Facts for UPSC Mains
Department of Rural Development: Year Ender 2025
Why in News?
The Department of Rural Development released its Year Ender 2025, highlighting major gains in rural connectivity, housing, livelihoods, employment, skilling, and social security, alongside the enactment of a new employment guarantee law- marking a significant push towards inclusive and resilient rural growth.
What were the Major Outcomes of India’s Rural Development Efforts in 2025?
- Rural Connectivity and Physical Infrastructure: Since its inception in 2000 the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) has completed nearly 95% of sanctioned rural roads (7.87 lakh km) were completed, strengthening economic integration, border connectivity, and all-weather access.
- In 2025, high-performing states such as Tamil Nadu (highest number of roads laid), and Himachal Pradesh (highest road length) and Bihar (highest number of bridges constructed ) demonstrate region-specific gains, while focused investments in border, hilly, Left-wing extremists (LWE)-affected, and northeastern regions strengthened both economic integration and strategic access.
- Digital reforms like e-Bank Guarantees, and Standard Bidding Document (SBD) improved transparency and execution efficiency.
- Women-Centric Livelihood Transformation: The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) emerged as a cornerstone of inclusive growth by mobilising 10.05 crore women into 90.9 lakh Self Help Groups (SHGs).
- The sharp decline in non-performing assets (NPAs) from 9.58% (2014) to 1.76% (2025) reflects institutional maturity, disproving the narrative that poor households are “high‑risk borrowers”.
- The creation of 2 crore Lakhpati Didis marks a structural shift from subsistence to sustainable income generation, corroborated by evidence of 19% income growth and 28% increase in savings (3ie–World Bank study).
- Housing Security and Human Development: Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G) achieved large-scale housing outcomes with 3.86 crore houses sanctioned and 2.92 crore completed by December 2025, including 23.4 lakh houses completed in 2025 alone.
- Under Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyaan (PM JANMAN), 4.71 lakh houses were sanctioned and 2.42 lakh completed for PVTG households, directly addressing historical deprivation.
- Digital initiatives like AwaasSoft, Awaas+, PAHAL (Pratyaksh Hanstantrit Labh), and Aadhaar-based e-KYC improved beneficiary targeting, transparency, and disaster-resilient housing design.
- Skill Development and Employment Linkages: Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) under National Rural Livelihood Mission strengthened placement-linked skilling by training around 82,000 rural youth in 2025, while cumulative placements reached 11.64 lakh.
- Complementing this, Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETIs) trained 59 lakh rural youth, achieving 43 lakh settlements, with RSETI 2.0 enhancing credit linkage targets to 50%.
- Together, these schemes improved employability, entrepreneurship, and non-farm income diversification.
- Employment Security and Asset Creation: MGNREGS generated 161.6 crore person-days in FY 2025–26, with 56.73% women participation.
- The emphasis on productivity is evident in 49.62 lakh completed works, of which 60.59% were Category-B assets (community assets or individual assets for vulnerable sections) linked to agriculture and livelihoods.
- Digital interventions like National Mobile Monitoring System (95% attendance capture), GeoMGNREGA (6.44 crore assets geotagged), and Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) (99% wage payments) enhanced transparency and reduced leakages.
- The Viksit Bharat- Guarantee For Rozgar And Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) (VB–G RAM G) Act, 2025 marked a paradigm shift by expanding the statutory employment guarantee to 125 days, embedding Gram Sabha-led, bottom-up planning through Viksit Gram Panchayat Plans (VGPPs).
- These plans are aggregated into the Viksit Bharat National Rural Infrastructure Stack (VBNRIS), which consolidates Gram Panchayat proposals at district and state levels.
- The Act aligns employment generation with durable asset creation and the vision of Viksit Bharat @ 2047.
- Social Security and Welfare Delivery: National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP) operationalised Article 41 of the Constitution by supporting 3.01 crore beneficiaries in 2025–26.
- Near-universal digitisation, 91.45% Aadhaar seeding, and 44 lakh Digital Life Certifications improved inclusion and efficiency, while state top-ups enhanced pension adequacy.
