Biodiversity & Environment
Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2026
For Prelims: Climate Risk Index, UNFCCC, Glacial Lake Outbursts, Ocean Acidification, Himalayan Glaciers, Arsenic Contamination, Black Carbon, Western Ghats, Mangroves, Coral Reefs, Cyclone, National Water Policy 2012, Traditional Water Systems, Green Hydrogen, Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari
For Mains: Key Findings of the Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2026 Report. global impact of Extreme Weather, Climate Change’s Threats to India, and Necessary Mitigation Measures
Why in News?
The Germanwatch Climate Risk Index 2026 report, presented at COP30 in Belém, Brazil, ranks India as the 9th most affected country by extreme weather events (EWEs) over the past three decades (1995-2024).
Climate Risk Index
- The Climate Risk Index, published annually by the environmental think tank Germanwatch since 2006, tracks the human and economic impacts of extreme weather events worldwide.
- Indicators: The index uses six key indicators, including fatalities, economic losses, and the number of people affected by climate-related disasters.
- Data for the index is sourced from reputable organizations like the EM-DAT International Disaster Database, World Bank, and IMF.
What are the Key Findings of the Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2026 Report?
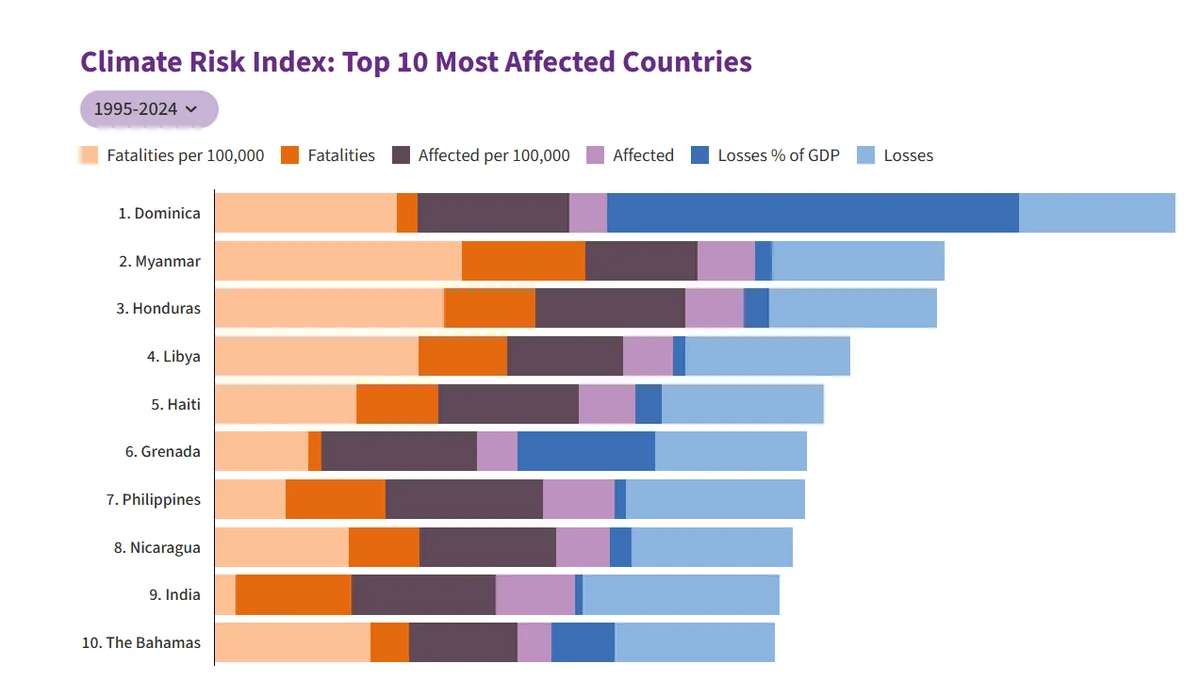
- Globally Most Affected Countries: The top 10 CRI countries are all in the Global South, highlighting unequal climate vulnerability.
- High-risk countries like Dominica, Myanmar, Honduras, and Libya have faced extreme events, e.g., Cyclone Nargis (2008) in Myanmar killed around 1,40,000 people.
- Between 1995–2024, 9,700 extreme weather events worldwide caused over 832,000 deaths and USD 4.5 trillion in economic losses.
- India’s Vulnerability: India's position in the CRI 2026 emphasizes its growing vulnerability to climate-related disasters. In 2024, India ranked 15th among countries most affected by climate change.
- Over three decades, 430 extreme weather events (EWEs) caused USD 170 billion losses, affected 1 billion people, led to 80,000+ deaths, placing India under “continuous threats” with Philippines, Nicaragua, and Haiti.
- India ranked 3rd globally in 2024 for the number of people affected by extreme weather, after Bangladesh and the Philippines.
