Indian Economy
Economic Capital Framework and RBI’s Dividend Transfer
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Economic Capital Framework (ECF), Contingency Risk Buffer (CRB), Bimal Jalan committee, Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Open Market Operations (OMOs), monetary policy, Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
For Mains: About Economic Capital Framework (ECF), Its related Provisions and Significance, Provisions Governing & Significance of RBI’s Surplus Transfer to Government.
Why in News?
The Central Board of Directors of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) assessed the Economic Capital Framework (ECF) for determining risk provisioning and the distribution of dividend (surplus) from the central bank to the government.
What is Economic Capital Framework (ECF)?
- About: The ECF is a structured mechanism adopted by the RBI to determine the appropriate level of risk provisions and the surplus (profit) that can be transferred to the Government of India under Section 47 of the RBI Act, 1934.
- The framework was recommended by the former RBI Governor, Bimal Jalan Committee (2018) and formally adopted in 2019.
- Objective: It aims to strike a balance between maintaining adequate financial buffers for monetary and financial stability and ensuring prudent surplus distribution.
- It enables the RBI to maintain a Contingency Risk Buffer (CRB) as a financial safeguard against unforeseen shocks like currency volatility and economic crises.
- CRB is a financial safety net of 5.5% to 6.5% of RBI’s balance sheet, ensuring its stability and capacity to act as Lender of Last Resort during crises.
- It enables the RBI to maintain a Contingency Risk Buffer (CRB) as a financial safeguard against unforeseen shocks like currency volatility and economic crises.
- Revised ECF (Bimal Jalan Committee Recommendations, 2019):
- Realized Equity (Contingency Fund-CF): The CF acts as a buffer against unforeseen losses and is to be maintained between 5.5% and 6.5% of the RBI’s balance sheet.
- Any excess above this range is transferred to the government. The RBI’s Central Board has fixed the target at the lower bound of 5.5%.
- Economic Capital (Capital and General Risk Account- CGRA): The CGRA includes the RBI’s capital, reserves, risk provisions, and revaluation balances arising from fluctuations in exchange rates, gold prices, and interest rates.
- It is to be maintained between 20.8% and 25.4% of the balance sheet size, and any excess may be transferred to the Centre.
- Realized Equity (Contingency Fund-CF): The CF acts as a buffer against unforeseen losses and is to be maintained between 5.5% and 6.5% of the RBI’s balance sheet.
- Review Mechanism: As per the committee's recommendations, ECF is reviewed every 5 years to adjust for evolving economic conditions and risks, with the latest review done in August 2024.
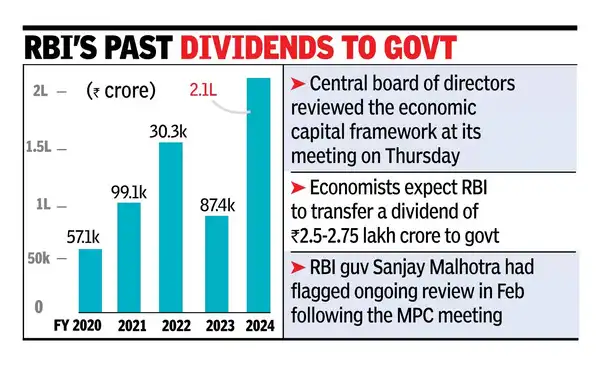
- Trends in Dividend Transfer: RBI’s dividend transfers to the government have increased from Rs 30,307 crore in FY22 to an estimated Rs 2.5-3 lakh crore in FY25.
- This sharp rise is attributed to strong earnings from dollar sales, rising gold prices, and appreciation in government securities.
- This higher dividend will help manage the fiscal deficit and boost banking liquidity and potentially easing short-term interest rates.
What are the Provisions Governing RBI’s Surplus Transfer?
- RBI Act, 1934: Section 47 of the RBI Act mandates that the net profits of the RBI, after making provisions for the Contingency Fund (CF) and Asset Development Fund (ADF), must be transferred to the Central Government.
