Indian Economy
National Biofoundry Network and Bioeconomy
- 01 Sep 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Biotechnology, BioE3, Lifestyle for Environment, National Biofoundry Network, Bio- RIDE Scheme
For Mains: Biotechnology policies and initiatives in India, India’s bioeconomy.
Why in News?
Marking one year of the BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy, the Ministry of Science & Technology launched the country’s first National Biofoundry Network, calling it a step towards making biotechnology a key driver of India’s bioeconomy.
- National Biofoundry Network comprises six institutions that aim to strengthen biomanufacturing by scaling up proofs of concept and moving innovations from labs to industry.
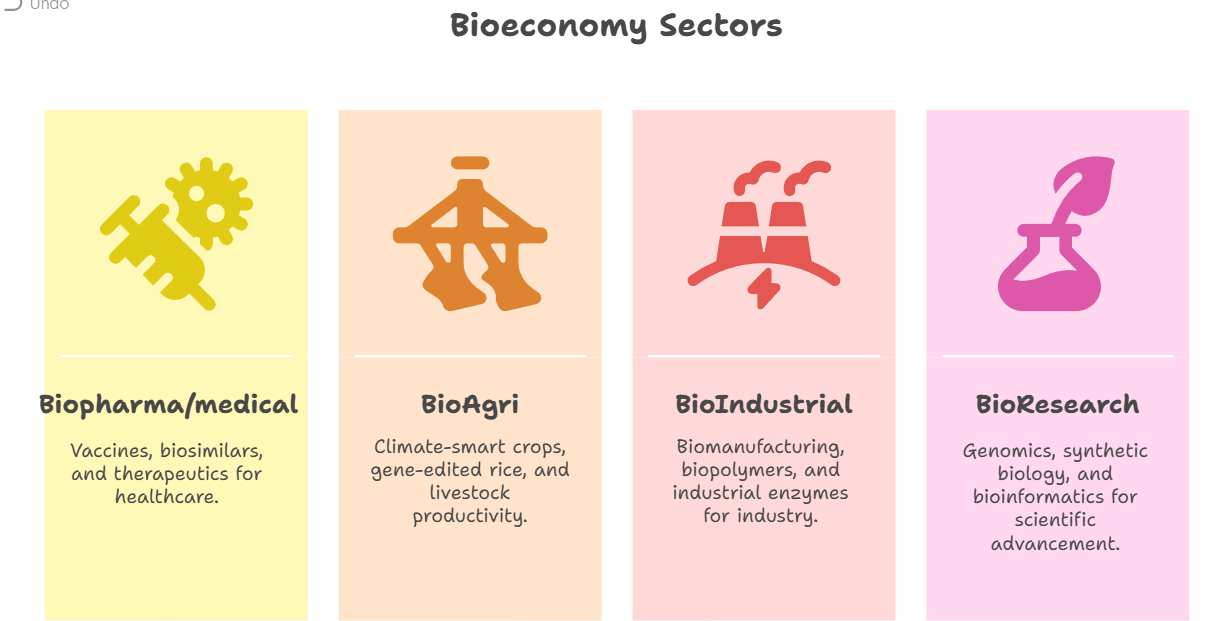
What is Bioeconomy?
- About: Bioeconomy refers to the production, utilization, and conservation of biological resources using scientific knowledge, technology, and innovation to provide products, processes, and services across all economic sectors, aiming for a sustainable and inclusive economy.
- India's bioeconomy has grown from USD 10 billion in 2014 to USD 165.7 billion in 2024, and now working towards a target of USD 300 billion by 2030.
- Significance of Bioeconomy:
- Bio-agriculture: Supports circular economy, biofertilizers, biopesticides, and bioremediation, and climate-smart agriculture.
- Enhances agricultural productivity through biofortified crops, precision farming, and advanced biotechnologies.
- Energy Security: Ethanol blending target reached to 20% (2025), reducing crude imports and CO₂ emissions. India saved Rs 1.36 lakh crore in forex by cutting crude oil imports.
- Entrepreneurship: Biotech startups grew from 50 to over 10,000 in just a decade, boosting innovation.
- Bio-agriculture: Supports circular economy, biofertilizers, biopesticides, and bioremediation, and climate-smart agriculture.
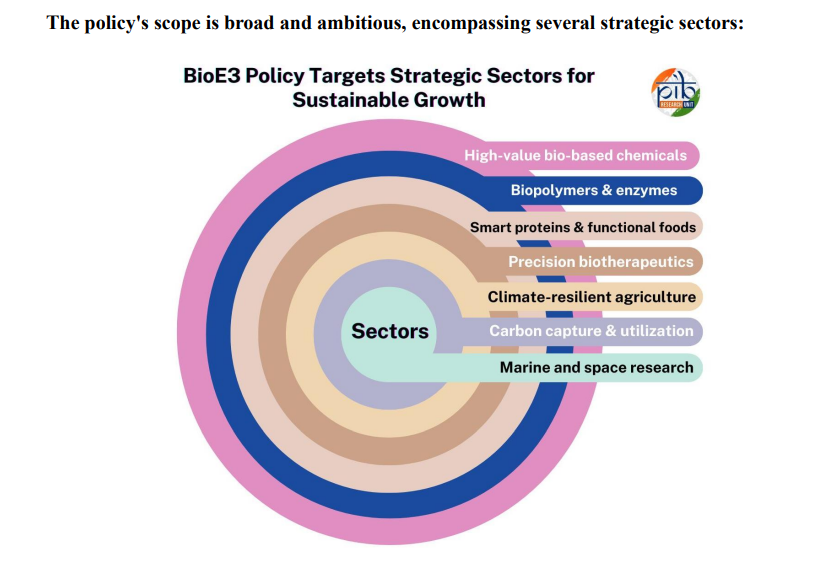
What is the BioE3 Policy?