- Governance and Cooperative Federalism: Designing Innovative Solutions for Holistic Access to Justice (DISHA) strengthened last-mile governance through district-level meetings, integrating 100 schemes from 35 ministries on a real-time dashboard.
- With district committees chaired by MPs and state-level committees led by Chief Ministers, DISHA institutionalised convergence, accountability, and cooperative federalism, improving coordination and on-ground delivery of rural development programmes.
Conclusion
Rural development outcomes in 2025 indicate a decisive shift from fragmented welfare delivery to an integrated, technology-enabled, and institution-driven development model. India is strengthening rural resilience, inclusiveness, and state capacity, aligning grassroots transformation with the long-term goal of Viksit Bharat.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. “Rural development in India is no longer about welfare delivery alone but about institution-building and resilience.” Discuss. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the significance of the VB–G RAM G Act, 2025?
It expands the statutory rural employment guarantee to 125 days, integrates bottom-up planning via Gram Sabhas, and links employment with durable infrastructure creation. - How did PMGSY contribute to rural connectivity by 2025?
Nearly 95% of sanctioned rural roads (7.87 lakh km) were completed, strengthening economic integration, border connectivity, and all-weather access. - Why is DAY-NRLM considered transformative for rural women?
It mobilised 10.05 crore women into SHGs, reduced NPAs to 1.76%, and enabled 2 crore Lakhpati Didis, signalling sustainable income generation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Which of the following grants/grant direct credit assistance to rural households? (2013)
- Regional Rural Banks
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development
- Land Development Banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q2. How does the National Rural Livelihood Mission seek to improve livelihood options of rural poor? (2012)
- By setting up a large number of new manufacturing industries and agribusiness centres in rural areas
- By strengthening ‘self-help groups’ and providing skill development
- By supplying seeds, fertilisers, diesel pump-sets and micro-irrigation equipment free of cost to farmers
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Despite consistent experience of high growth, India still goes with the lowest indicators of human development. Examine the issues that make balanced and inclusive development elusive. (2016)


Facts for UPSC Mains
Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024-25
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released its Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024-25 highlighting key trends in the Indian banking sector.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024-25?
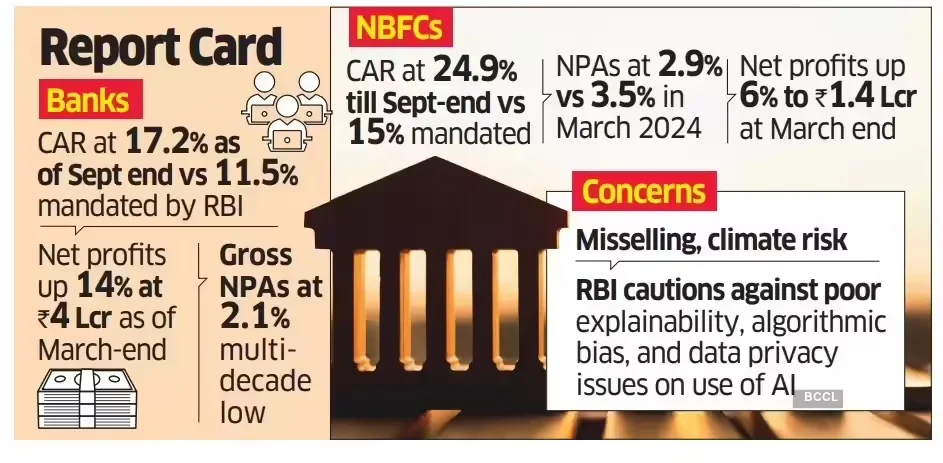
- Resilient Banking Sector: The Gross Non-Performing Asset (GNPA) ratio fell to a multi-decadal low of 2.2% (March 2025) and further to 2.1% (September 2025).
- The Capital to Risk-Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) stood at 17.4% ensuring the system can absorb potential shocks.
- Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) recorded double-digit balance sheet expansion (11.2%) and net profits rose to Rs 4 lakh crore.
