Rapid Fire
Exercise Bright Star 2025
Indian Armed Forces personnel are participating in the 19th edition of Exercise Bright Star 2025, which is being held in Egypt.
- About: It is a biennial multilateral military exercise, recognized as one of the largest and longest-running tri-service drills in the Middle East–North Africa (MENA) region.
- Hosted by Egypt in partnership with the US since 1980, it has evolved from a bilateral US-Egypt initiative into a full-scale multilateral military exercise.
- Objective: It aims to enhance jointness and interoperability among participating nations, promote regional peace, security, and stability, and strengthen multi-domain warfare preparedness through joint training.
Other Key Multilateral Military Exercises Involving India:
|
Exercise Name |
Hosting/Lead Countries (Along with India) |
|
Malabar (Naval) |
US, Japan, Australia |
|
MILAN (Naval) |
Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Thailand and several others |
|
RIMPAC (Naval) |
US, Australia, Canada, Japan, India and several others |
|
IBSAMAR (Naval) |
Brazil & South Africa |
|
Read More: Major Military Exercises of India |


Rapid Fire
Gangotri Glacier Retreat Signals Climate Peril
A study by IIT Indore and ICIMOD (Nepal) reveals that the Gangotri Glacier System (GGS), the primary source of the Ganga, has lost 10% of its snowmelt flow over 1980–2020 due to rising temperatures and climate change.
- Himalayan glaciers are thinning at an average of 46 cm/year, and Gangotri’s snout is steadily receding. Increasing rainfall-runoff and base flow indicate climate-induced hydrological changes.
- Glacial lakes and other water bodies across the Himalayan region saw a 10.81% increase in area from 2011 to 2024 due to climate change (Central Water Commission).
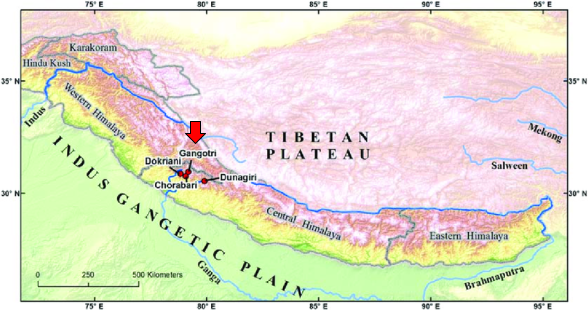
Gangotri Glacier
- About: Gangotri Glacier, located in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand is one of the largest Himalayan glaciers originating from the northern slopes of the Chaukhamba range.
- It is a compound valley glacier, fed by several tributary glaciers like Raktvarn, Chaturangi, and Swachand glaciers.
- It is fed by peaks including Shivling, Thalay Sagar, Meru, and Bhagirathi III & it terminates at Gaumukh, from where the Bhagirathi River emerges and later joins the Alaknanda to form the Ganga at Devprayag.
- Gangotri National Park: Established in 1989, it encompasses Gaumukh, the source of the Ganga, and the popular Gaumukh-Tapovan Trek.
- It has dense temperate coniferous forests including chirpine, deodar, fir, spruce, oak, and rhododendron, and is home to rare and endangered species such as Black Bear, Brown Bear, Himalayan Monal, Himalayan Snowcock, Himalayan Tahr, Musk Deer and Snow Leopard
|
Read More: River Ganga |


Indian Economy
National Biofoundry Network and Bioeconomy
For Prelims: Biotechnology, BioE3, Lifestyle for Environment, National Biofoundry Network, Bio- RIDE Scheme
For Mains: Biotechnology policies and initiatives in India, India’s bioeconomy.
Why in News?
Marking one year of the BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy, the Ministry of Science & Technology launched the country’s first National Biofoundry Network, calling it a step towards making biotechnology a key driver of India’s bioeconomy.
- National Biofoundry Network comprises six institutions that aim to strengthen biomanufacturing by scaling up proofs of concept and moving innovations from labs to industry.
