Important Facts For Prelims
Ayushman Bharat
- 05 Jan 2026
- 12 min read
Why in News?
Ayushman Bharat has gained renewed attention after the government reported significant progress in primary healthcare delivery, health insurance coverage, digital health integration, and health infrastructure development.
What are the Key Facts About Ayushman Bharat?
- About: Ayushman Bharat is a flagship health sector reform programme of the Government of India, launched in 2018, with the objective of achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in line with the National Health Policy, 2017 and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly the principle of “leave no one behind”.
- It aims to transform India’s healthcare system by shifting from a fragmented and sectoral approach to a comprehensive, need-based continuum of care.
- It covers preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative services across primary, secondary, and tertiary levels of healthcare.
Components of Ayushman Bharat:
Ayushman Arogya Mandir (AAM)
- About: AAM is the primary healthcare pillar of Ayushman Bharat, created by upgrading Sub-Health Centres and rural and urban Primary Health Centres.
- AAMs, earlier known as Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs), aim to bring comprehensive healthcare services closer to communities.
- Objective: To provide Comprehensive Primary Health Care through a continuum of care approach, addressing nearly 80–90% of an individual’s lifetime healthcare needs at the primary level.
- Scope of Services: AAMs strengthen reproductive, child health, and communicable disease services while expanding care for non-communicable diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and common cancers, with the gradual integration of mental health, geriatric, palliative, trauma care, and wellness services like yoga.
- Service Delivery Mechanism: AAMs focus on community outreach and population-based screening, ensuring early detection, timely referral, treatment adherence, follow-up care, and local availability of essential medicines and diagnostics.
- Achievements: As of November 2025, around 1.82 lakh AAMs are operational, having already exceeded the target of 1.5 lakh centres in 2022.
- These centres have recorded nearly 495 crore patient visits and enabled about 42 crore teleconsultations.
- Over 6.5 crore yoga and wellness sessions have also been organised, reflecting the scale of service delivery at the primary healthcare level.
Pradhan Mantri - Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
- About: AB PM-JAY is the second pillar of Ayushman Bharat, launched in 2018 at Ranchi, Jharkhand, and is the world’s largest publicly funded health assurance scheme.
- Originally introduced as the National Health Protection Scheme, it subsumed the Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana, integrating existing beneficiaries into a single national health coverage framework.
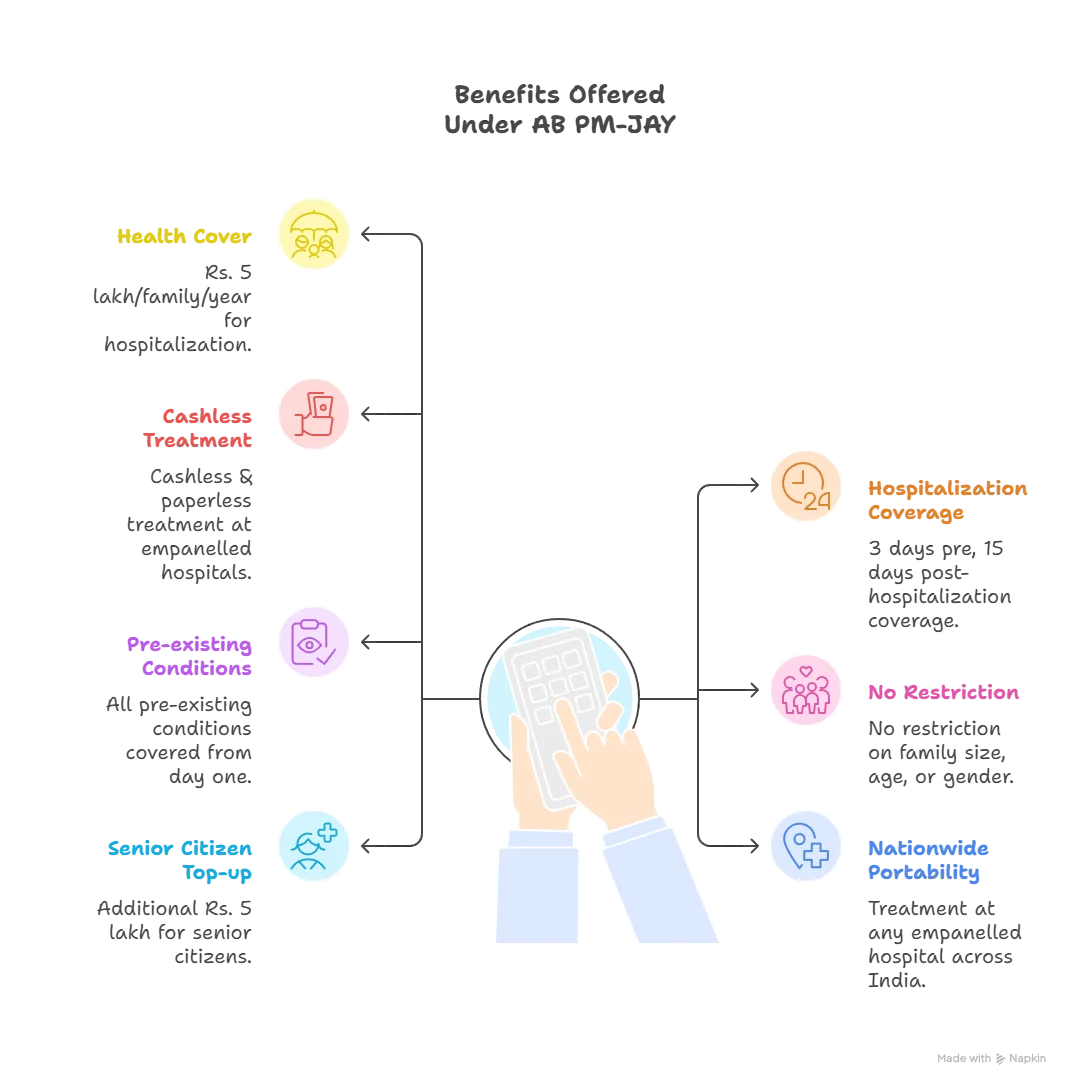
- Objective and coverage: PM-JAY aims to provide health insurance cover of up to Rs 5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalisation.
