Facts for UPSC Mains
Unlocking India’s Green Hydrogen Production Potential
- 14 Nov 2025
- 10 min read
Why in News?
India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) in 2023 to reduce fossil fuel dependence, achieve Net Zero by 2070, and enhance energy security through a green hydrogen(GH2) ecosystem.
What is Green Hydrogen (GH2)?
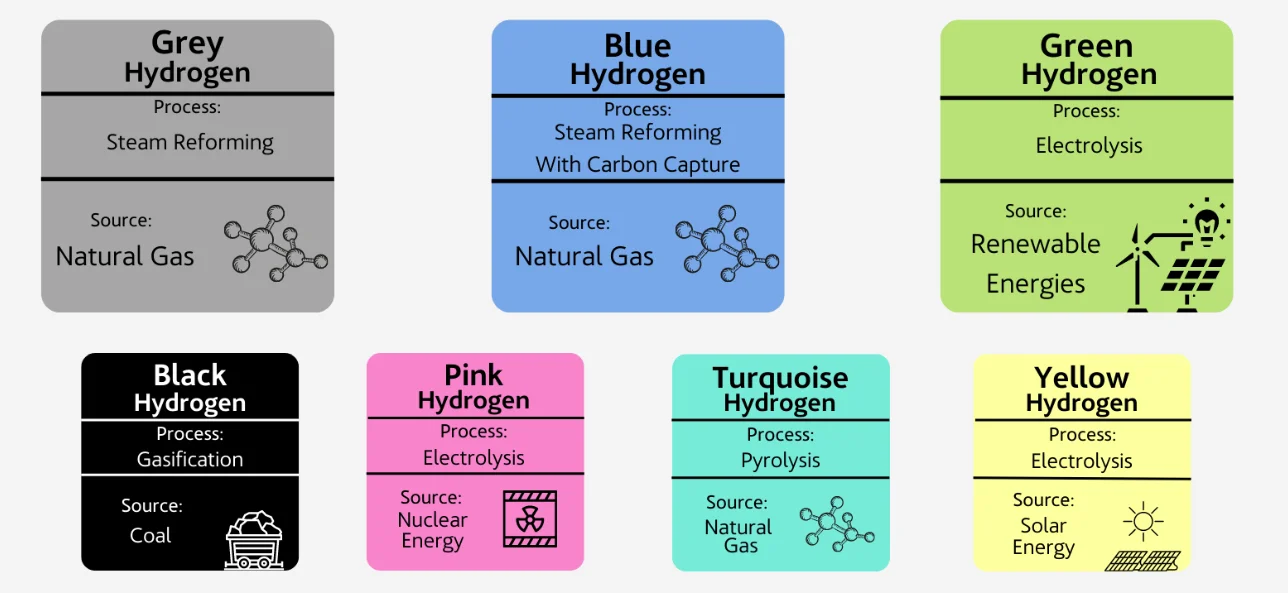
- About: Green hydrogen refers to hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, through the process of electrolysis, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen.
- It can also be produced by converting biomass, like agricultural waste, into hydrogen, provided the emissions remain below the safe limit.
- Emissions Standard: India classifies hydrogen as "green" if the total emissions from its production process do not exceed 2 kg of CO₂ equivalent per 1 kg of hydrogen produced.
- Other Types of Hydrogen:
- Key Applications:
- Steel Industry Innovation: Green hydrogen is being explored in the steel industry for carbon-based fuels in iron reduction and other steelmaking processes to reduce carbon emissions and enhance sustainability.
- Currently, five pilot projects are underway to test its feasibility and integration into steel production.
- Road Transport: The NGHM has launched five major pilot projects involving 37 hydrogen-powered vehicles (buses and trucks) across 10 routes, supported by ₹208 crore in financial aid.
- Shipping and Maritime Operations: A Green Hydrogen Pilot Project at V.O. Chidambaranar Port (₹25 crore) and a megawatt-scale green hydrogen facility at Deendayal Port Authority, Kandla, are being developed to support cleaner maritime operations.
- High-Altitude Mobility: In November 2024, NTPC launched the world’s highest altitude Green Hydrogen Mobility Project in Leh (3,650 m), featuring 5 hydrogen buses and a fueling station.
- Steel Industry Innovation: Green hydrogen is being explored in the steel industry for carbon-based fuels in iron reduction and other steelmaking processes to reduce carbon emissions and enhance sustainability.
What is National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM)?
- About: The NGHM seeks to establish India as a global leader in clean hydrogen, enhancing industrial competitiveness, reducing fossil fuel imports, and ensuring long-term energy security while promoting sustainability and self-reliance.
- Targets:
- By 2030, the mission aims to add 125 GW of renewable energy capacity for green hydrogen production and reduce 50 MMT of greenhouse gas emissions annually.
