Indian Economy
Reforming Special Economic Zones in India
For Prelims: Special Economic Zones (SEZ) Rules, 2006, Semiconductor, Foreign Exchange, Foreign Trade Policy, External Commercial Borrowing (ECB), OECD, World Trade Organization (WTO), Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme, Baba Kalyani Committee, Industrial Corridors, National Investment and Manufacturing Zones (NIMZ), National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP).
For Mains: Key reforms in SEZ rules to boost semiconductor and electronics manufacturing, Key challenges faced by SEZs and Baba Kalyani committee recommendations, Steps need to be taken to strengthen SEZs.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Commerce & Industry has introduced key amendments to the Special Economic Zones (SEZ) Rules, 2006, to encourage investment and streamline operations in semiconductor and electronics component manufacturing.
- These changes aim to foster high-tech sector growth, which is capital-intensive, import-dependent, and requires long gestation periods to become profitable.
- Following recent amendments, Micron will develop a semiconductor SEZ in Sanand, Gujarat. Aequs Group will also set up an electronics component SEZ in Dharwad, Karnataka.
What are the Key Changes in SEZ Rules for Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing?
- Reduced Land Requirement for SEZs: The minimum land requirement for SEZs in semiconductor and electronics manufacturing has been reduced from 50 Ha to 10 Ha, lowering entry barriers and facilitating the setup of high-tech units.
- Relaxation in Land Encumbrance Rules: The Board of Approval can now relax the encumbrance-free land requirement if land is mortgaged or leased to the Central/State governments or their agencies, offering greater flexibility in land acquisition and financing.
- The Board of Approval is the apex body for SEZs and is headed by the Secretary, Department of Commerce (Ministry of Commerce and Industry).
- Inclusion of Free-of-Cost Goods in Net Foreign Exchange: The amended rule allows free-of-cost goods to be included in Net Foreign Exchange (NFE) calculations i.e., their value can be added to exports or subtracted from imports, improving the SEZ unit’s NFE performance.
- Allowance to Domestic Sales: SEZ units in semiconductor and electronics manufacturing can now supply to the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) after paying duties, enhancing viability by accessing the Indian market and reducing export dependence.
What are Special Economic Zones (SEZ)?
- About: A SEZ is a duty-free enclave treated as foreign territory for the purpose of trade, tariffs, and operations. Any private/public/joint sector or State Government or its agencies can set up SEZ.
- SEZs were first introduced in India in 2000 under the Foreign Trade Policy, replacing the earlier Export Processing Zones (EPZs). They are governed by the SEZ Act, 2005 and SEZ Rules, 2006.
- The Development of Enterprise and Service Hubs (DESH) Bill, 2022 aims to replace the SEZ Act, 2005 and transform SEZs into more flexible and inclusive Development Hubs.
- These hubs will be exempt from many existing regulatory restrictions and will support both export-oriented and domestic investments, functioning as integrated zones for international and domestic trade.
- SEZ Types: The area under SEZ includes a wide range of zone types, such as Export Processing Zones (EPZ), Free Zones (FZ), Industrial Estates (IE), Free Trade Zones (FTZ), Free Ports, Urban Enterprise Zones, and others.
- Currently, 276 SEZs are operational in India. Total exports from SEZs in 2023-2024 stood at USD 163.69 billion.
- E.g., Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City, India).
- Objective:
- To create additional economic activity
- To boost the export of goods and services
- To generate employment
- To boost domestic and foreign investments
- To develop infrastructure facilities
- Incentives offered to SEZs:
- Duty-free import/domestic procurement of goods for the development, operation, and maintenance of SEZ units
- Exemption from Central Sales Tax, Service Tax, and State Sales Tax (now subsumed under GST)
- Other levies exempted by respective State Governments
- Supplies to SEZ are zero-rated under the IGST Act, 2017
- Single-window clearance for Central and State level approvals
- External Commercial Borrowing (ECB) by SEZ units is allowed up to USD 500 million per year with no maturity restriction, through recognized banking channels.
What are the Key Challenges Faced by SEZs in India?
- Declining Cost Competitiveness: Indian SEZs face declining cost competitiveness mainly due to rising input costs such as raw materials, energy, and logistics, which are significantly higher than in competing countries like China and Vietnam.