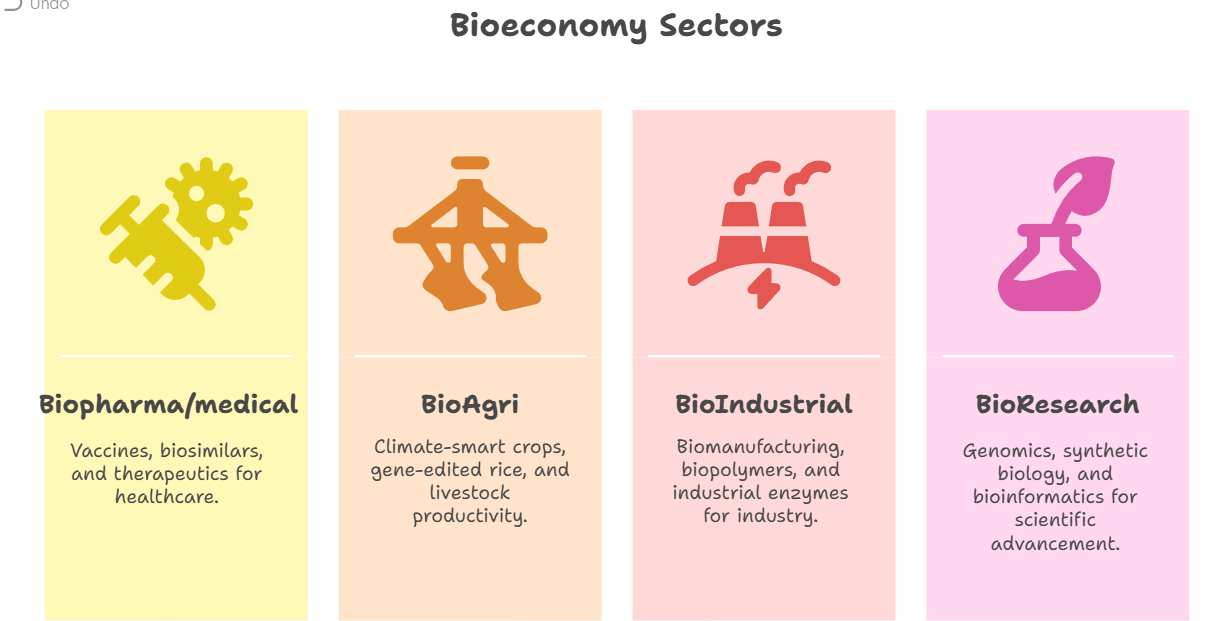
What is Bioeconomy?
- About: Bioeconomy refers to the production, utilization, and conservation of biological resources using scientific knowledge, technology, and innovation to provide products, processes, and services across all economic sectors, aiming for a sustainable and inclusive economy.
- India's bioeconomy has grown from USD 10 billion in 2014 to USD 165.7 billion in 2024, and now working towards a target of USD 300 billion by 2030.
- Significance of Bioeconomy:
- Bio-agriculture: Supports circular economy, biofertilizers, biopesticides, and bioremediation, and climate-smart agriculture.
- Enhances agricultural productivity through biofortified crops, precision farming, and advanced biotechnologies.
- Energy Security: Ethanol blending target reached to 20% (2025), reducing crude imports and CO₂ emissions. India saved Rs 1.36 lakh crore in forex by cutting crude oil imports.
- Entrepreneurship: Biotech startups grew from 50 to over 10,000 in just a decade, boosting innovation.
- Bio-agriculture: Supports circular economy, biofertilizers, biopesticides, and bioremediation, and climate-smart agriculture.
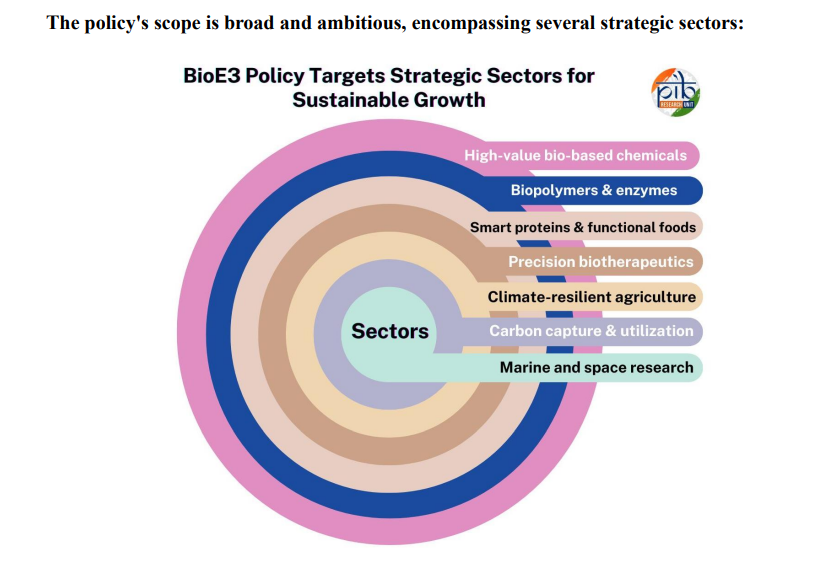
What is the BioE3 Policy?
