International Relations
24th ASEAN-India Meeting
For Prelims: ASEAN, Act East Policy, ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific
For Mains: Significance of ASEAN for India, India-ASEAN Areas of Cooperation
Why in News?
Recently, the 24th ASEAN-India Senior Official's Meeting (SOM) was hosted in Delhi.
- India and ASEAN celebrated the 30th anniversary of their Dialogue Relations.
- Earlier, the 2nd ASEAN Digital Ministers' (ADGMIN) Meeting with India held, where two sides finalized India-ASEAN Digital work plan 2022 for future collaboration in the field.
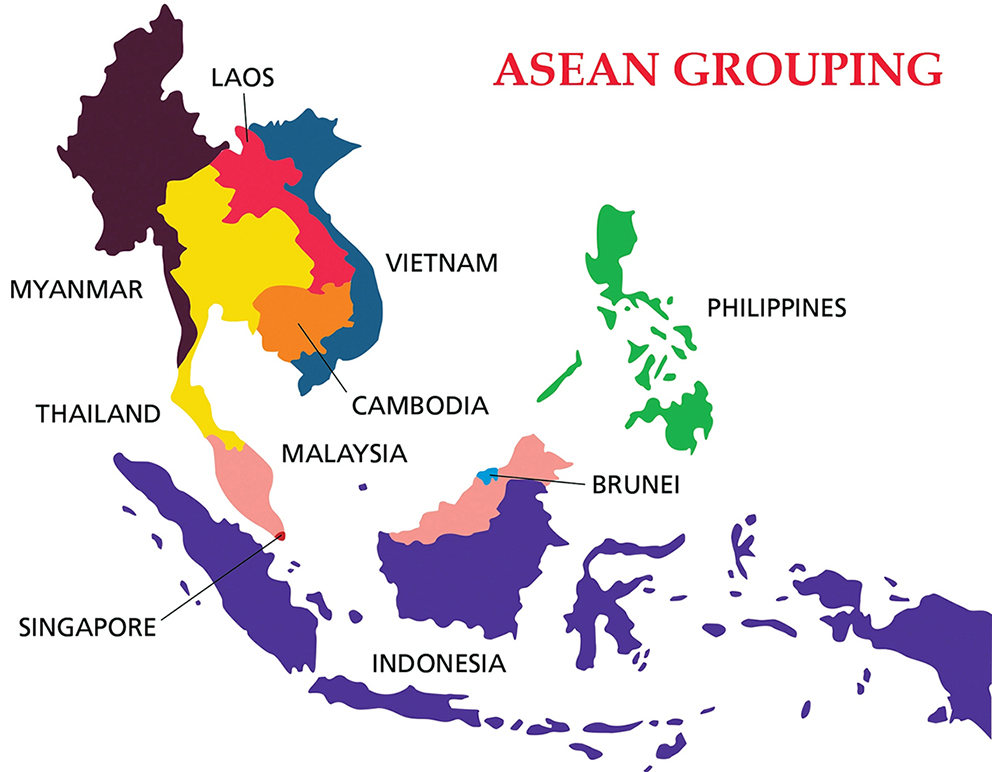
What is Association of Southeast Asian Nations?
- About:
- It is a regional grouping that promotes economic, political, and security cooperation.
- It was established in August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the founding fathers of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Its chairmanship rotates annually, based on the alphabetical order of the English names of Member States.
- ASEAN countries have a total population of 650 million people and a combined Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of USD 2.8 trillion. It is India’s 4th largest trading partner with about USD 86.9 billion in trade.
- Members:
- ASEAN brings together ten Southeast Asian states – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam – into one organisation.
What are the Key Highlights?
- The SOM reviewed the ASEAN-India strategic partnership and its future direction.
- The leaders made their assessment on the progress of cooperation under three pillars of Partnership – Political-Security, Economic and Socio-Cultural.
- The meeting deliberated on the steps for further implementation of the ASEAN-India Plan of Action (2021-2025).
- The two sides exchanged views on regional and international issues of mutual interest including the Covid-19 pandemic and post-pandemic recovery.
- Underlining the India’s vision of the Indo-Pacific, emphasized the implementation of the ASEAN-India Joint Statement on Cooperation on ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific (AOIP) to strengthen the ASEAN-India Strategic Partnership.