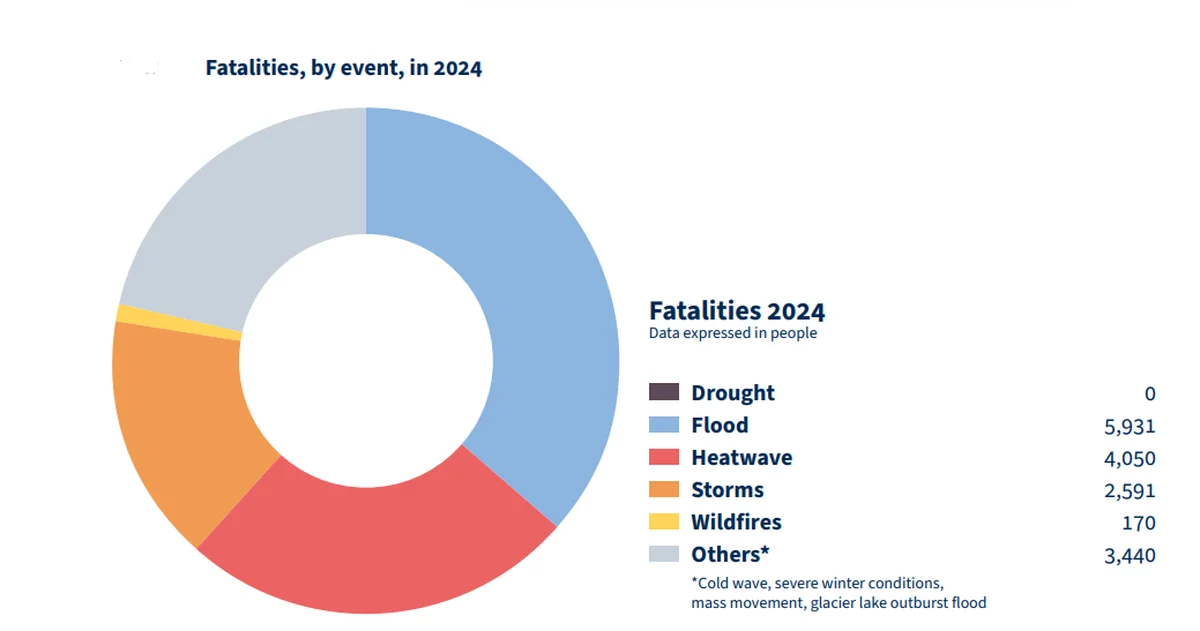
- Specific EWEs: In 2024, floods were the deadliest globally (~50 million affected), followed by heatwaves (~33 million) and droughts (~29 million); India’s monsoon adversely affected 8 million people.
- CRI ranks countries by extreme weather impacts, focusing on rapid onset events like floods, storms, heatwaves, wildfires, glacial lake outbursts, and excluding slow onset events such as rising temperatures, sea-level rise, and ocean acidification.
- Long-Term Vulnerability: Repeated disasters cause accumulating losses, keeping India’s 30-year CRI ranking high, as continuous exposure hinders recovery and raises long-term socio-economic risk.
What are the Impacts of Climate Change on India?
- Water Crisis:
- Melting Glaciers: Rising temperatures are shrinking Himalayan glaciers, threatening river flows of the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus.
- Depleting Groundwater: Groundwater use rose from ~10–20 km³ to 240–260 km³ over 50 years; Gangetic aquifers are falling ~4 cm/year, making many perennial rivers seasonal.
- Water Quality Degradation: Groundwater pumping brings arsenic contamination, ranking India 120th of 122 countries on the global water quality index.
- Disruption in Mountain Ecosystems:
- Increased Disasters: Events like GLOFs (e.g., 2023 Sikkim disaster), cloudbursts, and forest fires are becoming more frequent.
- Accelerated Melting: Black carbon from vehicles and fossil fuel use, especially along the Char Dham route, speeds up Himalayan ice melt.
- Threat to Biodiversity: The Himalayas, one of India’s four biodiversity hotspots (with the Western Ghats, Sundaland, and Indo-Burma), face severe ecological stress.
- Threat to Coastal Areas:
- Rising Sea Levels: Global seas are rising 3.6 mm/year, with Mumbai seeing a 4.44 cm rise (1987–2021); projections show a 0.4–0.8 m rise by 2100, endangering coastal cities.
- Salinisation: Seawater intrusion is damaging farmland and freshwater, affecting over 250 million coastal residents.
- Loss of Natural Defenses: Mangroves and coral reefs, vital cyclone and erosion buffers, are increasingly at risk.
- Socio-Economic Costs:
- Economic Losses: The World Bank warns the climate crisis could cut India’s GDP by 6.4–10% by 2100 and push 50 million into poverty.
- Agricultural Distress: Erratic weather and water scarcity are lowering farm productivity and threatening food security.
- Public Health Risks: The urban heat-island effect heightens heat stress and health risks in densely populated slums.
What Measures should India Take to Address the Impacts of Climate Change?
- Climate Change Mitigation: Drastically cut emissions to limit warming to 1.5°C and extreme weather, support National Adaptation Plans, and secure USD 300 billion by 2035 for climate adaptation and mitigation.
- Securing Water Resources: India must renew its National Water Policy 2012 for sustainable aquifer management and climate-resilient farming using drip irrigation and zero-tillage, while reviving traditional water systems and scaling up artificial recharge through pits, shafts, and trenches.
- Build Coastal Resilience: Restore mangrove forests and coral reefs as natural barriers. Develop early-warning systems for cyclones and storm surges, and create social safety nets for affected communities.
- Decarbonize Economy: Ramp up solar and wind capacity to exceed 500 GW of non-fossil fuel power by 2030, while promoting green hydrogen and battery storage.
- Promote sustainable urbanization with green buildings, urban greenery, and permeable surfaces, while enforcing eco-friendly land-use policies to curb deforestation and ensure sustainability.
- Governance and Social Measures: Mainstream climate adaptation in all development planning, promote community-led resource management through participatory models like Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari, and boost green R&D in technologies, carbon capture, and resilient crops.