- OECD tax norms (15% minimum corporate tax) may further reduce SEZ incentives for multinational companies in SEZs.
- SEZ subsidies are under World Trade Organization (WTO) scrutiny, with rising pressure to phase out export-linked incentives to align with global trade rules.
- Land Acquisition & Infrastructure Issues: SEZs face challenges such as high land costs, poor connectivity and logistics, and irregular power and water supply, all of which hinder timely development and reduce manufacturing efficiency.
- Regulatory & Compliance Burdens: Despite single-window clearance, SEZs face delays from multiple agencies, while positive forex obligations, frequent audits, and high compliance costs burden startups and R&D-focused firms.
- Limited Domestic Market Access: SEZ units face high duties on Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) sales and unequal competition from non-SEZ firms receiving Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme benefits, reducing their overall attractiveness.
- Furthermore, with around 70% of SEZs concentrated in IT and related services, manufacturing occupies a much smaller portion, potentially hindering wider industrial development goals.
- Underutilization & Vacant SEZs: A 40% gap between approved and notified SEZs and over 60% gap between notified and operational ones highlight long gestation periods, poor viability assessment.
- Some SEZs are misused for real estate development, shifting focus from export-oriented manufacturing to commercial hubs.
- Environmental & Sustainability Concerns: Rapid industrialization in SEZs often causes pollution and resource depletion, worsened by weak enforcement of environmental regulations.
Baba Kalyani Committee (2018)
- The Ministry of Commerce and Industry constituted a committee in June 2018, chaired by Mr. Baba Kalyani to review India’s SEZ policy and recommend strategic measures to align with global opportunities and domestic economic goals.
- Major Recommendations:
- Rename SEZs as 3Es – Employment and Economic Enclaves: Shift focus from export-centric zones to employment and economic growth hubs.
- Target domestic demand, not just exports.
- Delink from Net Foreign Exchange (NFE) Performance: Allow domestic supplies and payments in Rupees
- Incentives to be based on investment, job creation, women employment, value addition, and technology differentiation.
- Separate frameworks for manufacturing and services SEZs: Create sector-focused enclaves for better demand and synergy
- Ease of Doing Business (EoDB): Establish one integrated online portal for investment, operations, and exits
- Infrastructure Development: Develop high-quality infrastructure including high-speed rail, expressways, ports, warehouses, and airports.
- Enable walk-to-work zones for integrated industrial-urban development.
- Rename SEZs as 3Es – Employment and Economic Enclaves: Shift focus from export-centric zones to employment and economic growth hubs.
What Measures can be Adopted to Strengthen SEZs in India?
- Policy & Regulatory Reforms: Replace the SEZ Act, 2005 with the more flexible Development of Enterprise and Services Hub (DESH), and simplify de-notification and exit policies for non-performing SEZs.
- Implement Baba Kalyani Committee (2018) recommendations by renaming SEZs as Employment & Economic Enclaves (3Es), and creating separate rules for manufacturing and services.
- Infrastructure & Connectivity Upgrades: Integrate SEZs with industrial corridors and enhance last-mile connectivity to ports and airports for seamless logistics.
- Ensure 24/7 power, water recycling, and pre-approved infrastructure while promoting sector-specific clusters to attract global investment and boost manufacturing efficiency.
- Enhancing Competitiveness & Global Integration: Provide R&D tax incentives and link SEZs with National Research Foundation to promote innovation in semiconductors, AI, and biotech.
- Strengthen export infrastructure through customs hubs, e-commerce zones, and fast-track approvals for major global firms.
- Skill Development & Employment: Set up Skill Parks near SEZs in collaboration with ITIs/NSDC, offering industry-aligned training and German-style dual vocational programs.
- Incentivize local job creation through tax breaks and EPF support, and provide special visas for foreign experts in advanced manufacturing.
- Adopt Global Best Practices: India can adopt global best practices like China’s mega-cluster model (Shenzhen), and UAE’s tax-free zones with 100% foreign ownership (Dubai) to enhance SEZ competitiveness.
What are the Other Key Government Initiatives Related to Industrial Development?
- National Investment and Manufacturing Zones (NIMZ): NIMZs (like Prakasam in Andhra Pradesh and Sangareddy in Telangana) are large, integrated industrial townships developed under India’s National Manufacturing Policy (NMP), 2011 to boost manufacturing growth, create jobs, and enhance global competitiveness.
