Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Low Patient Turnout at Ayushman Arogya Mandirs
Why in News?
Ayushman Arogya Mandirs operating under the National AYUSH Mission in Barharwa block, Jharkhand, are witnessing low patient footfall. Despite free treatment services, the centers are underutilized due to a lack of awareness, inadequate infrastructure, a shortage of doctors and staff, and the unavailability of essential medicines.
Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs)
- About: AAM is an attempt to move from a selective approach to health care to deliver a comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative care.
- Components: It has two components that are complementary to each other.
- Under its first component, 1,50,000 Ayushman Arogya Mandir will be created to deliver Comprehensive Primary Health Care, which is universal and free to users, with a focus on wellness and the delivery of an expanded range of services closer to the community.
- The second component is the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) which provides health insurance cover of Rs. 5 lakhs per year to over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families for seeking secondary and tertiary care.
- Significance: AAMs are envisaged to deliver an expanded range services that go beyond Maternal and child health care services to include care for non-communicable diseases, palliative and rehabilitative care, Oral, Eye and ENT care, mental health and first-level care for emergencies and trauma, including free essential drugs and diagnostic services.
National AYUSH Mission (NAM)
- About: It is a Centrally Sponsored scheme which was approved and notified in 2014.
- Objective: The basic objective of NAM is to promote AYUSH Medical Systems through cost-effective AYUSH Services, strengthening of educational systems, facilitate the enforcement of quality control of Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani & Homeopathy (ASU & H Drugs) and sustainable availability of ASU & H raw- materials.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Workshop on Filaria Eradication
Why in News?
Under the Filaria Eradication Campaign, a health awareness workshop was organized at Arogya Ayushman Mandir, Chandkopa.
- The event focused on educating villagers about the prevention, symptoms, and treatment of lymphatic filariasis, a mosquito-borne disease affecting thousands across endemic regions.
Key Facts About Lymphatic Filariasis
- About: Lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis), is a neglected tropical disease (NTD) caused by infection with filarial parasites transmitted through mosquitoes.
-
Prevalence: In 2021, approximately 882.5 million people in 44 countries lived in areas requiring preventive chemotherapy to halt the spread of infection.
- 75% of Mass Drug Administration (MDA) districts are from 5 states Bihar, Jharkhand, UP, Odisha and Telangana.
- Cause: It is caused by infection with parasites classified as nematodes (roundworms) of the family Filariodidea. There are 3 types of these thread-like filarial worms:
- Wuchereria bancrofti (responsible for 90% of the cases)
- Brugia malayi (causes most of the remainder of the cases)
- Brugia timori (which also causes the disease)
- Symptoms: Most infections remain asymptomatic, but chronic cases cause lymphoedema, elephantiasis, and hydrocele, leading to disability and social stigma.
- Treatment and Prevention: The WHO-recommended Mass Drug Administration (MDA) provides annual preventive chemotherapy to at-risk populations to interrupt transmission.
- Global and National Initiatives: The Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF), launched in 2000, aims for elimination through preventive chemotherapy and morbidity management by 2030.
- India’s Mission Mode MDA Campaign, aligned with National Deworming Day (Feb 10 & Aug 10), targets elimination by 2027, three years ahead of the global goal.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
19th Death Anniversary of Kanshi Ram Ji
Why in News
The 19th Parinirvan Diwas (death anniversary) of Kanshi Ram, founder of the Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP), was commemorated on 9th October 2025, at Ambedkar Club in Latani, Dhanbad.
Kanshi Ram Ji
- Birth & Early Life: Born on 15th March 1934, in Punjab, he dedicated his life to uplifting the marginalized sections of society and empowering the Bahujan Samaj.
- From an early age, he displayed a deep sense of empathy and compassion towards the plight of oppressed communities.
- He recognized the inherent inequalities perpetuated by the caste system and resolved to challenge the status quo through organized political action.
- Founding of BSP: In 1984, he founded the Bahujan Samaj Party with the objective of uniting the Bahujan Samaj, comprising Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, and Religious Minorities, into a formidable political force.
- His vision was to provide a platform for the marginalized sections of society to assert their rights and demand their rightful place in the socio-political landscape of India.
- Other Key Organisations: He also founded the All India Backward and Minority Communities Employees Federation (BAMCEF) in 1971, and Dalit Shoshit Samaj Sangharsh Samiti (DS-4) in 1981.
- Death: He died on 9th October, 2006
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Tribal Protest Against Inclusion of Kurmi Community in ST List
Why in News?