Conclusion
The CRI 2026 underscores India’s high vulnerability to extreme weather events and long-term climate risks, affecting water, ecosystems, coasts, and socio-economic stability. Urgent measures in adaptation, water management, coastal resilience, decarbonization, and sustainable governance are essential to mitigate impacts, protect livelihoods, and ensure climate-resilient development.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the threats posed by global warming to India's Himalayan and coastal ecosystems. Suggest sustainable measures for building resilience in these regions. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the projected sea-level rise impacts for India?
Global sea level rose ~3.6 mm/yr (last decade); projections of 0.4–0.8 m by 2100 endanger coastal cities (Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata) and ~250 million residents within 50 km of the coast.
2. What is the scale of India’s groundwater depletion?
Groundwater use rose from ~10–20 km³ to 240–260 km³ over 50 years; Gangetic aquifers are falling ~4 cm/year, making many perennial rivers seasonal.
3. According to the World Bank, how much could climate change reduce India’s GDP by 2100?
The World Bank estimates climate impacts could cut India’s GDP by 6.4–10% and push 50 million people into poverty by 2100.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’? (2019)
- Global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits.
- Large deposits of ‘methane hydrate’ are found in Arctic Tundra and under the sea floor.
- Methane in atmosphere oxidizes to carbon dioxide after a decade or two.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q “Momentum for Change: Climate Neutral Now” is an initiative launched by (2018)
(a) The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(b) The UNEP Secretariat
(c) The UNFCCC Secretariat
(d) The World Meteorological Organisation
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. ‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017)
Internal Security
Countering Terrorism and Protecting India’s Internal Security
For Prelims: Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967, Multi-Agency Centre, Operation Sindoor
For Mains: Cross-border terrorism and proxy warfare, Urban terrorism, India’s counterterrorism doctrine
Why in News?
A deadly car blast near Delhi’s Red Fort has renewed concerns over India’s internal security, with investigators suspecting the involvement of an organised terror module.
- The First Information Report (FIR) has been filed under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967 and the incident underscores the need for a robust, and coordinated counterterrorism strategy.
How does Terrorism Continue to Threaten India’s Internal Security?
- Cross-Border Terrorism and Proxy Warfare: State actors like Pakistan continue to sponsor cross-border terrorism through non-state actors such as Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) and Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM).
- These groups have orchestrated several attacks, such as the 2001 Parliament Attack and the 2016 Uri attack in Jammu & Kashmir.
- Proxy warfare from Pakistan-based groups continues to be a persistent threat, as demonstrated by the 2025 Pahalgam attack.
- The ISI has long used religious extremism to radicalize and recruit youth, particularly in Kashmir, by exploiting Islamic radicalization and separatist sentiments to advance its agenda.
- The China-Pakistan nexus continues to pose a strategic threat to India through hybrid warfare.
- Urban Terrorism: Urban terrorism is on the rise, urban centers have become prime targets for terrorists seeking to cause mass casualties, instill psychological fear, and gain widespread media attention.
- High-profile attacks, such as the 2008 Mumbai terror strikes and the rise of lone-wolf incidents illustrate a growing shift toward targeting civilian spaces, making urban areas increasingly vulnerable.
- The use of ammonium nitrate explosives and urban anonymity expose vulnerabilities in India’s civil security infrastructure.
- White-collar terrorism, involving educated professionals using technical expertise for terror activities, highlights the need for stronger counter-terrorism frameworks in urban areas.
- Internal Insurgencies and Ethno-Nationalist Movements: India faces multiple internal insurgencies fueled by local grievances.
- Groups in Jammu & Kashmir and the Northeast seek greater autonomy or independence, often with external support.
- Similarly, Maoist insurgencies (Left-Wing Extremism) continue to destabilize regions in central India, exploiting socio-economic disparities.
- Cyber Terrorism: Terrorist groups have increasingly turned to technology for recruitment, funding, radicalization, and planning.
- Cyberterrorism poses a significant threat to India’s critical infrastructure, while online platforms are exploited to spread extremist ideologies.
- The use of cryptocurrencies and dark web networks makes it harder for authorities to track financial flows supporting terrorism.
- Organised Crimes: Terrorism in India is funded through illicit activities such as drug trafficking, fake currency, and smuggling.
- Pakistan’s ISI is known to use these channels to fund terrorist operations, while India’s proximity to drug production hubs in Afghanistan and Myanmar facilitates the movement of narcotics.
- Maritime Security and Coastal Vulnerabilities: India's extensive 7,500 km coastline is vulnerable to maritime terrorism.
- Groups such as LeT and JeM, along with drug cartels and smuggling networks, exploit coastal security gaps to infiltrate India via the Arabian Sea.
- The 1971 PNS Ghazi submarine incident and interceptions by the Indian Navy reveal attempts to infiltrate Indian waters for smuggling arms and explosives.
What is India's Counterterrorism Doctrine?
- India’s New Counterterrorism Doctrine: India’s Counterterrorism Doctrine unveiled after Operation Sindoor marks a decisive shift from earlier restraint to a more assertive and punitive security posture.
- It is built on three principles: decisive retaliation, zero tolerance for nuclear blackmail, and no distinction between terrorists and their state sponsors.
- Decisive Retaliation: It means India will hit back firmly and on its own terms after any terror attack, targeting terror hubs at the source to raise the costs for states backing such groups.
- This approach, seen in strikes on major Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed bases across Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Jammu and Kashmir (PoJK).
- Zero Tolerance for Nuclear Blackmail: India will not be deterred by nuclear threats and will strike terrorist safe havens even if they hide under a nuclear shield, asserting its right to self-defence and moving away from earlier strategic restraint.