- It targets over 12 crore poor and vulnerable families, covering nearly 55 crore beneficiaries belonging to the bottom 40% of India’s population, identified using deprivation and occupational criteria under Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011 (SECC 2011).
- Key features: The scheme offers cashless and paperless treatment at empanelled public and private hospitals across the country.
- It imposes no restriction on family size, age, or gender, and covers all pre-existing diseases from the first day.
- Nationwide portability allows beneficiaries to access healthcare services anywhere in India.
- Achievements: By December 2025, over 42 crore Ayushman Cards had been issued, enabling nearly 11 crore hospital admissions.
- The scheme has promoted gender equity, with women accounting for nearly half of all cards and hospitalisations.
- Further, the launch of the Ayushman Vay Vandana Card has extended PM-JAY benefits to all citizens aged 70 years and above, potentially covering around 6 crore elderly persons.
- Digital initiatives such as the Ayushman App have simplified self-verification and card creation.
- The expansion of PM-JAY to Delhi and Odisha in 2025 has further strengthened its national coverage.
Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM)
- About: PM-ABHIM a centrally sponsored scheme (CSS), is the third pillar of Ayushman Bharat, launched in 2021 with an outlay of about Rs 64,000 crore to strengthen healthcare infrastructure and system capacity across the country during 2021–26.
- Core objective: It focuses on building capacity across primary, secondary, and tertiary care, with special emphasis on pandemic and disaster preparedness, over and above the National Health Mission.
- PM-ABHIM provides for the creation of AAMs, Urban Health and Wellness Centres in slum areas, Block Public Health Units, District Integrated Public Health Laboratories, and Critical Care Hospital Blocks.
- It also supports biomedical research on Covid-19 and other infectious diseases and strengthens capacities under the One Health approach to prevent, detect, and respond to zoonotic outbreaks.
- Achievements: PM-ABHIM has approved large-scale upgradation and creation of public health facilities to strengthen primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
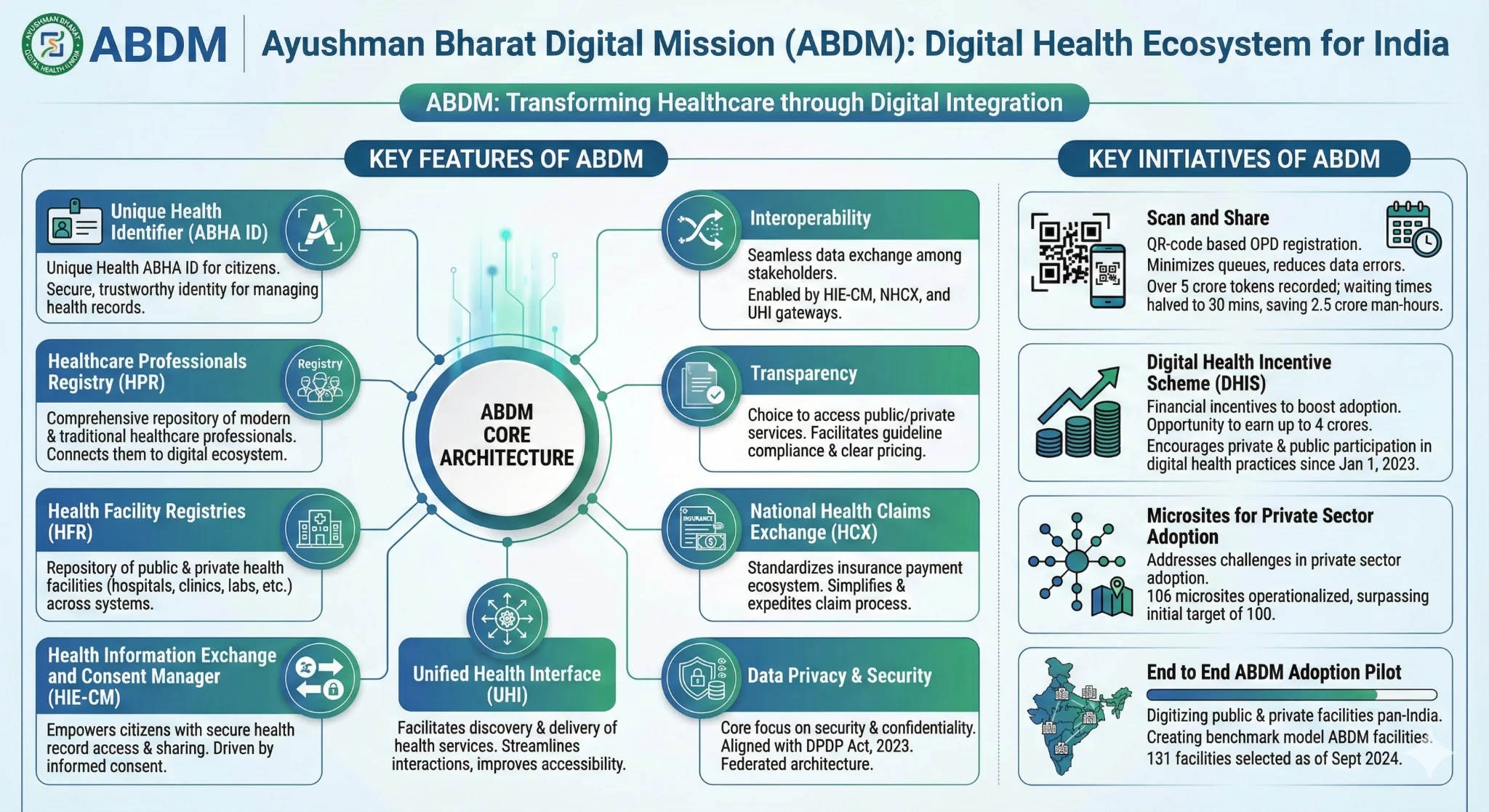
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)
- About: Launched in 2021, ABDM aims to build a citizen-centric, interoperable digital health ecosystem in India.
- It enables individuals to securely store, access, and share their medical records (such as prescriptions, diagnostic reports, and discharge summaries) based on informed consent, thereby creating a longitudinal health record and ensuring continuity of care.