- Industrial Parks: Industrial Parks (or Industrial Estates or Industrial Zones) are designated areas developed with infrastructure, utilities, and policy incentives to promote manufacturing, logistics, and industrial activities.
- They provide businesses with ready-to-use facilities, reducing setup costs and operational hassles.
- E,g., Manufacturing Parks (for factories & production units), Food Processing Parks (for agri-based industries).
- National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP): NICDP aims to develop world-class industrial nodes, smart cities, and logistics hubs along key transport routes, with 11 industrial corridors planned to connect major economic hubs across India.
Conclusion
The recent SEZ rule amendments aim to boost semiconductor and electronics manufacturing by easing land norms and allowing domestic sales. However, challenges like policy instability, infrastructure gaps, and WTO compliance persist. Implementing Baba Kalyani reforms, improving logistics, and adopting global best practices can strengthen SEZs, making India a competitive hub for high-tech manufacturing and exports.
|
Drishti Mains Question Evaluate the challenges faced by Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India and suggest a roadmap for their revitalization. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2009)
- The first telegraph line in India was laid between Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) and Diamond Harbour.
- The first Export Processing Zone in India was set up in Kandla.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. There is a clear acknowledgement that Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are a tool of industrial development, manufacturing and exports. Recognizing this potential, the whole instrumentality of SEZs requires augmentation. Discuss the issue plaguing the success of SEZs with respect to taxation, governing laws and administration. (2015)


Important Facts For Prelims
Birsa Munda Martyr’s Day
Why in News?
Prime Minister (PM) paid tribute to Bhagwan Birsa Munda on 9th June 2025 on the occasion of his Martyr’s Day.
Who was Birsa Munda?
- About: Birsa Munda was a tribal leader, religious reformer, and freedom fighter who led a strong resistance against British colonial policies in the Chotanagpur region.
- Also known as Dharti Abba (Father of the Earth), he is remembered for mobilising Adivasi communities around land rights, social reform, and spiritual unity.
- Early Life: Born on 15th November 1875 in Ulihatu (Khunti district, Jharkhand) to a poor Munda tribal sharecropper family, Birsa was initially named Daud Munda due to his father's temporary conversion to Christianity.
- Education: Educated at the German Mission School, Birsa was initially influenced by Christian teachings but rejected them due to cultural alienation.
- He was inspired by Vaishnavism, he founded the Birsait religion and was revered as Bhagwan by his followers.
- Beliefs and Teachings: He preached monotheism through the worship of Singhbonga (sun god), denounced alcoholism, black magic, superstitions, and forced labour (beth begari), and promoted hygiene, spiritual unity, pride in tribal identity, and community land ownership.
- Resistance Against British Rule: British land revenue policies dismantled the traditional Khunt Katti land system (collective land ownership within a clan), empowering zamindars and thikadars who exploited tribal peasants.
- Birsa mobilised tribal masses against these injustices and campaigned to reclaim their rights.
- The Ulgulan Movement (1895–1900): In 1895, Birsa Munda was arrested for rioting and jailed for 2 years; after his release in 1897, he resumed mobilising support across villages for a tribal-led self-rule movement.
- In 1899, he launched the Ulgulan (The Great Tumult) movement, which included guerrilla warfare tactics to resist British authority and promote the establishment of a self-governed tribal state known as "Birsa Raj"
- Aftermath and Legacy: He was captured in February 1900 and died in British custody on 9th June 1900 at the young age of 25, under mysterious circumstances, officially attributed to cholera.
- His movement led to the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act (1908), which recognised tribal land rights (Khuntkatti), banned land transfer to non-tribals, and abolished beth begari (forced labour).
- Since 2021, 15th November is observed as Janjatiya Gaurav Divas (Tribal Pride Day).
Key Initiatives Related to Tribal Communities
- Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan is an umbrella initiative that targets integrated development across 63,000 Scheduled Tribe-majority villages.
- PM-JANMAN was initiated in 2023 to support Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) with targeted schemes, including healthcare, financial inclusion, and community support.
- Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAAGY) aims to provide basic infrastructure in villages with a significant tribal population.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: C
Q.2 Consider the following pairs: (2013)
|
|
Tribe |
State |
|
1. |
Limboo (Limbu) |
Sikkim |
|
2. |
Karbi |
Himachal Pradesh |
|
3. |
Dongaria Kondh |
Odisha |
|
4. |
Bonda |
Tamil Nadu |
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Goa Achieves Full Functional Literacy
Why in News?
Goa has been declared fully functionally literate under the Ministry of Education’s ULLAS (Understanding of Lifelong Learning for All in Society)-Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram programme, also known as the New India Literacy Programme (NILP).
- While Goa’s literacy rate was 93.60% as per PLFS 2023–24, a state-level ULLAS survey confirmed it has crossed the 95% functional literacy benchmark.
- Earlier, Mizoram became the first state and Ladakh the first UT to achieve full functional literacy.
Functional literacy
- It refers to an individual’s ability to apply reading, writing, and numeracy skills in daily life to enhance personal development and community participation.
- The ULLAS not only covers basic literacy but also equips learners with critical life skills, encouraging lifelong learning and active citizenship.
What is ULLAS- Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram ?
- About: ULLAS is a centrally sponsored scheme being implemented from 2022 to 2027, designed to empower adults aged 15 years and above who missed out on formal schooling.
- It aimed at promoting Education for All, earlier known as Adult Education and it is in line with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Objective: Its target is to achieve Foundational Literacy and Numeracy for 5 crore learners during FY 2022–27 (1 crore learners per year).
- 5 Key Components of Scheme: Foundational Literacy and Numeracy, Critical Life Skills, Basic Education, Vocational Skills & Continuing Education.
- Implementation Mechanism: Scheme is implemented through volunteerism in hybrid (both in online and offline) mode to instill social responsibility and a strong sense of duty (‘Kartavya Bodh’) among citizens.
- Key Features:
- Offers access to learning resources through the DIKSHA platform and ULLAS mobile/web portal, with support for 22 Indian languages, promoting inclusive and multilingual education across regions.
- Incorporates the Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT), held twice a year or as needed in local schools for evaluation and certification.
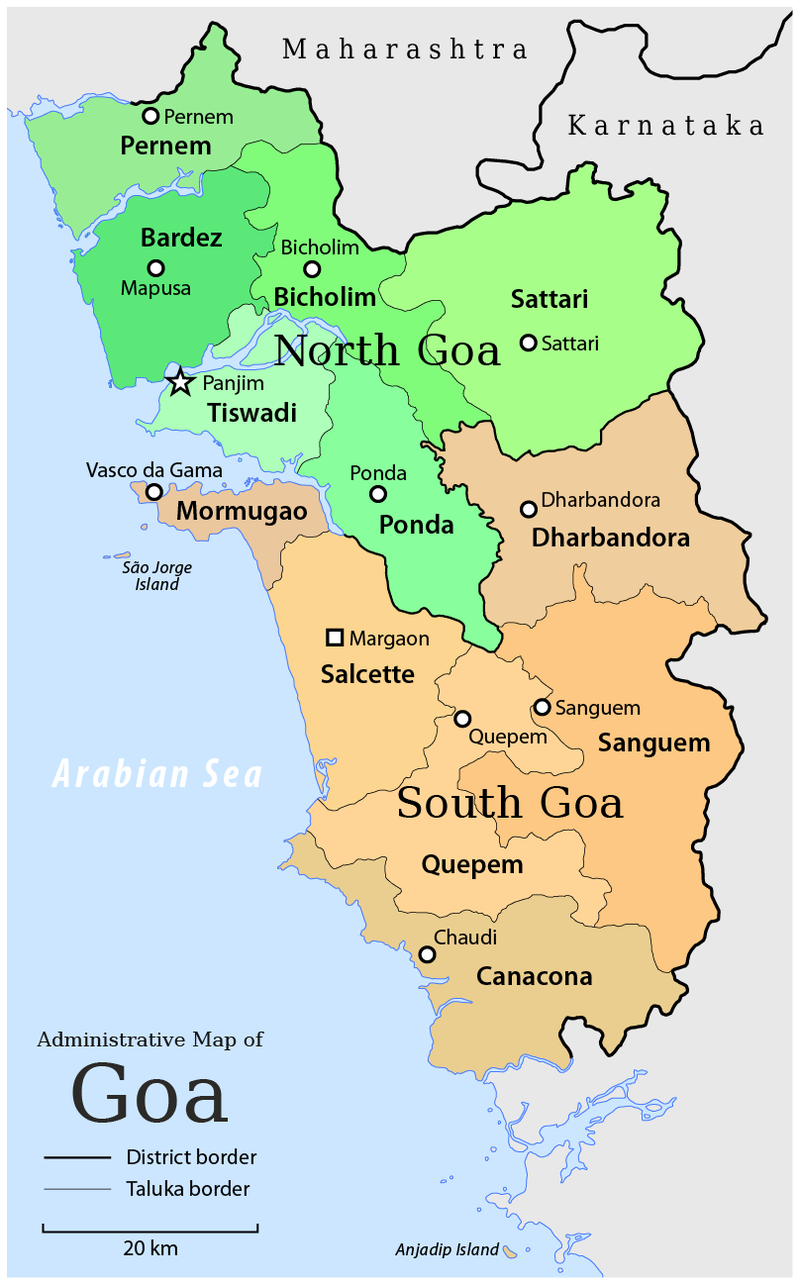
What are the Key Facts About Goa?