A large-scale protest and sit-in (dharna) was held outside in Chandil by tribal social organisations. The protest was aimed at opposing the demand to include the Kurmi (Kudmi) community in the Scheduled Tribes (ST) list.
- A delegation submitted a memorandum addressed to the President of India, demanding that the government not include Kurmis in the ST list.
Reasons Behind Tribal Opposition to the Inclusion of Kurmis in the ST List
- Perceived Threat to Tribal Identity: Tribal speakers asserted that including Kurmis in the ST list undermines the distinct identity, traditions, and constitutional rights of existing tribal communities.
- Tribal organisations from Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, and West Bengal expressed unity in opposing the move.
- Historical & Cultural Grounds: Protesters referenced tribal icons like Birsa Munda, Sidho-Kanhu, Budhu Bhagat, and Ganga Narayan Singh, emphasizing that the tribal identity is rooted in a unique socio-cultural history, distinct from that of Kurmis.
- Opposition to ‘Rail Roko’ Movement: The ongoing "Rail Teka Andolan" (Rail Blockade Movement) by Kurmis for ST status was criticized by tribal leaders as an unjust pressure tactic that challenges tribal autonomy.
Kurmi Community
- About: Kurmis are mainly a peasant community, with their population concentrated in the Junglemahal areas or the Chota Nagpur plateau of West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Odisha, and a few bordering areas of Bihar.
- Background of Caste Status: Kurmis were included among the communities classified as STs in the 1931 Census and were excluded from the ST list in 1950.
- After 1950, when the ST list was prepared in independent India, Kurmis did not find a place on it.
- The Kurmis argue that in the British era, various documents listed them as a tribe and an aboriginal community of India, and they want that identity restored. Also, they claim to follow the religious rituals of STs.
- In 2004, the Jharkhand government recommended that the community be added to the ST list rather than be categorised as OBCs.
- After 1950, when the ST list was prepared in independent India, Kurmis did not find a place on it.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Tributes Paid to Quit India Movement Martyrs
Why in News?
A tribute ceremony was held on 8th October 2025 in Patamda to honour the freedom fighters of the 1942 Quit India Movement. The event was jointly organized by the Rashtra Shaheed Samman Samiti of Patamda and Bodam.
- Local Leaders and Martyrs involved in QIM were Bhajhari Mahato, Laxman Mahato, Madiram Mahato, Bipra Mahato, Ratan Majhi, Judan Mudi, and Durga Charan Singh.
Quit India Movement
- Launch and Purpose: Launched by Mahatma Gandhi on 8th August 1942 during the All-India Congress Committee session in Bombay, the movement demanded the immediate end of British rule following the failure of the Cripps Mission.
- Gandhi's Call: Gandhi gave the powerful call of “Do or Die” at the Gowalia Tank Maidan (now August Kranti Maidan), urging Indians to demand an immediate end to British rule.
- Slogan & Symbolism: The slogan “Quit India” was coined by Yusuf Meherally, a socialist and trade unionist from Bombay, who had also created the earlier slogan “Simon Go Back.”
- During the movement, Aruna Asaf Ali became a prominent figure, famously hoisting the Indian flag at the Gowalia Tank maidan as a symbol of defiance.
- Rise of New Leaders: New leaders like Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia, Jayaprakash Narayan rose to prominence during this movement.
- Women also played a significant role, leading protests and sacrificing their lives, such as Matangini Hazra, who died with the Tricolour in hand, and Sucheta Kripalani, who later became India’s first female Chief Minister (Uttar Pradesh).
- Nature of the QIM: The QIM was distinct from earlier peaceful protests like Non-Cooperation and Civil Disobedience, as it was a mass uprising demanding the complete withdrawal of British rule.
- Though Gandhi emphasized non-violence, the movement was accommodating of violence in self-defense. It allowed spontaneous actions like sabotage and guerrilla attacks against British properties.
- Widespread protests, strikes, and sabotage erupted across India, with students and youth taking the lead, especially in urban centers, after Congress leaders were arrested.
- The Muslim community largely stayed absent from the QIM, it was seen as a Hindu nationalist cause, highlighting the growing communal divide and the Muslim League's push for a separate state.
- Legacy: The movement became a key turning point in India’s freedom struggle, demonstrating unity and determination that ultimately led to the end of British rule.
- The Quit India Movement was a watershed moment that shaped India’s future politics. In his speech at Gowalia Tank Maidan, Gandhi said power would belong to the people of India. The movement marked the freedom struggle truly belonging to “We the People.”
