Facts for UPSC Mains
Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024-25
- 03 Jan 2026
- 6 min read
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released its Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024-25 highlighting key trends in the Indian banking sector.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024-25?
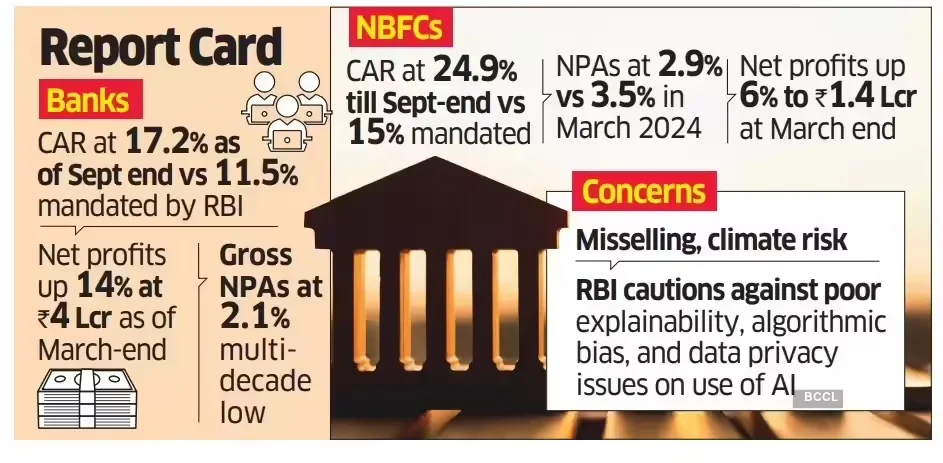
- Resilient Banking Sector: The Gross Non-Performing Asset (GNPA) ratio fell to a multi-decadal low of 2.2% (March 2025) and further to 2.1% (September 2025).
- The Capital to Risk-Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) stood at 17.4% ensuring the system can absorb potential shocks.
- Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) recorded double-digit balance sheet expansion (11.2%) and net profits rose to Rs 4 lakh crore.
- Banking Frauds: While the number of fraud cases declined, the total amount involved tripled to Rs 34,771 crore in 2024-25.
- Card/Internet frauds were most frequent (66.8% of cases), but advances-related (loan) frauds constituted the highest value (33.1% of amount).
- Private Banks reported most frauds by volume (59.3%), while Public Sector Banks bore the highest financial impact (70.7% of the total amount involved).
- Strong Performance of NBFCs: Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) recorded robust credit growth of 19.4% and account for about a quarter of SCB credit.
- NBFCs maintained strong capital buffers (CRAR of 25.9%) and saw improved asset quality.
- Mixed Picture for Cooperative Banks: Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) showed improvement in growth, asset quality (GNPA fell to 6.2%), and profitability.
- Rural Long-Term Cooperatives (like State co-operative agriculture and rural development banks) continued to face severe stress, with GNPA ratios alarmingly high at over 38%.
- Positive Macroeconomic Context: The report views India’s current macroeconomic phase positively, with inflation at multi-year lows and growth exceeding 8%, creating a conducive environment for financial stability. However, it calls for vigilance due to global uncertainties.
- Regulatory Concerns and Priorities: The RBI flagged several emerging risks and outlined its regulatory focus:
- Climate Risk: Warned that both physical and transition climate risks pose material threats to financial stability, terming climate finance a "national imperative."
- Consumer Protection: Expressed concern over misselling of financial products and plans to issue harmonised guidelines for advertising and recovery practices.
- Technological Challenges: Emphasised the need for ethical AI use, guarding against algorithmic bias, and managing risks from technological disruption and competition from non-banks.
Reports Released by RBI
Conclusion
The report underscores a resilient banking sector with strong fundamentals but cautions against emerging threats from high-value frauds, climate risks, and technological disruption, necessitating vigilant and adaptive regulation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the significance of the Reserve Bank of India integrating climate risk into its financial stability framework. What challenges might be faced in its implementation? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What was the GNPA ratio of scheduled commercial banks in 2024-25?
GNPA fell to a multi-decadal low of 2.2% (March 2025) and further to 2.1% (September 2025).
2. How did NBFCs perform during 2024-25?
NBFCs recorded 19.4% credit growth, contributed about 25% of SCB credit, maintained a CRAR of 25.9%, and improved asset quality.
3. What major emerging risk did the RBI term a "national imperative"?
The RBI emphasized that addressing climate-related financial risks (both physical and transition) is a national imperative, requiring coordinated action for financial stability
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Which one of the following links all the ATMs in India? (2018)
(a) Indian Banks’ Association
(b) National Securities Depository Limited
(c) National Payments Corporation of India
(d) Reserve Bank of India
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion. (2016)