- About: The BioE3 Policy approved in 2024, is India’s blueprint for strengthening biomanufacturing through advanced technologies and innovation-driven research.
- It is aligned with India’s vision of Green Growth (announced in the Union Budget 2023-24) promoting the bioeconomy while supporting Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), and Net-Zero emissions.
- Implementation: Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Objectives: Create a framework for adopting cutting-edge biomanufacturing technologies.
- Promote high-performance biomanufacturing across diverse sectors.
- Ensure efficiency, sustainability, and quality in production of bio-based high-value products.
- Establish BioEnablers (Bio-AI hubs, Biofoundries, Biomanufacturing hubs) to fast-track biotech commercialization.
- Train and skill manpower in interdisciplinary technical fields to support industry needs.
- Implementation Framework:
- Bio-Artificial Intelligence (AI) Hubs: Power research with data-driven analytics and AI models for innovation in bio-based products.
- Biofoundries & Biomanufacturing Hubs: These will provide infrastructure to scale up technologies and bridge the lab-to-industry gap, offering shared pilot and pre-commercial facilities to support early-stage manufacturing for researchers, startups, and SMEs.
How Can India’s Bioeconomic Initiatives Transform Key Development Sectors?
- Biopharma: BioE3 Policy fosters regenerative biomanufacturing, circular bioeconomy, and net-zero aligned growth.
- National Biopharma Mission co-funded by the World Bank boosts vaccines, biopharma, and diagnostics.
- India ranks 3rd in pharmaceutical production by volume and 14th by value, manufacturing every third tablet consumed globally.
- India developed the world’s first DNA Covid-19 vaccine and produces 65% of the world’s vaccines, benefiting low- and middle-income countries.
- Bio-Agriculture: Development of climate-smart crops (drought-tolerant chickpea, genome-edited rice), and Genomic tools ( Amaranth Genomic Resource Database (AGRDB)) improve crop identification, yield, and nutrition.
- Biotech-KISAN (Biotech-Krishi Innovation Science Application Network) enables farmer-scientist partnerships, benefiting rural, tribal, and women farmers, increasing productivity and incomes.
- Bioenergy: Ethanol blending National Policy on Biofuels (2018) increased from 1.53% (2014) to 20% (2025).
- It reduced crude oil imports, CO₂ emissions, and generated significant rural incomes through agro-industrial linkages.
- Innovation & Startups: Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) set up by the DBT in 2012, nurtures India’s biotech startups through 95 bio-incubation centres offering funding, infrastructure, and mentorship.
- Biotechnology Research Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development (Bio- RIDE) Scheme encourages innovation and academia-industry collaboration.
- Socio-Economic Impact: Bioeconomic initiatives create employment in tier-II & III cities, support MSMEs, and strengthen rural development.
- Policies foster inclusive, knowledge-driven growth, supporting India’s vision of a bio-enabled economy by 2047.
What are the Key Challenges Hindering the Growth of a Robust Bioeconomy in India?
- Insufficient Funding: DBT budget allocation is less than 1% of GDP, limiting research and innovation.
- High Initial Investment & Financial Risks: Establishing biomanufacturing hubs, biofoundries, and Bio-AI centres requires substantial upfront investment.
- Returns are long-term and uncertain, which may deter private investment and strain public finances.
- Regulatory and Ethical Concerns: Precision biotherapeutics, synthetic biology, and genetic modifications raise biosafety, biosecurity, and ethical issues.
- Skill Gaps & Workforce Challenges: India faces shortages in bioinformatics, synthetic biology, and biomanufacturing expertise.
- Potential Environmental Impact: Large-scale bio-based production may cause deforestation, water stress, monocultures, or improper biowaste disposal.
