bond Yields are influenced by which of the following? (2021)
- Actions of the United States Federal Reserve
- Actions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Inflation and short-term interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Tight monetary policy of US Federal Reserve could lead to capital flight.
- Capital flight may increase cost of firms with existing External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
- Devaluation of domestic currency decreases the currency risk associated with ECBs
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


International Relations
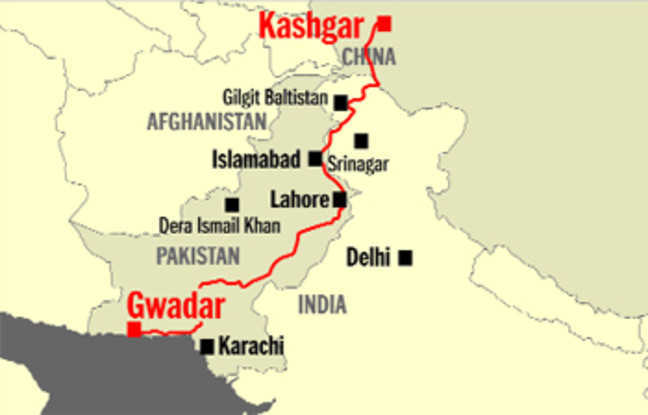
CPEC’s Extension to Afghanistan
For Prelims: CPEC Extension to Afghanistan, Gwadar Port, BRI, Indian Ocean, Central Asia, Iran’s Chabahar port.
For Mains: CPEC’s Extension to Afghanistan and its Implications for India.
Why in News?
Recently, China and Pakistan have held the 4th round of the Foreign Minister-level Pakistan-China Strategic Dialogue Islamabad, Pakistan, where they agreed to extend the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) into Afghanistan.
- Alongside, the 5th China-Pakistan-Afghanistan Trilateral Foreign Ministers Dialogue was also held where they agreed to combat terrorism and enhance cooperation in different economic fields.
- In 2021, China proposed construction of the Peshawar-Kabul motorway as an extension of CPEC in Afghanistan.
What is the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor?
- CPEC is a 3,000-km long route of infrastructure projects connecting China’s northwest Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region and the Gwadar Port in the western province of Balochistan in Pakistan.
- It is a bilateral project between Pakistan and China, intended to promote connectivity across Pakistan with a network of highways, railways, and pipelines accompanied by energy, industrial, and other infrastructure development projects.
- It will pave the way for China to access the Middle East and Africa from Gwadar Port, enabling China to access the Indian Ocean and in return China will support development projects in Pakistan to overcome the latter’s energy crises and stabilizing its faltering economy.
- CPEC is a part of the Belt and Road Initiative.
- The BRI, launched in 2013, aims to link Southeast Asia, Central Asia, the Gulf region, Africa and Europe with a network of land and sea routes.
Why does Afghanistan seem Significant for Both Pakistan and China?
- Access to Rare Minerals: Afghanistan has a large amount of Rare Earth Minerals (1.4 million tonnes) that are important for making electronics and military equipment. However, since the Taliban took over, the country has been facing economic difficulties because foreign aid has been withdrawn.
- Energy and Other Resources: Afghan participation in CPEC will allow Islamabad and Beijing to harness energy and other resources, as well as gain access to Afghanistan’s vast wealth of untapped natural resources, ranging from copper, gold, uranium, and lithium, which are critical components for a variety of advanced electronic technologies and high-tech missile guidance systems.
What can be the Implications for India on CPEC’s Extension to Afghanistan?
- Reduces India’s Scope in Central Asia:
- Afghanistan’s involvement in CPEC can reduce the scope of India’s investment in Iran’s Chabahar port. India intends to project the port as a gateway to lucrative prospects for commerce between India, Iran, and Afghanistan with Central Asian countries.
- Pakistan is also hoping to undermine India’s influence in Central Asia and CPEC might provide the perfect platform for this.
- China can take Lead from India in Development Aid:
- In terms of development aid, India has been the largest regional lender to Afghanistan, investing more than USD 3 Billion for projects such as
- Road construction, power plant construction, dam construction, parliament building, rural development, education, infrastructure, and much more.
- With the extension of CPEC, China is projected to displace India and take the lead in Afghanistan’s development sphere.
- In terms of development aid, India has been the largest regional lender to Afghanistan, investing more than USD 3 Billion for projects such as
- Security Concerns:
- China may control Afghanistan's Bagram air force base.