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Direct-Seeded Rice (DSR) Conclave 2025
Why in News?
Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath, speaking at the Direct-Seeded Rice (DSR) Conclave 2025 at International Rice Research Institute – South Asia Regional Centre (ISARC), reaffirmed Uttar Pradesh’s goal of becoming a global food basket by 2030 in line with its $1 trillion economy vision.
- The Chief Minister also launched new agricultural knowledge products, mechanisation innovations, and distributed mini kits to farmers to boost modernisation and technology adoption in agriculture.
Key Points
- About: The DSR Conclave 2025 is a platform for policymakers, scientists, and industry leaders to explore actionable pathways for resilient, inclusive, and climate-smart agricultural development in UP and beyond.
- Global Food Basket Vision: During a session on making UP the global food basket by 2030, the Chief Minister emphasised sustainable, climate-smart, and technology-driven agricultural transformations, marking the 150th anniversary of the UP Department of Agriculture.
- He underscored the state's ambition to support the Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centres (CGIAR), including partners like the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and the International Potato Centre (CIP). These collaborations will leverage advanced technologies to boost food production and quality.
- Agricultural Progress and Achievements: Uttar Pradesh is a key contributor to India’s food production, contributing 21% of the national output despite comprising only 11% of the country’s cultivable area.
- Over the past eight years, state government efforts have led to a fivefold increase in agri-food production, particularly in cereals, pulses, oilseeds, and vegetables.
- The success is a result of state-driven initiatives like the Soil Health Card, crop insurance, and the Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana, benefiting over 10 crore farmers annually.
- Capacity Building: The state's four agricultural universities, with plans for another, are central to the research and knowledge-sharing efforts that are driving agricultural transformation.
- Traditional Agricultural Wisdom: The Chief Minister highlighted that the rich agricultural traditions of Uttar Pradesh, such as the iconic Kalanamak rice, part of the One District One Product initiative, hold historical significance, having been offered as Mahaprasad by Lord Buddha.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh Bans Coldrif Cough Syrup
Why in News?
The Madhya Pradesh government has announced a complete ban on the sale of Coldrif Syrup across the state following several children's deaths due to kidney failure.
- The Tamil Nadu government conducted a probe and found that samples of Coldrif Syrup contained 48.6% Diethylene Glycol (DEG), a toxic chemical known to cause severe kidney damage.
Key Points
- About: The finding of Diethylene Glycol (DEG) led to state-level bans and triggered nationwide regulatory action under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- Diethylene Glycol (DEG): It is a colourless, sweet-tasting industrial chemical commonly used in brake fluids and antifreeze.
- It is misused as a cheap substitute solvent in drug production owing to its close physical similarity to safe pharmaceutical compounds.
- Consumption of DEG can cause abdominal pain, vomiting, kidney failure, and nervous system damage, and may be fatal at high doses.
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940: It regulates the import, manufacture, sale, and distribution of drugs and cosmetics in India through licences and permits.
- Its main aim is to ensure that marketed drugs and cosmetics are safe, effective, and meet national standards.
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945, complement the Act by classifying medications into schedules and providing guidelines for their storage, sale, presentation, and prescription.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana Revises Aravali Definition
Why in News?
The Haryana government has redefined 'Aravali hills and ranges' by adding minimum geological age and height criteria, raising concerns about reduced protection and its impact on conservation.
Key Points
- About: The effort to define the Aravalis commenced in 2024, following the Supreme Court's directive to the Union Environment Ministry and the four affected states—Delhi, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Gujarat—to create a unified definition.
- Haryana’s Definition: On 4th October 2025, the Department of Geology and Mines in Haryana finalised a new definition for the Aravali Hills, limiting it to hills rising more than 100 meters above the surrounding land and composed of rocks older than a billion years.
- The 100-metre elevation benchmark aligns with Rajasthan's standard, but while Rajasthan's classification focuses on mining, Haryana's is intended for conservation.
- Haryana’s new parameters, labelled as "scientifically measurable" and "field-verifiable" in line with Rajasthan and Geological Survey of India (GSI) standards, are seen by experts as more of a policy shift than a technical correction.
- Expert Concerns: Experts and environmentalists are concerned that the new definition may reduce the protection scope, especially in regions like Gurgaon, Faridabad, and Nuh, where the terrain doesn't meet the 100m elevation requirement, potentially allowing development in parts of Haryana's forested Aravalis.