- No Distinction Between Terrorists & their Sponsors: India now treats both terror groups and the states sheltering or supporting them as the same target.
- Operation Sindoor reflected this shift by striking deep inside Pakistan, signalling that state-backed terrorism will be met as a direct act of war.
- Doval Doctrine: Shaped by National Security Adviser Ajit Doval, it blends hard power, intelligence, diplomacy, and psychological warfare into a unified national security approach.
Core Principles
- Proactive National Defense: India asserts the right to strike first or strike back decisively, reflected in the 2016 surgical strikes and the 2019 Balakot airstrikes.
- Whole-of-Government Coordination: Military, intelligence, police, and diplomatic institutions operate in an integrated framework.
- Security Linked with Development: Security operations are paired with welfare and governance initiatives, especially in Kashmir (Abrogation of Article 370) and Left-Wing Extremism zones.
- Defensive–Offense Strategy: Instead of waiting to be attacked, India signals readiness for calibrated offensive action to raise the cost for adversaries.
What Measures are Needed to Build a Comprehensive Counterterrorism Policy for India’s Internal Security?
- Strengthening Intelligence and Coordination: Convert the MAC into a statutory, 24×7 national fusion centre with mandatory data-sharing by all agencies.
- Implement artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics to analyze and predict terrorist activity patterns, including online radicalization and the movement of terror groups.
- Improve intelligence coordination with neighboring countries, particularly Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Afghanistan, to counter cross-border terrorism.
- Modernise Policing and Forensic Capabilities: Equip state police with modern surveillance tools, cyber-forensics, drone-detection systems and predictive policing software.
- Establish fast-track anti-terror courts to expedite trials and improve conviction rates.
- Stronger Anti-Terror Financing Laws: Strengthen laws targeting terrorist financing, including tracking cryptocurrency transactions, hawala operations, and illegal charities.
- Enhance international partnerships through ‘No Money for Terror’ (NMFT) and bilateral intelligence exchanges.
- Coastal Surveillance: Enhance coastal security by deploying automated drones, radar systems, and marine surveillance technologies to prevent maritime terrorism and smuggling.
- Diplomatic Pressure: Push for greater international cooperation through forums like the UN to curb state-sponsored terrorism, particularly Pakistan’s support for cross-border terrorism.
- Increase the efforts for the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT) at the UN to criminalize all forms of international terrorism and cut off resources for terrorists
- Psychological and Informational Warfare: Develop a national strategy for information warfare to combat terrorist propaganda and counteract radical ideologies spread via social media and extremist websites.
- Develop a nationwide Counter-Radicalisation Framework based on global models ( like Singapore, UK).
- Institutionalise the post–Operation Sindoor doctrine, strengthen India’s deterrence posture with a mix of precision strikes, cyber capabilities, and information warfare tools.
Conclusion
Terrorism continues to threaten India’s internal security through external state sponsorship, internal insurgencies, and the use of technology. The persistent challenges include cyber terrorism, urban attacks, and the exploitation of India’s socio-political divisions. A comprehensive strategy that integrates military, intelligence, and cybersecurity efforts will be crucial in addressing these evolving threats.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the changing nature of urban terrorism and propose institutional measures to secure Indian cities against high-impact attacks. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the core principles of India’s new counterterrorism doctrine?
The doctrine is based on decisive retaliation, zero tolerance for nuclear blackmail, and no distinction between terrorists and their state sponsors.
2. Which groups primarily drive cross-border terrorism against India?
Pakistan-based groups like Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) and Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) continue to lead cross-border terror activities.
3. Why are Indian cities more vulnerable to urban terrorism?
Urban vulnerability stems from high population density, anonymity for attackers, ease of access to explosive precursors (e.g., ammonium nitrate), and critical-infrastructure exposure.
4. What is the main objective of the Multi-Agency Centre (MAC)?
MAC enables inter-agency intelligence sharing for real-time threat assessment, though current coordination gaps limit its effectiveness.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Hand-in-Hand 2007’ a joint anti-terrorism military training was held by the officers of the Indian Army and officers of Army of which one of the following countries? (2008)
(a) China
(b) Japan
(c) Russia
(d) USA
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What are India’s internal security challenges? Give out the role of Central Intelligence and Investigative Agencies tasked to counter such threats. (2023)
Q. Analyse the multidimensional challenges posed by external state and non-state actors, to the internal security of India. Also discuss measures required to be taken to combat the threats. (2021)
Q. The banning of ‘Jamaat-e – islaami’ in Jammu and Kashmir brought into focus the role of over-ground workers (OGWs) in assisting terrorist organizations. Examine the role played by OGWs in assisting terrorist organizations in insurgency affected areas. Discuss measures to neutralize the influence of OGWs. (2019)
Facts for UPSC Mains
Unlocking India’s Green Hydrogen Production Potential
Why in News?
India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) in 2023 to reduce fossil fuel dependence, achieve Net Zero by 2070, and enhance energy security through a green hydrogen(GH2) ecosystem.