- The ASEAN side appreciated India’s support to ASEAN and ASEAN-led architecture in the region.
How has Been the ASEAN-India Relations?
- About:
- ASEAN, a 10-nation grouping, is considered one of the most influential groupings in Southeast Asia.
- India and several other countries, including the US, China, Japan and Australia, are its dialogue partners.
- The ASEAN-India dialogue relations started with the establishment of a sectoral partnership in 1992.
- This graduated to full dialogue partnership in December 1995 and summit-level partnership in 2002.
- Traditionally the basis of India-ASEAN ties has been trade and people-to-people ties due to shared historical and cultural roots, a more recent and urgent area of convergence has been balancing China’s rise.
- Both India and ASEAN aim to establish a rules-based security architecture for peaceful development in the region, in contrast to China’s aggressive policies.
- Areas of Cooperation:
- Economic Cooperation:
- ASEAN is India’s 4th largest trading partner.
- India signed FTA (Free Trade Agreement) in goods in 2009 and an FTA in services and investments in 2014 with ASEAN.
- India has a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) with various countries of the ASEAN region which has resulted in concessional trade and a rise in investments.
- Political Cooperation:
- ASEAN-India Centre (AIC) was established to undertake policy research, advocacy and networking activities with organizations and think-tanks in India and ASEAN.
- Financial Assistance:
- India provides financial assistance to the ASEAN nations through various mechanism like ASEAN-India Cooperation Fund, ASEAN-India S&T Development Fund and ASEAN-India Green Fund.
- Connectivity:
- India has been undertaking several connectivity projects like India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral (IMT) Highway and the Kaladan Multimodal Project.
- India is also trying to establish a Maritime Transportation Agreement with ASEAN and also Plans for a Railway link between New Delhi in India to Hanoi in Vietnam.
- Socio-Cultural Cooperation:
- Programmes to boost People-to-People Interaction with ASEAN are organized, such as inviting ASEAN students to India, Special Training Course for ASEAN diplomats, Exchange of Parliamentarians, etc.
- Defence Cooperation:
- Joint Naval and Military exercises are conducted between India and most ASEAN countries.
- Vietnam has traditionally been a close friend on defense issues, Singapore is also an equally important partner.
- Economic Cooperation:
What is the Significance of ASEAN for India?
- India needs a close diplomatic relationship with ASEAN nations both for economic and security reasons.
- Connectivity with the ASEAN nations can allow India to improve its presence in the region.
- These connectivity projects keep Northeast India at the centre, ensuring the economic growth of the northeastern states.
- Improved trade ties with the ASEAN nations would mean a counter to China’s presence in the region and economic growth and development for India.
- ASEAN occupies a centralised position in the rules-based security architecture in the Indo-Pacific, which is vital for India since most of its trade is dependent on maritime security.
- Collaboration with the ASEAN nations is necessary to counter insurgency in the Northeast, combat terrorism, tax evasions etc.
Way Forward
- With China having three times more commercial flights than India to Southeast Asia, improving air connectivity between India and ASEAN countries should also be high on the agenda.
- India can become the military partner after the Atma Nirbar Bharat, Make in India projects are successfully implemented.
- There is need to expand the Concept of QUAD to include the ASEAN countries and become a QUAD+ arrangement.
- Vietnam and Indonesia have expressed a positive note on QUAD in the region.
- Tourism can be encouraged between India and the ASEAN with some creative branding by the two sides.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) has free trade agreements with six partners, namely the People’s Republic of China, Republic of Korea, Japan, India as well as Australia and New Zealand. Hence, 1, 3, 4 and 5 are correct.
Q. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the five countries (Australia, China, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand) with which ASEAN has existing FTAs. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
International Relations
I2U2 Initiative
For Prelims: I2U2 initiative, Abraham Accords, QUAD
For Mains: Groupings and Agreements including India and affecting India’s interest
Why in News?
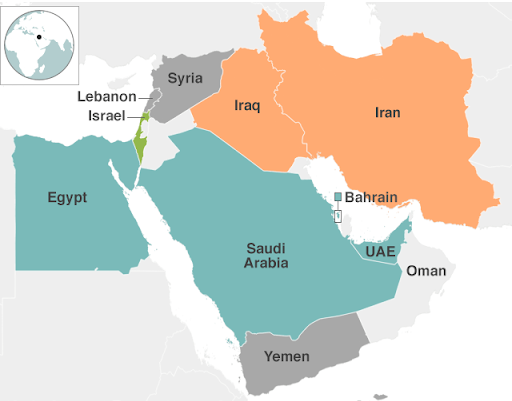
As part of I2U2 initiatives, India, Israel, UAE, and the US will hold its first virtual summit in July 2022.
