National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
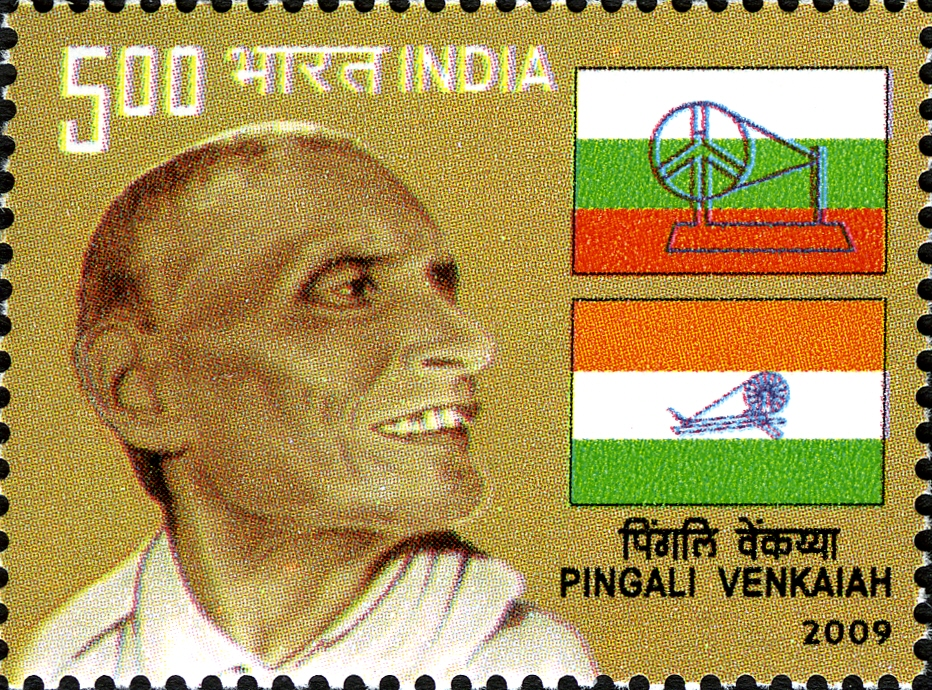
Birth Anniversary of Pingali Venkayya
Why in News?
On 2nd August, PM Modi paid tributes to Pingali Venkayya on his 149th birth anniversary, highlighting his immense contribution in designing India's national flag, a symbol of the nation's unity, diversity, and independence.
- He also urged citizens to support the Har Ghar Tiranga movement by unfurling the Tricolour at their homes.
Pingali Venkayya
- He was born on 2nd August 1876 in Bhatlapenumarru village, near Machilipatnam, Andhra Pradesh, and passed away on 4th July 1963 at the age of 86.
- He fought the Second Boer War (1899-1902).
- In 1913, he delivered a lecture in Japanese in Bapatla, Andhra Pradesh, called ‘Japan Venkayya’.
- He was also known as Patti Venkayya for his research into the Cambodia Cotton.
- In 2009, a postage stamp was released for his contribution.
Evolution of Flag
- In 1916, Pingali Venkayya published a booklet titled A National Flag for India, featuring nearly 30 designs for a potential Indian flag, inspired by flags of other nations.
- Venkayya’s design for the National Flag was finally approved by Mahatma Gandhi in a Congress meeting in Vijayawada in 1921.
- The initial flag, called the Swaraj flag, consisted of two red and green bands (representing the Hindus and the Muslims religious communities). The flag also had a charkha, which represented Swaraj.
- Mahatma Gandhi advised Venkayya to add a white band to represent peace.
- The Flag Committee (1931) replaced the red with saffron and placed saffron on top followed by white and then green. The charkha was placed on the white band in the middle.
- The colors stood for qualities and not communities i.e., the saffron for courage and sacrifice, white for truth and peace, and green for faith and strength. The charkha stood for the welfare of the masses.
- Post-Independence, a national flag committee under President Rajendra Prasad replaced the charkha with the Ashok Chakra.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Anjana Singh Raises Anti-Drug Banner at Mount Elbrus
Why in News?
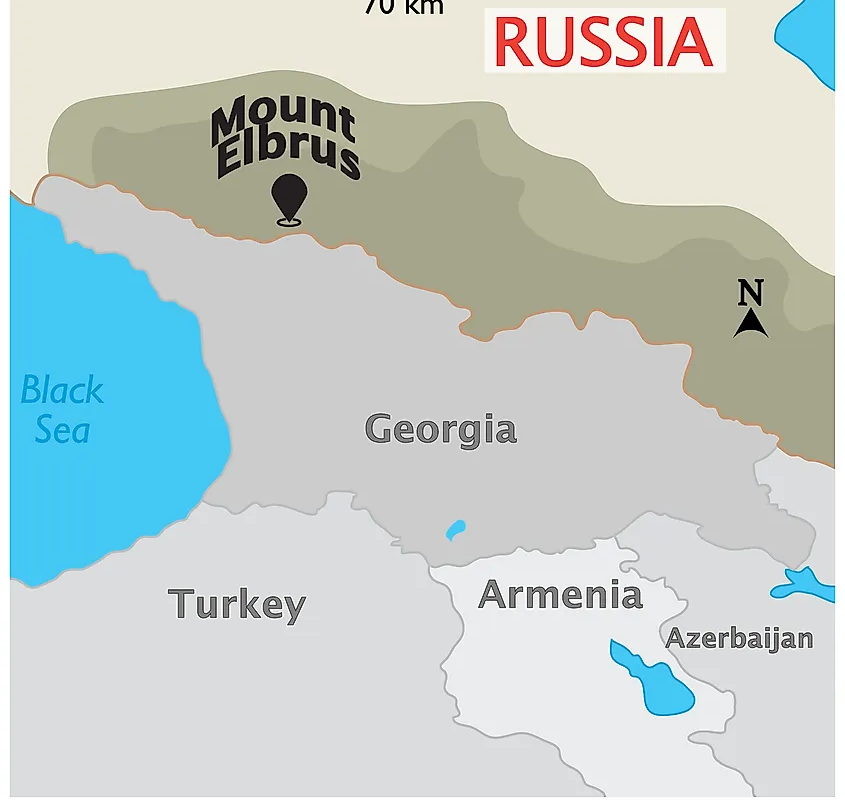
Anjana Singh, a 26-year-old from Amarpatan in Maihar, Madhya Pradesh, raised a banner with the message "Nashe Se Duri Hai Zaroori" (Say No to Drugs) atop Mount Elbrus, Europe's highest peak, at 18,510 feet.
