International Relations
Order of the Druk Gyalpo
For Prelims: Order of the Druk Gyalpo, Food Safety and Standards Authority Of India (FSSAI), Star labelling program, Self-Reliance.
For Mains: Order of the Druk Gyalpo, Regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
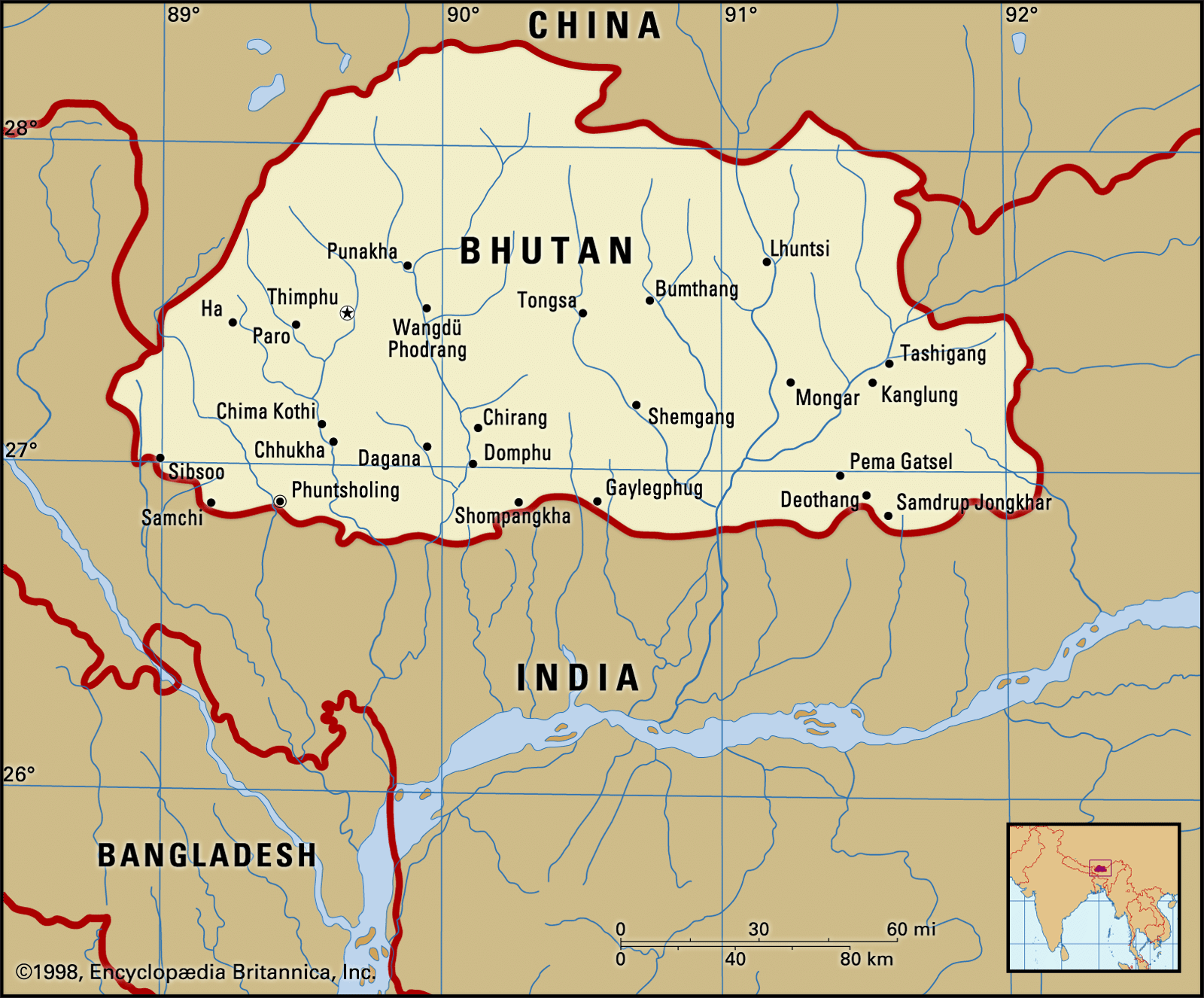
Recently, the Prime Minister of India received Bhutan’s highest civilian award, the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’, during his two-day State visit to Bhutan.
- He is the first foreign Head of the Government to receive the honour.
- India and Bhutan have also exchanged several MoUs and signed agreements in the fields of energy, trade, digital connectivity, space and agriculture, and finalised the MoU on the establishment of rail links between the two nations.
What is the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’ Award?
- About:
- The Order of the Druk Gyalpo stands as Bhutan’s most esteemed civilian accolade, reserved for individuals who have demonstrated exceptional contributions to society, embodying values of service, integrity, and leadership.
- Recipients of this prestigious award are carefully selected based on their outstanding accomplishments and positive impact on society.
- Their contributions are assessed in alignment with Bhutanese values, emphasising holistic development, cultural preservation, and regional harmony.
- Accolade on Indian PM:
- Indian PM’s selection as the first foreign Head of Government to receive this honour underlined the strong bilateral ties between the two countries.
- The award underscores his leadership, characterised by an unwavering commitment to progress, which aligns closely with Bhutan’s national vision of achieving Self-Reliance.
- Indian PM has emerged as a figure of destiny, transforming the ancient civilisation of India into a dynamic centre of technology and innovation.
- His commitment to safeguarding the environment and investing in renewable energy makes India’s progress truly well-rounded.
What are the Key Pacts Signed by India and Bhutan?
- Establishment of Rail Links:
- An MoU was finalised on the establishment of rail links between India and Bhutan, including the Kokrajhar-Gelephu rail link and Banarhat-Samtse rail link.
- Petroleum, Oil, Lubricants (POL):
- An agreement was made for the general supply of POL and related products from India to Bhutan, facilitating supply through agreed entry/exit points.
- Recognition of Bhutan Food And Drug Authority (BFDA):
- An agreement was reached for the recognition of official control exercised by BFDA by the Food Safety and Standards Authority Of India (FSSAI), promoting ease of doing business and reducing compliance costs.
- Cooperation in Energy Efficiency and Energy Conservation:
- An MoU aimed to assist Bhutan in enhancing energy efficiency in the household sector through various measures such as promoting a star labelling program and institutionalising training of energy auditors.
- Pharmacopoeia, Vigilance, and Testing of Medicinal Products:
- This MoU aimed to enhance cooperation and exchange information in the regulation of medicines, allowing for the acceptance of Indian Pharmacopoeia by Bhutan and the supply of generic medicines at affordable prices.
- Joint Plan of Action (JPOA) on Space Cooperation:
- A concrete roadmap was established for further developing space cooperation through exchange programs and training.
- Digital Connectivity:
- Both countries signed for renewal of the MoU on Peering Arrangement between the National Knowledge Network of India (NKN) and the Druk Research And Education Network of Bhutan.
- This MoU aims to enhance digital connectivity between India and Bhutan and will benefit the scholars and research institutions of Bhutan.
What are the Implications of Indian PM’s Visit to Bhutan at a Time of Regional Challenges?
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties:
- The visit underscores India's commitment to strengthening its bilateral relationship with Bhutan, especially during a period of regional uncertainty and challenges.
- This reaffirms the enduring friendship between the two nations and emphasises mutual support in the face of external pressures.
- The announcement of India’s doubling of support for Bhutan’s Five Year Plan, from Rs 5,000 crore to Rs 10,000 crore, was significant in this regard.
- Counterbalancing Chinese Influence:
- Against the backdrop of China's increasing engagement with Bhutan, the Indian PM’s visit serves to reinforce India's presence and influence in the region.
- By showcasing support for Bhutan's development and security interests, India aims to counterbalance any attempts by China to expand its influence in Bhutan.
- Enhancing Strategic Cooperation:
- The visit included discussions on strategic cooperation, including defence and security cooperation, to address common regional challenges such as border security and terrorism.
- Strengthening cooperation in these areas can contribute to regional stability and security.
- Promoting Economic Partnerships:
- The visit has also focused on promoting economic partnerships between India and Bhutan. This could involve initiatives to boost trade, investment, and infrastructure development, which are essential for both countries' economic growth and development.
- Addressing Regional Security Concerns:
- Given the geopolitical dynamics in South Asia, the Indian PM’s visit has addressed regional security concerns, including cross-border terrorism and the need for cooperation among neighbouring countries to maintain peace and stability in the region.
Way Forward
- Both countries should continue to emphasise the unbreakable nature of their ties and demonstrate a united front, especially in the face of external challenges. This solidarity is crucial for preserving the permanence of their relationship amidst regional changes and uncertainties.
- India should reaffirm its support for Bhutan's interests, particularly in the context of boundary talks with China. India needs to stand by Bhutan and ensure that its sovereignty and territorial integrity are upheld during negotiations.
- Enhancing communication and coordination between India and Bhutan's diplomatic and security establishments is vital. This includes sharing intelligence, conducting joint assessments, and formulating unified strategies to address common challenges, particularly those related to regional security.
Read more: India Bhutan Relations, Bhutan’s Gelephu Gambit
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. (2016).


Biodiversity & Environment
Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2024
For Prelims: Biodegradable Plastic, Compostable Plastic, Plastic Waste Management Rules, Central Pollution Control Board, Microplastics
For Mains: Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2022 and its significance, Conservation Environmental Pollution & Degradation Government Policies & Interventions.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of India has recently introduced amendments to the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, through the Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2024.
- These changes signify a significant effort to address plastic pollution in India, particularly by targeting microplastics and setting stricter criteria for biodegradable plastics.
What are the Key Highlights of the Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules 2024?
- Biodegradable Plastics:
- Biodegradable plastics are now defined as materials capable of degradation by biological processes in specific environments like soil and landfill, without leaving any microplastics.
- Microplastics are defined as any solid plastic particle insoluble in water, with dimensions between 1 micron and 1,000 microns (1 micron is one-thousandth of a millimetre).
- In recent years, they have been reported as a major source of pollution affecting rivers and oceans.
- Microplastics are defined as any solid plastic particle insoluble in water, with dimensions between 1 micron and 1,000 microns (1 micron is one-thousandth of a millimetre).
- Biodegradable plastics are now defined as materials capable of degradation by biological processes in specific environments like soil and landfill, without leaving any microplastics.
- Microplastics Testing:
- The rules do not specify which chemical tests can establish the absence of microplastics or the extent to which microplastics must be reduced for elimination.
- Expanded Definition of "Importer":
- The definition now includes imports of various plastic-related materials such as packaging, carry bags, sheets, raw materials, and intermediate materials used in plastic manufacturing for commercial purposes.
