Rapid Fire
WHO Classified Hepatitis D as Carcinogenic
- 08 Aug 2025
- 2 min read
The World Health Organization (WHO) has reclassified Hepatitis D Virus (HDV) as carcinogenic.
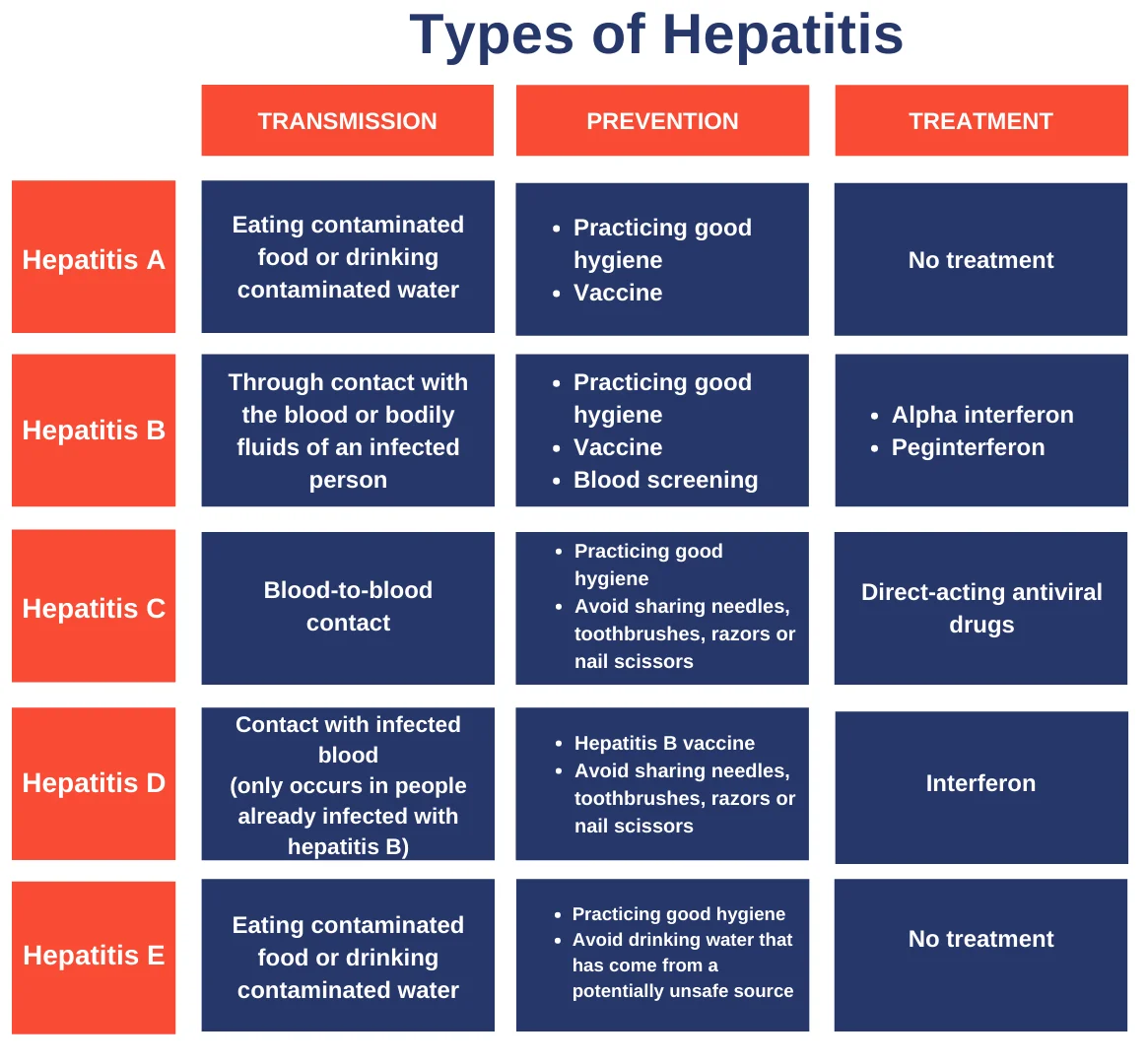
Hepatitis
- About: It is a liver inflammation from viral infections, autoimmune disorders, alcohol/drug toxicity. It can be acute or chronic, leading to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
- Symptoms: Often asymptomatic initially, later fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, dark urine, pale stools, joint pain, jaundice.
- Causes: Hepatotropic viruses (A, B, C, D, E), others like Varicella, SARS-CoV-2 & non-viral causes such as alcohol, drugs, autoimmune hepatitis, fatty liver.
- Prevalence: In 2022, WHO reported 254 million hepatitis B cases, 50 million hepatitis C cases, and 1.3 million deaths, with half of chronic cases in those aged 30–54.
- Hepatitis D: It is a defective virus that depends on the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) for infection and replication.
- Risk: Causes co-infection or superinfection with HBV, increasing risk of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (a type of liver cancer) by 2–6 times compared to HBV alone.
- Prevalence: Low but likely underreported in India, especially among intravenous drug users and chronic HBV patients.
- Diagnosis,Treatment & Prevention: Diagnosis relies on the HDV-RNA test, with limited treatment options, though new drugs like bulevirtide show promise.
- Prevention depends on universal Hepatitis B vaccination, which has about 50% coverage in India.
- Key measures include safe blood transfusions, needle safety, safe sexual contact, and screening high-risk groups.
- Key Initiatives:
- WHO’s 2022–2030 Strategy: Reduce new hepatitis infections by 90% and deaths by 65% from 2015 levels, targeting 520,000 cases and 450,000 deaths annually by 2030.
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program: Eliminate viral hepatitis from India by 2030.
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program.
- India's Universal Immunization Programme (UIP).
- World Hepatitis Day.
| Read More: Global Hepatitis Report 2024, World Hepatitis Day |