- The Bagram airport is the biggest airport and technically well-equipped as the Americans kept it for their use till the end, instead of the Kabul airport.
- Undermining India’s Sovereignty:
- The CPEC passes through PoK, which undermines India’s sovereignty. India has repeatedly raised concerns over this issue as a violation of its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- By extending the CPEC to Afghanistan, China and Pakistan are further consolidating their economic and strategic ties, which India sees as a threat to its security and regional interests.
- Terrorism and Strategic Concerns:
- If Afghanistan becomes a part of the CPEC, it will boost economic development but may also give Pakistan a strategic advantage in the region, which could be a threat to India's interests.
- It may lead to an increase in terrorism from Pakistan against India, as it seeks to gain the upper hand in the region.
- Exploitation of Rare Earth Minerals:
- With the extension of CPEC, China is also looking to exploit Afghanistan's rich minerals and highly lucrative rare-earth mines.
- Rare-earth metals, which are key components for a host of advanced electronic technologies and hi-tech missile guidance systems.
Way Forward
- CPEC has the potential to alter the power balance in the region in China’s favour, much to India’s displeasure. If not dealt with properly, this might change the strategic dynamics of the region and the credibility of India’s claim over PoK in the long run.
- India should strengthen its economic and trade ties with Afghanistan by investing in the country's infrastructure and development. This will not only improve the economic situation in Afghanistan but also help India in countering the influence of CPEC.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Belt and Road Initiative’ is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2016)
(a) African Union
(b) Brazil
(c) European Union
(d) China
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Proposed in 2013, the ‘Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)’ is an ambitious programme of China for connecting Asia with Africa and Europe via land and maritime networks.
- The BRI comprises a Silk Road Economic Belt – a trans-continental passage that links China with Southeast Asia, South Asia, Central Asia, Russia and Europe by land – and a 21st century Maritime Silk Road, a sea route connecting China’s coastal regions with Southeast and South Asia, South Pacific, Middle East and Eastern Africa, all the way to Europe. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is viewed as a cardinal subset of China’s larger ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative. Give a brief description of CPEC and enumerate the reasons why India has distanced itself from the same. (2018)
Q2. China and Pakistan have entered into an agreement for the development of an economic corridor. What threat does this pose for India’s security? Critically examine. (2014)
Q3. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)


Governance
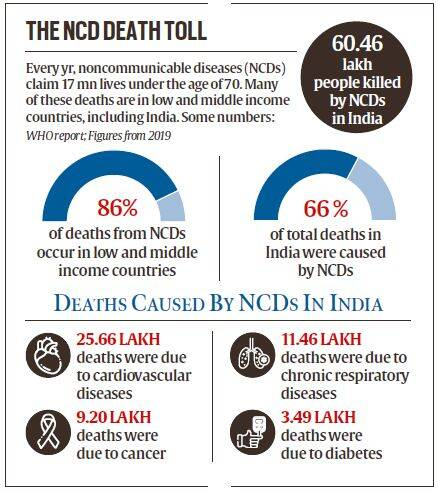
Government Programme for NCD Renamed
For Prelims: NPCDCS programme, National Health Mission, NP-NCD, Non-Communicable Diseases
For Mains: National Health Mission, Non-Communicable Diseases
Why in News?
The existing National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) programme has been renamed National Programme for Prevention & Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD).
- It has been renamed to subsume all types of NCDs.
- Further, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has renamed the Comprehensive Primary Healthcare Non-Communicable Disease (CPHC NCD IT) system as the National NCD Portal to cover a wider population for screening and management of non-communicable diseases.
What is NPCDCS/NP-NCD?
- About:
- NPCDCS is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM) across the country.
- Aim:
- It was launched in 2010 with a focus on strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, early diagnosis, management and referral.
- Management:
- Under NPCDCS, NCD Cells are being established at National, State and District levels for programme management, and NCD Clinics are being set up at District and Community Health Centres (CHC) levels, to provide services for early diagnosis, treatment and follow-up for common NCDs.
- Achievement:
- Under NPCDCS, 677 NCD district-level clinics, 187 District Cardiac Care Units, 266 District Day Care Centres and 5,392 NCD Community Health Centre-level clinics have been set up.
What is National Health Mission?
- NHM was launched by the government of India in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission and the National Urban Health Mission.