- Environmentalists argue that the protection should focus more on preserving the living landscape, including scrub forests, biodiversity, and groundwater recharge, rather than restricting it based on the age of the rocks.
- GSI’s Stance: The Geological Survey of India (GSI) had flagged Haryana's previous draft, questioning the inclusion of much older Archean formations, and emphasised more scientific accuracy in defining the Aravalis.
- The new definition restricts the Aravalis to rocks of the Aravali and Delhi supergroups (Paleoproterozoic and Mesoproterozoic), excluding younger Neoproterozoic intrusives like Erinpura granite and Malani rhyolite.
- The geology department's note reveals that intrusive granite constitutes less than 3% of Haryana's Aravali terrain, with the Ajabgarh and Alwar groups predominating the region.
- Supreme Court’s Role: The Supreme Court had earlier called for a uniform definition of the Aravalis across Delhi, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Gujarat, aiming to standardise regulations for these areas.
- The proposed revision could conflict with prior court rulings, particularly Rajasthan's 2011-12 rejection of a height-based criterion, and may narrow the definition of "Aravali hills and ranges," potentially reducing protected areas and allowing reclassification for development.
- Ecological Importance of Aravalis: The Aravalis, one of the world's oldest hill ranges, are essential in preventing desertification in the Delhi-NCR region by maintaining ecological balance.
- The Aravali-Delhi fold belt stretches from Gujarat to Delhi, consisting mainly of quartzites, schists, phyllites, dolomites, and marbles, playing a key role in controlling the expansion of the Thar desert.
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
World Cotton Day 2025
Why in News?
Union Ministers Shri Giriraj Singh and Shri Pabitra Margherita attended the World Cotton Day 2025 celebration in New Delhi on 7th October.
- The event was jointly organised by the Ministry of Textiles and the Confederation of Indian Textile Industry (CITI), with the theme "Cotton 2040: Technology, Climate & Competitiveness."
Key Points
- About: World Cotton Day was established in 2019 when four cotton-producing countries in sub-Saharan Africa—Benin, Burkina Faso, Chad, and Mali, collectively known as the Cotton Four—proposed to the World Trade Organisation the idea of celebrating World Cotton Day on 7th October.
- Objective: It aims to create awareness of the need for market access for cotton and cotton-related products from least developed countries, foster sustainable trade policies and enable developing countries to benefit more from every step of the cotton value chain.
- Interesting Facts About Cotton:
- The top five cotton-producing countries are China, India, Brazil, the United States of America, and Pakistan, which together account for more than three-quarters of global production.
- India is the largest producer of cotton globally, accounting for 23% of total global cotton production.
- Cotton sustains about 24 million growers and benefits over 100 million families globally.
- Cotton is the second-most used fibre globally after polyester, making up approximately 20% of total fibre demand.
- Approximately 80% of cotton is used in apparel, with the remainder used in home textiles and industrial products.
- The top five cotton-producing countries are China, India, Brazil, the United States of America, and Pakistan, which together account for more than three-quarters of global production.
- Governance in India: The Cotton Corporation of India (CCI), established in July 1970 under the Ministry of Textiles, stabilises cotton prices through price support measures and supports the domestic textile industry with commercial purchasing operations, especially during the lean season.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Abhidhamma Divas
Why in News?
The International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), in partnership with Gautam Buddha University, Antarrashtriya Baudh Shodh Sansthan, and the Ministry of Culture, celebrated International Abhidhamma Day(Abhidhamma Divas) on 6th–7th October 2025 at Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida.
Key Points
- About: Abhidhamma Divas commemorates the occasion when the Buddha preached the Abhidhamma to the gods of Tavatimsa Heaven, led by his mother Mahamaya, and later shared it with his disciple Arahant Sariputta.
- It commemorates the descent of Lord Buddha from the celestial realm of the thirty-three divine beings (Tāvatiṃsa-devaloka) to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur, Farrukhabad) in Uttar Pradesh.
- The importance of this location is highlighted by the presence of the Asokan Elephant Pillar.
- Mark of Event: Abhidhamma Divas coincides with the end of the rainy retreat (Vassa) and the Pavāraņā festival.
- Rainy retreat (Vassa) is an annual three-month monastic retreat practised especially in the Theravada Buddhist tradition during the monsoon season.
- The Pavāraṇā festival marks the conclusion of Vassa, where monks come together to confess any faults or mistakes made during the retreat and invite their fellow monks to point out any shortcomings they may have noticed.