- Societal and Environmental Concerns: Public skepticism towards Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) and biotherapeutics, and risks of large-scale biomanufacturing affecting ecosystems.
- Challenges in Scaling & Commercialisation: Translating lab research into mass-market products requires infrastructure, capital, and expertise; failure to do so may undermine policy goals.
What Measures are Needed to Fortify India’s Bioeconomy?
- Streamline Regulatory Framework: Establish a single-window approval system for biotech products, including GM crops and gene-edited organisms.
- Harmonize laws like the Patents Act, 1970 and the Protection of Plant Varieties & Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001 to balance innovation and farmers’ interests.
- Define clear regulatory guidance for emerging technologies, e.g., genetically engineered crops, to reduce uncertainty for researchers and funders.
- Enhance Innovation and Commercialization: Expand support to startups through BIRAC initiatives. Promote translational research in sectors like cell and gene therapy, functional foods, and climate-smart agriculture.
- Boost Investment and Funding: Increase DBT’s budget to support frontier research. Provide targeted tax incentives and outcome-linked funding for high-risk biotech innovations.
- Encourage private sector participation through corporate innovation funds and public-private partnerships.
- Strengthen Human Capital and Skills: Create Centers of Excellence for biotechnology, synthetic biology, and biomanufacturing. Expand training and bio-hubs to produce skilled manpower for startups and SMEs.
Conclusion
The BioE3 Policy is a cornerstone for India’s bioeconomy, combining sustainability with economic growth. By fostering innovation, green technologies, and entrepreneurship, it seeks to not only expand India’s global biotech footprint but also ensure a future of economic resilience, ecological balance, and energy security.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Critically examine the significance of India’s BioE3 Policy in promoting a sustainable and innovation-driven bioeconomy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q. How can biotechnology help to improve the living standards of farmers? (2019)
Q. Why is there so much activity in the field of biotechnology in our country? How has this activity benefited the field of bio pharma? (2018)


Rapid Fire
Mira Variable Stars
A new study by the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), co-authored by Nobel Laureate Adam Riess, uses oxygen-rich Mira variable stars to measure the Hubble constant with 3.7% precision.
Mira Stars (Omicron Ceti)
- About: Mira is a pulsating red giant star whose brightness varies regularly, with periods ranging from 100 to 1,000 days, due to expansion and contraction cycles in its outer layers.
- It was the first known variable star (a star that doesn't shine with a constant brightness), identified in the 17th century.
- They are relatively cool, with surface temperatures around 3,000 Kelvin, and are in the late stages of stellar evolution.
- Significance: They help measure cosmic distances and calibrate the extragalactic distance ladder (a series of methods to determine distances to far-off galaxies).
- They assist in determining the Hubble constant and resolving the Hubble tension (difference in the Universe’s expansion rate measured from early vs. late-Universe observations) in cosmology.
Hubble Constant (H₀)
- Formulated by Edwin Hubble in 1929, it measures the current expansion rate of the universe in kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc), indicating how fast galaxies move apart. H₀ helps estimate the universe’s size and age.
- Edwin Hubble observed that the farther a galaxy is, the faster it moves away. This is measured using redshift, a shift of light toward the red end of the spectrum, indicating the universe is expanding.
|
Read more: New Method to Determine Hubble Constant |


Rapid Fire
Biosensor For Parkinson’s Disease
Scientists at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali have developed a nanotechnology-based biosensor for the early detection of Parkinson’s Disease (PD).
Nanotechnology-based Biosensor
- Mechanism: The biosensor works using gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) coated with natural amino acids to selectively attach to specific forms of the α-synuclein protein (normally harmless but can misfold into toxic clumps (amyloids), damaging brain cells).
- Significance: This biosensor enables distinction between healthy and toxic α-synuclein, allowing early detection of PD before symptoms appear.
- It is low-cost, label-free, and suitable for point-of-care testing, and has potential applications for Alzheimer’s disease and other protein misfolding disorders.