- The main programmatic components include Health System Strengthening in rural and urban areas for - Reproductive-Maternal- Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A), and Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases. The NHM envisages achievement of universal access to equitable, affordable & quality health care services that are accountable and responsive to people's needs.
- The National Health Mission seeks to ensure the achievement of the following indicators:
- Reduce Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) to 1/1000 live births
- Reduce Infant Mortality rate (IMR) to 25/1000 live births
- Reduce Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to 2.1
- Prevention and reduction of anaemia in women aged 15–49 years
- Prevent and reduce mortality & morbidity from communicable, non- communicable; injuries and emerging diseases
- Reduce household out-of-pocket expenditure on total health care expenditure
- Reduce annual incidence and mortality from Tuberculosis by half
- Reduce the prevalence of Leprosy to <1/10000 population and incidence to zero in all districts
- Annual Malaria Incidence to be <1/1000
- Less than 1 per cent microfilaria prevalence in all districts
- Kala-azar Elimination by 2015, <1 case per 10000 population in all blocks
What are Non-Communicable Diseases?
- About:
- NCDs, also known as chronic diseases, tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioural factors.
- The main types of NCD are cardiovascular diseases (such as heart attacks and stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma) and diabetes.
- Causes:
- Tobacco use, unhealthy diet, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity and air pollution are the main risk factors contributing to these conditions.
- Indian Initiatives:
- The Central Government is implementing the Strengthening of Tertiary Care Cancer facilities scheme to support the setting up of State Cancer Institutes (SCI) and Tertiary Care Centres (TCCC) in different parts of the country.
- Oncology in its various aspects has a focus in case of new AIIMS and many upgraded institutions under Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY).
- Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) Deendayal outlets have been opened at 159 Institutions/Hospitals with an objective to make available Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases drugs and implants at discounted prices to the patients.
- Jan Aushadhi stores are set up by the Department of Pharmaceuticals to provide generic medicines at affordable prices.
- Global:
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).
- WHO plays a key leadership role in the coordination and promotion of the global fight against NCDs.
- Global Action Plan: In 2019, the World Health Assembly extended the WHO Global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013–2020 to 2030 and called for the development of an Implementation Roadmap 2023 to 2030 to accelerate progress on preventing and controlling NCDs.
- It supports actions to achieve a set of nine global targets with the greatest impact towards prevention and management of NCDs.
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).


Biodiversity & Environment
Convention on Migratory Species
For Prelims: Bonn Convention (UNEP/CMS), Central Asian Flyway, micro-plastic and single-use plastic, Wildlife Crime Control Bureau, Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
For Mains: Convention on migratory species and Efforts made by India
Why in News?
The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change in collaboration with the United Nations Environment Programme/ Convention on Migratory Species (UNEP/CMS) had organized a meeting of Range Countries to strengthen conservation efforts for migratory birds and their habitats in the Central Asian Flyway (CAF).
- The meeting was attended by 11 countries, including Armenia, Bangladesh, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Kuwait. The delegates agreed on an institutional framework for the CAF and a draft roadmap for updating the CMS CAF Action Plan.
What is CMS?
- About:
- It is an intergovernmental treaty under the UNEP- popularly known as Bonn Convention.
- It was signed in 1979 and in force since 1983.
- As of 1 March 2022, the CMS has 133 Parties.
- India is also a party to CMS since 1983.
- Aim:
- It aims to conserve terrestrial, marine and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- It lays the legal foundation to conduct conservation measures on a global scale.
- The legal instruments under CMS may range from legally binding Agreements to less formal MoU.
- Two appendices under CMS:
- Appendix I lists ‘Threatened Migratory Species’.
- Appendix II lists ‘Migratory Species requiring international cooperation’.
- India and the CMS:
- India has signed a non-legally binding Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with CMS on conservation and management of Siberian Cranes (1998), Marine Turtles (2007), Dugongs (2008), and Raptors (2016).
- With 2.4% of the world’s land area, India contributes to around 8% of the known global biodiversity.
- India also provides temporary shelter to several migratory species including Amur Falcons, Bar-headed Geese, Black-necked Cranes, Marine Turtles, Dugongs, Humpback Whales, etc.
What is a Migratory Species?
- A species or lower taxon of wild animals of which the entire population or any geographically separate part of the population cyclically and predictably cross one or more national jurisdictional boundaries.
- The word ‘cyclically’ relates to a cycle of any nature, such as astronomical (circadian, annual, etc.), life or climatic, and of any frequency.
