Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
National e-Governance Gold Award 2025
Why in News?
Sampada 2.0 (Stamps and Management of Property and Documents Application), developed by the Commercial Tax Department of Madhya Pradesh, was awarded the National e-Governance Gold Award for 2025 for its transformative use of technology in public service.
- Madhya Pradesh is the first state to implement fully paperless e-registration for documents.
Key Points
- About: Launched in 2024 in Madhya Pradesh, SAMPADA 2.0 aims to provide a user-friendly, transparent system for E-registration and E-stamping, ensuring improved governance, evidence-based processing, and simplified registration processes through Government Process Re-engineering (GPR) and policy recommendations.
- The application seeks to deliver efficient, transparent document registration services, utilizing modern technology, well-defined procedures, and timely execution to benefit users.
- Key Features:
- GIS Technology: Sampada 2.0 is equipped with Geographical Information System (GIS) technology, enabling better property mapping and management.
- Access Anywhere: The platform allows users to obtain an e-stamp anytime, anywhere via the Sampada 2.0 portal.
- Mobile App: The mobile app provides instant access to guideline rates for any location within the state.
- Faceless Registration: Under the Indian Stamp Act, 1899, video KYC enables faceless registration for 75 out of 140 types of documents, ensuring convenience and reducing the need for physical office visits.
- The new system also helps reduce impersonation and land-related disputes.
National Awards on e-Governance
- About: The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DAR&PG), Government of India, presents National Awards every year during the National Conference on e-Governance to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives.
- The National e-Governance Gold Award 2025 was presented in the category “Government Process Re-engineering by Use of Technology for Digital Transformation”.
- Purpose of Award:
- Recognize achievements in the area of e-Governance
- Disseminate knowledge on effective methods of designing and implementing sustainable e-Governance initiatives
- Encourage incremental innovations in successful e-Governance solutions
- Promote and exchange experiences in solving problems, mitigating risks, resolving issues, and planning for success.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
National Lata Mangeshkar and Kishore Kumar Awards
Why in News?
The Madhya Pradesh government has announced the recipients for the prestigious National Lata Mangeshkar Award and National Kishore Kumar Award for the years 2024 and 2025.
- The ceremony for the Lata Mangeshkar Award will be held at the legendary singer's birthplace, Indore, on 28th September 2025, while the Kishore Kumar Award will be presented in his birthplace, Khandwa, on 13th October 2025.
Key Points
- About: The National Lata Mangeshkar Award and the National Kishore Kumar Award, instituted by the Madhya Pradesh government, serve as a tribute to the legacies of two of India's most iconic performers, Lata Mangeshkar and Kishore Kumar.
- National Lata Mangeshkar Award: The award recognizes outstanding contributions to Indian music, particularly in music direction and singing.
- Recipients:
- 2024: Shankar-Ehsaan-Loy (Music Composer Trio)
- 2025: Sonu Nigam (Playback Singer)
- Recipients:
- National Kishore Kumar Award: The award honours achievements in Indian cinema, including lyric writing and filmmaking.
- Recipients:
- 2024: Prasoon Joshi (Lyricist)
- 2025: Sanjay Leela Bhansali (Filmmaker)
- Recipients:
- About the Recipients:
- Shankar-Ehsaan-Loy: Shankar Mahadevan, Ehsaan Noorani, and Loy Mendonsa, an iconic Indian music trio, are known for their diverse compositions across multiple languages, with notable works like Dil Chahta Hai and Zindagi Na Milegi Dobara.
- Sonu Nigam: A versatile playback singer celebrated across Hindi, Telugu, and Tamil cinema, famous for songs like Kal Ho Naa Ho and Suraj Hua Maddham.
Prasoon Joshi: A distinguished lyricist and poet, known for his impactful work in films like Taare Zameen Par and Chakde! India. - Sanjay Leela Bhansali: A legendary filmmaker and music composer, renowned for epic films such as Devdas and Padmaavat.
- Lata Mangeshkar: Lata Mangeshkar (28th September 1929 – 6th February 2022), known as the "Nightingale of India," was a legendary playback singer whose career spanned over seven decades.
- Kishore Kumar: Kishore Kumar (4th August 1929 – 13th October 1987) was a legendary Indian playback singer, actor, composer, lyricist, director, and producer who remains one of the most influential and beloved icons in the history of Indian cinema and music.
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
World Lion Day 2025
Why in News?
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), in collaboration with the Gujarat Forest and Environment Department, marked World Lion Day 2025 (10th August) at the Barda Wildlife Sanctuary in Dwarka district, Gujarat.
- The event celebrated the conservation achievements under Project Lion, aimed at protecting the Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica).
Key Points
- The lion population in Gujarat has risen by 32% since 2020, increasing from 674 to 891, according to the May 2025 lion population estimate (16th census).