- Goa (capital Panaji), is located on the southwestern coast of India in the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan by the Western Ghats.
- After India’s independence in 1947, Portugal continued to retain control over its Indian territories despite repeated diplomatic efforts by India. In 1961, India launched Operation Vijay, resulting in the liberation of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
- Goa Liberation Day is observed on 19th December to commemorate the event.
- On 30th May 1987, Goa attained statehood, while Daman and Diu remained a Union Territory so, 30th May is observed annually as Goa Statehood Day.
- On 26th January 2020, the UTs of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli were merged to form a single UT named Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Tardigrades Aboard Axiom-4 Mission to Test Space Resilience
Why in News?
Indian astronaut, Shubhanshu Shukla, will pilot the Axiom-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS) while Peggy Whitson (USA) will command the mission.
- As a part of the mission, ISRO is sending tardigrades (water bears)—microscopic, hardy organisms—to the ISS to study how life can survive in extreme space conditions.
What is the Axiom-4 Mission?
- About: Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4) is the 4th private spaceflight to the ISS, operated by Axiom Space, a US-based space company, using the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft.
- With this, Shubhanshu Shukla will become the 2nd Indian to travel to space (after Rakesh Sharma in 1984) and the 1st Indian to set foot on the ISS.
- Key Features: Axiom Space’s 14-day mission aboard the ISS will conduct scientific experiments, tech demonstrations, and educational outreach, advancing its goal to build the first commercial space station and transition from ISS reliance to an independent orbital platform.
- It features an international crew comprising members from the United States, India, Poland, and Hungary.
- Key Experiment:
- Physical and cognitive impact of using computer screens in microgravity.
- Behaviour and response of tardigrades (water bears) in space
- Impact of spaceflight on six varieties of crops specifically on moong dal.
- Growth rate, cellular responses, and biochemical activity of cyanobacteria (a group of bacteria that are known to produce energy through photosynthesis just like plants).
- Significance for India: Strengthens Indo-US space collaboration through ISRO-NASA partnership while conducting 10 critical experiments (microgravity, seed growth, tardigrade studies) to validate research for Gaganyaan mission (2027).
- Boosted the success of Gaganyaan mission by providing hands-on experience for Gaganyaan crew training, advancing astrobiology research, and positioning India as a key player in future commercial space stations.
Note: Zero-G indicator is a small item, often a plushie (soft, stuffed toy), that provides astronauts a visual cue that they have entered a state of weightlessness. The zero-G indicator for the Axiom-4 mission is a swan plushie named ‘Joy’.
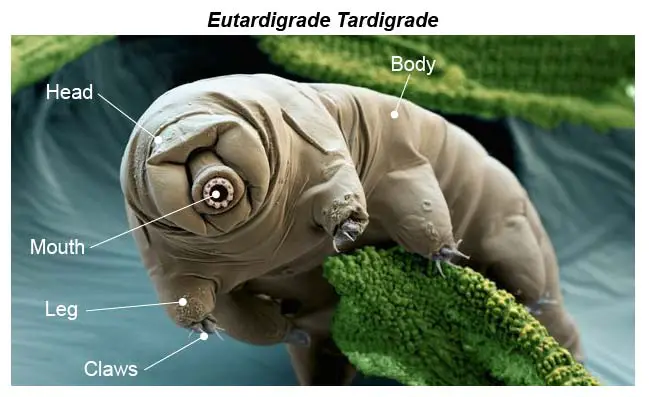
What are Key Points About Tardigrades?