- The word ‘predictably’ implies that a phenomenon can be anticipated to recur in a given set of circumstances, though not necessarily regularly in time.
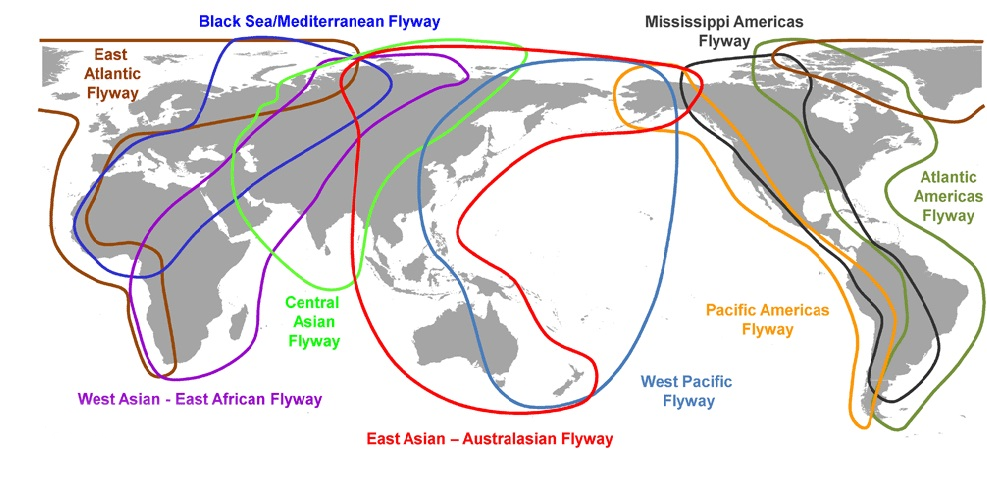
What is Central Asian Flyway?
- The CAF is a major migratory route for birds, covering 30 countries from the Arctic Ocean to the Indian Ocean.
- Indian subcontinent is a part of a CAF with at least 279 populations of 182 migratory waterbird species (including 29 globally threatened species).
- It is home to more than 400 species of migratory birds, including threatened and endangered species such as the Siberian crane and the lesser white-fronted goose.
What are Flyways?
- Flyways are the area used by a group of birds during their annual cycle which includes their breeding areas, stopover areas, and wintering areas.
- The CMS Secretariat has identified nine major flyways globally with respect to bird migration.
What are some Efforts made by India for Migratory Species?
- National Action Plan for the Conservation of Migratory Birds (2018-2023): India has launched the National Action Plan for the conservation of migratory species along the Central Asian Flyway.
- To reduce pressure on critical habitats and migratory routes by addressing the various challenges faced by migratory birds, including habitat loss, degradation and fragmentation, hunting, poaching, pollution, and climate change.
- To stop the decline of migratory birds and reverse the scenario by 2027.
- To avoid threats to habitats and migratory routes and ensure their sustainability for future generations.
- To support trans-boundary cooperation among various countries along the Central Asian Flyway to conserve migratory birds and their habitats.
- To improve the database on migratory birds and their habitats to enhance our understanding of their conservation needs.
- India also Announced:
- Conservation of marine turtles- by launching its Marine Turtle Policy and Marine Stranding Management Policy, by 2020,
- Reduction of pollution from micro-plastic and single-use plastic,
- Transboundary protected areas for conservation of species like Tigers, Asian elephants, Snow Leopard, the Asiatic Lion, the one-horned rhinoceros, and the Great Indian Bustard, and
- Sustainable infrastructure development like Linear Infrastructure Policy Guidelines to tailor development in ecologically fragile areas.
- Project Snow Leopard (PSL): PSL was launched in 2009 to promote an inclusive and participatory approach to conserve snow leopards and their habitat.
- Dugong Conservation Reserve: India has established its first Dugong conservation reserve in Tamil Nadu.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972:
- Rare and endangered species of birds including migratory birds are included in Schedule-I of the Act thereby according them highest degree of protection.
- Stringent punishments have been provided in the Act for violation of provisions of the Act.
- Important habitats of birds, including migratory birds have been notified as protected Areas under the Act for better conservation and protection of birds and their habitats.
- Other Initiatives:
- Focused protection measures involving the local communities have been taken up in the State of Nagaland for protection of Amur Falcons that migrate to Northeast India on their route to Southern Africa.