- Pavāraṇā festival is celebrated on the full moon day of the 11th lunar month, which is usually in October.
- Key Functions:
- An International Conference on “The Relevance of Abhidhamma in Understanding Buddhist Thought: Text, Tradition and Contemporary Perspectives” was held to explore Abhidhamma’s philosophical, ethical, and psychological dimensions in the modern context.
- A special exhibition of over 2,500 Buddhist stamps from 90 countries, curated by Mr Vinod Kumar, was showcased, offering a glimpse into Buddhist heritage through philately.
- Two thematic exhibitions were organised, including "Buddha Dhamma on Body and Mind" and a display highlighting the Piprahwa relics, emphasising Buddha's spiritual and cultural legacy.
- The event featured screenings of two films—“Dissemination of Buddha Dhamma in Asia” and “Kushok Bakula Rinpoche – The Extraordinary Story of an Extraordinary Monk,” directed by Dr Hindol Sengupta.
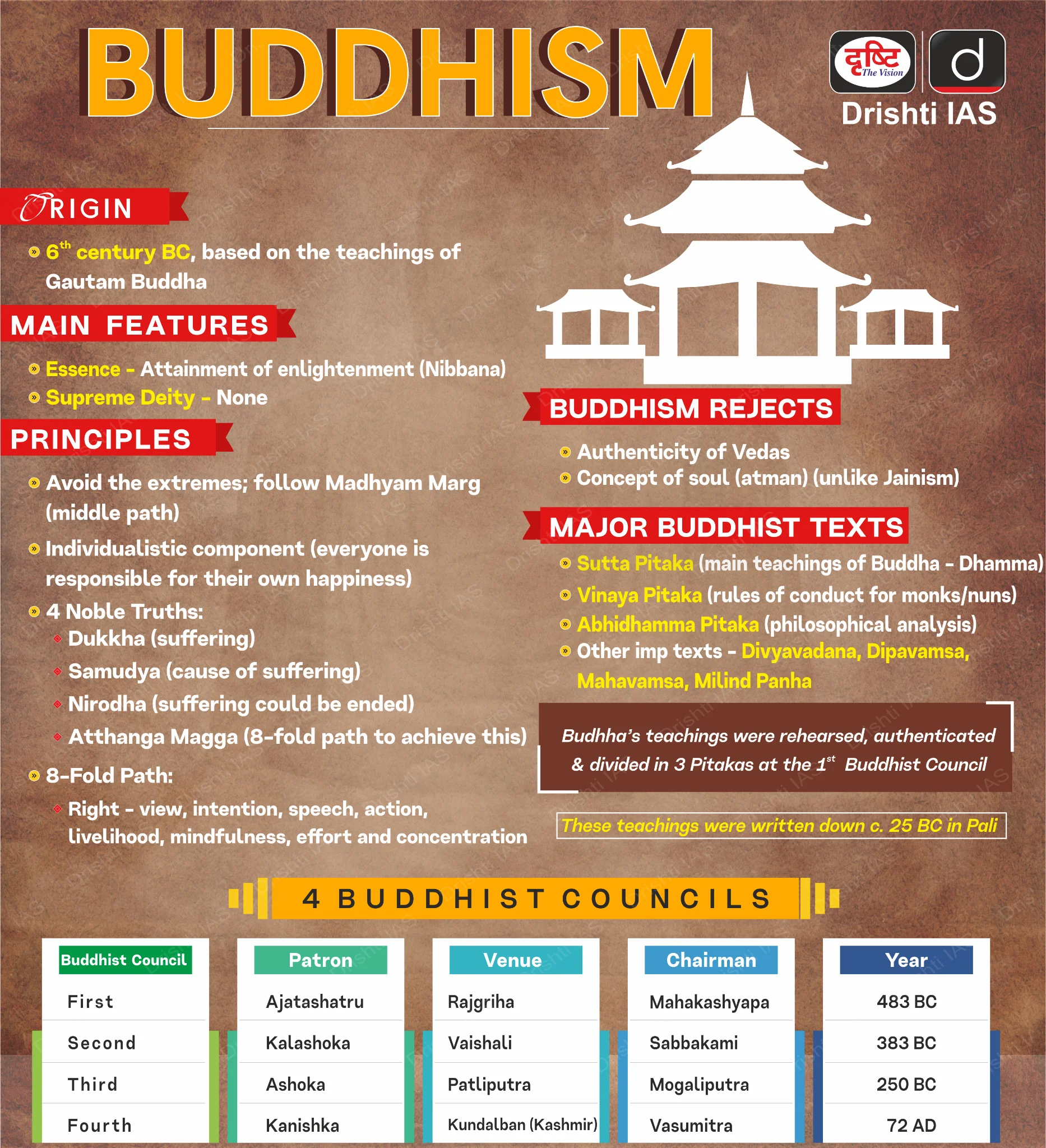
Abhidhamma Pitaka
- The Abhidhamma Pitaka is the last of three Pitakas that constitute to Pali Canon, one of the most popular scriptures of Theravada Buddhism.