- About: The BioE3 Policy approved in 2024, is India’s blueprint for strengthening biomanufacturing through advanced technologies and innovation-driven research.
- It is aligned with India’s vision of Green Growth (announced in the Union Budget 2023-24) promoting the bioeconomy while supporting Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), and Net-Zero emissions.
- Implementation: Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Objectives: Create a framework for adopting cutting-edge biomanufacturing technologies.
- Promote high-performance biomanufacturing across diverse sectors.
- Ensure efficiency, sustainability, and quality in production of bio-based high-value products.
- Establish BioEnablers (Bio-AI hubs, Biofoundries, Biomanufacturing hubs) to fast-track biotech commercialization.
- Train and skill manpower in interdisciplinary technical fields to support industry needs.
- Implementation Framework:
- Bio-Artificial Intelligence (AI) Hubs: Power research with data-driven analytics and AI models for innovation in bio-based products.
- Biofoundries & Biomanufacturing Hubs: These will provide infrastructure to scale up technologies and bridge the lab-to-industry gap, offering shared pilot and pre-commercial facilities to support early-stage manufacturing for researchers, startups, and SMEs.
How Can India’s Bioeconomic Initiatives Transform Key Development Sectors?
- Biopharma: BioE3 Policy fosters regenerative biomanufacturing, circular bioeconomy, and net-zero aligned growth.
- National Biopharma Mission co-funded by the World Bank boosts vaccines, biopharma, and diagnostics.
- India ranks 3rd in pharmaceutical production by volume and 14th by value, manufacturing every third tablet consumed globally.
- India developed the world’s first DNA Covid-19 vaccine and produces 65% of the world’s vaccines, benefiting low- and middle-income countries.
- Bio-Agriculture: Development of climate-smart crops (drought-tolerant chickpea, genome-edited rice), and Genomic tools ( Amaranth Genomic Resource Database (AGRDB)) improve crop identification, yield, and nutrition.
- Biotech-KISAN (Biotech-Krishi Innovation Science Application Network) enables farmer-scientist partnerships, benefiting rural, tribal, and women farmers, increasing productivity and incomes.
- Bioenergy: Ethanol blending National Policy on Biofuels (2018) increased from 1.53% (2014) to 20% (2025).
- It reduced crude oil imports, CO₂ emissions, and generated significant rural incomes through agro-industrial linkages.
- Innovation & Startups: Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) set up by the DBT in 2012, nurtures India’s biotech startups through 95 bio-incubation centres offering funding, infrastructure, and mentorship.
- Biotechnology Research Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development (Bio- RIDE) Scheme encourages innovation and academia-industry collaboration.
- Socio-Economic Impact: Bioeconomic initiatives create employment in tier-II & III cities, support MSMEs, and strengthen rural development.
- Policies foster inclusive, knowledge-driven growth, supporting India’s vision of a bio-enabled economy by 2047.
What are the Key Challenges Hindering the Growth of a Robust Bioeconomy in India?
- Insufficient Funding: DBT budget allocation is less than 1% of GDP, limiting research and innovation.
- High Initial Investment & Financial Risks: Establishing biomanufacturing hubs, biofoundries, and Bio-AI centres requires substantial upfront investment.
- Returns are long-term and uncertain, which may deter private investment and strain public finances.
- Regulatory and Ethical Concerns: Precision biotherapeutics, synthetic biology, and genetic modifications raise biosafety, biosecurity, and ethical issues.
- Skill Gaps & Workforce Challenges: India faces shortages in bioinformatics, synthetic biology, and biomanufacturing expertise.
- Potential Environmental Impact: Large-scale bio-based production may cause deforestation, water stress, monocultures, or improper biowaste disposal.
- Societal and Environmental Concerns: Public skepticism towards Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) and biotherapeutics, and risks of large-scale biomanufacturing affecting ecosystems.
- Challenges in Scaling & Commercialisation: Translating lab research into mass-market products requires infrastructure, capital, and expertise; failure to do so may undermine policy goals.
What Measures are Needed to Fortify India’s Bioeconomy?
- Streamline Regulatory Framework: Establish a single-window approval system for biotech products, including GM crops and gene-edited organisms.
- Harmonize laws like the Patents Act, 1970 and the Protection of Plant Varieties & Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001 to balance innovation and farmers’ interests.
- Define clear regulatory guidance for emerging technologies, e.g., genetically engineered crops, to reduce uncertainty for researchers and funders.
- Enhance Innovation and Commercialization: Expand support to startups through BIRAC initiatives. Promote translational research in sectors like cell and gene therapy, functional foods, and climate-smart agriculture.
- Boost Investment and Funding: Increase DBT’s budget to support frontier research. Provide targeted tax incentives and outcome-linked funding for high-risk biotech innovations.
- Encourage private sector participation through corporate innovation funds and public-private partnerships.
- Strengthen Human Capital and Skills: Create Centers of Excellence for biotechnology, synthetic biology, and biomanufacturing. Expand training and bio-hubs to produce skilled manpower for startups and SMEs.
Conclusion
The BioE3 Policy is a cornerstone for India’s bioeconomy, combining sustainability with economic growth. By fostering innovation, green technologies, and entrepreneurship, it seeks to not only expand India’s global biotech footprint but also ensure a future of economic resilience, ecological balance, and energy security.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Critically examine the significance of India’s BioE3 Policy in promoting a sustainable and innovation-driven bioeconomy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q. How can biotechnology help to improve the living standards of farmers? (2019)
Q. Why is there so much activity in the field of biotechnology in our country? How has this activity benefited the field of bio pharma? (2018)