Facts for UPSC Mains
Shaping India’s AI-Driven Economy
Why in News?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to drive India’s next phase of economic growth, with NITI Aayog estimating that AI could add USD 500–600 billion to GDP by 2030.
What does NITI Aayog Reports Say about AI’s Impact on the Indian Economy??
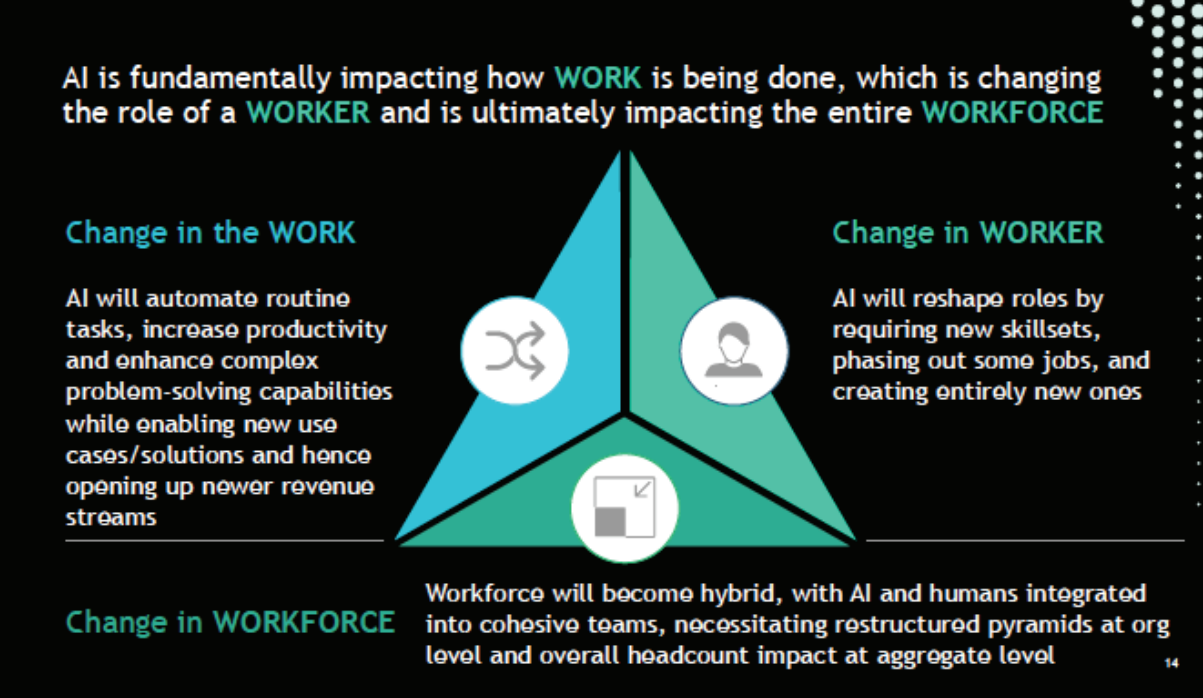
- Roadmap for Job Creation in the AI Economy: This report presents India’s strategic plan to address the disruptions caused by AI, aiming to position the country as the global hub for AI-driven workforce development.
- It introduces the 3W framework for AI and outlines its potential impact on work, workers, and the workforce.
- Roadmap on AI for Inclusive Societal Development: This report focuses on utilizing cutting-edge technologies to transition informal workers into a more formal, empowered, and future-ready labor force.
- It emphasizes AI’s potential to enhance inclusivity and foster sustainable development.
- AI as Both a Challenge and Opportunity for India: AI presents both challenges and opportunities for India’s economy.
- While it disrupts traditional formal jobs, it simultaneously provides a unique opportunity to formalize and significantly improve the productivity of the vast informal workforce.
What Potential does AI Hold for India's Economic Transformation?
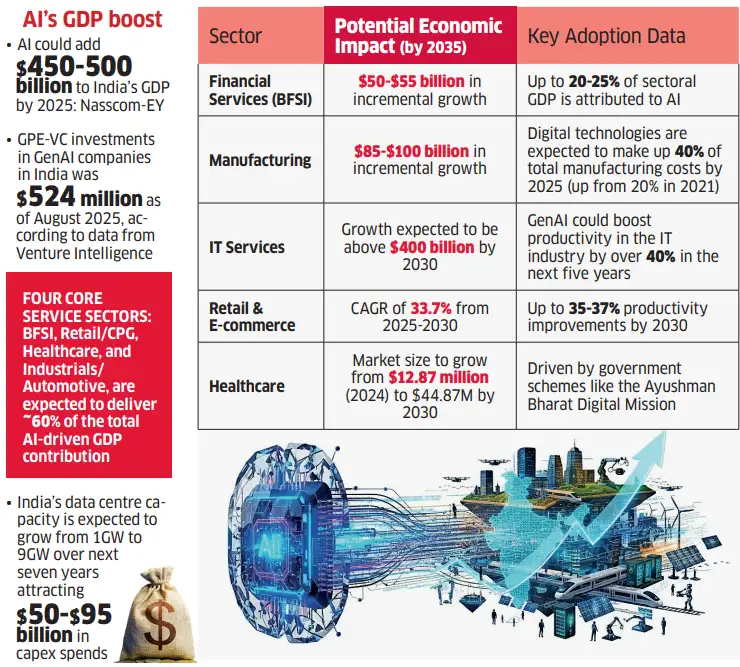
- Job Creation in New, High-Value Sectors: India could create up to 4 million new jobs by 2031, especially in tech and customer service, with jobs ranging from Prompt Engineers to Quantum ML Engineers and advanced AI model developers.