What is I2U2 Initiative?
- Background:
- I2U2 was initially formed in October, 2021 following the Abraham Accords between Israel and the UAE, to deal with issues concerning maritime security, infrastructure and transport in the region.
- At that time, it was called the ‘International Forum for Economic Cooperation’.
- That was referred as the ‘West Asian Quad’.
- I2U2 was initially formed in October, 2021 following the Abraham Accords between Israel and the UAE, to deal with issues concerning maritime security, infrastructure and transport in the region.
- About:
- I2U2 initiative is a new grouping of India, Israel, USA and UAE.
- In the grouping’s name, ‘I2’ stands for India and Israel, whereas ‘U2’ stands for USA and the UAE.
- This is a great achievement which tells the geopolitical changes that happen in the region.
- This will not only revitalize and re-energize the system of alliances and partnerships around the world, but also stitch together partnerships that did not exist previously or were not utilized to their full extent.
- Significance:
- Security Cooperation:
- This will help the countries in exploring security cooperation among the four nations within the framework of these new groupings.
- Technological Hubs:
- Each of these countries is a technological hub.
- Biotechnology, of course, is prominent in each of these countries as well.
- Each of these countries is a technological hub.
- Food Security:
- This initiative offers an opportunity to discuss food security.
- Work Together in Different Fields:
- These countries could cooperate on a number of levels, whether it's technologies, trade, climate, fighting against Covid-19, or even security.
- Security Cooperation:
What will be the Significance of I2U2 for India?
- Advantage from Abraham Accords:
- India will get advantage of the Abraham Accords to deepen engagement with Israel without risking its ties with the UAE and the other Arab states.
- Benefit Market:
- India is a massive consumer market. It’s a massive producer of high-tech and highly sought-after goods as well. India will benefit from this grouping.
- Alliances:
- It will help India in building alliances — political alliances, social alliances.
Economy
World Competitiveness Index 2022
For Prelims: World competitiveness Index, Atma Nirbhar Bharat, COP-26
For Mains: Growth and Development, Inclusive Growth
Why in News?
Recently, the annual World Competitiveness Index was released by the Institute for Management Development (IMD).
- IMD is a Swiss foundation, based in Switzerland, dedicated to the development of international business executives at each stage of their careers
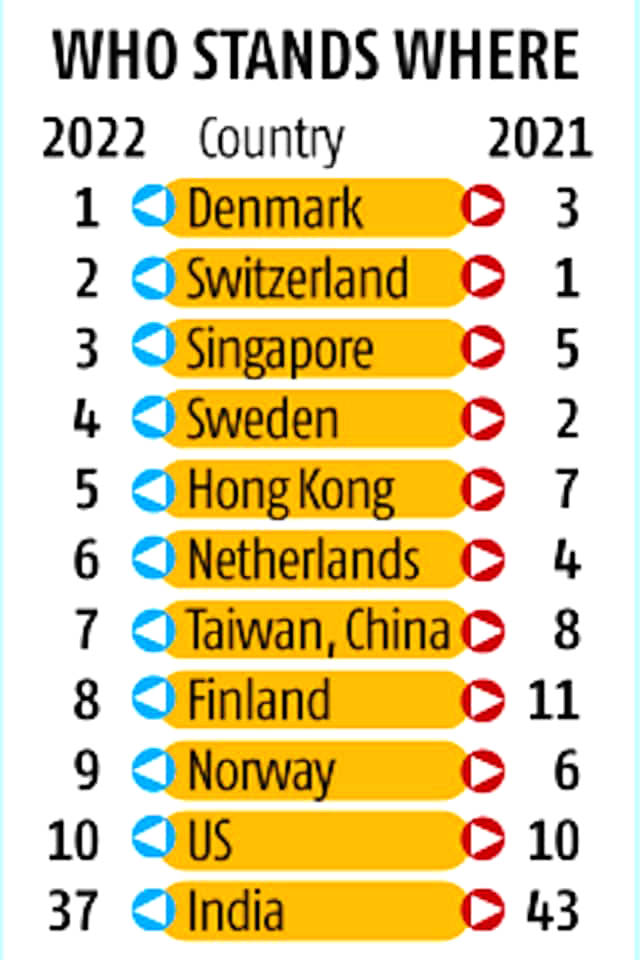
- India has witnessed the sharpest rise among the Asian economies, with a six-position jump from 43rd to 37th rank on the, largely due to gains in economic performance.
