International Relations
USA's Comprehensive Plan to End Gaza Conflict
- 04 Oct 2025
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Gaza Strip, Hamas, Mediterranean Sea, India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, Chabahar Port, Haifa Port.
For Mains: The US President unveiled a 20-point Gaza Peace Plan titled “Comprehensive Plan to End the Gaza Conflict” aimed at stabilizing the region, disarming Hamas, and rebuilding the Gaza strip.
Why in News?
The US President unveiled a 20-point Gaza Peace Plan titled “Comprehensive Plan to End the Gaza Conflict” aimed at stabilizing the region, disarming Hamas, and rebuilding the Gaza strip.
- While Hamas has not yet accepted the plan, it has been welcomed by several Arab nations and carries important implications for regional stability and Indian interests.
What are the Key Highlights of the USA's Gaza Peace Plan?
- Disarmament and Surrender of Hamas: The plan’s core goal is the disarmament of Hamas, making Gaza a terror-free zone. Hamas members will receive amnesty for peaceful coexistence or safe passage to countries like Jordan, Egypt, Qatar, and Iran, with no forced eviction of Gaza residents.
- International Security Force: A temporary International Stabilization Force (ISF) will be deployed to train Palestinian police and secure Gaza.
- The Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) will withdraw based on agreed milestones, maintaining only a "security perimeter"—a potential buffer zone—until the threat is neutralized.
- A New Governance Structure: Gaza will be governed by a temporary, "technocratic, apolitical Palestinian committee" overseen by an international "Board of Peace," to be chaired by Trump himself.
- Humanitarian Aid and Hostage Exchange: The plan mandates an immediate surge in humanitarian aid for rebuilding infrastructure.
- A hostage-prisoner swap is also outlined: all hostages will be returned within 72 hours of Israel's acceptance, in exchange for the release of Palestinian prisoners.
- Regional Guarantees: Many muslim and Arab nations, including Qatar, Jordan, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan, have jointly welcomed the plan, providing regional backing to ensure compliance.
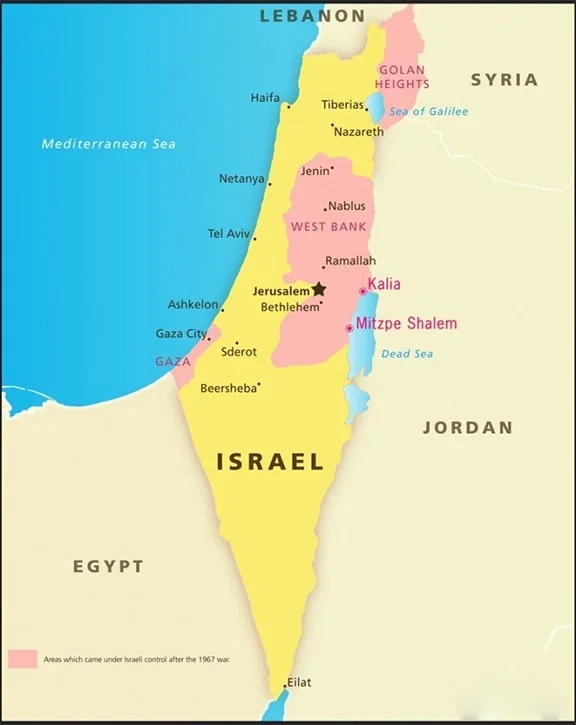
Israel-Gaza Conflict
- Historical Background:
- Balfour Declaration (1917): Issued by Britain, supporting the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, heightening tensions between the Jewish minority and Arab majority.
- Creation of Israel (1948): Following a 1947 UN proposal to divide Palestine, Jews declared Israel's independence. Arabs rejected the plan, leading to multiple wars.
- 1967 Middle East War: Israel gained control of the West Bank, Gaza, and East Jerusalem, affecting about a million Palestinians.
- Yom Kippur War (1973): Led to the Camp David Accords (1978), where Egypt became the first Arab country to recognize Israel. Israel returned the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt in 1979 but retained control over the West Bank.
- Location: The Gaza Strip is a densely populated coastal territory in west Asia, measuring about 41 km in length and 10 km in width, located along the Mediterranean Sea.
- It shares borders with Israel to the north and east, and Egypt to the southwest.
- Role of Gaza in Israel-Palestine conflict: As a strategically important region, the Gaza Strip remains at the heart of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, facing ongoing humanitarian, political, and security challenges.
- The United Nations has officially declared a famine in Gaza following a sharp escalation of the Israel-Hamas conflict, widespread displacement, and severe restrictions on humanitarian and commercial food supplies.
What Has Been India’s Policy on the Israel-Palestine Conflict?
- Historical Support for Palestine: India was among the first non-Arab countries to recognize the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people in 1974. It also recognized the State of Palestine in 1988.
- Two-State Solution: India has consistently advocated for a negotiated two-state solution, emphasizing the establishment of a sovereign, independent, and viable Palestinian state alongside Israel within recognized borders. This position is reflected in its voting patterns at the United Nations.
- De-hyphenation Policy: India has consciously moved to treat Israel and Palestine as separate, independent relationships, rather than a zero-sum game where support for one means opposition to the other.
- Consistent Diplomatic Support: India has actively supported Palestinian self-determination at the UN General Assembly and UN Security Council.
- India voted in favor of Palestine’s UNESCO membership in 2011, including contributions to the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees (UNRWA).
- Developmental Cooperation: India has provided USD 141 million in aid, including projects like the Palestine-India Techno Park and Jawaharlal Nehru Secondary Schools in Gaza.
- India signed Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) like the rehabilitation of Yasser Arafat Square and the solar grid system in Nablus.
- Strategic Importance for India: India’s engagement with Israel and Palestine supports its energy security and economic ties with the Middle East, while fostering regional stability
Conclusion
US’s 20-point Gaza Peace Plan, if successfully implemented, could stabilize the region, ensure diaspora safety, and bolster India’s energy and economic interests. However, challenges like Hamas acceptance, Iran’s exclusion, and Pakistan’s involvement create strategic uncertainties. India must carefully navigate regional dynamics to safeguard its long-term projects and strategic interests.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the implications of the Gaza Peace Plan for India’s strategic, economic, and diaspora interests. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Gaza Peace Plan?
It is a 20-point US proposal by Trump to stabilize Gaza, disarm Hamas, rebuild infrastructure, and ensure regional security.
2. What role will international forces play in Gaza?
A temporary International Stabilization Force (ISF) will train Palestinian police, secure Gaza, and oversee IDF withdrawal.
3. How will Gaza be governed under the plan?
A technocratic, apolitical Palestinian committee, supervised by the Board of Peace chaired by Trump, will run Gaza temporarily.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries? (2017)
- Jordan
- Iraq
- Lebanon
- Syria
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Q. The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2018)
(a) China
(b) Israel
(c) Iraq
(d) Yemen
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)