Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
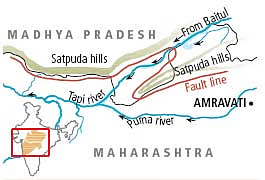
Tapti Basin Mega Recharge Project
Why in News?
In a significant step towards ensuring regional water security, the governments of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to jointly implement the Tapti Basin Mega Recharge Project.
Key Points
- About the Project:
- The MoU was signed after the first Madhya Pradesh–Maharashtra Inter-State Control Board meeting in 25 years, marking a joint commitment to sustainably manage inter-State river resources.
- Objective: The project seeks to address the drinking and irrigation water needs of key regions in both States.
- The project plans to divert water from the Tapti River (originating in Betul, MP and called Tapi in Maharashtra) to:
- Serve Nagpur and northeastern Maharashtra for drinking water.
- Support irrigation in southern and southeastern Madhya Pradesh, including Burhanpur and Khandwa districts.
- The project will use 3,362 hectares in Madhya Pradesh without displacing villages or requiring rehabilitation.
- The project plans to divert water from the Tapti River (originating in Betul, MP and called Tapi in Maharashtra) to:
- Irrigation and Land Coverage Targets: The project aims to provide permanent irrigation for:
- 1,23,082 hectares of Burhanpur and Khandwa district of Madhya Pradesh
- 2,34,706 hectares of Jalgaon, Akola, Buldhana, Amravati and Nagpur division in Maharashtra.
- Other Water Sharing Initiatives of MP: This project marks the third major inter-State water project by Madhya Pradesh within a year, after:
- Ken–Betwa link with Uttar Pradesh.
- Parvati–Kalisindh–Chambal link with Rajasthan.
Tapi River
- About: The Tapi River is one of the only three major rivers in India that flow westward, the other two being the Narmada and the Mahi rivers.
- The Narmada and Tapi rivers are the major rivers that flow through rift valleys.
- Origin: Gawilgarh Hills, part of the central Deccan Plateau in south-central Madhya Pradesh.
- States Covered:
- It covers a total basin area of 65,145 sq.km, which is nearly 2% of India’s total geographical area.
- The river flows through three Indian states:
- Maharashtra – 51,504 sq.km. of basin area
- Madhya Pradesh – 9,804 sq.km.
- Gujarat – 3,837 sq.km.
- Geographical Boundaries of the Basin:
- North – Bounded by the Satpura Range
- East – By the Mahadev Hills
- South – By the Ajanta Range and Satmala Hills
- West – Opens into the Arabian Sea
- Major Tributaries: The Tapti River’s three main tributaries—Purna, Girna, and Panjhra, all originating from the south in Maharashtra.
- Hydroelectric Infrastructure:
- The Ukai Dam is a major hydroelectric project built on the Tapi River.
- It plays a key role in irrigation, power generation, and water supply for the surrounding regions.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
PMAY–G in Chhattisgarh
Why in News?
Union Agriculture and Rural Development Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan is going to review the implementation of Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana–Gramin (PMAY–G) and PM Janman Yojana by the Chhattisgarh government in Raipur.
Key Points
- About the Programme:
- The Minister will be the Chief Guest at the "Mor Awas Mor Adhikar" event at Ambikapur.
- He distributed house keys under PMAY–G and PM Janman Yojana and led the grih pravesh ceremony for 51,000 new PMAY beneficiaries.
- He also felicitated Self-Help Group (SHG) members and 'Lakhpati Didis' who have shown outstanding achievement in rural empowerment.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G):
- About: Launched in 2016, the PMAY-G aims to provide housing for the poorest segments of society.
- The selection of beneficiaries involves a thorough three-stage validation process, including the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha approvals, and geo-tagging, ensuring that aid reaches the most deserving individuals.
- Under PMAY-G Beneficiaries Receive:
- Financial Assistance: Rs 1.20 lakh in plain areas and Rs 1.30 lakh in hilly states, including northeastern states and union territories.
- Additional Support for Toilets: Rs 12,000 for constructing toilets through convergence with schemes like Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin (SBM-G) or Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) or any other dedicated source of funding.
- Employment Support: Mandatory provision of 90/95 person-days of unskilled wage employment for beneficiaries through Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) for house construction.
- Basic Amenities: Access to water, Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and electricity connections through convergence with relevant schemes.
- About: Launched in 2016, the PMAY-G aims to provide housing for the poorest segments of society.
- PM-JANMAN Scheme:
- PM JANMAN is a government scheme that aims to bring tribal communities into the mainstream.
- The scheme (comprising Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes) will be implemented by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, in collaboration with the State governments and the PVTG communities.