- Banking Frauds: While the number of fraud cases declined, the total amount involved tripled to Rs 34,771 crore in 2024-25.
- Card/Internet frauds were most frequent (66.8% of cases), but advances-related (loan) frauds constituted the highest value (33.1% of amount).
- Private Banks reported most frauds by volume (59.3%), while Public Sector Banks bore the highest financial impact (70.7% of the total amount involved).
- Strong Performance of NBFCs: Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) recorded robust credit growth of 19.4% and account for about a quarter of SCB credit.
- NBFCs maintained strong capital buffers (CRAR of 25.9%) and saw improved asset quality.
- Mixed Picture for Cooperative Banks: Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) showed improvement in growth, asset quality (GNPA fell to 6.2%), and profitability.
- Rural Long-Term Cooperatives (like State co-operative agriculture and rural development banks) continued to face severe stress, with GNPA ratios alarmingly high at over 38%.
- Positive Macroeconomic Context: The report views India’s current macroeconomic phase positively, with inflation at multi-year lows and growth exceeding 8%, creating a conducive environment for financial stability. However, it calls for vigilance due to global uncertainties.
- Regulatory Concerns and Priorities: The RBI flagged several emerging risks and outlined its regulatory focus:
- Climate Risk: Warned that both physical and transition climate risks pose material threats to financial stability, terming climate finance a "national imperative."
- Consumer Protection: Expressed concern over misselling of financial products and plans to issue harmonised guidelines for advertising and recovery practices.
- Technological Challenges: Emphasised the need for ethical AI use, guarding against algorithmic bias, and managing risks from technological disruption and competition from non-banks.
Reports Released by RBI
Conclusion
The report underscores a resilient banking sector with strong fundamentals but cautions against emerging threats from high-value frauds, climate risks, and technological disruption, necessitating vigilant and adaptive regulation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the significance of the Reserve Bank of India integrating climate risk into its financial stability framework. What challenges might be faced in its implementation? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What was the GNPA ratio of scheduled commercial banks in 2024-25?
GNPA fell to a multi-decadal low of 2.2% (March 2025) and further to 2.1% (September 2025).
2. How did NBFCs perform during 2024-25?
NBFCs recorded 19.4% credit growth, contributed about 25% of SCB credit, maintained a CRAR of 25.9%, and improved asset quality.
3. What major emerging risk did the RBI term a "national imperative"?
The RBI emphasized that addressing climate-related financial risks (both physical and transition) is a national imperative, requiring coordinated action for financial stability
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Which one of the following links all the ATMs in India? (2018)
(a) Indian Banks’ Association
(b) National Securities Depository Limited
(c) National Payments Corporation of India
(d) Reserve Bank of India
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion. (2016)


Important Facts For Prelims
NATGRID–NPR Integration
Why in News?
National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) has been linked to the National Population Register (NPR), allowing authorised agencies real-time access to family-level demographic data of nearly 119 crore residents, significantly expanding India’s intelligence and investigation architecture.
What are the Key Facts About National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID)?
- NATGRID: It is a secure, integrated intelligence-sharing platform designed to help law enforcement and security agencies access multiple databases in real time for counter-terrorism and criminal investigations.
- NATGRID was conceived in 2009, in the aftermath of the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks (2008), to overcome information silos among security agencies and enable faster, intelligence-led responses.
- It became operational in 2023 and currently processes around 45,000 data access requests per month from authorised agencies.
- Initially limited to 10 central agencies (IB, RAW, NIA, ED, FIU, NCB, DRI, etc.) had access. It has now been expanded to SP-rank officers of State police, strengthening Centre–State coordination.
- NATGRID was conceived in 2009, in the aftermath of the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks (2008), to overcome information silos among security agencies and enable faster, intelligence-led responses.
- Key Tools: Advanced analytics tools like Gandiva support facial recognition, entity resolution, and multi-source data analysis, allowing investigators to identify suspects using images and family-linked NPR data.
- An Organised Crime Network Database is being developed on NATGRID to enable secure data-sharing between the NIA and State Anti-Terror Squads.