What is World Competitiveness Index?
- About:
- The IMD World Competitiveness Yearbook (WCY), first published in 1989, is a comprehensive annual report and worldwide reference point on the competitiveness of countries.
- It analyzes and ranks countries according to how they manage their competencies to achieve long-term value creation.
- Factors: It measures the prosperity and competitiveness of countries by examining the Four factors (334 competitiveness criteria):
- Economic performance
- Government efficiency
- Business efficiency
- Infrastructure
What are the Highlights of the Index?
- Top Global Performers:
- Europe: Denmark has moved to the top of the 63-nation list from the third position last year, while Switzerland slipped from the top ranking to the second position and Singapore regained the third spot from fifth.
- Asia: The top-performing Asian economies are Singapore (3th), Hong Kong (5th), Taiwan (7th), China (17th) and Australia (19th).
- Others: Both Russia and Ukraine were not assessed in this year’s edition due to the limited reliability of data collected.
- India’s Performance:
- Performance on four Parameters:
- Economic performance: It has improved from 37th in 2021 to 28th in 2022.
- Government efficiency: It has improved from 46th in 2021 to 45th in 2022.
- Business efficiency: It saw a huge improvement from 32nd rank in 2021 to 23rd in 2022.
- Infrastructure: It on the other hand, saw no change at 49.
- Reasons for India’s Good Performance:
- Major improvements in the context of retrospective taxes in 2021
- Re-regulation of a number of sectors, including drones, space and geo-spatial mapping.
- Significant improvement in the competitiveness of the Indian economy
- India as a driving force in the global movement to fight climate change and India’s pledge of net-zero by 2070 at the COP26 summit also sits in harmony with its strength in environment-related technologies in the ranking.
- India’s Weaknesses:
- The challenges that India faces include managing trade disruptions and energy security, maintaining high GDP growth post the pandemic, skill development and employment generation, asset monetisation and resource mobilisation for infrastructure development.
- India’s Strengths:
- The top five attractive factors of India's economy for business are - a skilled workforce, cost competitiveness, dynamism of the economy, high educational level and open and positive attitudes.
- Performance on four Parameters:
What are the Recent steps taken by India to Increase its Competitiveness?
- Towards Increasing Manufacturing Capacity: India has made appreciable efforts to ensure resilience in manufacturing capacity such as via Atmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India initiatives which are aimed at domestic supply chains and heavy investment in manufacturing hubs.
- The government has introduced the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme in various sectors for enhancing India’s manufacturing capabilities and exports.
- Technological Advancement: To facilitate technological advancement for increasing competitiveness, India’s Department of Telecom (DoT) has constituted six task forces on 6G technology.
- The Ministry of External Affairs, through its New, Emerging And Strategic Technologies (NEST) division is also ensuring India’s active participation in international forums on technology governance.
- It acts as the nodal division within the ministry for issues pertaining to new and emerging technologies and assists in collaboration with foreign partners in the field of technology
- The Ministry of External Affairs, through its New, Emerging And Strategic Technologies (NEST) division is also ensuring India’s active participation in international forums on technology governance.
Way Forward
- A nation that ensures balance between economic and social progress can enhance its productivity, followed by creating competitiveness and thus, prosperity.
- Therefore, it is necessary to create an environment which not only pushes the businesses to compete successfully in local as well as international markets but ensures that the average citizen’s standard of living also improves.
- Governments need to provide an environment characterized by efficient infrastructures, institutions and policies that encourage sustainable value creation by the enterprises.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous year Question (PYQ)
Q.Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Global Gender Gap Report is published by the World Economic Forum. The report’s Gender Gap Index, which is designed to measure gender equality ranks countries, according to the calculated gender gap between women and men in four key areas:health, education, economy and politics to gauge the state of gender equality in a country.