- Earlier, "importer" referred to someone who imported plastic packaging, products with plastic packaging, carry bags, multilayered packaging, plastic sheets, or similar items.
- The definition now includes imports of various plastic-related materials such as packaging, carry bags, sheets, raw materials, and intermediate materials used in plastic manufacturing for commercial purposes.
- Inclusive Definition of "Manufacturer":
- The scope now encompasses those engaged in the production of plastic raw materials, compostable plastics, and biodegradable plastics, reflecting a broader range of entities covered under this term.
- Extended Scope of "Producer":
- Beyond manufacturing plastic packaging, it now includes the production of intermediate materials used in plastic packaging and contract manufacturing for brand owners.
- Certification Requirement:
- Manufacturers are allowed to produce carry bags and commodities from compostable or biodegradable plastics, and must obtain a certificate from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) before marketing or selling their products.
Note:
- There are two categories of microplastics: primary and secondary.
- Primary microplastics are tiny particles designed for commercial use and microfibers shed from clothing and textiles, such as microbeads found in personal care products, plastic pellets, and plastic fibres.
- Secondary microplastics are formed from the breakdown of larger plastics, such as water bottles, caused by exposure to environmental factors like the sun's radiation and ocean waves.
- Microplastics act as carriers for various chemicals, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and pathogens, posing risks to aquatic life and human health if they bypass the water treatment process.
What are Biodegradable Plastics and Compostable Plastics?
| Biodegradable Plastic | Compostable Plastic | |
| Definition |
|
|
| Environmental Benefit |
|
|
| Potential Harm |
|
|
What are the Recent Plastic Waste Management Rules in India?
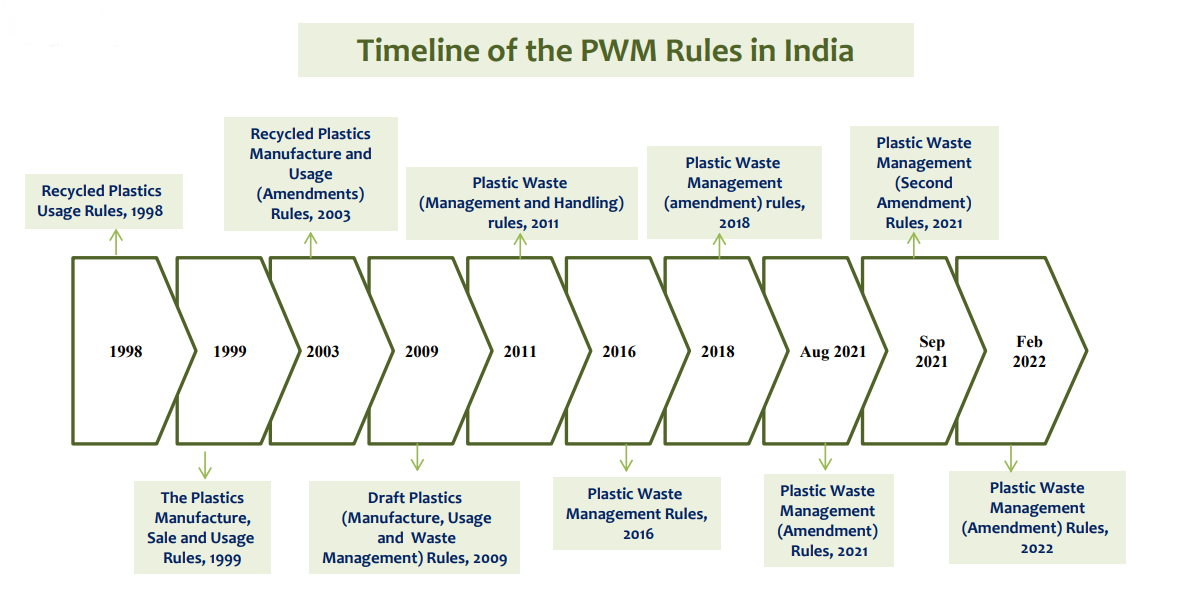
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016:
- The Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, mandate the generators of plastic waste to take steps to minimise the generation of plastic waste, not to litter the plastic waste, ensure segregated storage of waste at source & hand over segregated waste in accordance with rules.
- The PWM Rules, 2016 cast Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) on Producer, Importer, and Brand Owner and EPR shall be applicable to both pre-consumer and post-consumer plastic packaging waste.
- Increased the minimum thickness of plastic carry bags from 40 microns to 50 microns and stipulated a minimum thickness of 50 microns for plastic sheets.
- Expand the jurisdiction of applicability from municipal areas to rural areas.
- Responsibility for implementation of the rules is given to Gram Panchayat in rural areas.
- Introduction of waste segregation at source for individual and bulk generators
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules 2018:
- Phasing out of multi-layered plastic (MLP) (material used or to be used for packaging and having at least one layer of plastic) is now applicable to MLP which are "non-recyclable, or non-energy recoverable, or with no alternate use."
- Prescribed a central registration system for the registration of the producer/importer/brand owner of plastics.
- The centralised registration system will be evolved by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) for the registration of the producer/importer/brand owner.
- The rules aim to streamline the registration process for producers, importers, and brand owners, while also providing a mechanism for phasing out non-recyclable multi-layered plastics.
- Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021:
- Prohibits identified single-use plastic items that have low utility and high littering potential by 2022.