- Enhanced Global Economic Standing: India can become the “AI workforce capital of the world” by shifting from traditional IT services to AI-driven work and innovation, using its strong digital talent base.
- The proposed India AI Talent Mission can also help reverse brain drain, similar to efforts in Singapore and the UAE.
- New Revenue Pools and Industries: It opens new avenues like AI-driven drug discovery and smart manufacturing, while its convergence with Quantum Computing, IoT, and 5G is creating opportunities in smart cities and logistics optimization.
- Productivity Gains: AI boosts efficiency and global competitiveness, delivering 10–20% productivity gains in software development and reducing costs in customer service through chatbots and real-time translation.
- Foundation for a Future-Ready Economy: Creating an open-source India AI Commons will provide datasets, models, and benchmarks to democratize innovation, while India’s AI Compute Grid will offer shared high-performance computing access to boost local R&D and retain talent.
What are the Challenges Posed by AI to the Indian Economy?
- Job Losses in the Tech Sector: As per Niti Aayog, the IT services workforce may drop from 7.5–8 million (2023) to 6 million by 2031.
- Overall, 60% of formal jobs in India face automation risk by 2030, with the IT and BPO sectors especially vulnerable due to routine, scalable tasks.
- Education System Gaps: India faces gaps in computer science education, with limited access and outdated AI curricula that miss emerging concepts like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
- These weaknesses contribute to low research output, with AI patent shares dropping to under 5%, and fewer than 500 AI-related PhDs produced each year.
- AI Talent Supply-Demand Gap: AI talent demand is rising at 25% CAGR (from 800,000 to 1.25 million by 2026), while supply grows at only 15% CAGR.
- India also faces net negative talent migration, losing top AI researchers at a rate of 1.55 per 10,000.
- Broader Systemic Risks: India risks losing competitiveness and strategic ground to countries like China, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Singapore, while socially, limited protection for 400 million informal workers and uneven impacts across regions and groups create major challenges.
What Recommendations has NITI Aayog Made for the Sustainable Use of AI in India?
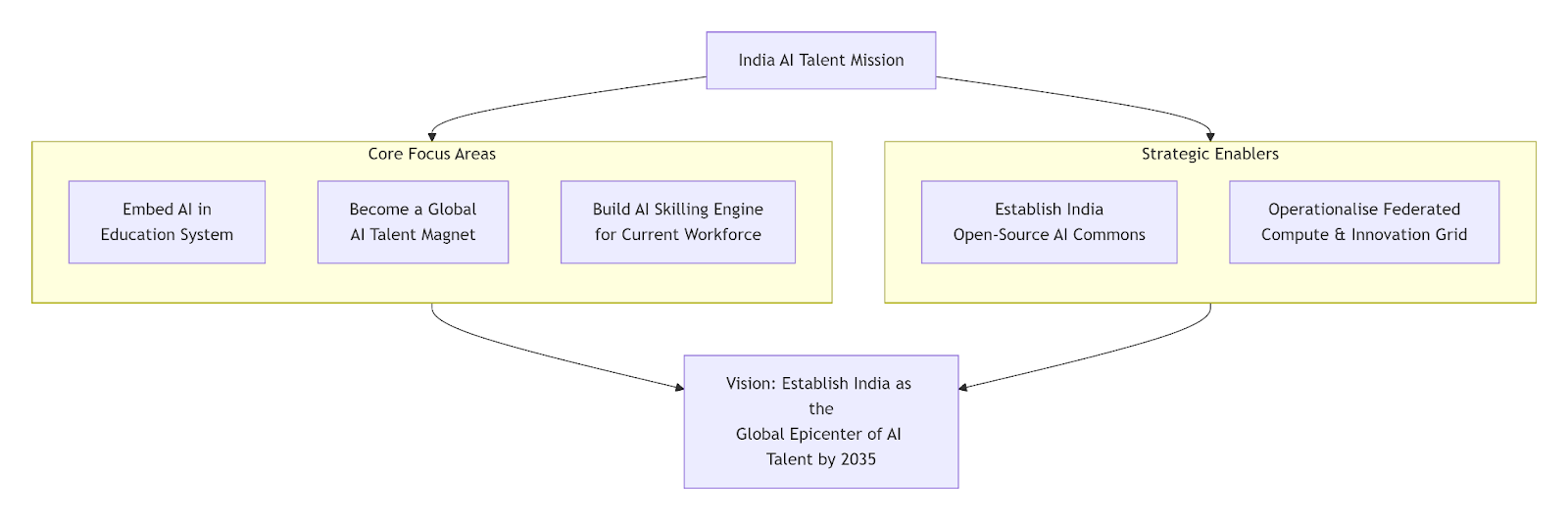
- Embed AI in the Education System: Integrate AI learning from schools, expand AI-focused higher education, and increase AI PhD fellowships to strengthen research, while ensuring curricula stay updated through faculty–industry collaboration.
- Become a Global AI Talent Magnet: Offer competitive grants, high salaries, and priority access to the national computer grid to retain and bring back Indian AI researchers, and introduce a dedicated AI talent visa to attract global experts.