- The scheme will concentrate on 11 critical interventions overseen by 9 line Ministries, ensuring the implementation of existing schemes in villages inhabited by PVTGs.
- It encompasses various sectors, including safe housing under the PM-AWAS Scheme, access to clean drinking water, improved healthcare, education, nutrition, road and telecommunications connectivity, as well as opportunities for sustainable livelihoods.
- The plan also includes the establishment of Van Dhan Vikas Kendras for trading in forest produce, off-grid solar power systems for 1 lakh households, and solar street lights.
Self Help Groups (SHGs)
- About: A Self Help Group is a self-governed, peer-controlled information group of people with similar socio-economic backgrounds and a desire to collectively perform a common purpose.
- An SHG normally consists of not less than five persons (with a maximum of twenty) of similar economic outlook and social status.
- Origins of Self-Help Groups in India:
- Early Efforts (Pre-1970s): There were scattered instances of informal SHGs, particularly among women, for collective action and mutual support.
- SEWA (1972): The Self-Employed Women's Association (SEWA), established by Ela Bhatt, is often considered a defining moment.
- It organised poor and self-employed women workers, providing a platform for income generation and advocacy.
- MYRADA and Pilot Programs (Mid-1980s): In the mid-1980s, Mysore Resettlement and Area Development Agencies (MYRADA) pioneered SHGs as a microfinance strategy to provide credit to the poor, especially women in rural areas.
- NABARD and SHG-Bank Linkage (1992): The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) launched the SHG-Bank Linkage Programme in 1992.
- This initiative connected SHGs with formal banking institutions, enabling access to credit and financial services for various groups.
- Government Recognition (1990s-Present): Since the 1990s, the Government has actively supported SHGs through various schemes like Swarn Jayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY) and the National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM).
- These initiatives have significantly expanded the reach and impact of the SHG movement in India.
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Thalassemia Burden in West Bengal
Why in News?
On World Thalassemia Day, West Bengal experts expressed concern over the State’s high Thalassemia prevalence, which exceeds the national average.
Key Points
- World Thalassemia Day:
- It is observed every year on 8th May as a global effort for prevention, awareness and early diagnosis for inherited blood disorder disease Thalassemia.
- The theme for 2025 is "Together for Thalassemia: Uniting Communities, Prioritizing Patients".
- National Burden and High-Risk Communities:
- According to the 2016 National Health Mission report, 10,000 to 15,000 babies with Thalassemia Major are born annually in India.
- Communities with higher carrier rates include Bengalis, Sindhis, Punjabis, and Gujaratis.
- Alarming Prevalence in West Bengal:
- According to the West Bengal Health Department, 6% to 10% of the State’s population carries the disease, compared to the national average of 3% to 4% (2011 Census data).
- West Bengal’s Thalassemia burden is worsened by:
- Low public awareness
- Intra-community marriages
- Insufficient early screening
- The State has over 18,000 transfusion-dependent patients and a 2.5% patient positivity rate, as per the State Health Department.
- State Efforts:
- West Bengal has established 36 Thalassemia Control Units (TCUs) across districts.
- These TCUs focus on first-trimester pregnancy screening and screening among adolescents to prevent future transmission.
- Legal and Social Challenges:
- There is no national law preventing marriages between Thalassemia carriers.
- Health officials identify intra-community marriages as a key social challenge and emphasize early screening and awareness to prevent Thalassemia in children.
- The Importance of Parental Screening:
- Experts recommend pre-marital or pre-conception screening for both partners to prevent the condition.
- Without regular care and transfusions, life expectancy may not exceed 30 years for Thalassemia patients.
- Early detection, informed parenting, and ongoing care can significantly improve quality of life and outcomes.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
India's First Beggar-Free City
Why in News?
Indore has become the country’s first beggar-free city after authorities rehabilitated beggars by providing them with employment opportunities and enrolled children involved in begging into schools.
Key Points
- Multi-Phase Campaign Strategy:
- In February 2024, the city launched an anti-begging campaign under the Women and Child Development Department.
- At the time, officials identified around 5,000 beggars, including 500 children, living on the streets of Indore.
- The campaign was conducted in two major phases:
- Phase 1: Awareness drives to inform the public and engage stakeholders.
- Phase 2: Rehabilitation of beggars through employment assistance and school enrolment for children.
- Many beggars were found to have migrated from Rajasthan, highlighting inter-state dimensions of urban begging.
- In February 2024, the city launched an anti-begging campaign under the Women and Child Development Department.
- National and International Recognition:
- The initiative has been recognised as a model project by the Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Indore is among 10 cities selected for a pilot project to eliminate begging in urban areas.
- A World Bank team has also acknowledged the campaign’s impact.