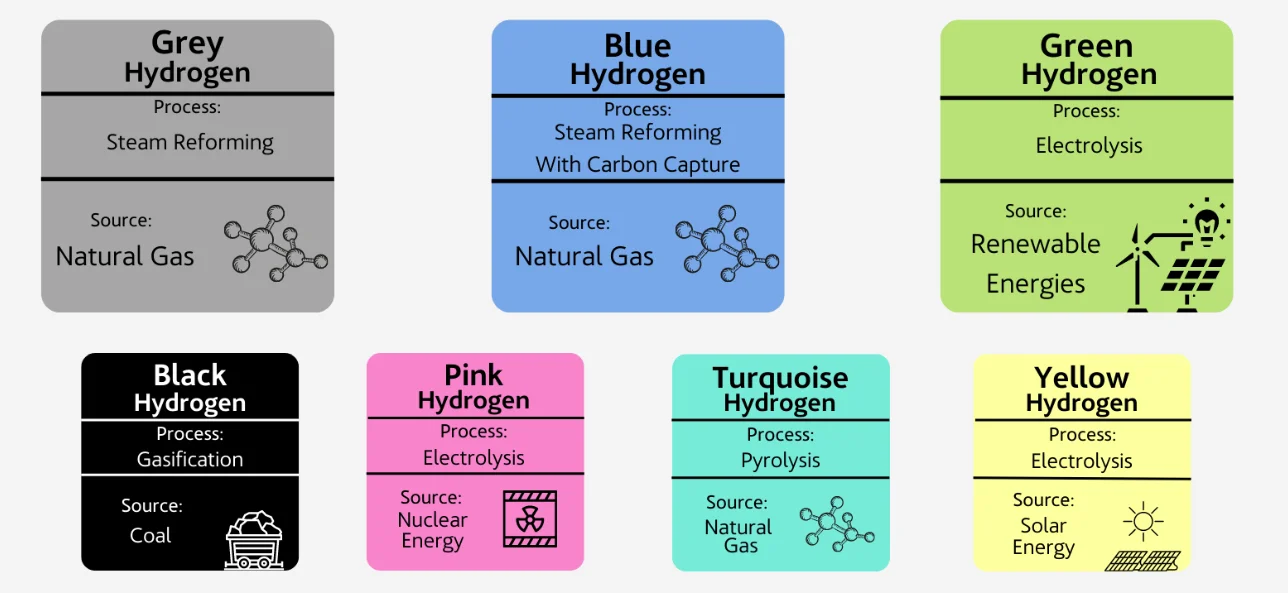
What is Green Hydrogen (GH2)?
- About: Green hydrogen refers to hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, through the process of electrolysis, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen.
- It can also be produced by converting biomass, like agricultural waste, into hydrogen, provided the emissions remain below the safe limit.
- Emissions Standard: India classifies hydrogen as "green" if the total emissions from its production process do not exceed 2 kg of CO₂ equivalent per 1 kg of hydrogen produced.
- Other Types of Hydrogen:
- Key Applications:
- Steel Industry Innovation: Green hydrogen is being explored in the steel industry for carbon-based fuels in iron reduction and other steelmaking processes to reduce carbon emissions and enhance sustainability.
- Currently, five pilot projects are underway to test its feasibility and integration into steel production.
- Road Transport: The NGHM has launched five major pilot projects involving 37 hydrogen-powered vehicles (buses and trucks) across 10 routes, supported by ₹208 crore in financial aid.
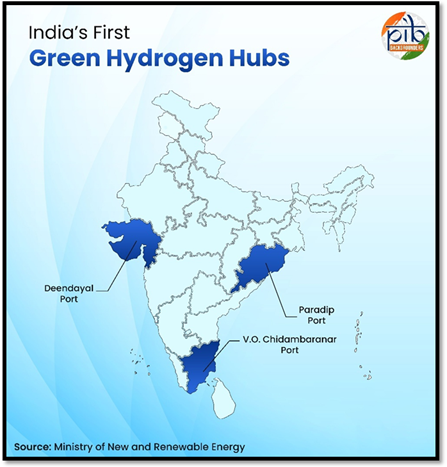
- Shipping and Maritime Operations: A Green Hydrogen Pilot Project at V.O. Chidambaranar Port (₹25 crore) and a megawatt-scale green hydrogen facility at Deendayal Port Authority, Kandla, are being developed to support cleaner maritime operations.
- High-Altitude Mobility: In November 2024, NTPC launched the world’s highest altitude Green Hydrogen Mobility Project in Leh (3,650 m), featuring 5 hydrogen buses and a fueling station.
- Steel Industry Innovation: Green hydrogen is being explored in the steel industry for carbon-based fuels in iron reduction and other steelmaking processes to reduce carbon emissions and enhance sustainability.
What is National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM)?
- About: The NGHM seeks to establish India as a global leader in clean hydrogen, enhancing industrial competitiveness, reducing fossil fuel imports, and ensuring long-term energy security while promoting sustainability and self-reliance.
- Targets:
- By 2030, the mission aims to add 125 GW of renewable energy capacity for green hydrogen production and reduce 50 MMT of greenhouse gas emissions annually.
- The mission aims to generate investments over ₹8 lakh crore, create 6 lakh jobs, reduce fossil fuel imports by ₹1 lakh crore annually, and has already certified over 5,600 trainees in hydrogen-related qualifications.
- Funding: The mission has an initial outlay of ₹19,744 crore until FY 2029-30, with funds allocated to key components, including the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme.
- Global Partnerships:
- EU-India Collaboration: Under the EU-India Trade and Technology Council, over 30 joint proposals on hydrogen production from waste have been received.
- India-UK Partnership: In February 2025, India and the UK strengthened their cooperation on hydrogen standardization through a dedicated Standards Partnership Workshop.
- Partnership with H2Global: In November 2024, India’s Solar Energy Corporation (SECI) signed an MoU with H2Global Stiftung (Germany) to facilitate market-based mechanisms for the export of Indian green hydrogen.