- Building an AI Skilling Engine: Launch national reskilling programs by scaling NAPS (National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme) and PMKVY (Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana) for widespread AI literacy, and introduce flexible AI master's and doctoral pathways for working professionals to upgrade into high-skill roles.
- Establishing India Open-source AI Commons: Create a central AI commons with high-quality datasets, models, and benchmarks, incentivize data contribution from universities and ministries, and ensure trust and transparency through reliable validation tools.
- Federated National Compute & Innovation Grid: Consolidate fragmented HPC resources into a unified compute grid, and provide tiered, affordable access for students, startups, and researchers to support advanced model training and reduce dependence on foreign infrastructure.
Conclusion
AI offers India a transformative economic opportunity—NITI Aayog estimates USD 500–600 billion GDP boost by 2030—if paired with reskilling, stronger AI education, robust data governance, open-source commons, and national computational infrastructure. Strategic policy, inclusive skilling, and research investments are essential to mitigate job displacement and regional inequality for sustainable growth.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. Artificial Intelligence is a double-edged sword for the Indian economy. Critically analyze this statement and suggest a strategic roadmap for India to become a global leader in inclusive AI. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the projected contribution of AI to India’s GDP by 2030?
NITI Aayog estimates that AI could contribute USD 500-600 billion to India’s GDP by 2030 through productivity and innovation gains.
2. How many jobs could AI create in India by 2031?
AI could generate up to 4 million new jobs by 2031, particularly in tech, customer service, and high-value AI roles.
3. How does AI pose a risk to India's formal job sector?
NITI Aayog highlights a risk of large-scale job displacement, with the IT services workforce potentially shrinking from 7.5-8 million to 6 million by 2031, affecting 60% of formal sector jobs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does Al help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of AI in healthcare? (2023)
Facts for UPSC Mains
Women Soldiers to Join Territorial Army Battalions
Why in News?
The Directorate General of Territorial Army has decided to induct women soldiers into Territorial Army (TA) Home & Hearth (H&H) Infantry battalions for the first time, marking a major step in expanding women’s roles in the defence forces.
What is the Territorial Army (TA)?
- About: The Territorial Army (TA) is a part-time voluntary military force that supports and augments the Regular Indian Army.
- It is based on a Citizen Soldiers’ army (‘Sons of Soil’) concept and officers undergo Annual Training on basic military skills.
- It functions under the Territorial Army Act, 1948 and allows trained civilian volunteers to serve in uniform while continuing their regular professions.
- Background: The roots of the TA trace back to the Volunteer Forces of 1857 formed after the First War of Independence in 1857.
- The Indian Defence Force Act of 1917 made universities raise defence units, with Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose and Jawaharlal Nehru joining the Calcutta University Corps in 1918.
- The Force had two parts, the European Auxiliary Force and the Indian Branch, which later became the Indian Territorial Force.
- After Independence, the Territorial Army Act, 1948 was passed, The TA was formally inaugurated on 9th October 1949 by first Indian Governor General Shri C Rajagopalachari ( now celebrated as Raising Day of Territorial Army).
- The Indian Defence Force Act of 1917 made universities raise defence units, with Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose and Jawaharlal Nehru joining the Calcutta University Corps in 1918.
- Evolution: The TA began with many unit types, but most were later merged or disbanded.
- It now includes Infantry Battalions, Home & Hearth units in J&K and the North-East, Ecological Battalions, Engineer units for Line of Control fencing, departmental units like Railway, and the Composite Eco Task Force for the National Mission for Clean Ganga.
- Significance: Relieves the Regular Army from static duties so that full-time soldiers can focus on core combat tasks.
- Assists in counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations, especially through TA Home & Hearth battalions in J&K and the North-East.
- Provides support during natural disasters, industrial unrest, and restoration of essential services.
- Plays a major role in environmental protection, afforestation, and reversing land degradation through TA Eco Battalions.
- Acts as a reserve force capable of being mobilised during national emergencies, war, and large-scale internal disturbances.
- Enhances civil–military coordination, as members are civilians who bring diverse skills to national service.
What is the Significance of Inducting Women into Territorial Army H&H battalions?
- The Territorial Army began commissioning women officers in 2019, allowing them to serve in Ecological Task Force units, oil sector TA units and the Railway Engineer Regiment.
- With the positive experience gained, the Army has now decided to expand their roles further and is preparing to induct women soldiers into Home & Hearth battalions, opening the door to wider operational responsibilities.
- It expands operational opportunities for women, enhances human resources for internal security and disaster response, and advances gender inclusion in India’s defence forces.
Women in Defence Forces
- Early Military Roles: Women first joined through the Military Nursing Service (1888) and later as doctors in the Indian Army Medical Corps (1958) with regular commissions.
- Non-Medical Entry: In 1992, the Women Special Entry Scheme (WSES) opened non-combat roles in branches like the Army Education Corps, Signals, Intelligence, and Engineers for Short Service Commission (SSC).
- Army Act, 1950 restricted women’s roles, allowing them only in notified branches such as Army Postal Service, Judge Advocate General’s (JAG) department, Army Education Corps (AEC), Ordnance Corps, and Service Corps, and Service Corps.
- Short Service Commission (SSC): In 2005, the SSC system was introduced, offering a 14-year tenure to women officers and marking a more formalized career structure.