- The Global Gender Gap Report 2021 benchmarks 156 countries on their progress towards gender parity across four thematic dimensions: Economic Participation and Opportunity; Educational Attainment, Health and Survival, and Political Empowerment. In addition, this year’s editionstudied skills gender gaps related to Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- India ranks 140th in WEF Gender Gap Index-2021.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Indian Economy
Linking Credit Cards With UPI
For Prelims: UPI, Financial Instrument, Digital Payment, RBI
For Mains: Linking Credit Cards With UPI, its Significance and Challenges, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has proposed to allow linking of credit cards with the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) platform.
- A credit card is a financial instrument issued by banks with a pre-set credit limit, help make cashless transactions. It enables cardholders to pay a merchant for goods and services based on her accrued debt.
- This is intended to provide additional convenience to users and enhance the scope of Digital Payments.
What is Unified Payment Interface?
- About:
- It is an advanced version of Immediate Payment Service (IMPS)- round–the-clock funds transfer service to make cashless payments faster, easier and smoother.
- UPI is a system that powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating bank), merging several banking features, seamless fund routing & merchant payments into one hood.
- UPI is currently the biggest among the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) operated systems including National Automated Clearing House (NACH), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), Aadhaar enabled Payment System (AePS), Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS), RuPay etc.
- Need to Link Credit Card with UPI:
- The UPI has, over time, become a popular mode of payment in India with more than 26 crore unique users and five crore merchants on the platform.
- In May 2022, about 594 crore transactions amounting to Rs 10.4 lakh crore were processed through the interface.
- At present, the UPI facilitates transactions by linking savings/current accounts through users’ debit cards.
What is the Significance of the Move?
- Additional Avenue for Payment:
- The arrangement is expected to provide an additional avenue for payment to customers and hence enhance convenience.
- Credit Card Usage will Increase:
- It will deepen the reach and usage of credit cards.
- It is anticipated that credit card usage will be zooming up in India given UPI’s widespread adoption.
- Avenues to build Credit on UPI:
- It opens up avenues to build credit on UPI through credit cards in India, where in the last few years, a number of startups like Slice, Uni, One etc. have emerged.
- Bolster Transactions at more Merchant Sites:
- It is expected to bolster transactions and acceptance at more merchant sites.
- People who generally prefer to pay by credit card so as to avail of a longer pay-back period or loans on credit-card outstanding, or who do not wish to touch their savings at the moment of purchase, can pay using credit cards via UPI.
- Boost Overall Spending:
- The move will provide a significant boost to overall spending via credit cards — currently, spending through the use of credit cards is more than double the average spend via debit cards. More spending is generally a force multiplier for the economy.
- Increase Average Ticket Size of Financial Transactions:
- Besides accelerating digital transactions this measure is also expected to affect the average ticket size of financial transactions.
- Currently the average ticket size per transaction is Rs 1,600 while it is Rs 4,000 in credit cards.
- So, with the new development the UPI transaction ticket size is likely to go up to somewhere around Rs 3,000 to Rs 4,000, analysts claim.
- Besides accelerating digital transactions this measure is also expected to affect the average ticket size of financial transactions.
What are the Challenges?
- It is not clear how the Merchant Discount Rate (MDR) will be applied to UPI transactions done through credit cards.
- The MDR is a fee that a merchant is charged by their issuing bank for accepting payments from their customers via credit and debit cards.
- According to a norm that has been in effect since January 2020, UPI and RuPay attract zero-MDR, meaning that no charges are applied to these transactions.
- Applicability of zero-MDR on UPI could also be a reason why other card networks such as Visa and Mastercard may not have been onboarded to UPI for credit cards yet.
Social Justice
Polio
For Prelims: Polio, Vaccine Derived Poliovirus, WHO, Universal Immunization Programme
For Mains: Poliovirus, Immunization, Eradication
Why in News?
Recently, Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus (VDPV) was detected in the environmental surveillance of sewage samples from Kolkata, Bengal.
- Most likely it has come from someone’s gut who is immune deficient and has since multiplied. It is not a case of human-to-human polio transfer.
- A VDPV is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in OPV (Oral poliovirus vaccines) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus.
What is Polio?
- About:
- Polio is a crippling and potentially deadly viral infectious disease that affects the nervous system.