- The Abhidhamma Pitaka is a detailed scholastic analysis and summary of the Buddha's teachings in the Suttas. It deals with the philosophy, doctrine, psychology, metaphysics, ethics, and epistemology of Buddhism
- The other remaining Pitakas of Tipitaka are the Vinaya Pitaka and the Sutta Pitaka.
- Vinaya Pitaka is the monastic rules of conduct for monks and nuns of the Sangha.
- Sutta Pitaka contains suttas (teachings/discourses) delivered by the Buddha and his close disciples.
- The Abhidharma Pitaka consists of seven different books.
- Dhammasangani (Enumeration of Phenomena)
- Vibhanga (Book of Treaties)
- Dhatukatha (Discussion with Reference to the Elements)
- Puggalapanatti (Description of Personality)
- Kathavatthu (Points of Controversy)
- Yamaka (Book of Pairs)
- Patthana (Book of Relations)
- The Government of India declared Pali a Classical Language, recognising its significance as the canonical language of Theravada Buddhist texts, including the Abhidhamma Pitaka.
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
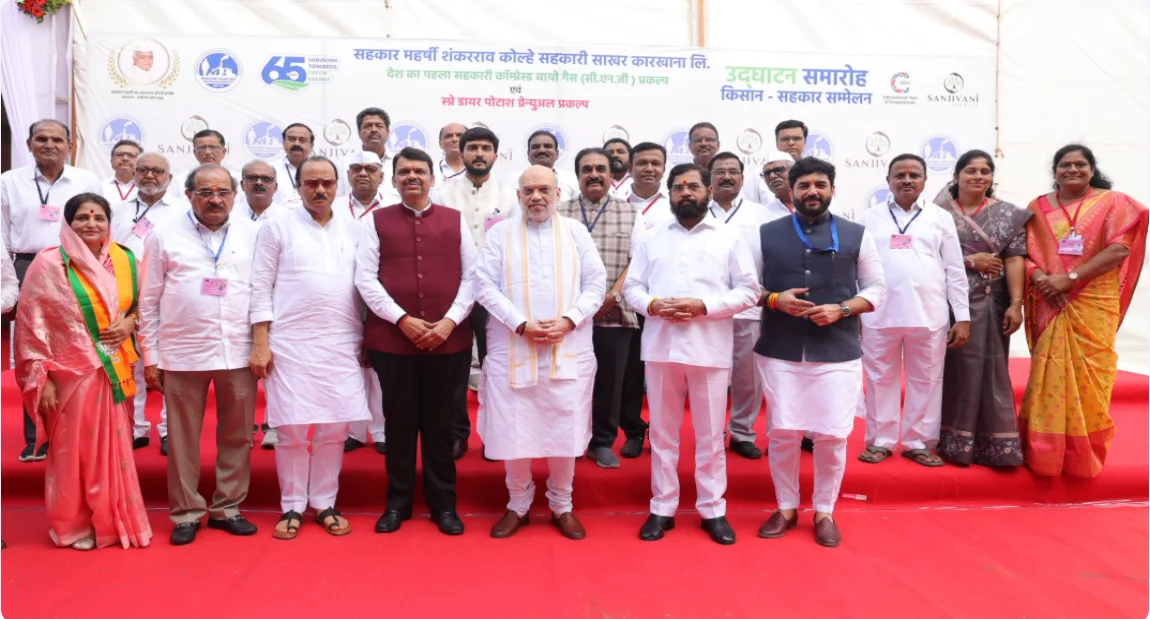
India’s 1st Cooperative-Run Compressed Bio-Gas Project Launched
Why in News?
Union Home and Cooperation Minister Amit Shah has inaugurated India’s first cooperative-based Compressed Bio-Gas (CNG) and Spray Dryer Potash Granule Project at the Sahakar Maharshi Shankarrao Kolhe Cooperative Sugar Factory in Kopargaon, Ahilyanagar district of Maharashtra.