- Section 48 exempts the RBI from paying income tax or super tax on its income, thereby enabling a more direct transfer of surplus to the exchequer.
- Committee Recommendations: Historically, the RBI retained a considerable portion of its profits to strengthen its internal reserves.
- Over the years, several expert committees have examined the adequacy of RBI’s capital buffers and the quantum of surplus to be transferred:
- V. Subrahmanyam Committee (1997)
- Usha Thorat Committee (2004)
- YH Malegam Committee (2013) recommended higher transfers to the government while maintaining prudent reserves.
- Bimal Jalan Committee (2018) introduced the revised Economic Capital Framework (ECF), balancing risk provisioning with fiscal needs.
- Following these recommendations, particularly the Malegam and Jalan Committees, the RBI has progressively increased its surplus transfers to the government, ensuring both macroeconomic stability and fiscal space for public spending.
- Over the years, several expert committees have examined the adequacy of RBI’s capital buffers and the quantum of surplus to be transferred:
What are the Major Income & Expenditure Heads of RBI?
|
Source of Income |
|
|
Expenditure |
|
|
Surplus |
|
What is the Significance of RBI’s Surplus Transfer to Government?
- Reduces Fiscal Deficit: Assists the government in meeting its fiscal deficit target of 5.1% in FY 2024–25 by augmenting non-tax revenue.
- Enhances Revenue Generation: Acts as a major non-tax revenue source, enabling higher public expenditure and supporting economic growth.
- Lowers Government Borrowing: May reduce gross borrowings by up to Rs 1 trillion, freeing fiscal space for capital expenditure.
- Reduces Borrowing Costs: Lower borrowing needs can soften G-Sec yields, reducing the government’s debt servicing burden.
- Keeps Interest Rates in Check: Falling sovereign yields influence broader market rates, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and households.
Conclusion
The Economic Capital Framework ensures a balanced approach between RBI’s autonomy and the government’s fiscal needs. By setting clear risk buffers and surplus transfer rules, it promotes financial stability and fiscal prudence. This framework supports sustainable economic growth and strengthens macroeconomic resilience.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What is the Economic Capital Framework (ECF) and how does it manage the balance between the Reserve Bank of India’s autonomy and the government’s fiscal requirements? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: A
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: B


Facts for UPSC Mains
Quasi-steady State Cosmology Theory
Why in News?
Renowned astrophysicist and one of India’s most influential scientists, Professor Jayant Vishnu Narlikar, passed away in Pune. He was best known globally for his pioneering work on the quasi-steady state cosmology theory of the universe.
What is the Quasi-steady State Cosmology Theory of the Universe?
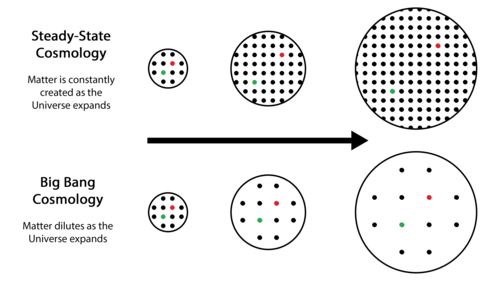
- About: The Quasi-Steady State Cosmology (QSSC) is a refined version of the Steady-State Theory of the universe. It was developed in the early 1990s by Fred Hoyle, Jayant Narlikar, and Geoffrey Burbidge as a response to the increasing dominance of the Big Bang theory, while addressing some of its limitations.
- Key Features of QSSC:
- Combines Steady-state and Cyclic Concepts: QSSC proposes that the universe follows a cyclical pattern of periodic expansion and contraction over vast timescales, while still maintaining an overall steady-state appearance.
- No Singular Origin: While the Big Bang theory posits a singular origin of the universe, QSSC rejects the idea of a singular explosive beginning.
- Instead, it suggests that the universe has existed eternally and undergoes periodic episodes of matter creation and expansion.