- Nature of Data Access: NATGRID allows access to Aadhaar, banking, tax, FASTag, passport, travel, Financial Intelligence Unit and social media data. The information is categorised as non-sensitive, sensitive, and highly sensitive (bank statements, financial and tax data, export-import details).
- Privacy and Safeguards: Each query is logged, purpose-based, and subject to senior officer oversight, but data access without a First Information Report (FIR) raises concerns over privacy, proportionality, and due process.
- Federal Dimension: States have been encouraged to actively use NATGRID, strengthening Centre–State intelligence coordination.
- NATGRID’s architecture is designed to integrate databases connected to nearly 14,000 police stations across the country.
National Population Register (NPR)
- The NPR is a nationwide database containing demographic and family-wise details of residents in India, including name, age, gender, address, and family relationships.
- NPR is the first step for the creation of a countrywide National Register of Citizens (NRC).
- The NPR is prepared under the provisions of the Citizenship Act 1955 and the Citizenship (Registration of Citizens and Issue of National Identity Cards) Rules, 2003. It is mandatory for every “usual resident of India” to register in the NPR.
- A usual resident is a person who has lived in a local area for six months or more, or intends to reside there for the next six months or more.
- NPR data was collected during the 2010–11 Census and last updated in 2015. no decision has been taken to update it during the upcoming Census 2027.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is NATGRID and why was it created?
NATGRID is a secure intelligence-sharing platform conceived after the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks to break information silos and enable real-time data access for counter-terrorism and criminal investigations. - What new capability does linking NATGRID with NPR provide?
It allows authorised agencies real-time access to family-level demographic data of residents, improving suspect identification and network analysis. - Which law governs the National Population Register?
NPR is prepared under the Citizenship Act, 1955 and the Citizenship (Registration of Citizens and Issue of National Identity Cards) Rules, 2003.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2009)
- Between Census 1951 and Census 2001, the density of the population of India has increased more than three times.
- Between Census 1951 and Census 2001, the annual growth rate (exponential) of the population of India has doubled.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue
Ambassadors of the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) countries- the US, India, Australia, and Japan, held a rare publicised meeting in Beijing, describing their ties as “stable and strong.”
- About: The QUAD began as a humanitarian coordination mechanism after the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami.
- Originally proposed in 2007 by Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, the framework remained inactive after Australia stepped back in 2008 before being revived in 2017 against the backdrop of China’s growing Indo-Pacific assertiveness.
- It focuses on regional security, economic cooperation, maritime safety, infrastructure, and supply chain resilience, while not being a formal military alliance.
- Vision of the Quad: The 2021 QUAD Leaders’ Summit adopted the “Spirit of the Quad”, reaffirming a free, open, inclusive Indo-Pacific anchored in democratic values, rule of law, and freedom from coercion.
- Key QUAD Initiatives:
- QUAD At Sea Ship Observer Mission: Launched under the Wilmington Declaration (2024) of the QUAD, it is an initiative to boost interoperability, maritime domain awareness, and operational coordination in the Indo-Pacific.
- Malabar Exercise: It is a major annual multilateral naval drill involving the Quad nations, focused on enhancing maritime coordination, interoperability, and readiness in the Indo-Pacific.
- Expansion Potential: The “Quad Plus” engagements have involved countries such as South Korea, New Zealand, and Vietnam, reflecting the grouping’s potential for future expansion.
- China’s Opposition: It has repeatedly opposed the Quad, describing it as “bloc politics like NATO” and warning against cooperation that targets third countries, reinforcing China’s discomfort with Indo-Pacific coalitions.
- Despite China’s claims, the Quad has no mutual defence treaty. It focuses on strategic coordination, maritime security, economic cooperation, and rules-based order, not collective military defence.
| Read more: Quad Marks 20 Years of Cooperation |


Rapid Fire
Birth Anniversary of Mannathu Padmanabhan
The Prime Minister paid tribute to Mannathu Padmanabhan (2nd January 1878 – 25th February 1970) on his birth anniversary, remembering him as a towering social reformer who dedicated his life to dignity, equality, and nation-building.