- About: Tardigrades (also known as water bears or moss piglets) are microscopic, eight-legged organisms about 0.5 mm long that feed on plant and algae fluids.
- They’ve existed for ~600 million years and survived all five mass extinctions, making them one of the most resilient life forms on Earth.
- They are found in diverse moist habitats—from mountaintops to deep seas—and are known for their extreme durability.
- Survival Abilities: Tardigrades can survive extreme conditions—from temperatures of –272.95°C to 150°C, intense UV radiation, vacuum of space, and pressures up to 40,000 kilopascals, even reviving after 30 years in frozen states.
- Survival Mechanisms:
- Cryptobiosis: Near-complete metabolic shutdown in harsh conditions.
- Anhydrobiosis: Reduces water content by >95%, entering a durable shrunken state called tun.
- Unique Proteins (CAHS): Cytoplasmic-abundant heat soluble (CAHS) proteins form a protective gel within their cells, protecting essential cellular components from destruction.
- Scientific Importance: Research on tardigrades could lead to climate-resilient crops, advanced UV-protective sunscreens, and improved organ preservation techniques for transplants.
- Space Survivors: Tardigrades made history in 2007 as the first animals to survive direct exposure to space during ESA's Foton-M3 mission, proving their extraordinary resilience beyond Earth's atmosphere.
Note: Batillipes chandrayaani is a newly discovered species of marine tardigrade found along India's southeast coast of Tamil Nadu.
- It was named in honour of India's Chandrayaan-3 moon mission, reflecting a symbolic connection between India's advancements in space exploration and marine biology.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following space missions: (2025)
- Axiom-4
- SpaDeX
- Gaganyaan
How many of the space missions given above encourage and support microgravity research?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: (c)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
Giant Planet Orbiting Red Dwarf Star
Astronomers have discovered a Saturn-sized gaseous planet orbiting the red dwarf star TOI-6894 beyond our solar system.
- The planet was studied primarily using data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and the Very Large Telescope (VLT) operated by the European Southern Observatory in Chile.