- Digital architecture and components: The technological framework of ABDM is built around four key registries that establish a trusted digital identity across the health ecosystem:
- The Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) for citizens, the Healthcare Professional Registry (HPR), the Health Facility Registry (HFR), and the Drug Registry.
- Interoperability and data exchange are enabled through three gateways—the Health Information Consent Manager (HIE-CM), the National Health Claims Exchange (NHCX), and the Unified Health Interface (UHI)—which together support seamless, secure, and consent-based digital health services.
- Data Privacy and Security: ABDM places strong emphasis on the security, confidentiality, and privacy of health data, aligned with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Its federated architecture ensures secure, consent-based sharing of patient health information without centralised data storage.
- Achievements: As of 2024, over 67 crore ABHA IDs have been created, with more than 42 crore health records linked.
- About 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals have been registered on the national digital health registries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Ayushman Bharat?
Ayushman Bharat is India’s flagship health reform launched in 2018 to achieve Universal Health Coverage through primary care, insurance, infrastructure, and digital health integration.
2. What is the role of Ayushman Arogya Mandirs?
They provide comprehensive primary healthcare, addressing up to 80–90% of lifetime health needs through preventive, promotive, and curative services.
3. How does PM-JAY support financial protection?
PM-JAY provides ₹5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary hospitalisation with cashless and paperless access across empanelled hospitals.
4. Why is PM-ABHIM important for public health?
PM-ABHIM strengthens health infrastructure, disease surveillance, critical care capacity, and pandemic preparedness across all levels of care.
5. What is the significance of ABDM?
ABDM creates an interoperable digital health ecosystem enabling longitudinal health records, consent-based data sharing, and continuity of care.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: B
Q. With reference to the National Rural Health Mission, which of the following are the jobs of ‘ASHA’, a trained community health worker? (2012)
- Accompanying women to the health facility for antenatal care checkup
- Using pregnancy test kits for early detection of pregnancy
- Providing information on nutrition and immunization.
- Conducting the delivery of baby
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. The public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector could help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives would you suggest? (2015)