- Permanent Commission Milestone: Women were first granted Permanent Commission in 2008 in limited branches like JAG and AEC.
- The Supreme Court of India in 2020 Babita Puniya judgment, mandated Permanent Commission in all arms where SSC exists, enabling women to hold command roles.
- The Supreme Court of India in 2020 Babita Puniya judgment, mandated Permanent Commission in all arms where SSC exists, enabling women to hold command roles.
- Women in Combat Roles: IAF inducted women fighter pilots in 2016, making combat roles a permanent scheme in 2022.
- Agnipath Scheme (2022): Women included as Agniveers across the Army, Navy, and Air Force, expanding soldier-level opportunities.
- Current Representation: Women constitute about 4% of the Army. Since 2022, the Navy has opened all branches, including submarines and aviation, to women officers, with several already serving onboard ships and in combat aviation roles.
- Key Achievements: Col. Sofiya Qureshi and Wg Cdr. Vyomika Singh led roles in Operation Sindoor.
- Lt. Cdr. Dilna K and Lt. Cdr. Roopa A completed Navika Sagar Parikrama II, a 25,600-nautical-mile global expedition.
Conclusion
The induction of women soldiers into the Territorial Army's Home & Hearth battalions marks a significant step towards gender inclusion in India's defense forces. This move reflects the ongoing evolution of women’s roles in India's armed forces, paving the way for greater equality and empowerment.
| Read more: Women in Indian Armed Forces |
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Breaking gender barriers in the armed forces is not only a question of equality, but also operational necessity. Discuss. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Territorial Army (TA)?
The TA is a part-time voluntary military force under the Territorial Army Act, 1948, that supports and augments the Regular Indian Army while allowing civilians to serve part-time.
2. When is Territorial Army Raising Day celebrated?
Territorial Army Raising Day is observed every year on 9th October, marking its formal inauguration in 1949 by C. Rajagopalachari.
3. Why is induction of women in TA significant?
It expands operational opportunities for women, enhances human resources for internal security and disaster response, and advances gender inclusion in India’s defence forces.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In the context of the Indian defence, what is ‘Dhruv’? (2008)
(a) Aircraft-carrying warship
(b) Missile-carrying submarine
(c) Advanced light helicopter
(d) Intercontinental ballistic missile
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)
Facts for UPSC Mains
Revisiting Gender Neutrality in POCSO Act, 2012
Why in News?
The Supreme Court issued notice in a case where a woman is accused of ‘penetrative sexual assault’ on a minor boy under Section 3 of the POCSO Act, 2012.
- The case has renewed debate on the Act’s gender neutrality, especially whether it covers female perpetrators of child sexual abuse.
What is the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012?
- About: POCSO Act, 2012 was enacted by the Ministry of Women and Child Development to address the heinous crimes of sexual abuse and exploitation of children.
- It was amended in 2019 that increased punishments, including the death penalty for aggravated penetrative sexual assault of a child.
- Salient Features:
- Gender Neutrality: The Act is gender-neutral and safeguards all children, irrespective of gender.
- Definition of a Child: It defines a child as any person below 18 years of age.
- Coverage of Abuse: The Act covers penetrative and non-penetrative assault, sexual harassment, and pornography. Offences are aggravated if committed by someone in trust or authority or against a mentally ill child, and child trafficking for sexual purposes is also punishable.
- Graded Punishments: Punishments range from 10 years to life imprisonment for penetrative sexual assault and 20 years to life for aggravated cases, with stricter terms if the child is under 16.
- Use, possession, attempt, and abetment of offences, including child pornography, are also punishable, with fines or imprisonment up to 7 years depending on severity and intent.
- Judicial Process: The Act requires Special Courts to try offences. It ensures that the evidence of the child is recorded within 30 days, and the trial is completed within 1 year, wherever possible.
- Scope and Overriding Effect: The POCSO Act has an overriding effect over other laws if there is inconsistency. It applies only to child survivors and adult offenders, while cases of child-on-child offences or child-on-adult offences are governed by the Juvenile Justice Act, 2000.
Does the POCSO Act, 2012 Uphold Gender Neutrality?
- Statutory Interpretation: Section 3 of POCSO act defines penetrative sexual assault using gender-neutral terms and does not explicitly limit the offence to male perpetrators.
- The use of the pronoun ‘he’ in statutory language is governed by Section 13(1) of the General Clauses Act, 1897, which states masculine words include the feminine unless the context specifies otherwise.
- Scope of Offences: The definition includes oral, digital, and object-based penetration, which can be committed by individuals of any gender.
- Section 3(d) also criminalises inducing a child to perform a sexual act on another person — expanding applicability.
- Legislative Intent: The Ministry of Women and Child Development, in a written response to a question in the Lok Sabha, stated unambiguously that POCSO ‘is a gender neutral Act’.
- The Statement of Objects and Reasons of the POCSO Amendment Bill, 2019 explicitly confirms that the POCSO Act is gender-neutral.
How can India Ensure Balanced Legal and Policy Frameworks for Child Protection?
- Strengthening the Legal Framework: Resolve definitional gaps in the POCSO Act, 2012 especially regarding gender neutrality, to ensure uniform and fair application of the law.
- Additionally, harmonize POCSO, JJ Act, and BNS while introducing nuanced sentencing guidelines that balance stringency with reformative justice.