- Planets beyond our solar system are called exoplanets.
- It is the smallest-known star to host such a massive planet challenging conventional theories of planetary formation.
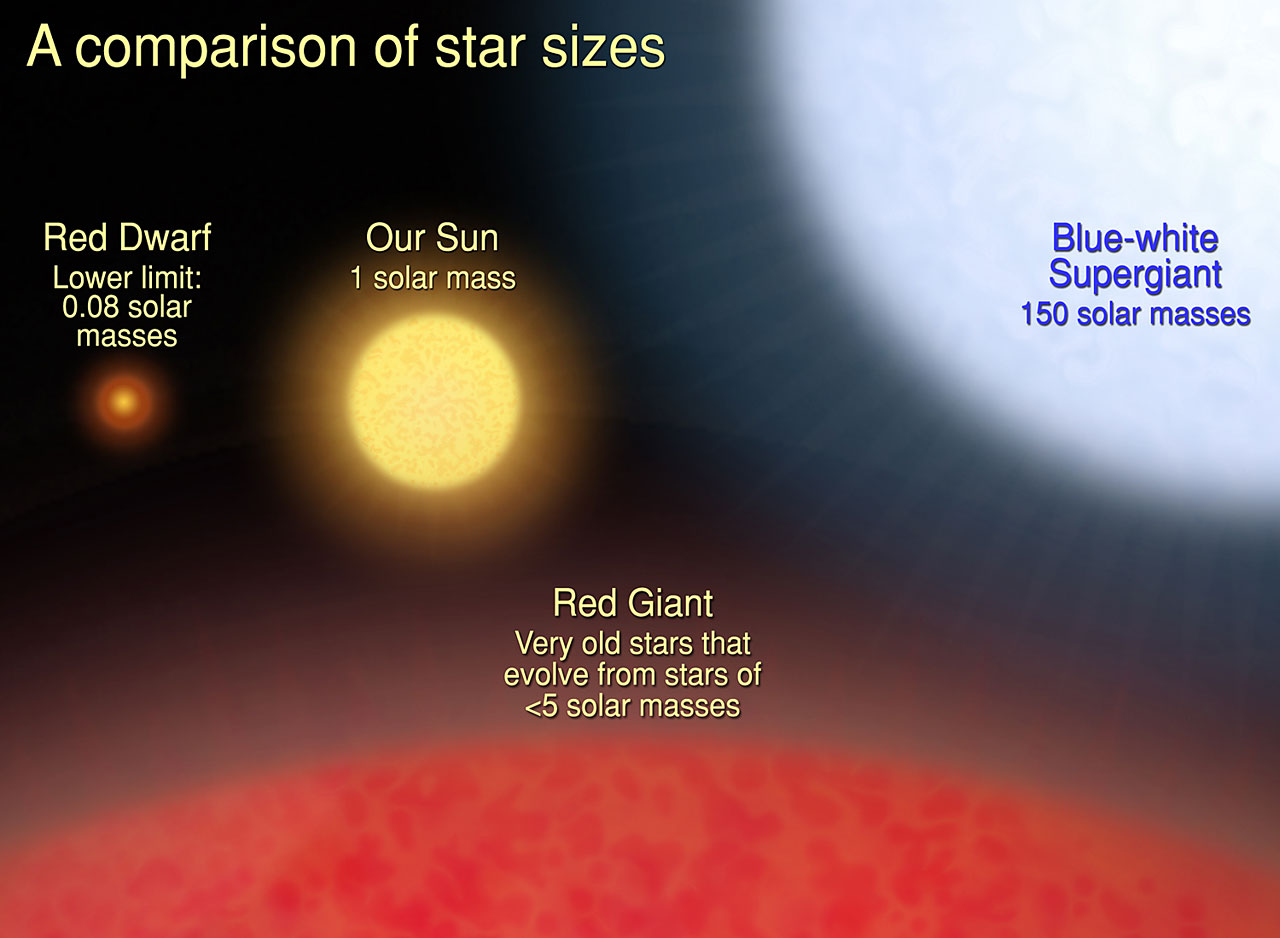
- It is located in the Leo constellation, is just 21% of our Sun’s mass, yet hosts a Saturn-sized gas giant—defying current models that suggest small stars typically form only rocky planets like Earth or Mars.
- Red Dwarf: Red dwarfs are the smallest stars, with masses between 7.5% and 50% of the Sun.
- They have very low luminosity, emitting just 0.01% to 10% of the Sun’s brightness, and low surface temperatures give them a red or orange glow.
- Their slow hydrogen burning allows them to shine for trillions of years, far longer than the Sun’s 10-billion-year lifespan.
- They are the most common type of star in the Milky Way galaxy. The closest star to the Sun, Proxima Centauri, is a red dwarf.
| Read More: Binary Brown Dwarfs |


Rapid Fire
Great Indian Bustard
The Rajasthan Forest Department named newly hatched Great Indian Bustard (GIB) (Ardeotis nigriceps) chicks Sindoor, Vyom, Mishri, and Sophia to honour Operation Sindoor and military personnel involved.
- GIB, Rajasthan’s state bird, is India’s most critically endangered bird. It is one of the heaviest flying birds in the world, and mainly found in Rajasthan’s Thar Desert, with small populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- GIB is one among four bustard species found in India, alongside the Lesser Florican, Bengal Florican, and Macqueen's Bustard.
- GIB is omnivorous and vulnerable to power line collisions due to lack of frontal vision.
- Ecological Importance: GIB acts as an indicator species, it reflects the health of grassland ecosystems. Their decline signals degradation of native grasslands.
- Protection Status: IUCN Red List (Critically Endangered), CITES (Appendix 1), Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) (Appendix I), and Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (Schedule I).
- Threats: Habitat loss from agriculture, mining, and infrastructure, along with collisions with power lines (the leading cause of adult mortality) threaten the GIB.
- Poaching has declined but human disturbance and unsustainable land use continue to impact the species.
