International Relations
Israel-Palestine Conflict
- 10 Oct 2023
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Israel, Palestine, Middle-East, Arab World, Yom Kippur War, Zionism, Al-Aqsa, Gaza Strip, Jerusalem, Palestinian Liberation Organisation (PLO)
For Mains: Impact of Israel-Palestine Conflict on India and International geopolitical scenario.
Why in News?
Recently, the Hamas, the militant group ruling the Gaza Strip, have mounted a scathing attack on Israel from the land, air and water leading to multiple casualties. This has revived the century-old dispute between Israel-Palestine Conflict once again, necessitating the intervention by global and regional powers.
- Israel, in the recent times, has cemented many peace agreements with neighboring countries such as UAE, Saudi Arabia etc which is set to feel a jolt due to the recent attack.
What is the Israel-Palestine Conflict?
- Balfour Declaration:
- The seeds of the conflict were laid in 1917 when the then British Foreign Secretary Arthur James Balfour expressed official support of Britain for a Jewish "national home" in Palestine under the Balfour Declaration.
- Creation Of Palestine:
- Unable to contain Arab and Jewish violence, Britain withdrew its forces from Palestine in 1948, leaving responsibility for resolving the competing claims to the newly created United Nations.
- The UN presented a partition plan to create independent Jewish and Arab states in Palestine which was not accepted by most of Arab nations.
- Unable to contain Arab and Jewish violence, Britain withdrew its forces from Palestine in 1948, leaving responsibility for resolving the competing claims to the newly created United Nations.
- Arab Israel War (1948):
- In 1948, the Jewish declaration of Israel's independence prompted surrounding Arab states to attack. At the end of the war, Israel controlled about 50 % more territory than originally envisioned by the UN partition plan.
- UN Partition Plan:
- As per the Plan, Jordan controlled the West Bank and Jerusalem's holy sites, and Egypt controlled the Gaza Strip. But it fell short of solving the palestinian crisis which led to the formation of Palestinian Liberation Organisation in 1964.
- Palestinian Liberation Organisation (PLO):
- PLO was founded, with the aim of freeing Palestine from clutches of Israel and Jewish domination and setting up the dominance of Muslim Brotherhood in the Arab world.
- The United Nations granted the PLO observer status in 1975 and recognizes Palestinians' right to self-determination.
- PLO was founded, with the aim of freeing Palestine from clutches of Israel and Jewish domination and setting up the dominance of Muslim Brotherhood in the Arab world.
- Six-Day War: In 1967 war, Israeli forces seized the Golan Heights from Syria, the West Bank & East Jerusalem from Jordan and Sinai Peninsula & Gaza strip from Egypt.
- Camp David Accords (1978):
- "Framework for Peace in the Middle East" brokered by the U.S. set the stage for peace talks between Israel and its neighbors and a resolution to the "Palestinian problem". This however remained unfulfilled.
- Emergence of Hamas:
- 1987: Founding of Hamas, a violent offshoot of Egypt's Muslim Brotherhood seeking to fulfill its agenda through violent jihad.
- Hamas- It is regarded as a terrorist organization by the U.S. government. In 2006, Hamas won the Palestinian Authority's legislative elections. It ejected Fatah from Gaza in 2007, splitting the Palestinian movement geographically, as well
- 1987: Tensions in the occupied territories of West Bank and Gaza reached boiling point resulting in the First Intifada (Palestinian Uprising). It grew into a small war between Palestinian militants and the Israeli army.
- 1987: Founding of Hamas, a violent offshoot of Egypt's Muslim Brotherhood seeking to fulfill its agenda through violent jihad.
- Oslo Accords:
- 1993: Under the Oslo Accords Israel and the PLO agree to officially recognize each other and renounce the use of violence. The Oslo Accords also established the Palestinian Authority, which received limited autonomy in the Gaza Strip and parts of the West Bank.
- 2005: Israel begins a unilateral withdrawal of Jews from settlements in Gaza. However, Israel kept tight control over all border crossings (blockade).
- 2012- UN upgrades Palestinian representation to that of "non-member observer state".
