Important Facts For Prelims
ICMR Launches First Stigma Scale for Sickle Cell Disease
- 27 May 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has developed the ICMR-SCD Stigma Scale for India (ISSSI), the country's first tool to measure and address stigma faced by sickle cell disease (SCD) patients and their caregivers. The scale includes two components: ISSSI-Pt for patients and ISSSI-Cg for caregivers.
What are the Key Features of ICMR-SCD Stigma Scale for India?
- Multi-Dimensional Tool: Assesses stigma in 5 areas- familial/reproductive stigma, disclosure issues, illness burden, discrimination, and healthcare stigma.
- Culturally Grounded: Developed in 6 SCD-endemic districts to reflect India's tribal, regional, and linguistic diversity.
- Existing 3 SCD stigma scales from Africa and America were unsuitable for India due to phenotypic, socio-cultural, and contextual differences, necessitating a locally relevant tool.
- Validated & Reliable: Psychometrically robust, suitable for clinical use, research, and policy evaluation.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
- About:
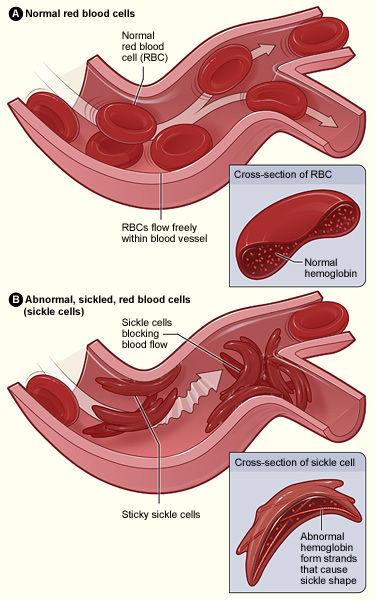
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a hereditary blood disorder caused by a genetic mutation in the haemoglobin gene, leading to abnormal, crescent- or sickle-shaped red blood cells (RBC) instead of the usual round shape.
- These sickle-shaped RBCs are less flexible and do not move easily through small blood vessels, potentially leading to blockages.
- This impairs blood circulation and leads to anaemia, organ damage, severe pain, and reduced lifespan.
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a hereditary blood disorder caused by a genetic mutation in the haemoglobin gene, leading to abnormal, crescent- or sickle-shaped red blood cells (RBC) instead of the usual round shape.
- Causes :
- Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder caused by inheriting two mutated β-globin genes, one from each parent, resulting in the production of abnormal sickle haemoglobin.
- Treatment:
- Gene Therapy: SCD can be treated by bone marrow or stem cell transplantation by methods like CRISPR.
- Blood Transfusions: These can help relieve anemia and reduce the risk of pain crises.
- Medications for SCD include Voxelotor (prevents sickling and anemia), Crizanlizumab (reduces vessel blockage and pain crises), Hydroxyurea (lowers complications), and L-glutamine (reduces pain episodes), along with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opiates for pain relief.
- Prevalence:
- SCD is a major public health concern in India, with the world's second-largest SCD burden, with over 1 million affected individuals, and ranks 3rd globally in SCD births after Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Carrier rates among tribal groups range from 1% to 40%, with most patients concentrated in the tribal belt across Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Government Initiatives:
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission: Under this, CSIR is developing gene-editing therapies for SCD.
- National Health Mission (NHM) 2013: Special focus on SCD.
- The National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research 2017: It restricts the commercialisation of stem cell therapies to clinical trials, except for Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwDs) Act, 2016: SCD is included in the 21 disabilities that provide for benefits of reservation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anemia Mukt Bharat Strategy : (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of child-birth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.