- Matter is continuously created in localized, non-singular events called ‘mini-bangs’ or creation events, which occur intermittently in the universe, avoiding a single origin point.
- Modified General Relativity: The theory introduces modifications to Einstein’s equations of general relativity to account for continuous matter creation, a key contribution by Jayant Narlikar.
- Scientific Acceptance: QSSC considered a minority alternative to the Big Bang, with some mathematical innovations, but not widely accepted in mainstream cosmology.
Note: The steady-state theory, proposed in 1948 by Hermann Bondi, Thomas Gold, and Fred Hoyle, posits that the universe is eternally expanding while maintaining a constant average density.
What is Big Bang Theory?
- About: The Big Bang Theory, proposed in 1927 by Belgian cosmologist Georges Lemaître, explains the origin and evolution of the universe, proposing that it began around 13.7 billion years ago from an extremely hot, dense point known as a singularity.
- The evolution of the universe started with a phase of cosmic inflation (an incredibly rapid expansion that occurred within a fraction of a second after the Big Bang).
- As the universe expanded and cooled, energy converted into fundamental particles, forming matter and radiation. This led to the creation of atoms, stars, galaxies, and planets, along with the emergence of the four fundamental forces: gravity, electromagnetism, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces.
- Planck Epoch: The Planck Epoch is the first 10⁻⁴³ seconds after the Big Bang, when the universe was extremely hot and dense. Current physics (General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics) cannot describe this period, and a theory of quantum gravity is needed to understand it.
- Evidence Supporting Big Bang:
- Edwin Hubble's observations, famously known as Hubble's Law, showed that galaxies are moving away from each other, with farther galaxies receding faster, indicating the universe is expanding.
- The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation, discovered by Penzias and Wilson, is the cooled leftover radiation from the first light that traveled freely through the Universe shortly after the Big Bang.
- It is considered a fossil or echo of the Big Bang, this ancient light has since cooled and weakened and is now detected as microwaves.
- The European Space Agency’s Planck mission observed this oldest detectable radiation, providing valuable insights into the Universe’s origin and evolution.
Who was Dr. Jayant Vishnu Narlikar?
- Early Life: Born on 19th July 1938 in Kolhapur, Maharashtra, Dr. Jayant Vishnu Narlikar pursued higher studies at Cambridge University.
- Institutional Building: In 1988, he was invited by the University Grants Commission (UGC) to establish the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA) in Pune as its Founder Director. His leadership made IUCAA a global science hub.
- Bibliography: Dr. Narlikar was also a noted science communicator and author of popular science fiction works, including An Introduction to Cosmology.
- His autobiography, A Tale of Four Cities (Char Nagaratale Majhe Vishva), was awarded the Sahitya Akademi Award in 2014 for its literary merit in Marathi.
- Awards: Received Padma Bhushan (1965) and Padma Vibhushan (2004). In 1996, Narlikar received the UNESCO Kalinga Prize for his exceptional work in popularizing science.
- Additionally, in 2011, he was conferred the Maharashtra Bhushan, the highest civilian honor awarded by the Government of Maharashtra.
| Read more: Challenging Big Bang Theory |
|
Drishti Mains Question: Differentiate between the Big Bang Theory and the Quasi-Steady State Cosmology in explaining the origin and evolution of the Universe. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.The terms ‘Event Horizon’, ‘Singularity’, ‘String Theory’ and ‘Standard Model’ are sometimes seen in the news in the context of (2017)
(a) Observation and understanding of the Universe
(b) Study of the solar and the lunar eclipses
(c) Placing satellites in the orbit of the Earth
(d) Origin and evolution of living organisms on the Earth
Ans: (a)
Q. Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidences for the continued expansion of universe? (2012)
- Detection of microwaves in space
- Observation of redshift phenomenon in space
- Movement of asteroids in space
- Occurrence of supernova explosions in space
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) None of the above can be cited as evidence
Ans: (a)
Q. Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched? (2008)
Theory/Law Associated Scientist
- Continental Drift : Edwin Hubble
- Expansion of Universe : Alfred Wegener
- Photoelectric Effect : Albert Einstein
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Code:
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 only
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
16th Asiatic Lion Census 2025
Why in News?
Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica) population in Gujarat goes up from 674 to 891 in 5 years, according to the 16th census 2025 released by the Gujarat Forest Department.
What are the Key Findings of 16th Asiatic Lion Census 2025?
- Total Population: 891 Asiatic lions recorded in Gujarat, a 32.2% increase from 674 lions in 2020 (15th census).
- Population Distribution: 384 lions live inside protected forest and sanctuary areas. Lions in non-forested areas have risen from 340 in 2020 to 507 in 2025.
- 44.22% of the lion population now resides outside traditional protected habitats.
- Gir National Park and adjoining sanctuaries (Gir Wildlife Sanctuary, and Pania Wildlife Sanctuary) house 394 lions, forming the core population.
- Amreli district has the highest count with 257 lions, while Mityala Wildlife Sanctuary doubled its population to 32 lions.
- Barda Wildlife Sanctuary near Porbandar has become a newly established lion population area, with 17 lions recorded, the first since 1879.
- The 2025 census also identified new satellite populations around Jetpur and Babra-Jasdan.
- Adult Females: 330 adult females recorded, a 27% rise since 2020, indicating strong potential for further growth.
- Reasons of Population Boom: Project Lion has helped in restoring habitats, strengthening the prey base, and mitigating conflicts to support Asiatic lion conservation.
- Census methodology: Conducted using direct beat verification (the area was divided into regions, zones, and sub-zones with designated officials, enumerators, supervisors, and volunteers), a more scientific and statistically robust method compared to pugmark-based tiger surveys.
- Completed in just three days, unlike the tiger census which takes two years.
What is Project Lion?
- Project Lion: Announced in 2020, Project Lion is a long-term initiative aimed at securing the future of Asiatic lions by creating a sustainable environment that enhances the overall health of their ecosystems.
- The project, being implemented in the Gir landscape in Gujarat, focuses on habitat improvement, the use of advanced technologies such as radio-collaring and camera traps for monitoring, and the mitigation of human-wildlife conflict.
- The Gujarat Forest Department plays a central role in implementing these conservation measures, conducting regular lion censuses to track population trends and health.
- Technologies in Lion Conservation: Advanced tools such as Global Positioning System-based tracking are used to monitor lions and vehicles, ensuring efficient surveillance.
- An automated sensor grid, which includes magnetic, movement, and infrared heat sensors, helps detect and track wildlife activity.
- Geographic Information System (GIS)-based real-time monitoring enables timely analysis, report generation, and effective management of conservation efforts.
Note: The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) released the first Green Status Assessment for lions in 2025, providing a global standard to measure species recovery and conservation impact.
- IUCN Green Status of Species covers all species except microorganisms and uses eight categories (Extinct in the Wild, Critically Depleted, Largely Depleted, Moderately Depleted, Slightly Depleted, Fully Recovered, Non-Depleted and Indeterminate).
- Unlike the IUCN Red List, which focuses on extinction risk, the Green Status highlights recovery potential and necessary conservation actions. Lions have been placed in the Largely Depleted category.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only.
- Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only.
- One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
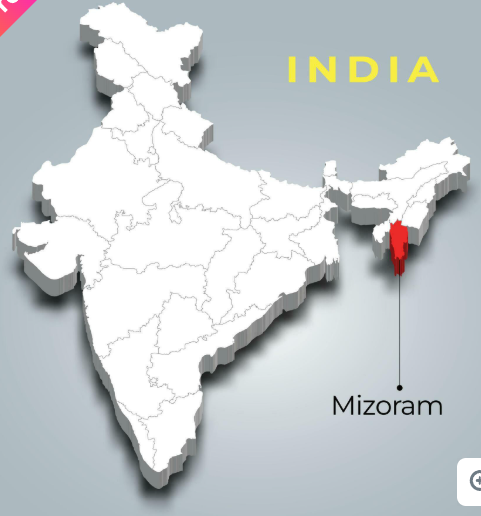
Mizoram: India’s First State to Attain Full Functional Literacy
Why in News?