- Conservation Efforts: Project GIB (launched in 2018) a joint initiative of the Ministry of Environment, Wildlife Institute of India, and Rajasthan Forest Department
- Captive breeding centres in Sudasari and Sam, Jaisalmer, use AI-enabled monitoring, incubators, and sensor-based systems to improve chick survival.
| Read more: Great Indian Bustards |


Rapid Fire
Chenab Rail Bridge and Anji Khad Bridge
The Prime Minister inaugurated the Chenab rail bridge over the Chenab River and Anji Khad bridge over the Anji River (a Chenab tributary) in Jammu and Kashmir.
- About Chenab Rail Bridge: Located in Reasi district, it is the world’s highest railway arch bridge, standing 359 metres tall—35 metres higher than the Eiffel Tower.
- Construction and Design: It was constructed by Konkan Railway Corporation, with the foundation designed by IISc Bengaluru. IIT Delhi and IIT Roorkee conducted seismic analysis, while DRDO ensured the bridge is blast-proof.
- Durability and Safety: It is designed to withstand magnitude 8 earthquakes, explosions up to 40 tonnes of TNT, temperatures as low as -20°C, and wind speeds reaching 266 km/h.
- Uniqueness: A key feature is its ability to remain stable and operational even if one of its eight piers fails, allowing trains to continue at a reduced speed.
- About Anji Khad Bridge: It is India’s 1st cable-stayed rail bridge and the 2nd-highest railway bridge in the country, after the Chenab rail bridge.
- Significance: Both bridges are part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project, providing all-weather rail connectivity between Kashmir and the rest of India.
- About Chenab River: Chenab (or Chandrabhaga river) is the largest tributary of the Indus River, formed by the confluence of the Chandra and Bhaga rivers at Tandi, in Himachal Pradesh.
| Read More: Anji Khad Bridge |


Rapid Fire
Rail Connectivity in Aizawl
Mizoram’s capital Aizawl has been successfully connected to the national railway network via the Bairabi–Sairang rail line, becoming the 4th Northeastern capital with rail access after Assam (Dispur), Tripura (Agartala), and Arunachal Pradesh (Itanagar).
- Earlier, railway connectivity in Shillong (Meghalaya) faced opposition from Khasi pressure groups, who fear that it may lead to a significant influx of outsiders into the state.
About Indian Railways
- Established in 1853, the country's first train journey covered 21 miles between Bombay and Thane.
- India has the 4th largest railway network in the world, following the US, China and Russia.
- In 2022–23, Indian Railways generated 69% of its internal revenue from freight operations and 24% from passenger services, while the remaining 7% came from other sources such as parcel services, coaching receipts, and platform ticket sales.
- It contributed approximately 1.5% to the GDP in FY24.
- By 2050, India is expected to contribute around 40% of global rail activity.
- The National Rail Plan (NRP) for India 2030 has been formulated to modernize the sector and build a future-ready railway system.
| Read More: Rerouting Indian Railways' Future |


Rapid Fire
World Accreditation Day 2025
The Quality Council of India (QCI) celebrated World Accreditation Day (WAD) 2025 on 9th June to highlight the role of accreditation in trade and economy, with the theme "Accreditation: Empowering Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)".
- QCI also launched the revamped NABL Portal and Gunvatta Samarpan Initiative to enhance digital accreditation access for MSMEs and promote public commitment to quality standards
Accreditation
- Accreditation is a formal verification that an institution meets quality standards in testing, inspection, or certification. It enhances quality in sectors like health, education, and food, promotes standardization, and boosts global competitiveness.
Quality Council of India (QCI)
- Established: 1997 as an autonomous body under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Chairperson: Appointed by the Prime Minister based on industry recommendations.
- Mandate: To develop and manage the National Accreditation Structure (NAS) for conformity assessment bodies in sectors like health, education, and quality promotion.
- Key Bodies: National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies (NABCB) and National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL) are the 2 accreditation boards of the QCI.
- These work closely to support the Government and regulators to ensure that the data provided by accredited conformity assessment bodies is robust, reliable, trustworthy in terms of decision making, compliance testing and standards setting.
- Industry Representation: Includes ASSOCHAM, CII, and FICCI, reflecting strong industry-government collaboration.
| Read More: Quality Council of India (QCI) |