- There are three individual and immunologically distinct wild poliovirus strains:
- Wild Poliovirus type 1 (WPV1)
- Wild Poliovirus type 2 (WPV2)
- Wild Poliovirus type 3 (WPV3)
- Symptomatically, all three strains are identical, in that they cause irreversible paralysis or even death. However, there are genetic and virological differences, which make these three strains separate viruses which must each be eradicated individually.
- Spread:
- The virus is transmitted by person-to-person mainly through the faecal-oral route or, less frequently, by a common vehicle (for example, through contaminated water or food).
- It largely affects children under 5 years of age. The virus multiplies in the intestine, from where it can invade the nervous system and can cause paralysis.
- Symptoms:
- Most people with polio do not feel sick. Some people have only minor symptoms, such as fever, tiredness, nausea, headache, pain in the arms and legs, etc.
- In rare cases, polio infection causes permanent loss of muscle function (paralysis).
- Polio can be fatal if the muscles used for breathing are paralysed or if there is an infection of the brain.
- Prevention and Cure:
- There is no cure, but it can be prevented through Immunisation.
- Vaccines:
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV): It is given orally as a birth dose for institutional deliveries, then primary three doses at 6, 10 and 14 weeks and one booster dose at 16-24 months of age.
- Injectable Polio Vaccine (IPV): It is introduced as an additional dose along with the 3rd dose of DPT (Diphtheria, Pertussis and Tetanus) under the Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP).
- Recent Outbreaks:
- In 2019, polio outbreaks were recorded in the Philippines, Malaysia, Ghana, Myanmar, China, Cameroon, Indonesia and Iran, which were mostly vaccine-derived in which a rare strain of the virus genetically mutated from the strain in the vaccine.
- According to the WHO (World Health Organisation), if the oral vaccine-virus is excreted and allowed to circulate in an unimmunised or under-immunised population for at least 12 months, it can mutate to cause infections.
- In 2019, polio outbreaks were recorded in the Philippines, Malaysia, Ghana, Myanmar, China, Cameroon, Indonesia and Iran, which were mostly vaccine-derived in which a rare strain of the virus genetically mutated from the strain in the vaccine.
- India & Polio:
- India received polio-free certification by the WHO in 2014, after three years of zero cases.
- This achievement has been spurred by the successful Pulse Polio Campaign in which all children were administered polio drops.
- The last case due to wild poliovirus in the country was detected on 13th January 2011.
- India received polio-free certification by the WHO in 2014, after three years of zero cases.
What are the Polio Eradication Measures?
- Global:
- Global Polio Eradication Initiative:
- It was launched in 1988 by the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI), by national governments and WHO. Presently, 80% of the world’s population is now living in certified polio-free regions.
- An estimated 1.5 million childhood deaths have been prevented, through the systemic administration of vitamin A during polio immunization activities.
- It was launched in 1988 by the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI), by national governments and WHO. Presently, 80% of the world’s population is now living in certified polio-free regions.
- World Polio Day:
- It is observed every year on 24th October in order to call on countries to stay vigilant in their fight against the disease.
- Global Polio Eradication Initiative:
- Indian:
- Pulse Polio Programme:
- It was started with an objective of achieving hundred percent coverage under Oral Polio Vaccine.
- Intensified Mission Indradhanush 2.0:
- It was a nationwide immunisation drive to mark the 25 years of Pulse polio programme (2019-20).
- Universal Immunization Programme (UIP):
- It was launched in 1985 with the modification to ‘Expanded Programme of Immunization (EPI). The objectives of the Programme include:
- Rapidly increasing immunization coverage, Improving the quality of services, Establishing a reliable cold chain system to the health facility level, Introducing a district-wise system for monitoring of performance, Achieving self-sufficiency in vaccine production.
- It was launched in 1985 with the modification to ‘Expanded Programme of Immunization (EPI). The objectives of the Programme include:
- Pulse Polio Programme:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to (2016)
(a) immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Mission Indradhanush is an immunization scheme launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, GoI on 25th December, 2014.
- Depicting seven colours of the rainbow, it aimed to cover all those children by 2020 who are either unvaccinated, or are partially vaccinated against seven vaccine preventable diseases which include diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio, tuberculosis, measles and hepatitis B.
- The mission is technically supported by WHO, UNICEF, Rotary International and other donor Partners.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Science & Technology
Coping with Type-1 Diabetes
For Prelims: Type-1 Diabetes, ICMR, World Diabetes Day
For Mains: Diabetes, Healthcare, Initiatives to curb Diabetes, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) issued guidelines regarding diagnosis, treatment, and management for type-1 diabetes.