Mizoram has exceeded the 95% literacy rate benchmark, achieving 98.20% literacy as per the PLFS Survey 2023-24, meeting the Ministry of Education’s criteria for full functional literacy under the ULLAS (Understanding of Lifelong Learning for All in Society) programme.
- Prior to this, Ladakh was the first UT to be declared fully functionally literate.
Note: Functional literacy refers to an individual's capability to use reading, writing, and numerical skills in everyday tasks that contribute to personal growth and community participation.
What is ULLAS- Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram or New India Literacy Programme (NILP)?
- About: ULLAS (Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society) is a centrally sponsored scheme being implemented from 2022 to 2027.
- It is designed to empower adults aged 15 years and above who missed out on formal schooling, in line with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Implementation Mechanism: Encouraging volunteerism to foster social responsibility and a sense of duty, or ‘Kartavya Bodh’.
- Key Components: Foundational Literacy and Numeracy, Critical Life Skills, Basic Education, Vocational Skills, and Continuing Education.
- Key Features: Provides access to educational resources via the DIKSHA platform and ULLAS mobile/web portal, supporting content in regional languages.
- Includes the Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT), conducted biannually or as required at local schools for assessment and certification.
Other Government Initiatives Related to Education
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)


Rapid Fire
Indian Yak Genomics
For the first time, Indian scientists have successfully assembled a chromosome-level genome of the Indian yak (Bos grunniens), an essential high-altitude bovine species.
- Indian Yak Genomics: The project used long-read sequencing technology and advanced bioinformatics, enabling precise mapping of genes to specific chromosomes.
- Long-read sequencing is a DNA sequencing method that reads long stretches of DNA, thousands to millions of base pairs, unlike short-read sequencing, which reads shorter fragments (typically 100–300 base pairs).
- Bioinformatics combines biology, computer science, and math to analyze and interpret large biological datasets, such as DNA, RNA, and protein sequences.
- Moreover, this genomics study will help in allele mining, enhancing scientific research and local livestock management.
- Allele mining identifies genetic variations linked to desirable traits like disease resistance, drought tolerance, or high yield within or across species.
- Indian Yak: In India, yaks are found above 7,000 feet in Ladakh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Himachal Pradesh.
- Food Animal: In 2022, Food Safety and Standard Authority of India (FSSAI) approved the Himalayan Yak as a ‘food animal’, allowing its use in food production or consumption to help arrest its declining population.
| Read More: Himalayan Yak |


Rapid Fire
Shirui Lily Festival
After a two-year hiatus due to ethnic conflict, Manipur’s Shirui Lily Festival returns in 2025, symbolizing both a cultural revival and a cautious attempt at restoring inter-community movement and peace in the state.
- Shirui Lily: The Shirui Lily (Lilium mackliniae), Manipur’s State Flower, is a rare pinkish-white bloom found only in the Shirui Hills of Ukhrul district.
- It was discovered in 1946 by Dr. Frank Kingdon Ward, and was named after his wife, Jean Macklin. The flower received the Royal Horticultural Society’s merit award in 1948.
- It blooms from April to June, grows about a foot tall, and has a bell-shaped flower.
- The Shirui Lily is endangered, with climate change, habitat loss, and invasive species like wild dwarf bamboo contributing to its decline.
- Shirui Lily Festival: First held in 2017, the festival is one of Manipur’s two major tourism events (the other being the Sangai Festival).
- The Shirui Lily Festival celebrates ecotourism, Tangkhul Naga culture, and conservation. It features music concerts, cultural performances, and other community events.
| Read more: Violence in Manipur |


Rapid Fire
Metrology and India’s Initiatives
The Department of Consumer Affairs, Government of India, celebrated World Metrology Day 2025.