- Prohibition of manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale, and use of certain single-use plastic items including polystyrene and expanded polystyrene from 1st July 2022.
- Plastic packaging waste not covered by the phase-out of single-use plastic items will be collected and managed in an environmentally sustainable way through Extended Producer Responsibility.
- This responsibility is legally enforced through the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021.
- Increase in the thickness of plastic carry bags from 50 microns to 75 microns with effect from 30th September 2021, and to 120 microns with effect from 31st December 2022.
- Prohibits identified single-use plastic items that have low utility and high littering potential by 2022.
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022:
- Introduced guidelines on EPR for plastic packaging. These guidelines set mandatory targets for EPR, recycling of plastic packaging waste, reuse of rigid plastic packaging, and the use of recycled plastic content.
- Environmental compensation will be imposed on those who fail to meet EPR targets, based on the polluter pays principle.
- This is to protect and improve the environment, and prevent, control, and reduce pollution.
- The principle holds polluters responsible for compensating for the damage caused to the environment, regardless of their intent.
- The guidelines provide a framework to strengthen the circular economy of plastic packaging waste.
What are the other Initiatives taken to Curb Plastic Waste?
- Swachh Bharat Mission
- India Plastics Pact
- Project REPLAN
- Un-Plastic Collective
- GoLitter Partnerships Project
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
- The CPCB was constituted in 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- CPCB was also entrusted with powers and functions under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- It serves as a field formation and provides technical services to the Ministry of Environment and Forests.
- Principal functions include promoting the cleanliness of streams and wells, improving air quality, and preventing, controlling, or abating water and air pollution.
Read more: India's Battle Against Single-Use Plastics, Banning Single-Use Plastic, Eliminating Plastic Pollution by 2040
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q.1 In India, ‘extend producer responsibility’ was introduced as an important feature in which of the following? (2019)
(a) The Bio-medical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 1998
(b) The Recycled Plastic (Manufacturing and Usage) Rules, 1999
(c) The e-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011
(d) The Food Safety and Standard Regulations, 2011
Ans: (c)
Q.2 How is the National Green Tribunal (NGT) different from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)? (2018)
- The NGT has been established by an Act whereas the CPCB has been created by an executive order of the Government.
- The NGT provides environmental justice and helps reduce the burden of litigation in the higher courts whereas the CPCB promotes cleanliness of streams and wells, and aims to improve the quality of air in the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into environment? (2019)
(a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystems.
(b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children.
(c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields.
(d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants.
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q: What are the impediments in disposing the huge quantities of discarded solid waste which are continuously being generated? How do we remove safely the toxic wastes that have been accumulating in our a habitable environment? (2018)


Science & Technology
Sickle Cell Disease
For Prelims: Biotechnology, Sickle Cell disease, Genetic disorder, Tribal communities
For Mains: Challenges and Governmental Initiatives faced by the tribal communities relating to the treatment and accessibility of sickle cell disease (SCD)
Why in News?
Amidst the unavailability of essential drugs to treat Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) at district healthcare institutions, there is growing concern about the challenges faced by people from marginalised Indigenous Tribal communities in managing the treatment of SCD.
What is Sickle-Cell Disorder?
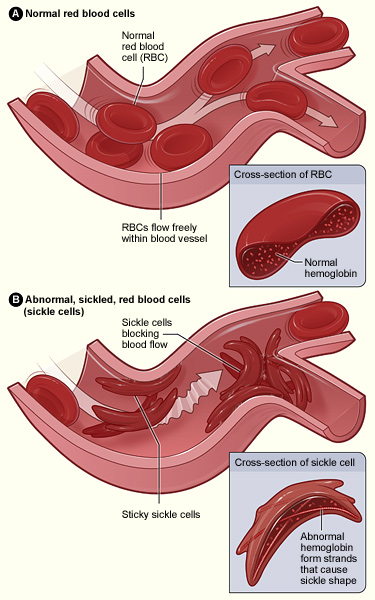
- About:
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is an inherited haemoglobin disorder characterised by a genetic mutation that causes red blood cells (RBCs) to assume a sickle or crescent shape rather than their normal round shape.
- This abnormality in RBCs results in increased rigidity, impairing their ability to circulate effectively throughout the body. Consequently, individuals with SCD often experience complications such as anaemia, organ damage, recurrent and severe pain episodes, and a shortened lifespan.
- As per the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, marginalised tribal populations are most vulnerable to SCD.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of sickle cell disease can vary, but some common symptoms are-
- Chronic anaemia which leads to fatigue, weakness, and paleness.
- Painful episodes (also known as sickle cell crisis) cause sudden and intense pain in the bones, chest, back, arms, and legs.
- Delayed growth and puberty.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: These can help relieve anaemia and reduce the risk of pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: This medication can help reduce the frequency of painful episodes and prevent some of the disease's long-term complications.
- Gene Therapy: It can also be treated by bone marrow or stem cell transplantation by methods like Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR).
What is India's Current Status of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)?
- India ranks third globally in terms of the number of SCD births, following Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Regional studies indicate that an estimated 15,000 to 25,000 babies with SCD are born in India annually.
- Most of these births occur in tribal communities, highlighting the geographical and socioeconomic disparities in healthcare access and awareness.
What are the Challenges Related to the Treatment and Accessibility of SCD?
- Limited Awareness: There is a lack of understanding about SCD among the public and healthcare providers, leading to delayed diagnosis and inadequate treatment.
- Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure: Many rural and tribal areas lack specialised healthcare facilities and trained medical personnel for managing SCD.
- High Treatment Costs: The long-term management of SCD can be financially burdensome for many families due to the cost of medications, regular check-ups, and potential hospitalizations.
- For Example, Treatments like CRISPR cost $ 2-3 million, and it's difficult to find bone marrow donors.
- Limited Access to Medications: Inconsistent availability of essential medications for SCD treatment, such as hydroxyurea and pain relievers, is a concern in certain regions.
- Inadequate Screening Programs: The absence of systematic newborn screening and early detection initiatives results in missed opportunities for early intervention and genetic counselling.
- Geographical and Socioeconomic Barriers: Rural, remote, and tribal communities face challenges in accessing quality healthcare due to geographical isolation, lack of transportation, and socioeconomic factors.
- Stigma and Discrimination further hinder access to healthcare services.
What are the Government Initiatives Regarding SCD?
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission:
- Aimed at enhancing the care for all Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) patients and reducing the disease's prevalence through an integrated approach encompassing screening and awareness campaigns.
- Targeting complete elimination of sickle cell disease as a public health concern by 2047.
- Under the Sickle Cell Anaemia Mission, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) is developing gene-editing therapies for SCD.
- National Health Mission (NHM) 2013:
- It is, a flagship programme of the Indian government, that encompasses provisions for disease prevention and management, with a specific focus on hereditary anomalies such as sickle cell anaemia.
- Dedicated programs within NHM focus on raising awareness, facilitating early detection, and ensuring timely treatment of sickle cell anaemia.
- NHM facilitates drugs like hydroxyurea to treat SCD in its “essential medicines List”.
- The National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research 2017:
- It restricts the commercialisation of stem cell therapies to clinical trials, except for Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- Gene editing on stem cells is permitted only for in-vitro studies.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy Product Development and Clinical Trials 2019: It provides guidelines for the development and clinical trials of gene therapies for inherited genetic disorders.
- India has also approved a five-year project to develop CRISPR techniques for sickle cell anaemia treatment.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:
- It aims to address the challenges in screening and management of the disease.
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwDs) Act, 2016:
- SCD is included in the 21 disabilities that provide for benefits such as reservation in higher education (minimum 5%), government jobs (minimum 4%), and allocation of land (minimum 5%), for persons with benchmark disabilities and those with high support needs.
- Free education is guaranteed for every child with a benchmark disability between 6 and 18 years.
Note
- Recently, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two gene therapies designed for sickle cell disease.
- The approved therapies include Lyfgenia and Casgevy.
- Both treatments received clearance for individuals aged 12 years and above.
- Casgevy also approved in the U.K., is the first CRISPR-based therapy to have received regulatory approval.
- Lyfgenia doesn’t use CRISPR but depends on a viral vector to change blood stem cells.
- Both treatments entail collecting a patient’s blood stem cells, modifying them, and administering high-dose chemotherapy to destroy the damaged cells in the bone marrow.
- The modified cells are then infused into the patient through a hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Way Forward
- Early Detection and Screening:
- Strengthen and expand genetic counselling and testing programmes.
- Prioritising basic treatments like hydroxyurea is essential for urgent needs.
- Identify carriers at an early stage to provide essential information to affected families.
- Ensuring equitable access to clinical trials is important to address the issue from the grassroots level.
- Public Education and Awareness:
- Implement sustained public awareness initiatives.
- Educate communities about the disease's hereditary nature and the importance of genetic testing.
- Public involvement in regulatory discussions is necessary.
- Research and Development:
- Allocate resources for ongoing research.
- Gain deeper insights into the genetic and molecular aspects of SCD to develop more effective treatment options and potential cures.
- Comprehensive healthcare access is vital for better long-term health outcomes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anemia Mukt Bharat Strategy : (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of child-birth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)


Science & Technology
Google DeepMind’s SIMA and AlphaGeometry
For Prelims: Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent, AI gaming agent, OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, Generative AI.
For Mains: Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent, Applications of Generative AI, Issues Associated with Generative AI.
Why in News?
Recently, Google DeepMind has revealed its various AI (Artificial Intelligence) products based on Predictive AI Models, such as SIMA (Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent) and AlphaGeometry.
- OpenAI's ChatGPT and Google's Gemini have garnered significant attention from various sectors, with companies and researchers, including those in oil and gas as well as pharmaceutical industries, increasingly turning to Generative AI or Predictive AI for applications such as oil exploration and drug discovery.
What is Predictive AI?
- Predictive AI models are a type of artificial intelligence system designed to forecast or predict future outcomes based on historical data, patterns, and trends.
- These models utilise advanced algorithms, statistical techniques, and machine learning methods to analyse vast amounts of data and make informed predictions about future events or behaviours.
What is SIMA?
- About:
- SIMA is an AI Agent, which is different from AI models such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google Gemini.
- AI models are trained on a vast data set and are limited when it comes to working on their own.
- On the other hand, an AI Agent can process data and take action themselves.
- It is a game assisting AI, making it a valuable asset for enhancing the gaming experience.
- SIMA can be called a generalist AI Agent that is capable of doing different kinds of tasks.
- It is like a virtual buddy who can understand and follow instructions in all sorts of virtual environments – from exploring mysterious dungeons to building lavish castles. It can accomplish tasks or solve challenges assigned to it.