- This is the first time the ICMR has issued guidelines specifically for type 1 diabetes, which is rarer than type 2.
What do we Need to know about Diabetes?
- About: Diabetes is a Non-Communicable Disease (NCD) that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar, or glucose), or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin, it produces.
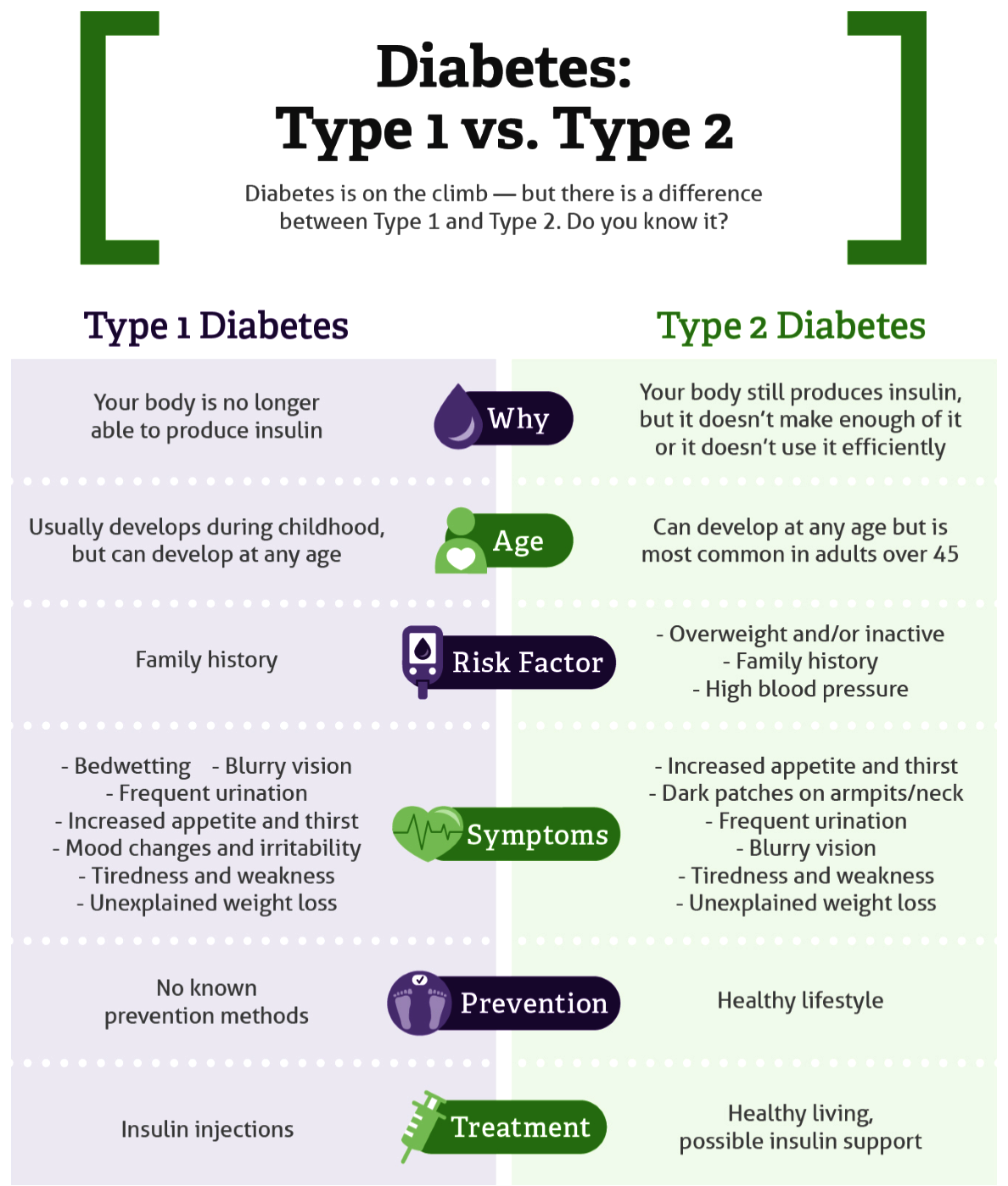
- Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- It is also known as juvenile diabetes (as it mostly affects children of age 14-16 years), this type occurs when the body fails to produce sufficient insulin.