- Robust Institutional Capacity: Mandate specialized training for all stakeholders and strengthen infrastructure, including Special Courts and Forensic Science Laboratory (FSL) capacity, to ensure faster and child-sensitive case handling.
- Proactive and Preventive Policies: Mandate strict child protection policies, including annual Personal Safety Education (PSE) for students. Use technology to enhance monitoring through a national child-protection database, data analytics, and safe, anonymous reporting platforms for children.
- Address Digital Age Challenges: Strengthen responses to Online Child Sexual Abuse and Exploitation (OCSAE) through updated protocols, specialized cyber cells, and collaboration with tech companies to remove content and identify victims.
Conclusion
The POCSO Act, 2012 is gender-neutral, protecting all children from sexual abuse, harassment, and exploitation. Its provisions, intent, and judicial interpretation allow prosecution of offenders of any gender, ensuring justice and comprehensive child protection.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. Discuss the significance of the POCSO Act, 2012 in safeguarding children from sexual offences in India. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the POCSO Act, 2012?
It is a gender-neutral law enacted to protect children under 18 from sexual abuse, harassment, and exploitation, with provisions for Special Courts and child-friendly trials.
2. Is the POCSO Act applicable to female offenders?
Yes, statutory interpretation and legislative intent confirm gender neutrality, allowing prosecution of both male and female perpetrators.
3. How does the Act ensure speedy and child-friendly trials?
Evidence recording within 30 days, trial completion within 1 year, in-camera proceedings, female officers for statements, and immediate rehabilitation via shelter homes or hospitals.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are envisaged by the Right against Exploitation in the Constitution of India?(2017)
- Prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour
- Abolition of untouchability
- Protection of the interests of minorities
- Prohibition of employment of children in factories and mines
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016)
Important Facts For Prelims
Tier II Bonds
Why in News?
Several banks are actively issuing Tier II bonds to bolster their capital adequacy ratios (CAR) as required under Basel III norms, with total issuances expected to reach Rs 25,000 crore in FY 2025–26.
What are Tier II Bonds?
- About: Tier II bonds are subordinated debt instruments banks issue to boost capital and support operations. They count as Tier II (supplementary) capital under Basel-III and help improve the CAR.
- CAR indicates a bank’s financial strength, with a higher ratio providing a stronger buffer against distress. CAR = (Eligible Capital ÷ Risk-Weighted Assets) × 100%.
- Tier II Bonds are different from Tier I Bonds as they strengthen a bank’s supplementary capital, whereas Tier I (AT1) Bonds strengthen its core capital (equity and retained earnings).
- Key Features of Tier II Bonds:
- Maturity: They are typically long-term instruments with original maturities of at least 5 years.
- Subordination: Tier II bondholders are paid after all depositors, senior debt holders, and general creditors in the event of a liquidation. However, they rank above equity holders.
- Coupon Payments: They pay regular interest (coupons) and generally offer higher coupon rates than senior bonds due to higher risk.
- Call Options: Most Tier II bonds include a call option, allowing the bank to redeem the bonds after a specified period (e.g., 5 or 10 years).
- Loss Absorbency (Gone-Concern Capital): Tier I capital is considered "gone-concern" capital, meaning it is intended to absorb losses if a bank fails and is in the process of being wound up.
- This is in contrast to Tier I capital, which absorbs losses on a "going-concern" basis while the bank is still operational.
- Issued By: Both public and private banks issue Tier II bonds to meet regulatory capital requirements, support business expansion, and comply with CAR norms without issuing new equity and diluting shareholders.
- Investors in Tier II Bonds: Institutional investors such as insurance companies, pension funds, mutual funds, and hedge funds, as well as retail investors through platforms or public issues, invest in Tier II bonds.
What is the Difference Between Tier I and Tier II Bonds?
|
Feature |
Tier I Bonds (Commonly called Additional Tier 1 or AT1) |
Tier II Bonds (Subordinated Debt) |
|
Core Purpose |
To act as shock absorbers during ongoing stress. They are the first line of defense after equity. |
To act as a loss-absorbing buffer during liquidation or winding up. |
|
Nature & Seniority |
Perpetual; they have no maturity date. They are the most junior form of debt, just above equity. |
Have a fixed maturity. They are senior to Tier I but junior to regular debt. |
|
Trigger Mechanism |
Can be written down to zero or converted to equity if the bank's Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio falls below a pre-specified level. |
Loss absorption typically only happens during the point of non-viability or liquidation, after Tier I is used. |
What are Basel Norms?
- About: Basel Norms are a set of international banking regulations developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) to strengthen the global financial system by ensuring that banks hold enough capital to absorb unexpected losses.
- Pillars of Basel Norms: The Basel framework rests on three pillars:
- Pillar 1 – Minimum Capital Requirements: Banks must hold capital proportional to their risk-weighted assets (RWA), with riskier assets requiring more capital.
- Pillar 2 – Supervisory Review: Regulators assess each bank’s internal risk processes and ensure capital stays above minimum requirements.
- Pillar 3 – Market Discipline: Banks must disclose their risk profiles and capital levels to promote transparency and encourage prudent behavior through market scrutiny.
