Important Facts For Prelims
Urban Heat Island Effect
- 30 Apr 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
A recent study highlights the dual impact of the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect—while it elevates heat-related mortality, it substantially reduces cold-related deaths.
- In 2018, the global decline in cold-related fatalities was 4.4 times greater than the rise in heat-related deaths, with cities like Moscow witnessing even larger differentials.
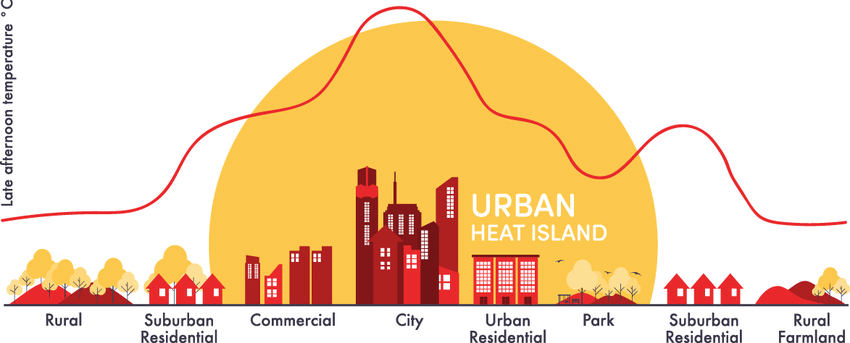
What is Urban Heat Island?
- About: An Urban Heat Island (UHI) is a metropolitan area significantly warmer than nearby rural surroundings.
- Urban areas heat up more than natural landscapes because materials like concrete and asphalt absorb and retain heat more effectively.
- The effect is most noticeable in large, densely populated cities like New Delhi, New York, Paris, and London.
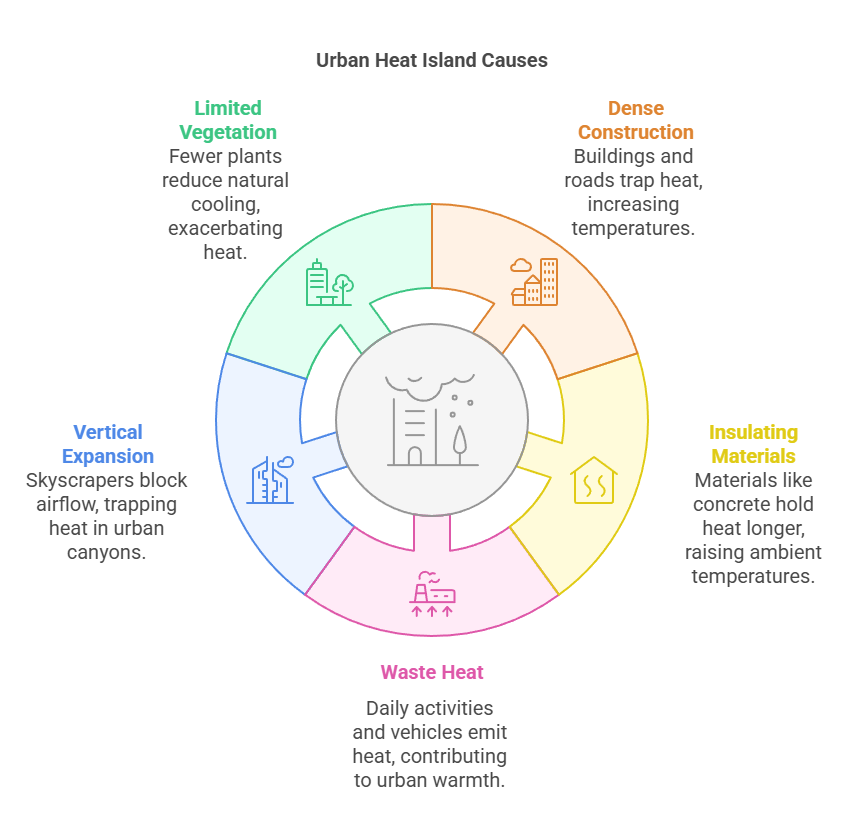
- Causes:
- Impervious Surfaces: Materials like asphalt, concrete, and steel absorb daytime heat and release it slowly at night due to low albedo, trapping more heat.