- The initiative has been recognised as a model project by the Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
Legal Framework Regarding Begging
- Colonial Law: The Criminal Tribes Act of 1871 criminalised nomadic tribes, associating them with vagrancy and begging.
- Current Legal Framework: The Constitution of India allows both the Union and state governments to enact laws on vagrancy (includes beggary), nomadic, and migratory tribes under the Concurrent List (List III, Entry 15).
- There is no central Act on beggary. Instead, many states and Union Territories have based their laws on the Bombay Prevention of Begging Act, 1959.
- The Act defines a beggar as anyone soliciting alms, performing or offering articles for sale, or appearing destitute without visible means of subsistence.
- There is no central Act on beggary. Instead, many states and Union Territories have based their laws on the Bombay Prevention of Begging Act, 1959.
- Jurisprudence: The Delhi High Court, in 2018, ruled that the Bombay Act (criminalising begging) was arbitrary and violated the right to live with dignity, underscoring the importance of addressing poverty without criminalizing it.
- The Supreme Court of India in 2021 rejected a Public Interest Litigation seeking to remove beggars from public spaces, emphasizing that begging is a socio-economic problem rather than a criminal issue.
- SMILE: Launched in 2022, Support for Marginalised Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE) by Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, aims to rehabilitate beggars by providing medical care, education, and skills training, working toward a "beggar-free" India by 2026.
- As of 2024, 970 individuals have rehabilitated under SMILE, including 352 children.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Brahmos Missile
Why in News?
BrahMos supersonic cruise missile production unit was inaugurated by the Union Defence Minister in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh. 
Key Points
- About Brahmos Missile:
- An Indo-Russian joint venture, the BrahMos missile has a range of 290 km and is the world's fastest cruise missile with a top speed of Mach 2.8 (about three times the speed of sound).
- It is named after the Brahmaputra River of India and the Moskva River of Russia.
- It is a two-stage (solid propellant engine in the first stage and liquid ramjet in the second) missile.
- It is a multiplatform missile which can be launched with great accuracy from land, air and sea having multi-capability capabilities and can operate during day and night despite bad weather.
- It operates on the "fire and forget" principle i.e. it does not require guidance after launch.
- An Indo-Russian joint venture, the BrahMos missile has a range of 290 km and is the world's fastest cruise missile with a top speed of Mach 2.8 (about three times the speed of sound).
- About Lucknow Brahmos Unit:
- The unit has been set up under the Uttar Pradesh Defence Industrial Corridor (UP DIC) at a cost of Rs 300 crore.
- It is a joint venture between the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of the Government of India and the Russian company NPOM.
- India has a share of 50.5% and Russia has a share of 49.5% in it.
- In the first phase, parts of the BrahMos missile will be assembled here and later the full manufacturing work will be started.
- The unit will manufacture 100 to 150 next-generation missiles per year.
- The new version's weight has been reduced from 2,900 kg to 1,290 kg.
- Its range will be more than 300 km.
Uttar Pradesh Defence Industrial Corridor
- It is an ambitious project aimed at reducing the foreign dependency of the Indian aerospace and defence sector.
- It has 6 nodes – Aligarh, Agra, Kanpur, Chitrakoot, Jhansi and Lucknow.
- Uttar Pradesh Expressway Industrial Development Authority (UPEIDA) has been made the nodal agency to execute the project in collaboration with various state agencies.
- The aim of this corridor is to establish the state as one of the largest and advanced defence manufacturing hubs and put it on the world map.
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
- Introduction:
- DRDO was established in 1958 by merging the Indian Army's Technical Development Establishment (TDE), Directorate of Technical Development and Production (DTDP) and Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
- DRDO is the research and development wing of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- Initially DRDO had 10 laboratories, currently it operates 41 laboratories and 5 DRDO Young Scientist Laboratories (DYSL).
- Principle:
- The guiding principle of DRDO is "Balasya Mulam Vijnanam" (power lies in science), which guides the nation in both peace and war situations.
- Mission:
- Its mission is to achieve self-reliance in critical defence technologies and systems by equipping the Indian Armed Forces with state-of-the-art weapon systems and equipment as per the requirements of the three services.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP-AGREES and AI Pragya Programme
Why in News?
The Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh launched the 'UP-AGREES' and 'AI Pragya' programmes in Lucknow in the presence of the World Bank President.
Key Points
- About UP-AGREES:
- It will be implemented in 28 districts of Purvanchal and Bundelkhand regions of Uttar Pradesh.
- Its main objective is to increase agricultural productivity, ensure conservation of natural resources and increase the income of farmers.
- The Rs 3,900 crore project includes a Rs 2,737 crore World Bank loan and RS 1,166 crore from the state government.