- It is predominantly diagnosed in children and adolescents. Although the prevalence is less, it is much more severe than type 2.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- It affects the way the body uses insulin. While the body still makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes can occur at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs in women during pregnancy when the body sometimes becomes less sensitive to insulin. Gestational diabetes does not occur in all women and usually resolves after giving birth.
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- Impacts of Diabetes: It affects the five major organs namely, Kidney, Heart, Blood vessels, Nervous System, and Eyes (retina).
- Factors Responsible: Factors that lead to increase in diabetes are an unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, harmful use of alcohol, overweight/obesity, tobacco use, etc.
How Rare is Type-1 Diabetes?
- Out of 10 lakh children and adolescents living with type 1 diabetes in the world, India holds the highest numbers.
- Out of 2.5 lakh people living with type 1 diabetes in India, 90,000 to 1 lakh are under the age of 14 years.
- Only 2% of all hospital cases of diabetes in the country are type 1 — but which is being diagnosed more frequently.
What Factors Exacerbate the Condition?
- Genetic Factors: It plays a role in determining whether a person will get type-1 diabetes. The risk of disease in a child is:
- 3% when the mother has it
- 5% when the father has it
- 8% when a sibling has it.
- Presence of Certain Genes: It is also strongly associated with the disease. For example, the prevalence of genes called DR3-DQ2 and DR4-DQ8 is 30-40% in patients with type 1 diabetes as compared to 2.4% in the general population.
- DR3- DQ2 and DR4-DQ8 means the patient is permissive for celiac disease and is capable of developing or having the disease.
What are the Treatments?
- Glucose monitoring: Continuous glucose monitoring devices can help monitor the blood glucose levels throughout 24 hours with the help of a sensor.
- Artificial pancreas: It can automatically deliver insulin when required.
What are Related Initiatives?
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS):
- In order to prevent and control major NCDs, this initiative was launched by India in 2010 with focus on strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, early diagnosis, management and referral.
- World Diabetes Day:
- It is observed on 14th November every year. The 2022 campaign will focus on access to diabetes education. access to diabetes education.
- Global Diabetes Compact:
- WHO launched a Global Diabetes Compact to better fight the disease while marking the centenary of the discovery of insulin.
Important Facts For Prelims
Amendments in IBBI Regulations, 2017
Why in News?
Recently, the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India has amended Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Grievance and Complaint Handling Procedure) Regulations, 2017 and the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Inspection and Inspection and Investigation) Regulations, 2017.
What are IBBI Regulations, 2017?
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Grievance and Complaint Handling Procedure) Regulations, 2017:
- It provides a mechanism for redressal of complaints and grievances filed against insolvency professionals, insolvency professional agencies and information utilities.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Inspection and Investigation) Regulations, 2017:
- It provides a mechanism for carrying out inspections and investigations on insolvency professional agencies, insolvency professionals and information utilities and passing orders by Disciplinary Committee.
What are the Key Highlights of the Amendment?
- About:
- Revisions in various timelines related to enforcement process provided in the (Grievance and Complaint Handling Procedure) Regulations, 2017 and (Inspection and Investigation) Regulations, 2017 for addressing the issue of delay in present mechanism.
- Effective participation of IPAs (Insolvency Professional Agency) in regulating the IPs (Insolvency Professional) through examination of grievances received against IPs.
- Intimation to Committee of Creditor (CoC)/ Adjudicating Authority (AA) about the outcome of Disciplinary Committee (DC) order.
- Reason for Amendment:
- To have expeditious redressal and also to avoid placing an undue burden on the service providers.
What is Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India?
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India was established in 2016 under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (Code).
- It is a key pillar of the ecosystem responsible for implementation of the Code that consolidates and amends the laws relating to reorganization and insolvency resolution of corporate persons, partnership firms and individuals in a time bound manner for maximization of the value of assets of such persons, to promote entrepreneurship, availability of credit and balance the interests of all the stakeholders.
- It is a unique regulator as it regulates a profession as well as processes.
- It has regulatory oversight over the Insolvency Professionals, Insolvency Professional Agencies, Insolvency Professional Entities and Information Utilities.
- It has also been designated as the ‘Authority’ under the Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation Rules), 2017 for regulation and development of the profession of valuers in the country.