- He announced that similar units will be established in 15 cooperative sugar factories across the country, with Maharashtra expected to play a leading role.
Key Points
- About: The plant will produce 12 tons of CBG daily and 75 tons of potash from jaggery/molasses, reducing imports.
- Compressed Biogas (CBG): It is a renewable fuel produced from biomass and organic waste (agricultural residue, cattle dung, sugarcane press mud, sewage) via anaerobic decomposition (breakdown of organic matter by bacteria in the absence of oxygen).
- Properties: Similar calorific value (amount of energy released on complete combustion) to CNG. CBG can replace CNG in automotive, industrial, and commercial sectors.
- CBG Benefits:
- Eco-Friendly: Cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, supporting India’s target of net zero emissions by 2070.
- Waste Management: Converts organic waste into fuel, reducing pollution and promoting a circular economy.
- Energy Security: Reduces oil imports and increases the share of natural gas in India’s energy mix (currently ~6%, targeted 15% by 2030).
- India’s Initiatives:
- SATAT (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation) Scheme: Aims to produce CBG by utilising 62 Million Metric Tonnes of annual waste, thereby reducing import dependence, generating jobs, and lowering vehicular emissions and pollution.
- National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC): Plans to support 15 sugar mills via NCDC for CBG and potash units.
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
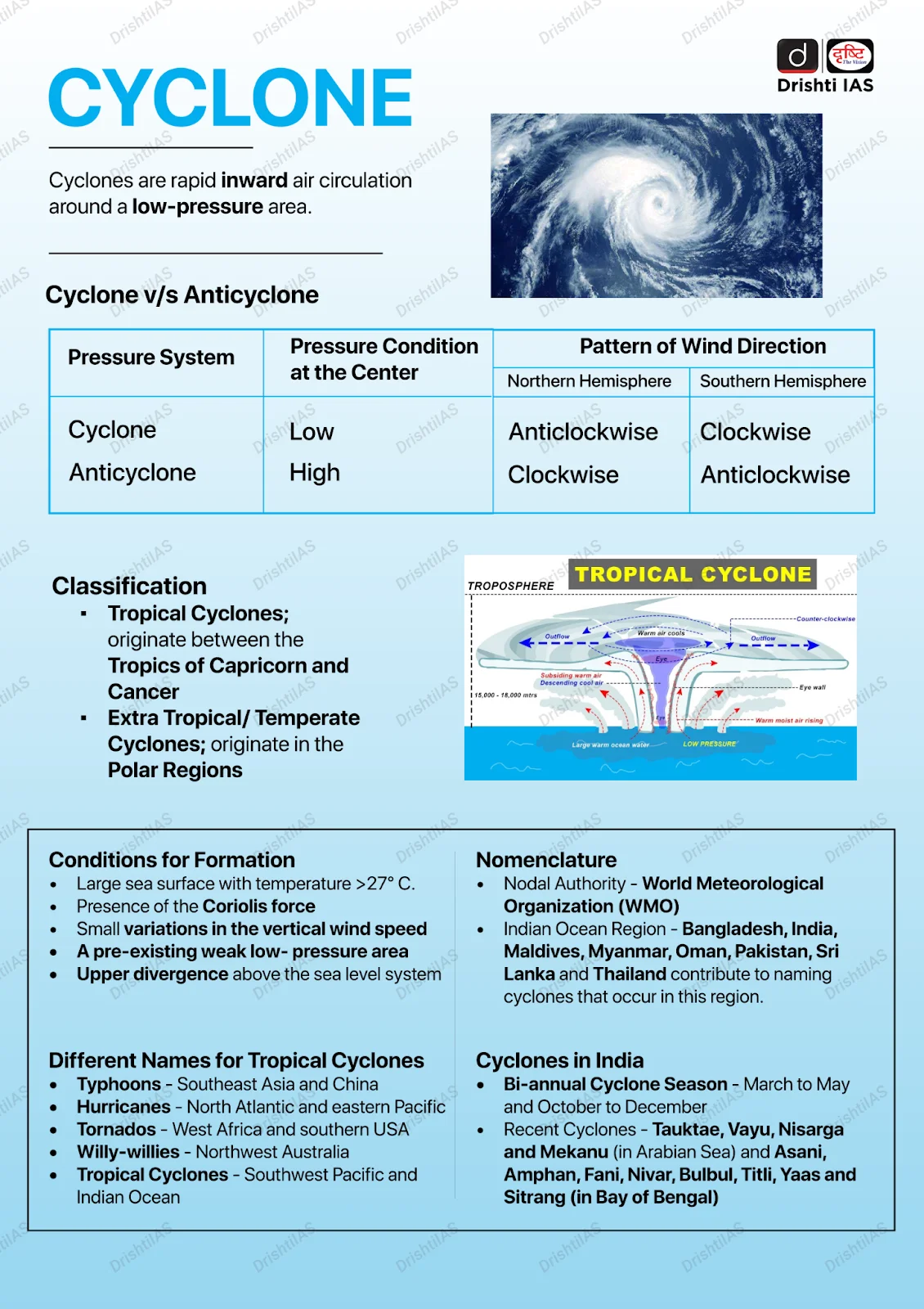
Cyclone Shakhti
Why in News?