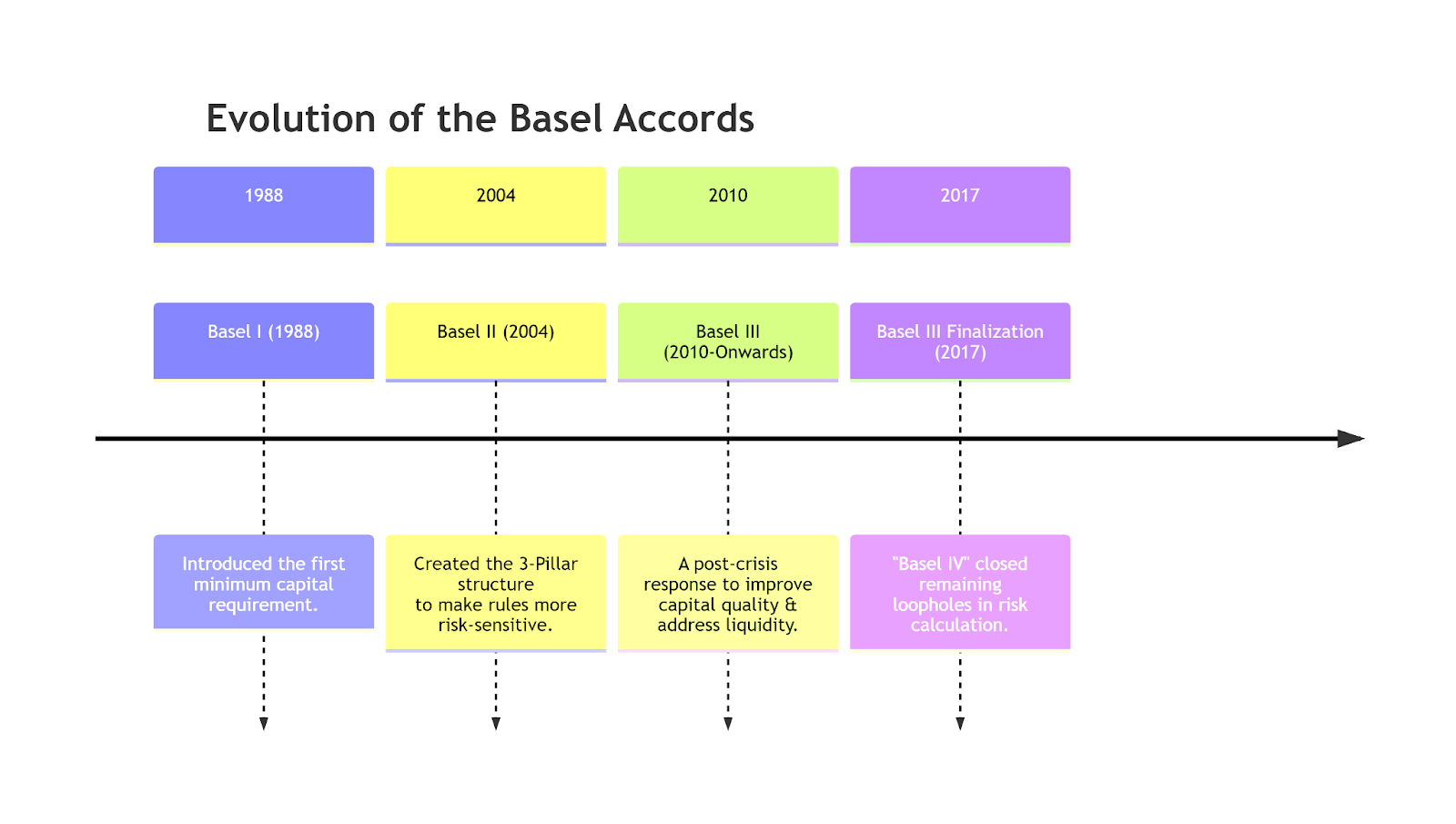
- Evolution: Basel has evolved from Basel I, II, III, and now IV to strengthen the banking system and respond to financial crises.
- Basel I (1988) introduced a capital measurement system focused on credit risk and risk-weighted assets, setting minimum capital requirements for banks.
- Basel II (2004) refined this by adding the three-pillar framework of minimum capital, supervisory review, and market discipline.
- Basel III (2010), developed after the 2007–08 crisis, strengthened banks’ capital base, liquidity, and leverage standards.
- Basel IV (2017) aims to tighten remaining gaps by making RWA calculations more consistent across banks and limiting the misuse of internal models to reduce capital requirements.
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS)
- About: BCBS is the global standard-setter for banking regulation, creating frameworks like Basel I–III to strengthen financial stability.
- It was formed in 1974 after the Herstatt crisis, when a German bank collapsed.
- Membership: Includes 45 members from 28 jurisdictions, covering major advanced and emerging economies including India.
- Functions: Sets banking standards, promotes supervisory cooperation, monitors implementation, and identifies global financial risks.
- Governance: The BCBS operates under the guidance of the Group of Central Bank Governors and Heads of Supervision (GHOS).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are Tier II bonds?
Tier II bonds are subordinated debt instruments counted as supplementary capital under Basel-III, issued by banks to bolster the Capital Adequacy Ratio without issuing equity.
2. What is the primary objective of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS)?
The BCBS sets international banking standards (like Basel III) to promote financial stability by ensuring banks maintain sufficient capital, improve risk management, and enhance supervisory practices globally.