- The mission aims to generate investments over ₹8 lakh crore, create 6 lakh jobs, reduce fossil fuel imports by ₹1 lakh crore annually, and has already certified over 5,600 trainees in hydrogen-related qualifications.
- Funding: The mission has an initial outlay of ₹19,744 crore until FY 2029-30, with funds allocated to key components, including the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme.
- Global Partnerships:
- EU-India Collaboration: Under the EU-India Trade and Technology Council, over 30 joint proposals on hydrogen production from waste have been received.
- India-UK Partnership: In February 2025, India and the UK strengthened their cooperation on hydrogen standardization through a dedicated Standards Partnership Workshop.
- Partnership with H2Global: In November 2024, India’s Solar Energy Corporation (SECI) signed an MoU with H2Global Stiftung (Germany) to facilitate market-based mechanisms for the export of Indian green hydrogen.
- Singapore Collaboration: In October 2025, Sembcorp Industries signed MoUs with V.O. Chidambaranar and Paradip Port Authorities to develop integrated green hydrogen and ammonia hubs for production, storage, and exports.
What are the Key Initiatives Taken by India to Promote Green Hydrogen?
- SIGHT Scheme: The SIGHT scheme provides financial incentives for the manufacturing of electrolysers used in green hydrogen production, aiming to accelerate the transition to sustainable energy.
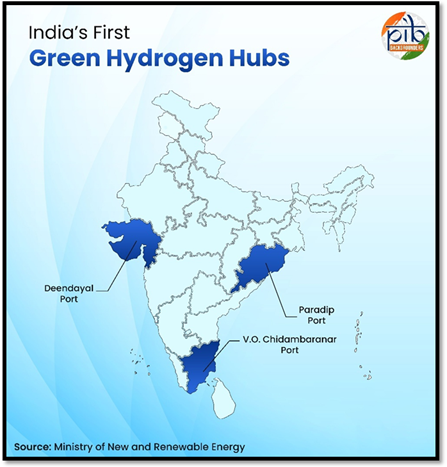
- Development of Green Hydrogen Hubs: In October 2025, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) recognized three major ports;
- Deendayal Port Authority (Gujarat), V.O. Chidambaranar Port Authority (Tamil Nadu), and Paradip Port Authority (Odisha)—as Green Hydrogen Hubs, which will serve as integrated centers for production, consumption, and export.
- Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme (GHCI): Launched in April 2025, the GHCI provides a framework to certify hydrogen as “green,” ensuring it meets emission standards and is produced using renewable energy.
- It aims to ensure transparency, traceability, and credibility in hydrogen production.
- R&D and Certification Requirements: Under the GHCI, any green hydrogen production facility receiving government subsidies or selling hydrogen domestically must obtain a Final Certificate.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) will oversee accreditation and certification processes.
- Strategic Hydrogen Innovation Partnership (SHIP): The SHIP fosters collaboration between government, industry, and academia to develop competitive hydrogen technologies.
- It includes a dedicated R&D fund and encourages consortium-based research to drive innovation and support domestic manufacturing capabilities.
Conclusion
Green hydrogen is pivotal to India’s future clean energy landscape, driving the shift to a low-carbon, self-reliant economy. The National Green Hydrogen Mission will accelerate domestic production, innovation, and global market access, reducing fossil fuel dependence and positioning India to lead the global clean energy transition toward a sustainable and secure future.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Evaluate the potential of Green Hydrogen in achieving India’s Net Zero target by 2070. How can the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) play a crucial role in this transition? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Green Hydrogen (GH2)?
Green hydrogen refers to hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power through electrolysis, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen. It can also be produced from biomass, provided emissions are below the safe limit set by India.
2. What are the key applications of Green Hydrogen in India?
Green hydrogen is being explored in the steel industry for iron reduction, road transport with hydrogen-powered vehicles, shipping and maritime operations, and high-altitude mobility projects like the hydrogen-powered buses in Leh.
3. What are the targets of the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM)?
The NGHM aims to add 125 GW of renewable energy capacity for green hydrogen production by 2030, reduce 50 MMT of greenhouse gas emissions annually, and generate investments exceeding ₹8 lakh crore while creating 6 lakh jobs.
4. What initiatives has India taken to promote Green Hydrogen?
Key initiatives include the SIGHT Scheme for electrolyser manufacturing, the development of Green Hydrogen Hubs at major ports, the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme (GHCI), and the Strategic Hydrogen Innovation Partnership (SHIP) for R&D collaboration.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following heavy industries: (2023)
- Fertilizer plants
- Oil refineries
- Steel plants
Green hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in decarbonizing how many of the above industries?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (c)
Q. With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fuel cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (c)
Q. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce one of the following as “exhaust” (2010)
(a) NH3
(b) CH4
(c) H2O
(d) H2O2
Ans: (c)