- SIMA is an AI Agent, which is different from AI models such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google Gemini.
- Working:
- SIMA “understands” any person's commands as it has been trained to process human language. So when one asks it to build a castle or find the treasure chest, it understands exactly what these commands mean.
- One distinct feature of this AI Agent is that it is capable of learning and adapting. SIMA does this through the interactions it has with the user.
- Training:
- Google DeepMind collaborated with eight game studios to train SIMA, an AI agent, on nine different video games including Teardown and No Man’s Sky.
- SIMA learned various skills like navigation, menu use, resource mining, and spaceship flying.
- They also tested SIMA in four research environments, one of which was the Construction Lab in Unity.
What is AlphaGeometry?
- About:
- DeepMind's AlphaGeometry is a specialised AI system designed to tackle complex geometry problems.
- Unlike general-purpose AI models like OpenAI's ChatGPT or Google's Gemini, AlphaGeometry is tailored specifically for geometric reasoning tasks.
- It combines advanced neural language modelling techniques with a symbolic deduction engine specialised in algebraic and geometric reasoning.
- Neural language models are built using neural network architectures, which are computational models inspired by the structure and function of the human brain.
- Symbolic deduction is a method of logical reasoning that operates on symbols and logical rules to derive conclusions from premises. In symbolic deduction, statements are represented using symbols, such as variables and logical operators, and logical rules are applied to manipulate these symbols according to predefined inference rules.
- Working:
- It leverages both neural language models for intuitive idea generation and symbolic deduction for precise reasoning.
- When faced with geometry problems, AlphaGeometry first utilises its language model to suggest potential geometric constructs that could aid in solving the problem.
- These suggestions help inform the symbolic deduction engine, which then makes further deductions and approaches the solution systematically.
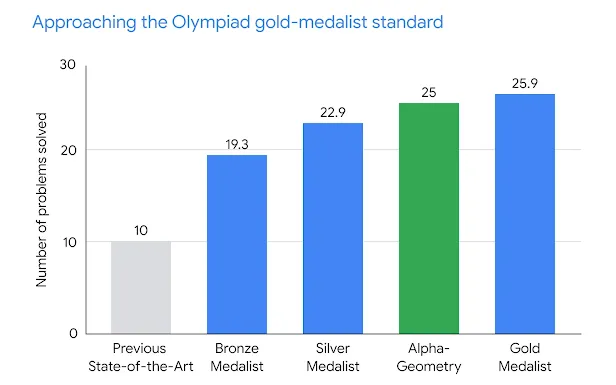
- AlphaGeometry's performance was evaluated using a benchmarking set of geometry problems compiled from the International Mathematical Olympiads (IMO).
- It demonstrated impressive results, solving a significant portion of the problems within competition time limits, surpassing previous AI systems in geometry and approaching the performance levels of human gold medallists in the IMO.
How Predictive AI Models are Gaining Traction?
- Volcanic Ash Monitoring:
- Companies like Moscow-based Yandex are utilising advanced mathematical models and neural networks to develop interactive maps for real-time monitoring of volcanic ash dispersion.
- This enables authorities and communities to respond swiftly to ashfall, safeguarding public safety and infrastructure.
- Oil and Gas Exploration:
- Major oil and gas companies are investing in AI strategies for both upstream (exploration) and midstream (pipeline and logistics) operations.
- AI algorithms are employed to analyse past surveys and explorations, identify patterns and correlations in data, predict probable reserves, optimise extraction methods, and reduce costs.
- For instance, Shell and Saudi Aramco are leveraging generative AI tools to improve subsurface imaging, analyse drilling plans, and make precise forecasts for refined products.
- Medicine Research:
- Deep Neural networks are being applied in drug discovery to develop predictive models for assessing the properties of chemical compounds and their potential effectiveness in targeting specific diseases.
- Pharmaceutical companies like Merck are using machine learning techniques to enhance drug discovery processes, leading to the development of new models for compound assessment.
- Collaborative initiatives such as the European Union’s (EU’s) MELLODDY Project aim to improve predictive models through federated learning, ensuring data privacy and protection while pooling resources for enhanced research outcomes.
What are India's Initiatives for Generative AI?
- Launching the Generative AI Report: INDIAai, the Government of India's National AI Portal, conducted numerous studies and hosted three roundtable discussions with some of the most prominent voices in Generative AI, AI Policy, AI Governance and Ethics, and academia to examine the impact, ethical and regulatory questions, and opportunities it brings to India.
- Joining the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI): In 2020, India joined forces with 15 other countries to form the GPAI. The purpose of this alliance is to establish frameworks for the responsible utilisation of emerging technologies.
- Fostering an AI Ecosystem within the Country: The Indian government has been dedicated to fostering an AI ecosystem within the country by investing in research and development, supporting startups and innovation hubs, creating AI policies and strategies, and promoting AI education and skilling.
- National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence:
- The Government has published the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence with the objective of developing an ecosystem for the research and adoption of Artificial Intelligence.
- National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems:
- Under this Mission, Technology Innovation Hubs (TIH) has been established on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur, which aims to provide the state-of-the-art training and capacity building for the creation of next-generation scientists, engineers, technicians, and technocrats in the field of Artificial Intelligence.
- Artificial Intelligence Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation Platform:
- It is a Cloud computing platform, aiming to make India a pioneer amongst emerging economies with regards to AI and transform sectors like education, health, agriculture, urbanization and mobility.