3. Name the three pillars of the Basel regulatory framework.
The three pillars are: Pillar 1 - Minimum Capital Requirements, Pillar 2 - Supervisory Review Process, and Pillar 3 - Market Discipline.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is the amount that banks have to maintain in the form of their own funds to offset any loss that banks incur if the account-holders fail to repay dues.
- CAR is decided by each individual bank.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q. ‘Basel III Accord’ or simply ‘Basel III’, often seen in the news, seeks to (2015)
(a) develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity
(b) improve banking sector’s ability to deal with financial and economic stress and improve risk management
(c) reduce the greenhouse gas emissions but places a heavier burden on developed countries
(d) transfer technology from developed countries to poor countries to enable them to replace the use of chlorofluorocarbons in refrigeration with harmless chemicals
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire
India Re-Elected to Codex Executive Committee
India was unanimously re-elected to the Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CCEXEC) at 48th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC48) securing its seat for Asia until CAC50 in 2027, strengthening its role in setting global food safety and quality standards.
- Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC): It was created in 1963 by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO), sets global food safety and quality standards to protect consumers and ensure fair food trade. It has 189 members, and India joined in 1964.
- CAC is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- CCEXEC oversees the management of the CAC, guides strategic planning, and manages standards development.
- India is a member of CCEXEC in its capacity as the Regional Coordinator for Asia (CCASIA).
- Codex Alimentarius: The Codex Alimentarius, or "Food Code", adopted by CAC is a collection of international standards, guidelines, and codes covering food hygiene, additives, pesticide residues, contaminants, labelling, and inspection.
- The Agreement on Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) of the World Trade Organization (WTO) recognizes Codex standards, guidelines and recommendations as reference standards for international trade and trade dispute settlement
- India and CAC: India has been chairing the Codex Committee on Spices and Culinary Herbs (CCSCH) since its inception in 2014, with the Spices Board of India serving as the secretariat.
- India actively engaged in discussions around the Codex Strategic Plan 2026–2031, advocating for SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) Key Performance Indicators.
| Read more: India’s Millet Standards Recognised at Codex Alimentarius Commission |
Rapid Fire
75th Anniversary of National Sample Survey (NSS)
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the National Industrial Classification (NIC) 2025 during the ‘Culmination Ceremony' of the 75th anniversary of National Sample Survey (NSS).
- NIC 2025: The NIC is a fundamental tool used in statistical surveys, censuses, economic research, and policy formulation.
-
It groups businesses and activities into structured categories so data can be collected, compared, and analysed consistently across the country.
- India’s classification system, introduced in 1962 and later updated as NIC 1970, 1987, 1990, 1998, 2004 and 2008, has now been comprehensively revised to reflect the country’s evolving economic structure.
- The NIC 2025 is in line with International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC) Revision 5, developed by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD).
-
National Sample Survey (NSS)
- The NSS was established in 1950 on the recommendation of the National Income Committee (1949), chaired by Professor P.C. Mahalanobis, which had identified major gaps in socio-economic data in the country.
- NSS is headed by a Director General, it conducts large-scale sample surveys across India on socio-economic subjects, including household surveys, Annual Survey of Industries (ASI), and rural–urban price collection.
- It supports improvement of crop statistics by supervising area enumeration and crop estimation surveys of State agencies.
- The NSS has Four Divisions:
-
Survey Design and Research Division (SDRD), Kolkata.
-
Field Operations Division (FOD), Delhi/Faridabad.
-
Data Processing Division (DPD), Kolkata.
-
Survey Coordination Division (SCD), New Delhi.
-
| Read more: Review of Methodology of National Surveys |
Rapid Fire
UNSC Approves Trump's Plan for Gaza
The UN Security Council (UNSC) adopted Resolution 2803, endorsing the Trump Gaza Peace Plan and authorizing the establishment of an International Stabilization Force (ISF) in Gaza.
- The resolution passed with 13 votes in favor and none against, although China and Russia abstained.
- Trump Gaza Plan: The Plan, announced in September 2025, aims to transform Gaza from a conflict zone to a peaceful region. It outlines a phased approach:
- Phase 1: Ceasefire, hostages' release, and partial Israeli troop withdrawal.
- Subsequent Phases: Demilitarization, transitional governance, and reconstruction, with the goal of creating a "deradicalized, terror-free zone."
- BoP & International Stabilization Force (ISF): A Board of Peace (BoP), chaired by President Trump, will oversee Gaza’s transition, reconstruction, and governance reforms until December 2027, after which control will transfer to a reformed Palestinian Authority.
- The BoP is authorized to establish the International Stabilization Force (ISF), responsible for securing Gaza’s borders, supporting demilitarization, protecting civilians, and facilitating humanitarian aid.