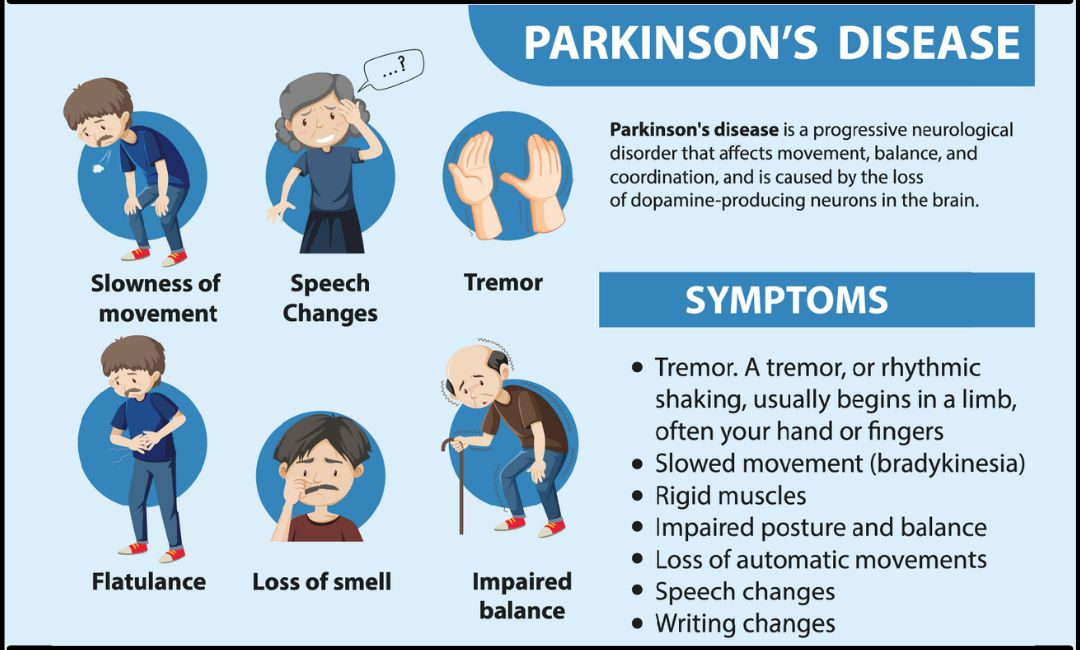
Parkinson’s Disease
- About: PD is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder marked by motor symptoms (tremors, rigidity, postural instability) and non-motor symptoms (cognitive decline, mood disorders).
- Causes & Prevalence: Caused by loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra (region in the midbrain) leading to impaired movement.
- It is believed to result from a combination of genetic mutations and environmental factors like pesticides and pollution.
- Affected 8.5 million people in 2019, India accounts for approx. 10% of cases (0.58 million).
- By 2050, India’s cases are projected to rise 168% to 2.8 million, while global cases may reach 25.2 million.
- Treatment & Management: No cure exists, management includes medications (Levodopa/Carbidopa), surgery, and rehabilitation to reduce symptoms.
- National Parkinson Network (NPN) was established in 2024 by Movement Disorder Society of India (MDSI).
|
Read More: Sensor for Parkinson’s Disease Management, Neurodegenerative Diseases |


Important Facts For Prelims
Indian Ocean Naval Symposium
Why in News?
The Indian Navy hosted the Emerging Leaders Panel under Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) at Kochi, providing young naval leaders a platform to discuss maritime cooperation, and regional security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
What is the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS)?
- About: The IONS is a voluntary initiative aimed at enhancing maritime cooperation among the navies of IOR littoral states.
- It provides an open forum for discussing regional maritime issues, sharing information, and fostering common understanding for cooperative solutions.
- Members: IONS has a collective strength of 34 states (25 Members, including India, and 9 Observers).
- Inaugural Seminar: The inaugural IONS conclave was held in 2008 in New Delhi, with the Indian Navy as Chair (2008–2010). India is set to chair IONS again (2025–27) during the 9th CoC planned in India at the end of 2025.
- Functional Areas & Working Groups (IWG):
- Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR): Planning and conducting joint relief operations during natural disasters.
- Capacity Building: Member states regularly host maritime training exercises and workshops under IONS to enhance skills and interoperability among regional navies.
- Counter-Piracy & Maritime Crime: Develop Strategies to combat piracy, smuggling, and illegal maritime activities.
What are the Key Facts About the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)?
- About: It covers about one-fifth of the world’s ocean area. The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean in the world after the Pacific, Atlantic.