- National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q2. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
| Terms sometimes seen in news | Context/Topic | |
| 1. | Belle II experiment | Artificial Intelligence |
| 2. | Blockchain technology | Digital/Cryptocurrency |
| 3. | CRISPR–Cas9 | Particle Physics |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Gulaal Gota
Why in News?
In Jaipur, Rajasthan, the age-old tradition of celebrating Holi continues. This celebration involves the practice of "Gulaal Gota," a unique tradition dating back around 400 years.
What is Gulaal Gota?
- History:
- Gulaal Gota is a small ball made of lac, filled with dry gulaal, and weighs around 20 grams when filled.
- Lac is a resinous substance that is secreted by certain insects. The female scale insect is one of the sources of lac.
- To produce 1 kg of lac resin, around 300,000 insects are killed. The lac insects also yield resin, lac dye and lac wax.
- It is used in various applications, including the production of lac bangles.
- Lac is a resinous substance that is secreted by certain insects. The female scale insect is one of the sources of lac.
- Gulaal Gota is a small ball made of lac, filled with dry gulaal, and weighs around 20 grams when filled.
- The process of making Gulaal Gotas involves boiling lac in water to make it flexible, shaping it, adding colour, heating it, and then blowing it into a spherical shape with the help of a blower called "phunkni".
- Raw Materials and Artisan Community:
- Lac, the primary raw material for Gulaal Gota, is sourced from Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand.
- Gulaal Gotas are made by Muslim lac makers, known as Manihaars, in Jaipur, who learned lac-making from Hindu lac makers in Bagru, a town near Jaipur.
- Historical Significance and Economic Aspects:
- Established in 1727 by Sawai Jai Singh II, Jaipur, known for its vibrant culture, dedicates a lane at the Tripoliya Bazaar to the Manihaar community.
- Named "Manihaaron ka Raasta," this lane remains a hub for selling lac bangles, jewellery, and Gulaal Gota, preserving the city's artistic legacy to this day.
- In the past, kings would ride through the city on elephant backs on Holi and toss Gulaal Gotas to the public, and the erstwhile royal family ordered Gulaal Gota at its palace for the festival.
- Established in 1727 by Sawai Jai Singh II, Jaipur, known for its vibrant culture, dedicates a lane at the Tripoliya Bazaar to the Manihaar community.
- Challenges and Future Prospects:
- The demand for lac-only bangles has fallen, as Jaipur has become a hub of factories producing cheap, chemical-based bangles.
- The government of India has provided "artisan cards" to Lac Bangle and Gulaal Gota makers, allowing them to avail benefits from government schemes.
- Some Gulaal Gota makers have demanded a Geographical Indication (GI) tag to safeguard their product against imitation and boost awareness of its location-specific exclusivity.
Unique Holi Traditions Across India:
- Holla Mohalla in Punjab:
- Integral to Sikh tradition, Holla Mohalla is observed in Anandpur Sahib with martial arts demonstrations, poetry, and kirtans.
- Phaguwa in Bihar:
- Phaguwa, also known as Phagwah or Phalgunotsava, celebrates the arrival of spring and the harvest season.
- Folk songs and Holika Dahan precede the colourful festivities, creating a vibrant environment.
- Phaguwa, also known as Phagwah or Phalgunotsava, celebrates the arrival of spring and the harvest season.
- Lathmar Holi in Uttar Pradesh:
- Celebrated in Barsana and Nandgaon, the hometowns of Radha and Lord Krishna, Lathmar Holi reenacts a playful tale of Lord Krishna teasing Radha.
- Women playfully hit men with sticks, symbolising the enduring love between Radha and Krishna.
- Celebrated in Barsana and Nandgaon, the hometowns of Radha and Lord Krishna, Lathmar Holi reenacts a playful tale of Lord Krishna teasing Radha.
- Yaoshang in Manipur:
- A blend of Hindu and Manipuri traditions, Yaoshang features the Thabal Chongba dance (folk dance from Manipur) and sports competitions.
- The festival is generally celebrated at the same time as Holi.
- Ukuli in Kerala:
- Celebrated by the Kudumbi and Konkani communities, Ukuli in Kerala features music, dance, and turmeric colours.
- Boat races add excitement to the festivities, while praises of Lord Krishna resonate throughout the celebrations.
- Celebrated by the Kudumbi and Konkani communities, Ukuli in Kerala features music, dance, and turmeric colours.


Important Facts For Prelims
Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre
Why in News?
The Union Agriculture Minister recently launched the Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) at Krishi Bhavan in New Delhi, marking a major stride forward in the field of agricultural technology.
What is Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC)?
- About:
- The Krishi ICCC is a state-of-the-art tech-based solution housed in the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare, designed to aid in making informed decisions using multiple IT applications and platforms such as weather data from the India Meteorological Department (IMD); sowing data from Digital Crop Survey; farmer-and farm-related data from Krishi Mapper (an application for geo-fencing and geo-tagging of land); market intelligence information from the Unified Portal for Agricultural Statistics (UPAg); and yield estimation data from the General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES).
- It leverages technologies such as artificial intelligence, remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect and process granular agricultural data.
- The ICCC gives information on crop yields, production, drought situation, cropping patterns, relevant trends, outliers, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
- It also provides insights, alerts, and feedback on agriculture schemes, programs, projects, and initiatives.