| Read More: USA's Comprehensive Plan to End Gaza Conflict |
Rapid Fire
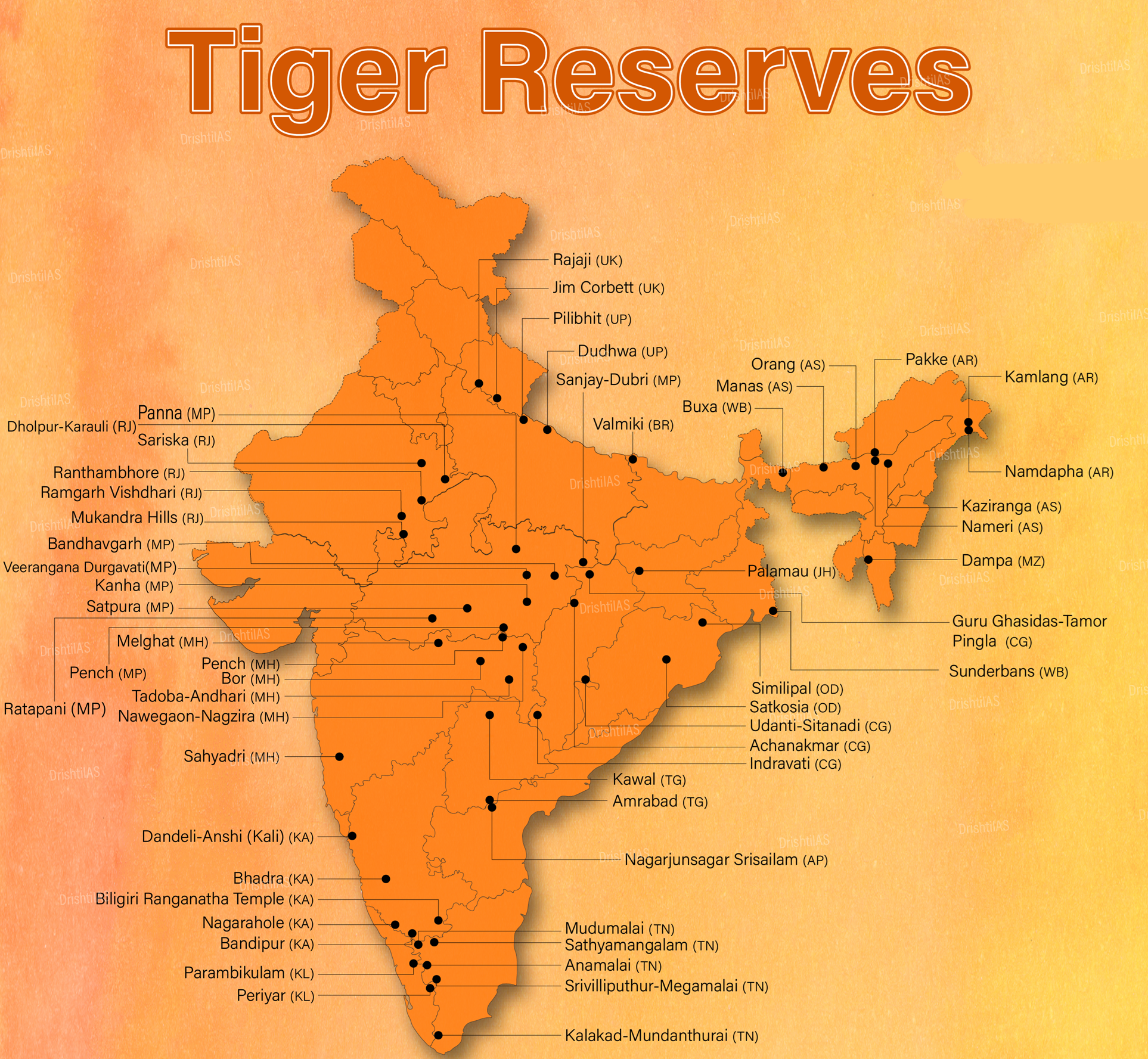
SC Calls for Stronger Tiger Conservation Measures
The Supreme Court of India has directed Uttarakhand to fully restore the Corbett Tiger Reserve after findings of illegal tree-felling and construction, and issued reforms for tiger conservation and management across all States.
- Uttarakhand must restore Corbett, submit a restoration plan within 2 months, demolish illegal structures within 3 months, and file a compliance report within 1 year.
- SC Directive to States:
- SC has ordered all States to notify the core and buffer areas of every tiger reserve within six months, and to declare Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) around these reserves within one year.
- To prepare a Tiger Conservation Plan within three months and directed to ban tiger safaris in core and critical tiger habitats.
- To treat human–wildlife conflict as a potential natural disaster and ensure stronger compensation systems, including an ex-gratia payment of Rs 10 lakh to victims under the Centrally Sponsored Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats scheme.
Corbett Tiger Reserve
- About: Corbett Tiger Reserve is Asia’s first national park established in 1936, renowned for its biodiversity including the world's highest density of tigers.
- It was established as Hailey National Park and later renamed in 1956 to honour Jim Corbett, the hunter-turned-conservationist who helped create it.
- It became the first national park to be included under Project Tiger in 1973.
- Location: Corbett lies in the Himalayan foothills of Uttarakhand. It has an undulating landscape with several valleys through which the Ramganga, Pallaen, and Sonanadi rivers flow.
- The reserve falls largely in the Bhabar and lower Shivalik region, known for its porous soil and deep water table.
- Flora & Fauna: Corbett’s vegetation includes moist and dry deciduous forests dominated by sal, mixed woodland, riparian vegetation, and shrub species.
- The reserve is known for its open grasslands, called chaurs, formed from old settlements and clearings. Important chaurs such as Dhikala and Bijrani support rich wildlife.
- Tigers and elephants are the flagship species, accompanied by leopards, smaller carnivores, sambar, hog deer, spotted deer, and a variety of birds and reptiles such as gharials and crocodiles.
| Read more: Corbett Tiger Reserve: Uttarakhand |