- India has taken several steps to conserve vultures like imposing ban on veterinary use of diclofenac, establishment of Vulture breeding centres etc.
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau has been established for control of illegal trade in wildlife and its parts and products.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2020)
| International agreement/set-up | Subject | |
| 1. | Alma-Ata Declaration | Healthcare of the people |
| 2. | Hague Convention | Biological and chemical weapons |
| 3. | Talanoa Dialogue | Global climate change |
| 4. | Under2 Coalition | Child rights |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
- Alma-Ata Declaration: It was adopted at the International Conference on Primary Health Care (PHC) which was held in Almaty, Kazakhstan in 1978. It urged all the governments, health care workers and development workers to promote and protect the primary health of all the people. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Hague Convention: There are a series of Hague Convention on different subjects such as Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict, Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction, etc. But it is not related to biological and chemical weapons. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- Talanoa Dialogue: The Dialogue was launched at the UN Climate Change Conference (COP 23) in Bonn (Germany) in 2017. Talanoa is a traditional word used in Fiji and across the Pacific to reflect a process of inclusive, participatory and transparent dialogue. The purpose of Talanoa is to share stories, build empathy and to make wise decisions for the collective good. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.
- Under2 Coalition: The Under2 Coalition is a global community of state and regional governments committed to ambitious climate action in line with the Paris Agreement. The coalition brings together more than 220 subnational governments who represent over 1.3 billion people and 43% of the global economy. Currently, Maharashtra, Jammu & Kashmir, West Bengal, Telangana and Chhattisgarh are signatories to this pact from India. Signatories commit to keeping global temperature rises to well below 2°C with efforts to reach 1.5°C. Hence, pair 4 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
ALH (Advanced Light Helicopters) DHRUV
The three defense services and the Coast Guard had all grounded their ALH fleets after a Navy ALH-MkIII was ditched at sea on March 8, 2023, followed by a Coast Guard ALH also suffering an incident.
ALH Dhruv is a multi-role, twin-engine, utility, and advanced light helicopter designed and developed by the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The major variants of ALH Dhruv are:
- Mk-I
- MK-II & Mk-III
- MK-III Maritime Role (Navy/ Coast Guard)
- MK-IV Armed version
Dhruv MkIII is fitted with modern surveillance radar and electro-optical equipment, which enable them to undertake the role of maritime reconnaissance in addition to providing long-range Search and Rescue, both by day and night. In addition to special operations capabilities, ALH MK III is also fitted with a heavy machine gun to undertake constabulary missions.
Read more: Dhruv MK III: Advanced Light Helicopter
Foreign Investment in Nuclear Power
A government panel, established by the Niti Aayog, has recommended that India should lift its ban on foreign investment in the nuclear power industry and increase involvement of domestic private companies.
Under India's Atomic Energy Act 1962, the government plays a central role in developing and running nuclear power stations. Domestic private companies are allowed to participate as "junior equity partners" by supplying components and helping build them.
Presently, India does not allow foreign investment in the nuclear power sector and State-run Nuclear Power Corp of India Ltd. (NPCIL) and Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam are the only two nuclear power generators in India.
The panel has recommended changes to the act and to India's foreign investment policies so that both domestic and foreign private companies can complement nuclear power generation by public companies.
The aim is to reduce carbon emissions and nuclear is in focus because it can supply energy 24/7, unlike solar energy. Nuclear energy generation accounts for 3% of the total production while coal accounts for approx. 75%.
India is a signatory to international conventions on nuclear safety and will have to ensure that private companies comply with standards.
Read More: Revisiting the Need of Nuclear Energy
Malcha Mahal
The Delhi Tourism Department has launched its much awaited ‘haunted walks’, for which the Malcha Mahal was chosen as the first destination of the journey.
The Malcha Mahal or Wilahat Mahal is a Tughlaq-era hunting lodge, built by Feroz Shah Tughlaq in the 14th century. It is situated 1.5 km from the main road, deep inside a forest in Chanakyapuri, Delhi. It is named after Malcha Marg, which houses the elite of the city, including diplomats, businessmen and authors.
Feroz Shah Tughlaq was a Sultan of Delhi from the Tughlaq dynasty who ruled from 1351 to 1388. He is more famous for commissioning buildings of architectural shapes that were seen as unconventional during his era. He was also considered the father of the irrigation system in India by the British for channelizing rivers to provide water through canals to a large part of the country.
Read More: Malcha Mahal