- Barda Wildlife Sanctuary, part of the larger Gir Lion Landscape, is home to 17 Asiatic lions.
Key Facts About Project Lion
- Launched: 2020, to secure the future of Asiatic lions in Gujarat's Gir landscape.
- Focus Areas: Habitat improvement, ecosystem health, and human-wildlife conflict mitigation.
- Technologies Used:
- Radio-collaring & Camera Traps: For monitoring lion movements.
- GPS Tracking: Ensures efficient surveillance of lions and vehicles.
- Automated Sensor Grid: Includes magnetic, movement, and infrared heat sensors for wildlife tracking.
- GIS-based Real-Time Monitoring: Facilitates timely analysis and conservation management.
Key Facts About Lions
- The lion is divided into two subspecies: the African lion (Panthera leo leo) and the Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica).
- Asiatic lions are slightly smaller than African lions.
- Characteristics:
- Lions are known for their distinctive appearance, including a tawny coat, a tufted tail, and a prominent mane in males.
- They are social animals and live in groups called prides. A pride typically consists of multiple females, their offspring, and a few adult males.
- Distribution and Habitat: Lions are found in sub-Saharan Africa, and a small population exists in the Gir Forest National Park (India).
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List:
- African Lion: Vulnerable (Globally)
- Asiatic Lion: Vulnerable.
- IUCN Green Status of Species Assessment:
- Lions: Largely Depleted category
- CITES: Appendix I for populations of India, all other populations are included in Appendix II.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Schedule I and IV
- IUCN Red List:
- Conservation Efforts in India:
- Project Lion
- Asiatic Lion Conservation Project
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
Rudrastra – Asia’s Longest Freight Train
Why in News?
Indian Railways has achieved a significant milestone with the successful trial run of Rudrastra, the longest freight train in India and Asia, measuring 4.5 km.
Key Points
- About: On 7th August 2025, the Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyay (DDU) Division of East Central Railway conducted a trial service between Ganjkhwaja station in Chandauli (Uttar Pradesh) and Garhwa (Jharkhand), covering 209 km in 5 hours 10 minutes at an average speed of 40.5 km/h.
- The train, consisting of six BOXN rakes with 354 wagons, was powered by seven engines—two at the front and one after every 59 bogies—carrying approximately 72 tonnes of goods per wagon, marking the largest freight load ever moved by Indian Railways in a single operation.
- The train ran on the Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) from Ganjkhwaja to Sonnagar, and then on the normal track to Garhwa Road.
- Significance: Running Rudrastra as a unified system reduces logistical overheads, enhances train capacity, and boosts the speed and efficiency of freight transportation in India.
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
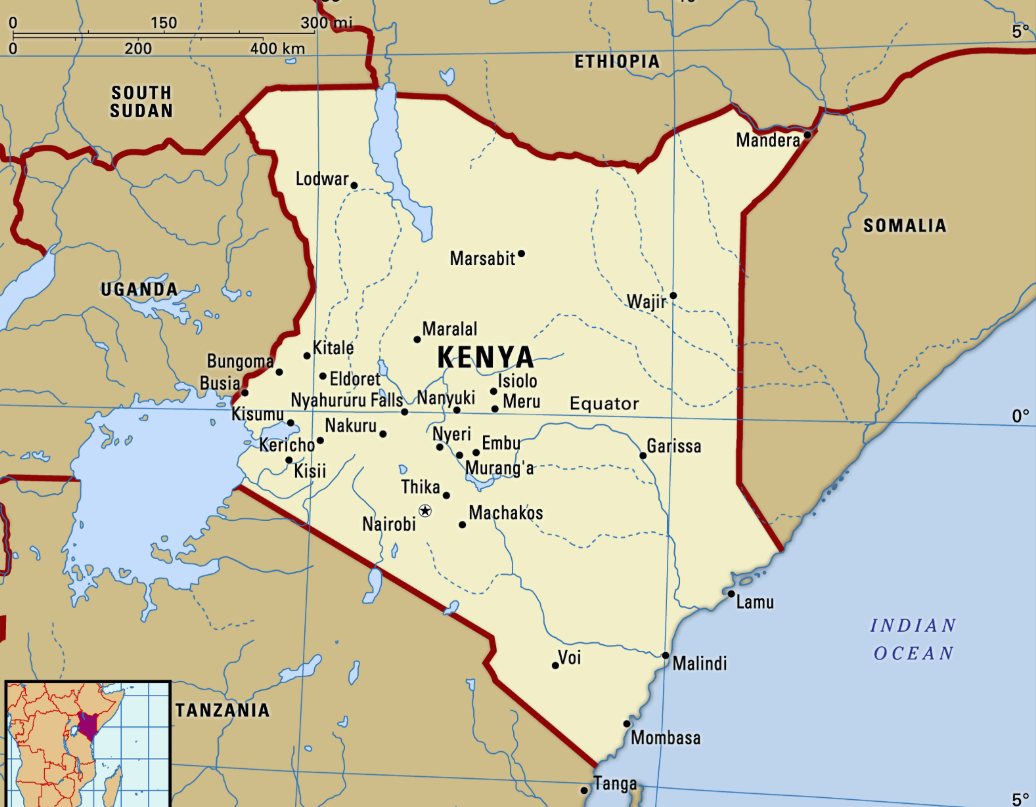
Kenya Eliminated Sleeping Sickness
Why in News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has officially certified Kenya as free from human African trypanosomiasis—commonly known as sleeping sickness—marking a significant public health victory for the nation.