Cyclone Shakti, the season's first storm, has intensified into a severe cyclonic storm southwest of Gujarat, though it is not expected to significantly impact the Indian landmass.
- Originating in the Arabian Sea and named by Sri Lanka, Cyclone Shakti has reached wind speeds of 100 km/h.
Key Points
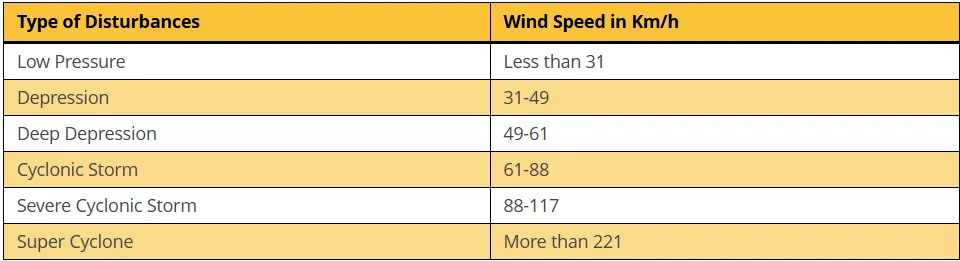
- Definition: Cyclones are fast air circulations around low-pressure areas, rotating anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern, often causing storms and severe weather.
- Cyclone Formation in Arabian Sea: The Arabian Sea, particularly its central and southern parts, serves as a warm pool with ideal Sea Surface Temperature (SST) (at least 27°C), favourable for cyclone formation.
- Also, the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) is a large weather system that moves eastward around the tropics.
- When its active phase is over the Arabian Sea, it creates favourable conditions for cyclones — including more moisture, low wind shear, and strong upward air movement.
- Also, the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) is a large weather system that moves eastward around the tropics.
- Classification of Cyclones: IMD classifies low-pressure systems in the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea by damage potential, following World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) guidelines.
- Naming of Cyclones: The WMO/ESCAP (United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific) Panel on Tropical Cyclones, which includes 13 North Indian Ocean countries, manages cyclone naming for the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
- The panel has a pre-set list of names submitted by 13 countries to be used sequentially.
- Names are chosen in order, column by column, regardless of where the cyclone forms.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Phulo-Jhano Scheme
Why in News?
A Jharkhand State Livelihood Promotion Society (JSLPS) review meeting in Chaibasa, chaired by Deputy Development Commissioner (DDC), reviewed Phulo Jhano Aashirvad Abhiyan progress and livelihood activities in West Singhbhum.
Phulo Jhano Aashirvad Abhiyan (PJAA)
- About: The PJAA aims to end the practice of making and selling haria (country liquor) in rural areas.
- Launched by the Rural Development Department in September 2020, it empowers women by providing them with dignified and sustainable livelihood opportunities.
- Purpose and Vision: The initiative seeks to rehabilitate and mainstream women previously engaged in the liquor trade by providing them with respectable and sustainable income sources.
-
The campaign is designed to promote economic independence, social inclusion, and women empowerment at the grassroots level.
-
-
Support Mechanism: Under this initiative, Self-Help Group (SHG) members are entrusted with reaching every affected household and ensuring necessary support.
- Interest-free loan up to ₹10,000 through Sakhi Mandal to start new ventures.
- The scheme provides technical support, handholding, and counselling to help women shift from liquor production to sustainable livelihoods.
- Achievements:
- Total women identified: 15,284 (through door-to-door survey)
- Women rehabilitated: 14,003 women now earning a dignified livelihood through alternative income-generating activities.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan
.webp)