- Singapore Collaboration: In October 2025, Sembcorp Industries signed MoUs with V.O. Chidambaranar and Paradip Port Authorities to develop integrated green hydrogen and ammonia hubs for production, storage, and exports.
What are the Key Initiatives Taken by India to Promote Green Hydrogen?
- SIGHT Scheme: The SIGHT scheme provides financial incentives for the manufacturing of electrolysers used in green hydrogen production, aiming to accelerate the transition to sustainable energy.
- Development of Green Hydrogen Hubs: In October 2025, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) recognized three major ports;
- Deendayal Port Authority (Gujarat), V.O. Chidambaranar Port Authority (Tamil Nadu), and Paradip Port Authority (Odisha)—as Green Hydrogen Hubs, which will serve as integrated centers for production, consumption, and export.
- Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme (GHCI): Launched in April 2025, the GHCI provides a framework to certify hydrogen as “green,” ensuring it meets emission standards and is produced using renewable energy.
- It aims to ensure transparency, traceability, and credibility in hydrogen production.
- R&D and Certification Requirements: Under the GHCI, any green hydrogen production facility receiving government subsidies or selling hydrogen domestically must obtain a Final Certificate.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) will oversee accreditation and certification processes.
- Strategic Hydrogen Innovation Partnership (SHIP): The SHIP fosters collaboration between government, industry, and academia to develop competitive hydrogen technologies.
- It includes a dedicated R&D fund and encourages consortium-based research to drive innovation and support domestic manufacturing capabilities.
Conclusion
Green hydrogen is pivotal to India’s future clean energy landscape, driving the shift to a low-carbon, self-reliant economy. The National Green Hydrogen Mission will accelerate domestic production, innovation, and global market access, reducing fossil fuel dependence and positioning India to lead the global clean energy transition toward a sustainable and secure future.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Evaluate the potential of Green Hydrogen in achieving India’s Net Zero target by 2070. How can the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) play a crucial role in this transition? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Green Hydrogen (GH2)?
Green hydrogen refers to hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power through electrolysis, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen. It can also be produced from biomass, provided emissions are below the safe limit set by India.
2. What are the key applications of Green Hydrogen in India?
Green hydrogen is being explored in the steel industry for iron reduction, road transport with hydrogen-powered vehicles, shipping and maritime operations, and high-altitude mobility projects like the hydrogen-powered buses in Leh.
3. What are the targets of the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM)?
The NGHM aims to add 125 GW of renewable energy capacity for green hydrogen production by 2030, reduce 50 MMT of greenhouse gas emissions annually, and generate investments exceeding ₹8 lakh crore while creating 6 lakh jobs.
4. What initiatives has India taken to promote Green Hydrogen?
Key initiatives include the SIGHT Scheme for electrolyser manufacturing, the development of Green Hydrogen Hubs at major ports, the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme (GHCI), and the Strategic Hydrogen Innovation Partnership (SHIP) for R&D collaboration.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following heavy industries: (2023)
- Fertilizer plants
- Oil refineries
- Steel plants
Green hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in decarbonizing how many of the above industries?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (c)
Q. With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fuel cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (c)
Q. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce one of the following as “exhaust” (2010)
(a) NH3
(b) CH4
(c) H2O
(d) H2O2
Ans: (c)
Important Facts For Prelims
Double Helix Model of DNA
Why in News?
James Watson, one of the co-discoverers of the double-helix structure of Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), recently passed away.
What is Double Helix Model of DNA?
- Discovery: The DNA double helix model was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, revolutionized the field of biology, laying the foundation for modern genetics, biotechnology, and medical research.
- This milestone remains a cornerstone in the understanding of heredity, evolution, and genetic diseases.
- Watson and Crick deciphered DNA’s structure as a double helix based on Rosalind Franklin’s critical X-ray crystallography (Photo 51).
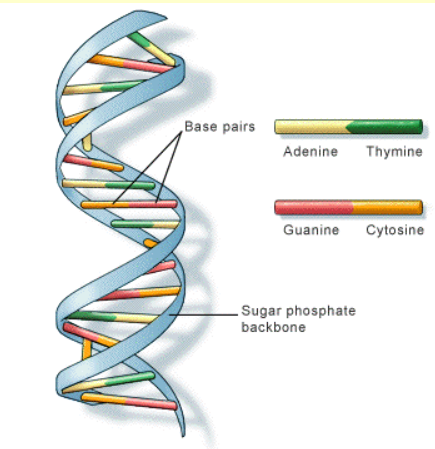
- Structure: DNA consists of two long strands that twist around each other to form a helical shape, creating the "double helix."
- Each strand is made up of sugar and phosphate molecules, which form the backbone of the structure.
- The majority of DNA is found in the cell nucleus so it is called nuclear DNA.
- Base Pairs: The two strands are connected by nitrogenous base pairs, with Adenine (A) always pairing with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) pairing with Guanine (G). These base pairs form the "rungs" of the helical ladder.
- Antiparallel Strands: The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions, a feature known as "antiparallel," which ensures that the base pairs align correctly for complementary bonding.
- Core Features:
- Complementary Base Pairing: The two strands are noted as being connected through specific base-pairing rules where Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine. This pairing is highlighted as a fundamental principle of DNA stability.
- Mechanism of Accurate Replication: This complementary pairing is emphasized for explaining how DNA replicates with high accuracy, ensuring faithful transmission of genetic information across generations.
- Significance of Discovery:
- It gave rise to fields such as Molecular Biology, Biotechnology, and Genetic Engineering.