- With this achievement, Kenya becomes the tenth country globally to eliminate the disease as a public health challenge.
- This is the second neglected tropical disease eliminated in Kenya, following the country’s WHO certification as Guinea worm disease-free in 2018.
Key Points About Sleeping sickness
- Sleeping sickness, caused by protozoan parasites transmitted by tsetse flies, is characterized by initial symptoms such as fever, headaches, and joint pain.
- In advanced stages, patients suffer from neurological effects, disrupted sleep patterns, confusion, and behavioral changes.
- The sleeping sickness is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Sleeping sickness significantly reduces the productivity of both humans and cattle (zebu cattle raised by Maasai tribes of eastern Africa).
Disease Eradicated by India
- India has eradicated Smallpox (1980), Polio (2014), Plague, Rinderpest (the Cattle Plague), Yaws and Maternal And Neonatal Tetanus (2015), trachoma (2024).
- India received Guinea worm disease-free certification status from the WHO in 2000.
Diseases Targeted for Elimination in India
- Malaria: Achieve zero indigenous cases by 2030.
- Lymphatic Filariasis (LF): Achieve <1% microfilaria rate in endemic areas (elimination by 2030).
- Kala-azar: Achieve annual incidence of <1 case per 10,000 population at block level.
- Certification requires 3 years of sustained elimination.
- Tuberculosis (TB): End TB by 2025 under the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
International Day of the World's Indigenous Peoples
Why in News?
To mark the occasion of the International Day of the World's Indigenous Peoples, the MP postal department, in collaboration with the Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Manav Sangrahalaya (IGRMS), has organized a three-day philatelic exhibition.
- The event was inaugurated by Chief Postmaster General Vineet Mathur and Director of IGRMS, Prof. Amitabh Pande.
International Day of Indigenous Peoples
- About: Observed annually on 9th August, following the UN General Assembly's recognition of this day in December 1994.
- The day recognizes the first meeting of the United Nations Working Group on Indigenous Populations in Geneva in 1982.
- Theme for 2025: "Indigenous Peoples and AI: Defending Rights, Shaping Futures.”
- Key Facts Related to Indigenous Peoples Globally:
- There are an estimated 476 million Indigenous Peoples in the world living across 90 countries.
- They make up less than 6% of the world's population, but account for at least 15% of the poorest.
- They speak an overwhelming majority of the world’s estimated 7,000 languages and represent 5,000 different cultures.
2025 Equator Prize
- The UN Development Programme (UNDP) has announced the ten Indigenous-led, community-based organizations selected for the 2025 Equator Prize, recognizing their environmentally focused solutions that align with this year’s prize theme, "Nature for Climate Action."
- Bibifathima Swa Sahaya from India, one of the winners, supports village farmers through multi-cropping, seed banks, and solar-powered processing, blending traditional knowledge with regenerative agriculture and renewable energy.
Key Facts Related to Tribals in India
- About: In India, the term 'Adivasi' refers to various ethnic and tribal groups recognized as the aboriginal population, with Scheduled Tribes (STs) being those indigenous communities acknowledged by the government for special protection and support.
- According to the 2011 census, these ancestral groups make up approximately 8.6% of India's general population, which adds up to around 104 million people.
- Essential Characteristics: According to the Lokur Committee (1965), the essential characteristics of the tribes are:
- Indication of Primitive Traits
- Distinctive Culture
- Shyness of Contact with the Community at Large
- Geographical Isolation
- Backwardness
- Constitutional Provisions for STs:
- Article 15(4): Special provisions for the advancement of other backward classes (it includes STs)
- Article 29: Protection of Interests of Minorities (it includes STs)
- Article 46: The State shall ensure the welfare of weaker sections (including Scheduled Tribes) and protect them from injustice and exploitation.
- Article 275: Allocation of special funds from the Union Government to the State Government for enhancing the welfare and administration of Scheduled Tribes.
- Article 350: Right to conserve distinct language, script, or culture.
- Article 330 and 332: Reservation of seats for STs in Lok Sabha and State Legislatures.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan