Facts for UPSC Mains
Rising Cancer Burden in India
- 06 Oct 2025
- 8 min read
Why in News?
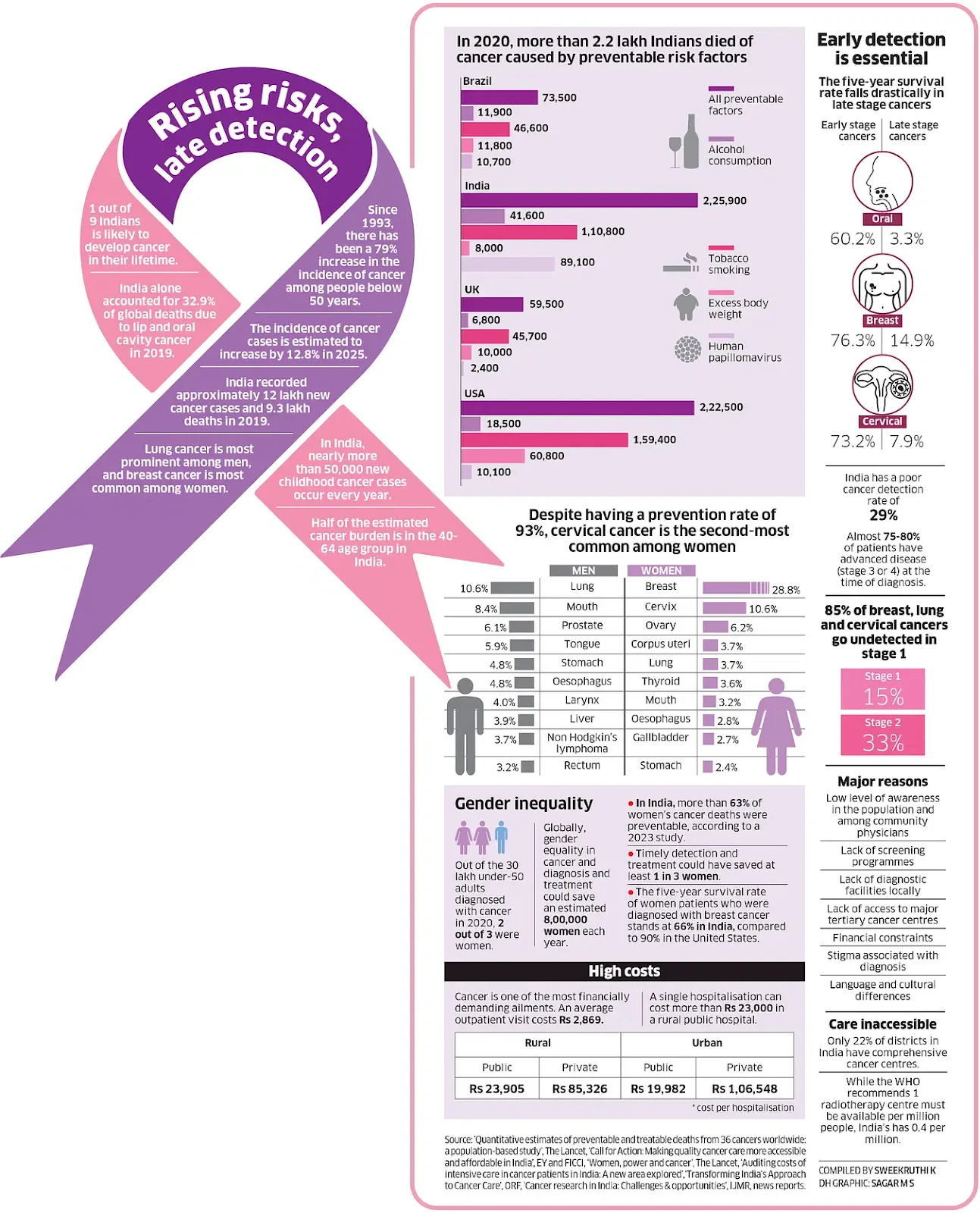
According to the latest Global Burden of Disease estimates by The Lancet, cancer incidence and mortality are on the rise in India, in contrast to the global trend of decline, with an estimated 15 lakh new cases and over 12 lakh deaths reported in 2023.
What are the Key Findings of the Global Burden of Disease?
- Rising global caseloads: Global cancer incidence declined from 220.6 per 100,000 in 1990 to 205.1 in 2023, and is projected to reach 192.9 in 2025. However, the absolute number of cancer cases and deaths is expected to rise sharply by 2050 due to population growth and aging.