- World Metrology Day 2025: The day commemorates the 150th anniversary of the Metre Convention signed in Paris on 20th May 1875, which established the metric system to standardize units globally.
- The celebration was first initiated in 1999 by the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM).
- The theme for 2025 is “Measurements for all times, for all people,” highlighting measurement’s continuous impact across history, present, and future.
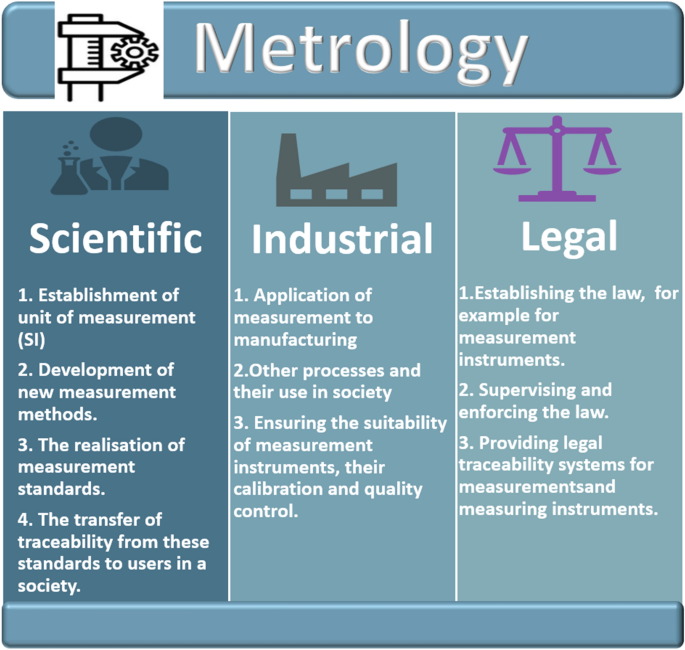
- Metrology: It is the scientific study of measurement, establishes common standards for units and instruments. It plays a vital role in various fields such as navigation, construction, product development, environmental monitoring, medicine, and food processing.
- Metrology aligns with UNESCO’s vision of advancing science for a better world.
- India’s Initiatives in Metrology: India joined the Metre Convention in 1957 following the enactment of the Standards of Weights and Measures Act, 1956.
- India became the 13th country globally to issue OIML (International Organization of Legal Metrology) certificates, boosting global trust in its measurement systems.
- The eMaap portal, digitizes legal metrology processes across 18 states for easier licensing, registration, and enforcement.
- The launch of the “One Nation, One Time” initiative under Draft IST Rules 2025 aims to provide millisecond-accurate Indian Standard Time through Regional Reference Standard Laboratories, benefiting critical sectors like telecom and banking.
| Read more: India Authorised to Issue OIML Certificates |


Rapid Fire
Guttala Drought Inscription
A rare Kannada inscription discovered in Haveri, Karnataka, marks the first known historical record in India to document a mass humanitarian disaster (6,307 deaths) due to bara" (drought), dating back to 18th August 1539 CE.
- The bodies were buried after paying respects to God Basaveshwara. It is India’s earliest known inscription explicitly recording the human toll of a natural disaster.
- Inscriptions are texts carved on durable materials like stone or metal, serving as historical records to commemorate events, royal decrees, donations, or victories.
- Notable Inscriptions in Karnataka:
- Maski Rock Edict (3rd Century BCE): One of Ashoka’s minor edicts, it first uses the title "Devanampriya" (Beloved of the Gods) for Ashoka.
- Aihole Inscription (634 CE): Composed by Ravikirti in Sanskrit, it records Pulakeshin II victories, including over Harshavardhana.
- Halmidi Inscription (450 CE): It is the oldest known Kannada inscription, and written in early Kannada script and poetic form.
- It mentions Kadamba king Kakusthavarma and has 16 lines carved on a sandstone slab.
| Read More: 900-Year-Old Chalukyan Inscription |