- Territorial Disputes of Israel with Neighboring Countries:
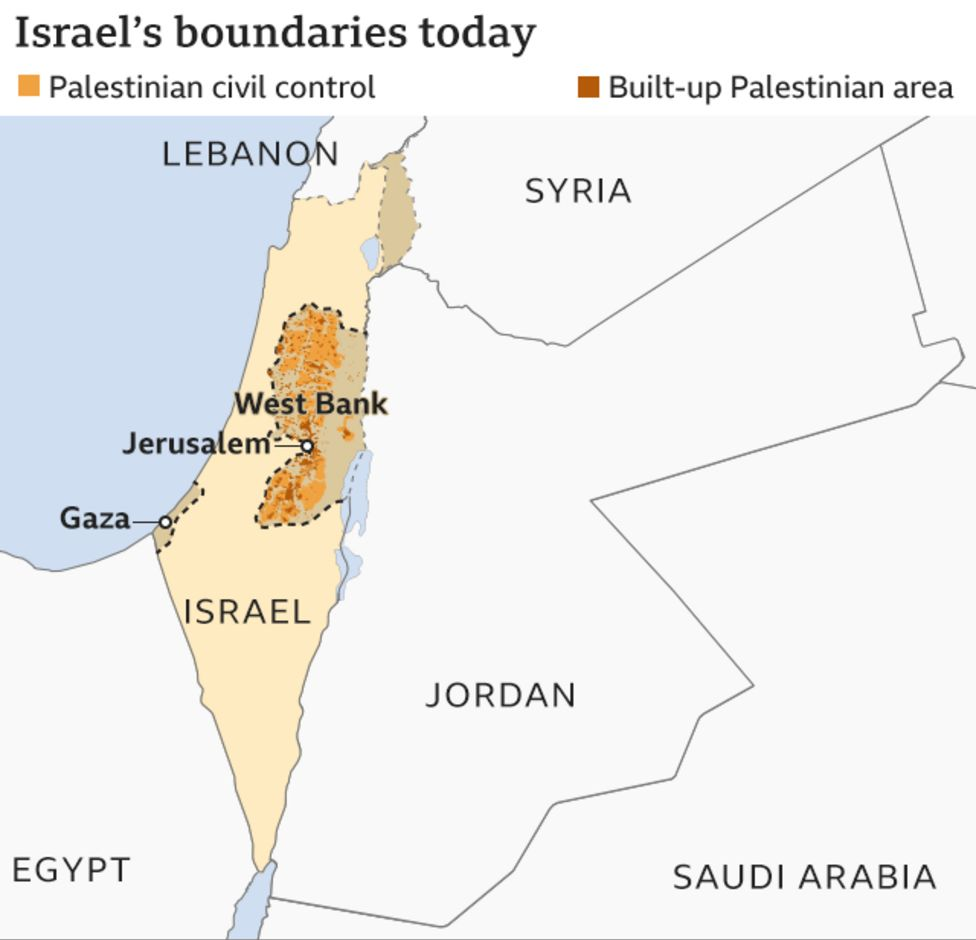
- West Bank: The West Bank is sandwiched between Israel and Jordan. One of its major cities is Ramallah, the de facto administrative capital of Palestine. Israel took control of it in the 1967 war and has over the years established settlements there.
- Gaza: The Gaza Strip located between Israel and Egypt. Israel occupied the strip after 1967, but relinquished control of Gaza City and day-to-day administration in most of the territory during the Oslo peace process. In 2005, Israel unilaterally removed Jewish settlements from the territory, though it continues to control international access to it.
- Golan Heights: The Golan Heights is a strategic plateau that Israel captured from Syria in the 1967 war. Israel effectively annexed the territory in 1981. Recently, the USA has officially recognized Jerusalem and Golan Heights as a part of Israel.
How has the relationship of India with Israel evolved over the years ?
- India’s Stand on the Israel-Palestine Conflict:
- India was one of the few countries to oppose the UN’s partition plan in 1947, echoing its own experience during independence a few months earlier.
- India recognised Israel in 1950 but it is also the first non-Arab country to recognise Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) as the sole representative of the Palestinian. India is also one of the first countries to recognise the statehood of Palestine in 1988.
- In recent times, India is being seen shifted towards a Dehyphenation of Policy.
- Dehyphenation of Policy:
- India’s policy on the longest running conflict in the world has gone from being unequivocally pro-Palestine for the first four decades, to a tense balancing act with its three-decade-old friendly ties with Israel.
- In recent years, India’s position has also been perceived as pro-Israel.
- Further, India believes in a Two-State Solution with respect to Israel-Palestine conflict, and proposes the right to self-determination to both the countries in a peaceful manner.
What is the Impact of Assault on Israel-Saudi Arabia Ties ?
- One of the reasons for Hamas' assault on Israel can be attributed to disrupting efforts to bring Saudi Arabia and Israel together, along with other countries that may be interested in normalizing relations with Israel.
- Hamas had highlighted threats to Jerusalem’s Al-Aqsa Mosque, the continuation of an Israeli blockade on Gaza and Israeli normalization with countries in the region.
- Dehyphening Saudi Arabia from Israel will help promote the agenda of Muslim Brotherhood and territorial sovereignty over the Arab and Middle East region.
- Normalization of ties of regional powers with Israel will further embolden and strengthen the position of Israel vis-a-vis reclaiming Palestinian territories.
- Ties with UAE,Egypt,Saudi Arabia etc will provide a vigorous push to infrastructural development, and create inter-dependence and inter-relationships among these countries, much to the chagrin of Palestinians.
Way Forward
- The world at large needs to come together for a peaceful solution but the reluctance of the Israeli government and other involved parties have aggravated the issue more. Thus a balanced approach would help to maintain favorable relations with Arab countries as well as Israel.
- The recent normalization agreements between Israel and the UAE, Bahrain, Sudan, and Morocco, known as the Abraham Accords, are the steps in the right direction. All regional powers should envisage peace between the two countries on line of Abraham Accords.
- India’s role in multilateral organizations requires “strenuous efforts in cooperation with all related parties to achieve security and stability in the Middle East and West Asia”.
- India is currently serving as a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council for 2021-22 and was re-elected to the Human Rights Council for the 2022-24. India should use these multilateral forums to act as a mediator to resolve the Israel-Palestine issue.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q 1. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q1. ‘Too little cash, too much politics, leaves UNESCO fighting for life.’ Discuss the statement in the light of US’ withdrawal and its accusation of the cultural body as being ‘anti-Israel bias’. (2019)
Q2 . “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)