- Trends in Cancer Incidence: India's cancer incidence rate rose from 84.8 (1990) to 107.2 (2023) per 100,000, and the death rate increased from 71.7 to 86.9 per 100,000 in the same period.
- Disproportionate Burden on LMICs: The study warns that low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) like India are projected to account for over half of new cancer cases and two-thirds of deaths.
- Modifiable Risk Factors: Around 42% of global cancer deaths are linked to modifiable risk factors like tobacco, alcohol, unhealthy diets, and infections, with India’s share possibly as high as 70%.
- Future Prediction: It forecasts 30.5 million new cancer cases globally and a 75% increase in deaths to 18.6 million by 2050. In India, the major causes of cancer mortality are breast, lung, oesophagus, oral, cervical, stomach, and colon cancers.
What Factors are Contributing to India’s Growing Cancer Burden?
Mnemonic: CANCER
- C - Changing Demographics (Ageing): Rising life expectancy and population in India increase older adults at cancer risk, raising the total cases even if rates per 100,000 stay stable.
- Longer life expectancy has led to a higher prevalence of non-communicable diseases, including cancer.
- A - Adoption of Unhealthy Lifestyles: High tobacco use, unhealthy diets, sedentary lifestyles, and alcohol consumption in India increase risks of lung, mouth, throat, esophagus, pancreatic, and liver cancers.
- N - National Health System Deficiencies: Late-stage diagnosis (III or IV), shortage of cancer specialists (oncologists), radiotherapy machines, and catastrophic health expenditure lead to delayed treatment, poor outcomes, and higher cancer deaths.
- C - Carcinogenic Environmental Exposure: High outdoor air pollution (PM2.5, Class I carcinogen), indoor air pollution from solid fuels, and industrial and chemical exposure increase the risk of lung cancer.
- E - Economic Hardship from Treatment: The high cost of cancer treatment—surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy—limits access to care, causing many to delay or skip treatment, which increases cancer cases and deaths.
- R - Rising Infection-Linked Cancers: Infections contribute significantly to cancer burden, including Human Papillomavirus (HPV) virus (cervical cancer), Hepatitis B and C virus (liver cancer), and H. Pylori (stomach cancer).
India's Initiatives for Cancer Control
What Measures can India Adopt to Address India’s Growing Cancer Burden?
- Mnemonic: CURE
- C – Control Carcinogens: Strengthening the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (2003) and raising tobacco taxes can curb cancer by reducing tobacco use, deterring new users, and generating funds for prevention, awareness, and treatment programs.
- U – Universal Vaccination & Screening: Ensure HPV (cervical cancer) and Hepatitis B (liver cancer) vaccinations, and regulate occupational carcinogens like asbestos and pesticides.
- R – Robust Treatment Infrastructure: Reduce out-of-pocket expenditure by strengthening Ayushman Bharat to cover all cancer care and expand public sector capacity with more Tertiary Care Cancer Centres and advanced oncology departments.
- E – Evidence & Research: Expand National Cancer Registry Programme (NCRP) for accurate cancer data, promote indigenous research, and implement a robust National Cancer Control Plan with clear targets.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyse the reasons for the rising cancer burden in India despite global declining trends. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the current cancer burden in India?
India reported an estimated 15 lakh new cases and over 12 lakh deaths in 2023, with rising incidence and mortality rates despite global declines.
2. What are the primary modifiable risk factors driving India's cancer burden?
Key modifiable risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol consumption, unhealthy diets, and infections (like HPV and Hepatitis), which are estimated to contribute to up to 70% of cancer deaths in India.
3. What are the major national initiatives for cancer control in India?
Initiatives include the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS), National Cancer Grid, National Cancer Awareness Day.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the treatment of cancerous tumours, a tool called cyberknife has been making the news. In this context, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2010)
(a) It is a robotic image guided system
(b) It delivers an extremely precise dose of radiation
(c) It has the capability of achieving sub-millimetre accuracy
(d) It can map the spread of tumour in the body
Ans: (d)
Q. ‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why? (2019)
- It is used in developing gene-silencing therapies.
- It can be used in developing therapies for the treatment of cancer.
- It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies.
- It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q1. What do you understand about nanotechnology and how is it helping in the health sector? (2020)
Q2. Stemcelltherapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including Leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments? (2017)