- Lack of Vegetation: Limited green cover and tree canopy reduce evapotranspiration, cutting off natural cooling and increasing urban heat buildup.
- Anthropogenic Heat: Vehicular emissions, industrial processes, and air conditioning release excess heat, significantly raising urban temperatures.
- Air Pollution and Soot: Black carbon and other particulate matter absorb solar radiation, raising ambient temperatures and worsening the UHI effect.
- Urban Morphology: Dense buildings, narrow streets, and poor airflow create an urban canyon effect, trapping heat within confined spaces.
- Skyscrapers and high-rises restrict air flow and trap heat.
- Consequences:
- Increased Energy Demand: UHI raises cooling energy use, straining grids and increasing carbon emissions.
- By elevating local temperatures, urban areas drive up energy consumption for cooling and positioning urban heat islands as localized accelerators of climate change.
- Deterioration of Air Quality: Higher temperatures boost ground level ozone formation, worsening smog and respiratory issues.
- Heat-Related Health Risks: UHI increases heat strokes, dehydration, and cardiovascular stress, especially in vulnerable groups.
- Strain on Water Resources: UHI accelerates evaporation, reducing water availability and increasing cooling water demand.
- Biodiversity Loss: UHI harms native vegetation, disrupts ecosystems, and threatens urban wildlife due to excessive heat and reduced green spaces
- Increased Energy Demand: UHI raises cooling energy use, straining grids and increasing carbon emissions.
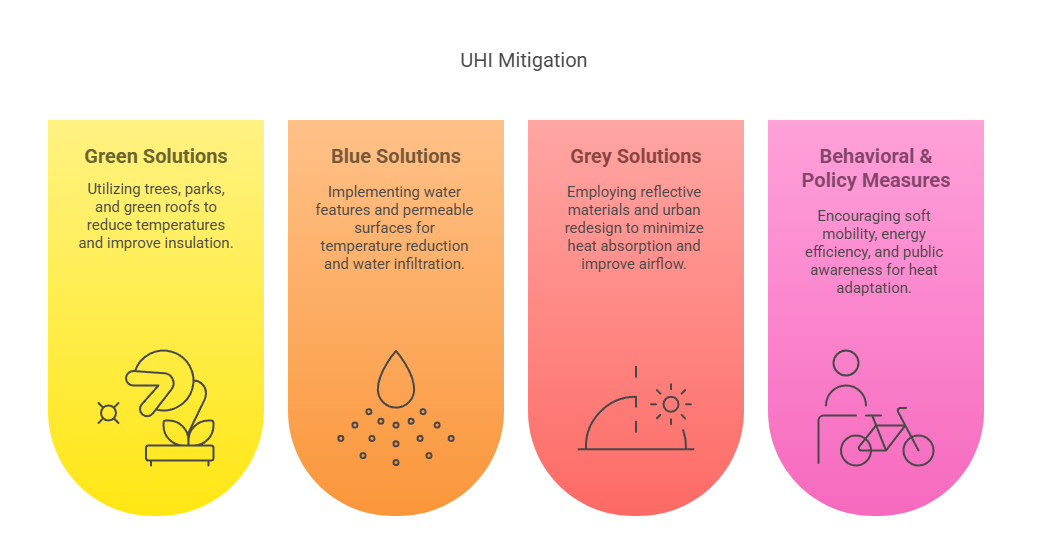
- UHI Mitigation Strategies:
UHI Mitigation Case Studies:
|
| Click Here to Read More: Heat Waves |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What are the possible limitations of India in mitigating global warming at present and in the immediate future? (2010)
- Appropriate alternate technologies are not sufficiently available.
- India cannot invest huge funds in research and development.
- Many developed countries have already set up their polluting industries in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)