- Awarded the Nobel Prize (1962) in Physiology or Medicine (Watson, Crick, and Maurice Wilkins) for their DNA model, highlighting its foundational importance.
- Paved the way for the Human Genome Project (2003), CRISPR gene editing tool, and personalized medicine.
- In agriculture, DNA analysis reshaped farming practices by enabling the creation of genetically modified crops and pest-resistant plant varieties.
- DNA has also become indispensable in forensic science, assisting in crime-solving.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why was the discovery of the DNA double helix historically significant?
It revealed how genetic information is stored and replicated, transforming heredity studies, launching molecular biology, and enabling advances like genetic engineering, genome sequencing, CRISPR, and personalised medicine.
2. What is the core idea of Watson and Crick’s double-helix model?
The model shows two antiparallel DNA strands forming a spiral staircase, stabilized by complementary base pairing (A–T, G–C), ensuring structural stability and accurate genetic replication.
3. What makes DNA central to heredity and evolution?
DNA stores genetic instructions in nucleotide sequences, passes traits across generations, mutates to create variation, and thus drives evolutionary change, adaptation, and species diversification.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:(2022)
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q: With reference to the recent developments in science, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Functional chromosomes can be created by joining segments of DNA taken from cells of different species.
(b) Pieces of artificial functional DNA can be created in laboratories.
(c) A piece of DNA taken out from an animal cell can be made to replicate outside a living cell in a laboratory.
(d) Cells taken out from plants and animals can be made to undergo cell division in laboratory petri dishes.
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
Ammonium Nitrate
Why in News?
A blast near Delhi’s Red Fort has put “Ammonium Nitrate” in the spotlight, as investigators suspect the chemical may have been used in the explosion by a “white-collar” terror module linked to Jaish-e-Mohammed.
What is Ammonium Nitrate?
- About: Pure ammonium nitrate (NH₄NO₃) is a white, crystalline, water-soluble, nitrogen-rich compound made by reacting ammonia with nitric acid, and it melts at about 170°C.
- The substance is classified as an oxidising agent. It is one of the base ingredients used in the manufacture of commercial explosives.
- It is classified as a dual-use substance, meaning it has legitimate industrial uses but can also be weaponised.
- Legitimate Uses of Ammonium Nitrate: In agriculture, it is widely used as a nitrogen fertilizer due to its high nutrient content.
- It is used for controlled blasting in quarries and excavation projects, and also forms a key component of various emulsions and gels used in mining-grade explosives.
- Weaponization of Ammonium Nitrate: Pure ammonium nitrate is not explosive by itself and is classified as an oxidiser under United Nations classification of dangerous goods.
- It becomes volatile when combined with fuel oil, potassium chlorate, sulphur or other accelerants. This mixture creates ANFO (Ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil), a commonly used explosive.
- However, ANFO cannot detonate on its own, it requires a trigger such as a detonator, often initiated with primary explosives like RDX or TNT.
- ANFO is frequently used by terror groups to make Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs).
- Ammonium Nitrate has been repeatedly exploited in major terror attacks in India, including the 2019 Pulwama attack and multiple Indian Mujahideen strikes between 2000 and 2011 in Mumbai and Delhi.
- It becomes volatile when combined with fuel oil, potassium chlorate, sulphur or other accelerants. This mixture creates ANFO (Ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil), a commonly used explosive.
- Regulation: All activities (manufacture, conversion, bagging, import, export, transport, possession, sale, and use) are governed under the Ammonium Nitrate Rules, 2012.
- Storage of large quantities in populated areas is prohibited under these rules.
- A separate Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organisation (PESO)-issued licence under the Ammonium Nitrate Rules, 2012 is required for carrying out any activity involving ammonium nitrate.
- Industrial licence under the Industrial Development and Regulation Act, 1951 is mandatory for manufacturing ammonium nitrate.
- Any mixture containing over 45% ammonium nitrate (including emulsions, suspensions, melts, or gels) is legally classified as an explosive under the Explosives Act, 1884.
- However, this does not apply to fertilisers from which ammonium nitrate cannot be extracted by physical or chemical methods.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is ammonium nitrate?
Ammonium nitrate (NH₄NO₃) is a nitrogen-rich oxidiser used as fertilizer and in controlled blasting; mixed with fuel oil it forms ANFO, a commonly weaponised IED component, making it a high-risk dual-use chemical.
2. Which laws and agencies regulate ammonium nitrate in India?
Activities involving ammonium nitrate are regulated under the Ammonium Nitrate Rules, 2012, the Explosives Act, 1884, and manufacture also requires industrial licence under the Industrial Development & Regulation Act, 1951.
3. When is an ammonium nitrate mixture legally treated as an explosive?
Any mixture (emulsion, gel, melt, suspension) containing over 45% ammonium nitrate is legally classified as an explosive under the Explosives Act, 1884, and attracts stricter controls.
Important Facts For Prelims
Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPV&FRA) Act, 2001
Why in News?
India marked the Silver Jubilee of the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPV&FRA) Act, 2001 and the 21st Foundation Day of PPV&FRA with the Plant Genome Saviour Awards Ceremony in New Delhi.
- The award honours individuals who conserve and preserve the genetic diversity of economically important plants and their wild relatives.
What is the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPV&FRA) Act, 2001?
- About: The PPV&FR Act, 2001 under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, establishes a sui generis system for protecting plant varieties.
- The Act provides legal recognition to both commercial plant breeders and farmers, promoting conservation and improvement of plant genetic resources.
- It also aligns with India's TRIPS obligations and the International Union for Protection of New Plant Varieties (UPOV Convention) addressing the country's agricultural needs.