- It is bounded by Asia (north), Africa (west), Australia (east), and Antarctica (south), and its deepest point at the Sunda Deep, Java Trench (Indonesia).
- Major Seas and Bays: The Indian Ocean has the fewest marginal seas among major oceans, including the Red Sea, Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea, Andaman Sea, Bay of Bengal, Gulfs of Aden and Oman, and the Great Australian Bight.
- The Indian Ocean has major epipelagic currents that influence global ocean circulation.
- Strategic Significance of IOR:
- Hosts 40+ states, nearly 40% of global population.
- Handles ~2/3 of world’s oil shipments, 1/3 cargo, ~50% container traffic.
- Key chokepoints: Suez Canal, Bab el-Mandeb, Strait of Hormuz, Strait of Malacca → critical for global trade, energy flows, strategic security.
- Resource-rich: fisheries, offshore oil (~40% of global output), mineral sands.
- For India: 7,500 km coastline, 80%+ energy imports pass through IOR → vital for trade, defence, energy security.
- Governance of IOR: Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) established in 1997, is an intergovernmental forum with its apex body, the Council of Foreign Ministers (COM), meeting annually to set policies.
- Sri Lanka is the current Chair of IORA, while India, currently Vice-Chair and part of the Troika, will assume the Chairship for 2025–2027.
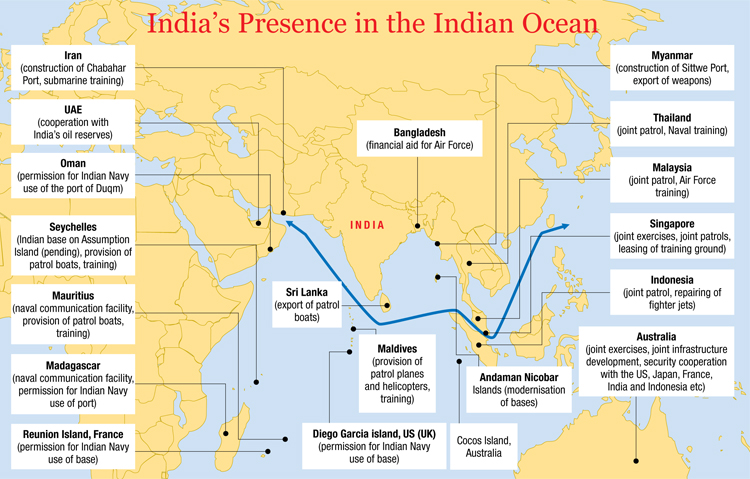
What is the Role of India in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)?
India as a Unifier in the IOR:
- Shared Vision: Through SAGAR and Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security Across the Regions (MAHASAGAR), India drives collective security, growth, and sustainable development in the IOR.
- Geo-Strategic Engagement: India is expanding its presence beyond its borders, including potential military bases in the Indo-Pacific region.
- India aims to build trust, transparency, and maritime cooperation while upholding international law, particularly the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- Security & Defense Cooperation: India builds trust as a net security provider via defense exercises like AIKEYME (Africa), MILAN (multinational), SIMBEX (with Singapore) and joint patrols with island states.
- Institutional Role: India leads platforms like IORA, IONS, and the Indian Ocean Conference, acting as a bridge among diverse littoral states.
- Through initiatives like “Act East”, “Neighbourhood First”, India is enhancing maritime connectivity and regional influence.
- Economic & Development Partner: India invests in blue economy, trade integration, renewable energy, and capacity building.