- About: Mannathu Padmanabhan was a leading social reformer from Kerala, known for challenging caste discrimination and social exclusion.
- Founded the Nair Service Society (NSS) in 1914, he institutionalised social reform, education, and community upliftment, ensuring his ideals endured well beyond his lifetime.
- Influence of Gandhian Thought: Deeply inspired by Mahatma Gandhi, he embraced Satyagraha as a moral and political tool for social justice.
- Champion of Anti-Untouchability Movements: He led the Savarnajatha Satyagraha, advocating temple access for oppressed communities, which contributed to the historic Temple Entry Proclamation.
- His participation in the Vaikom (1924) and Guruvayoor (1931) Satyagraha placed him at the forefront of India’s struggle against caste discrimination.
- He consistently promoted peace, unity, and inter-community harmony, strengthening Kerala’s pluralistic ethos.
- Awards & Recognition: He was awarded the Padma Bhushan (1966) and honoured with the title Bharata Kesari by the President of India for his contributions to social reform.
- Freedom Fighter: Actively involved in the Indian national movement especially in Travancore, he faced imprisonment, reflecting his commitment to both political freedom and social reform.
- Transformational Legacy: He revitalised an entire community by teaching the philosophy of action, unity, and self-change. His influence continues across generations, firmly embedded in Kerala’s social, political, and cultural history.
| Read more: 100 Years of Vaikom Satyagraha |


Rapid Fire
Galaxy Frogs
A study reports that seven rare Galaxy Frogs have disappeared and are presumed dead, with unethical wildlife photography and rising photo tourism in the Western Ghats identified as the key causes.
- About: Galaxy Frog (Melanobatrachus indicus) is a rare, endemic amphibian found only in the Western Ghats of Kerala.
- Named for its shiny black skin with blue speckles and orange markings, resembling a star-filled galaxy.
- Habitat and Distribution: Found exclusively under rotten logs in cool, moist forest patches, the species is endemic to the wet evergreen forests of the southern Western Ghats in Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
-
Galaxy Frogs were declared the flagship species of Mathikettan Shola National Park in Idukki, Kerala.
Physical and Behavioural Features: Measuring only 2–3.5 cm, the species is non-vocal, cold-blooded, and relies partly on moist skin for respiration, making it highly sensitive to heat, drying, and disturbance..
-
- Conservation Status: It is listed as Vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Low population density and limited habitat increase extinction risk.
|
Read more: Agroforestry's Impact to Endemic Frogs |


Rapid Fire
Adult Skill Assessment Survey, 2026
India is set to conduct its first nationwide assessment of adult skill competencies in 2026 to generate crucial data for tackling workforce challenges and harnessing the demographic dividend.
Adult Skill Assessment Survey
- Conducting Body: The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) will conduct the survey using the Comprehensive Modular Survey (CMS) framework, at the request of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- CMS enables the conduct of targeted, short-duration household surveys on specific topics (narrower in scope and shorter in duration) to address immediate policy needs of ministries and departments.
- Scope & Objective: It will cover the population aged 18 years and above (3-month survey), categorising their abilities into basic, intermediate, and advanced skill levels.
- Need of the Survey: The need is urgent as India’s working-age population (15-59 year) is projected to reach 68.9% by 2030. Presently, there is no dedicated data on overall skill levels in India.
- Data Gaps in Existing Surveys: The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) only records whether individuals have received vocational or technical training, not the quality or level of skills acquired. This limits the ability to assess workforce readiness accurately.
- Skill–Employability Mismatch: Nearly three-fourths of the employed population possess only basic education. Employability among graduates is just 54.8%, highlighting a serious mismatch between education outcomes and labour market needs.
- Trends in Vocational Training: The share of those aged 15–59 receiving vocational/technical training rose to 34.7% in 2023–24, up from 27.4% in 2022–23.
- However, rising participation has not translated proportionately into employability, reinforcing the need for skill-quality assessment.
| Read More: Restructuring Skill India Programme |