- Rights under the Act:
- Breeders’ Rights: Breeders get exclusive rights to produce, sell, market, distribute, import, or export protected varieties. They may appoint agents or licensees and can seek legal action for infringement.
- Researchers’ Rights: Researchers may use any registered variety for experiments or to develop new varieties but repeated use needs prior permission of the registered breeder.
- Farmers’ Rights: Under the act, a farmer who has evolved or developed a new variety is entitled to register it and receive protection in the same manner as a breeder.
- A farmer can continue to save, use, sow, re-sow, exchange, share, or sell his farm produce, including seed, even if the variety is protected under the PPV&FR Act, but he cannot sell it as branded seed.
- Implementing Authority: Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Authority (PPV&FRA) is the primary body responsible for the implementation of the Act.
- Significance: The act promotes agricultural innovation while ensuring seed sovereignty for farmers.
- It protects traditional knowledge and rewards community conservation efforts.
- It supports both public and private sector plant breeding institutions and enhances India's compliance with global IPR norms without compromising food and livelihood security.
Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Authority (PPV&FRA)
- About: The PPV&FRA was formally set up on 11 November 2005 is a statutory body established under the PPV&FRA, 2001, under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare, Government of India. It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- Composition: The Authority is led by a Chairperson and has 15 members. The Registrar General serves as the ex-officio Member Secretary.
- Objectives: The PPV&FRA provides breeders’ rights, rewards farmers for conserving traditional varieties, protects farmers’ rights to use and share farm-saved seed, supports research and innovation.
- It maintains the National Register of Plant Varieties, helping preserve biodiversity and traditional knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the PPV&FRA Act, 2001?
The PPV&FRA Act, 2001 is a sui generis law that provides intellectual property protection to plant breeders while formally recognising farmers’ rights to save, use, exchange and sell farm-saved seed and register farmer-developed varieties.
2. Who implements the PPV&FRA and what is its function?
The Protection of Plant Varieties & Farmers’ Rights Authority (PPV&FRA), headquartered in New Delhi, implements the Act, maintains the National Register of Plant Varieties and adjudicates rights, benefit-sharing and registrations.
3. What rights does a breeder get under the Act?
Registered breeders obtain exclusive rights to produce, sell, market, distribute, import or export the protected variety and can license or take legal action against infringement.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- According to the Indian Patents Act, a biological process to create a seed can be patented in India.
- In India, there is no Intellectual Property Appellate Board.
- Plant varieties are not eligible to be patented in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Rapid Fire
NGT Flags Severe Chromium Contamination in Drinking Water
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has raised serious concerns over the lack of adequate safe drinking water in chromium-contaminated regions of Uttar Pradesh, directing the State government to ensure immediate and sufficient water supply.
- Chromium (Cr) is a potentially toxic metal occurring in water and groundwater as a result of natural and anthropogenic sources.
- Hexavalent form Cr(VI) is highly toxic, its exposure can cause severe health problems, including skin disorders, respiratory issues, and cancer.
- However, trivalent chromium (Cr(III)) is considered essential in trace amounts for the normal nutrition of humans and animals.
- Sources of Chromium Contamination in Water Bodies: Chromium contamination enters water bodies mainly through industrial effluents, mining waste, urban runoff, polluted irrigation, improper disposal, and accidental spills.
- Natural leaching from chromium-rich rocks also adds to groundwater pollution.
- Regulation: As per Indian standard (IS) 10500 for drinking water, the maximum permissible concentration of Cr(VI) in drinking water is 50 microgram per litre.
- Remedy for Chromium Pollution: Methods like adsorption (attachment of pollutants to surfaces), biosorption (use of biological materials to absorb pollutants), and ion exchange (replacing harmful ions with less toxic ones) are commonly used, though they vary in cost and efficiency.
- Advanced techniques, such as sunlight-driven photocatalysis with TiO2 nanoparticles, offer high efficiency in reducing Cr(VI) to Cr(III).
| Read more: India's Groundwater Contamination Crisis |
Rapid Fire
Discovery of Largest and Most Distant Black Hole Flare
Astronomers have detected the largest and most distant flare from a black hole, originating from the supermassive black hole at the heart of the Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN) J2245+3743, located 10 billion light-years away from Earth.
- Brightest Flare: First observed in 2018, this black hole is responsible for the brightest flare ever recorded, linked to a tidal disruption event (TDE) caused by the consumption of a star.
- A TDE is a cataclysmic phenomenon where a star is torn apart by the intense gravitational forces of a supermassive black hole, releasing an intense flash of radiation.
- Flare Characteristics: The flare intensified by 40 times over several months, peaking at 30 times the brightness of any previous black hole flare and releasing energy equivalent to 10 trillion suns.
- Star Consumption: In 2023, data from the Keck Observatory confirmed the flare’s intense energy and ruled out the possibility of a supernova, showing that the star being consumed is 30 times the mass of the Sun, much larger than those in previous TDEs.
- Time Dilation Effect: The black hole's immense gravity causes cosmological time dilation, stretching the light and allowing researchers to observe the event at a slower pace, offering valuable insights into black hole dynamics.
- Solar Flare: A solar flare is a powerful explosion on the Sun caused by the sudden release of energy stored in twisted magnetic fields, often above sunspots, appearing as bright areas on the Sun.
- These flares can last from minutes to hours, heating materials to millions of degrees and emitting a burst of radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum, including radio waves, x-rays, and gamma rays.
| Read More: Black Hole |