- The Indian Navy (IN) acts as a “first responder,” offering humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR), as seen after the 2004 Asian Tsunami and in subsequent evacuations from conflict or disaster zones.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
National Sports Day 2025
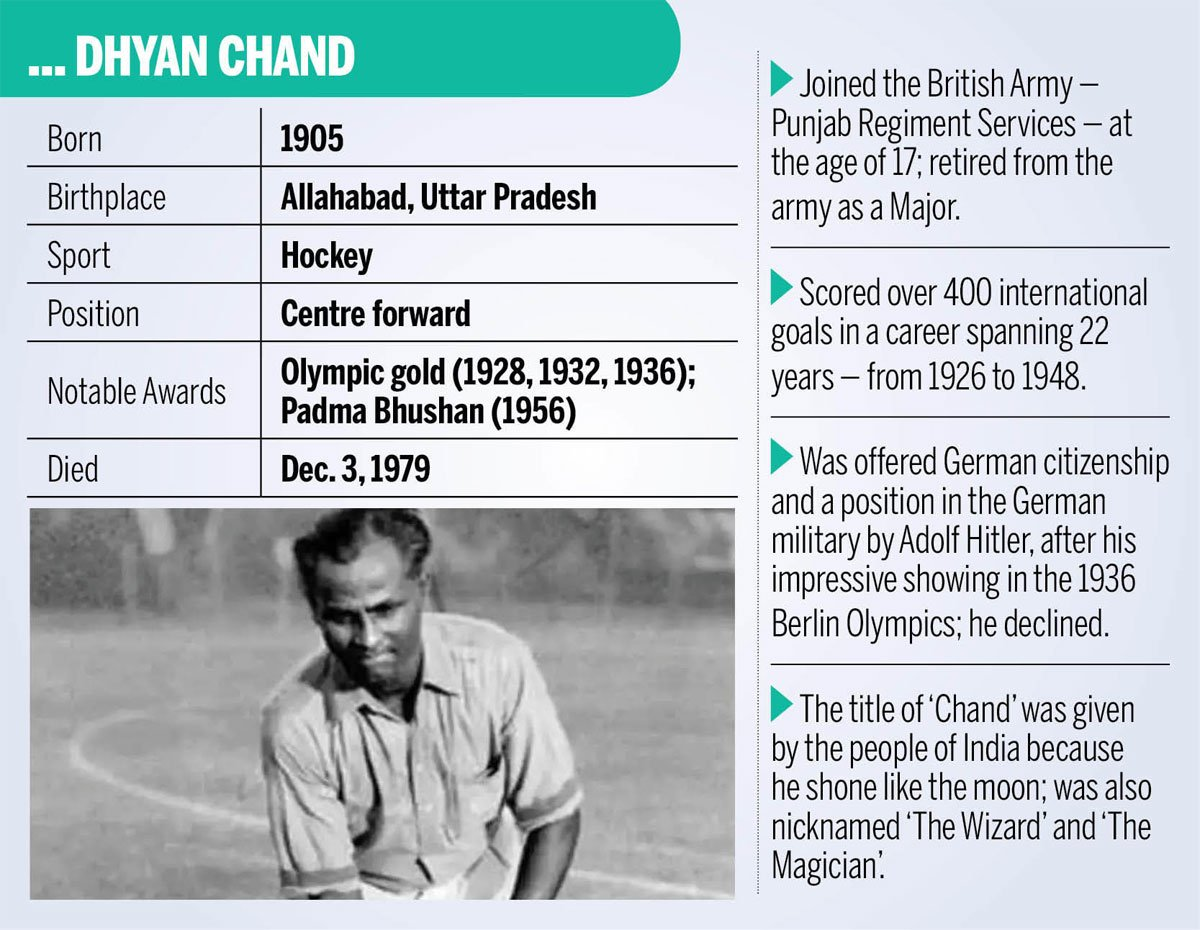
National Sports Day is observed annually on 29th August to commemorate the birth anniversary of one of the greatest field hockey players of India, Major Dhyan Chand.
National Sports Day
- About: This day was declared a national observance in 2012. In 2019, the Fit India Movement was launched on this day, marking a milestone in India’s fitness and sports journey.
- Theme 2025: Under the Fit India Mission, it will be celebrated with the theme “Ek Ghanta, Khel ke Maidan Main”, encouraging citizens to devote 60 minutes daily to physical activity.
- Key National Sports Awards: Annual award presented on 29th August by President of India includes:
|
Award |
Description |
|
Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award |
Highest sporting honour in India. Instituted in 1991–92, earlier known as the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Award & renamed in 2021 to honour hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand. |
|
Arjuna Award |
Second highest sporting honour. |
|
Dronacharya Award |
Highest honour for coaches |
|
Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar |
For organisations promoting sports in the last three years. |
Major Dhyan Chand (1905–1979)
- Achievements: Known as the Hockey Wizard.
- Legacy: Even after his retirement, India’s hockey supremacy continued with Olympic golds in 1948, 1952, 1956, and 1964, and a silver in 1960.
- Retiring as a Major in the Army in 1956, he was awarded the Padma Bhushan.
|
Read More: Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award |