- It includes map, timeline, and drill-down views, offering a comprehensive macro picture through the Krishi Decision Support System (DSS).
- This integrated visualisation facilitates quick and efficient decision-making and can be linked with the PM-Kisan chatbot in the future.
- Practical Applications:
- Farmer’s Advisory:
- The ICCC allows visualisation of GIS-based soil carbon mapping and soil health card data, enabling the generation of customised advisories for farmers regarding suitable crops and their water and fertiliser requirements.
- Drought Actions:
- The ICCC correlates yield data with weather and rainfall information, facilitating proactive decision-making in response to changes in yield from specific regions.
- Crop Diversification:
- Analysis of crop diversification maps and field variability for paddy assists in identifying regions with potential for diversified cropping, enabling tailored advice for farmers.
- Farm Data Repository:
- The Krishi Decision Support System (K-DSS) acts as an agriculture data repository, supporting evidence-based decision-making and the preparation of customised advisories for farmers.
- Validation of Yield:
- The ICCC validates yield data captured through Krishi MApper with data generated through the General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES) application for a plot, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
- Farmer’s Advisory:
- Way Forward:
- ICCC can create an ecosystem for generating individual farmer-level advisories through apps like Kisan e-mitra and a chatbot developed for PM-Kisan beneficiaries.
- The Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence based system will identify a farmer through their mobile number or Aadhaar, match it with their field information from land records, historical crop sowing information, and weather data from IMD, and generate a customised advisory in the local language using the Bhashini platform for translation into several Indian languages.
- ICCC can create an ecosystem for generating individual farmer-level advisories through apps like Kisan e-mitra and a chatbot developed for PM-Kisan beneficiaries.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In the context of India’s preparation for Climate -Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements:
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
The nation-wide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at
- expanding the cultivable area under irrigation.
- enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality.
- checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


Rapid Fire
India's Foreign Direct Investment Trends
The Finance Ministry has released a comprehensive review shedding light on India's foreign direct investment (FDI) landscape, revealing both declines and hopeful prospects.
- India's net FDI inflows dropped by almost 31% to USD 25.5 billion over the first ten months of 2023-24.
- Overall global FDI flows rose by 3% to an estimated USD 1.4 trillion in 2023, but flows to developing countries fell by 9% due to economic uncertainty and higher interest rates.
- While a modest increase in global FDI flows is anticipated in 2024, significant risks remain, including geopolitical tensions, high debt levels, and global economic uncertainties.
- Around 65% of India's FDI equity inflows were observed in services, drugs and pharmaceuticals, construction (infrastructure activities), and non-conventional energy sectors.
- The Netherlands, Singapore, Japan, the USA, and Mauritius accounted for approximately 70% of the total FDI equity inflows into India.
Read more: Foreign Direct Investment


Rapid Fire
Heat Wave Conditions in Coastal Regions of Kerala
Recently, the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) issued an alert warning of heatwave for 40°C in Thrissur and 39°C in Kollam and Palakkad districts of Kerala.
- Heatwaves are prolonged periods of excessively hot weather that can cause adverse impacts on human health, the environment, and the economy.
- India, being a tropical country, is particularly vulnerable to heat waves.
- IMD Criteria for Declaring Heat Wave in India:
- Heat Wave is considered when the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C for Plains and at least 30°C for Hilly regions.
- The criteria for the coastal station maximum temperature should be greater than or equal to 37°C.
- If the normal maximum temperature of a station is less than or equal to 40°C, then an increase of 5°C to 6°C from the normal temperature is considered to be a heat wave condition.
Read More: Heat Waves and Heat Dome


Rapid Fire
Revised Wages under MGNREGS
The Union government recently announced revised wages under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), prompting varied responses from different states.
- Several states reported an increase in wages ranging from 8% to 10%. The Union Rural Development Ministry obtained special permission from the Election Commission for this routine annual exercise, considering the constraints imposed by the model code of conduct.
- Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Goa recorded notable hikes ranging from 8% to 10.5%.
- Haryana offers the highest wages at Rs 374 per day, whereas Uttar Pradesh has one of the lowest at Rs 237.
- The revised rates will come into effect from 1st April 2024.
- Despite the revision, the nation-wide average days of employment provided per household in the financial year 2023-24 remained at 51 days, falling short of the promised 100 days.
- Launched in 2005, MGNREGA is one of the world's largest work guarantee programs, initiated by the Ministry of Rural Development.
Read more: Social Audit of MGNREGA Scheme


Rapid Fire
Statio Shiv Shakti as Name of the Chandrayaan-3 Landing Site
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) working group for Planetary System Nomenclature has approved the name ‘Statio Shiv Shakti’ for the landing site of Chandrayaan-3’s Vikram lander.
- Significance of ‘Statio Shiv Shakti’:
- Earlier, the Prime Minister emphasised that the "Shiv Shakti" point on the moon signifies a connection spanning from the Himalayas to Kanyakumari.
- "Shiv" symbolizes determination for the betterment of humanity.
- "Shakti" represents the strength to achieve these resolutions.
- Other Key Locations:
- Prime Minister previously designated the location of Chandrayaan-2's lander crash in September 2019 as "Tiranga Point."
- Former President A.P.J. Abdul Kalam proposed naming the site where the Chandrayaan-1 moon impact probe landed in November 2008 as "Jawahar Point."
Read more: Chandrayaan-3 Successfully Lands on Moon's South Pole