- The 6-year loan, repayable over 35 years at 1.23% interest, will benefit 10 lakh farmers—30% of them women.
- The project will link 10,000 women producer groups and send 500 farmers abroad for advanced training.
- AI Pragya Program:
- The main objective of the 'AI Pragya' program is to establish Uttar Pradesh as a leading state in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital technologies.
- Under this program, 10 lakh youth will be provided training and certification in cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, data analytics and cyber security.
- This initiative will promote AI based startups in the state, increase employment opportunities and create a digitally skilled workforce.
- The programme will be conducted in collaboration with various state departments like Education, Health, Agriculture, Revenue, Secretariat Administration.
World Bank
- About:
- It was established in 1944 as the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) along with the IMF. The IBRD later became the World Bank.
- The World Bank Group is a unique global partnership of five institutions working to advance lasting solutions that reduce poverty and build shared prosperity in developing countries.
- The World Bank is one of the specialized agencies of the United Nations.
- Member:
- 189 countries are its members.
- India is also its member.
- Five Development Institutions:
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)
- International Development Association (IDA)
- International Finance Corporation (IFC)
- Multilateral Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
- International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID)
- India is not a member of ICSID.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Krishak Uphar Scheme
Why in News?
The Rajasthan government conducted a state-level online lottery under the Krishak Uphar Yojana, awarding prizes worth several lakhs to farmers.
Key Points
- About Krishak Uphar Yojana:
- Through this scheme, farmers are being encouraged to sell their agricultural products and receive payment through eNAM portal and e-payment .
- This will empower farmers to maximize the value of their produce by minimizing the influence of middlemen, enabling them to sell directly to consumers.
- The Event was organized under the chairmanship of Secretary of Agriculture and Horticulture at Pant Krishi Bhawan, Jaipur .
eNAM Portal
- The eNAM portal was launched by the Central Government in April 2016.
- E-NAM is a pan India e-trading platform. It has been created with the aim of creating a unified national market for agricultural products.
- Under this, farmers can sell their produce online from their nearest market and traders can pay for their produce from anywhere.
- As a result, the number of traders will increase, which will also increase competition.
- Through this, prices can be determined well and farmers will get a fair price for their produce.
- Currently, 150 commodities including food grains, oilseeds, fibres, vegetables and fruits are being traded on the e-NAM portal. Also, more than 1,005 'Farmer Producer Organizations' are registered on it.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Irrigation Projects in MP
Why in News?
The Deputy Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh reviewed the Sitapur-Hanumana Lift Irrigation, Bansagar Project, and other pending schemes in Rewa, urging timely completion of construction work.
Key Points
- About Sitapur-Hanumana Lift Irrigation Project:
- This project is helpful in strengthening the irrigation system of Mauganj, Sidhi and Singrauli districts.
- Through this project, 1 lakh 20 thousand hectares of agricultural land in a total of 653 villages will be connected with irrigation facilities.
- Administrative approval of Rs 4,167 crore has been given by the state government for this project .
- Challenges:
- The dam proposed in this project is to be built on the Son River in Amiliya area of Sidhi district .
- The area falls under the Son Gharial Sanctuary, making environmental and wildlife clearance mandatory.
- Emphasizing environmental protection, officials were instructed to ensure that no harm is caused to gharial conservation efforts.
- Bansagar Dam:
- Bansagar Dam is located on the Son River in Rewa district of Madhya Pradesh .
- It is a multi-purpose project, aimed at ensuring irrigation, hydropower generation and water supply.
- Authorities have been directed to accelerate the construction of the 18 km Bela Minor Canal, tunnel lining in Chuhiya Valley, aqueduct development, and canal lining.
- Bela Minor Canal is a tributary canal of the Bansagar Project.
- The total length of this canal is 51 km, out of which only 21 km of work has been completed so far.
- Benefits:
- On completion of the dam and canal project, irrigation facilities will be ensured in lakhs of hectares of area in Rewa, Mauganj, Sidhi and Singrauli districts.
- This project will provide sustainable irrigation facilities to millions of farmers, leading to crop diversification, increased productivity, and improved income.
Son Gharial Sanctuary
- It is an important sanctuary located in the Son River area of Madhya Pradesh, which was established in 1981 with the aim of conserving gharials and increasing their numbers.
- Under this sanctuary, a total area of 210 km has been protected including 161 km of Son River, 23 km of Banas River and 26 km of Gopad River.
- This sanctuary comes under Project Crocodile, the main attraction of the sanctuary is the sandy habitats, which mainly include gharial, Indian soft shell turtle (Chitra Indica) and Indian skimmer (Rynchops albicollis).
- These areas provide protection to various endangered species.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