- This initiative is part of a broader campaign by the Madhya Pradesh Police to raise awareness about drugs and support recovery for addicts.
- The Maihar Police is also running the 'Prabodhini' program to educate adolescent girls on safety, social risks, and to inspire them to focus on education and career goals.
Key Points
- About Anjana Singh: She reached the summit of Mount Elbrus in about 72 hours and proudly promoted Hindi as the primary language for the banner's message.
- Upon returning from Mount Elbrus, she was honored by senior police officials for her contributions to the anti-drug campaign.
- In addition to her mountaineering accomplishments, Singh serves as the brand ambassador for the 'Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao' campaign in her district.
- This initiative focuses on empowering women and promoting their education and safety.
Mt. Elbrus
- Mt. Elbrus, the summit of the Caucasus Mountains, is located in southern Russia just north of the Georgian border, and is distinguished as Europe’s highest peak (5642 m).
- The Caucasus Mountains form a long (more than 1200 kilometers) and steep spine connecting the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea.
- Elbrus is also an ancient volcano (dormant volcano), although it has not erupted for nearly 2000 years.
- Elbrus’s profile comprises two volcanic peaks (East and West).
- They are popular trekking and mountain climbing destinations; the saddle between them provides access to the region.
Prabodhini Campaign for Adolescent Girls
- The Prabodhini campaign was launched in October 2024 and has since involved extensive outreach to schools and villages.
- It was launched to educate adolescent girls in the district and focuses on safety, social risks, and encourages girls to pursue educational and career goals.
- Police teams visit schools and villages, aiming to raise awareness and reduce the vulnerabilities of young girls.
- As part of the ongoing expansion of the campaign, a WhatsApp group will be created for schoolgirls to create a strong network of informed and empowered young girls who can identify and report abuse, inspiring others to take similar action.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
‘Operation Mahakal’ to Tackle Land Mafia and Extortionists
Why in News?
Kanpur's police have initiated a bold crackdown on land mafia and extortion gangs with the launch of 'Operation Mahakal.'
- This operation, launched on 5th August 2025, aims to identify, prosecute, and dismantle illegal land-grabbing activities, involving not only criminals but also influential individuals aiding them.
Key Points
- Phases of Operation: The operation is structured in two phases:
- Phase 1 (until 5th September 2025): Focuses on compiling a list of suspects involved in land-grabbing and extortion.
- Phase 2: From 15th September 2025, action will be taken, including asset confiscation and filing of charges.
- Action against Collaborators: Investigations have uncovered connections between the land mafia and several white-collar professionals, including government employees, representatives, and journalists.
- The collaboration between these groups will be probed further.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme (RIPS)
Why in News?
The Rajasthan government has disbursed ₹765.78 crore in investment incentives under the Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme (RIPS) for the 2024-25 fiscal year.
Key Points
- About: RIPS 2024 is the Rajasthan government’s flagship scheme to promote investments across manufacturing, services, renewable energy, MSMEs, startups, and sunrise sectors.
- Launched at a UK roadshow in October 2023, the scheme operates until 31st March 2029, with potential revisions as needed.
- Priority Sectors and Categories:
- Manufacturing, services, sunrise sectors, MSMEs, startups, industrial infrastructure, logistics, warehousing, R&D, and global capability centers.
- Special focus on women, youth, and startups; logistic infrastructure requires minimum investments ranging from ₹2 crore (warehouse or cold chain) to ₹50 crore (multi-modal logistics parks).
- Key Incentives:
- Capital Subsidy: Up to 28% of eligible investment for some sectors.
- SGST Reimbursement: Up to 75% of State GST for a defined period.
- Stamp Duty Reimbursement: Up to 75% exemption and reimbursement for the remainder.
- Renewable Energy Focus: 100% exemption of electricity duty, 75% exemption in stamp duty and conversion charges (remainder reimbursed), banking and transmission exemptions, and dedicated benefits for green hydrogen and energy storage.
- Eligibility:
- For new/expansion investments and for projects starting commercial production within the operative policy period or two years from entitlement, whichever is later.
- Eligible entities may access single-window clearance through the Rajnivesh portal, streamlining applications and approvals.
- Implementation and Scale:
- Rajasthan has signed MoUs worth ₹35 lakh crore as per the 2024 Rising Rajasthan Global Investment Summit, with over ₹4.12 lakh crore under implementation.
- Regular partnership conclaves and roadshows to attract both domestic and global investors.
- The Rajasthan government will host the Rising Rajasthan Partnership Conclave in Jaipur on 11-12 December 2025 to further strengthen partnerships with industry leaders, institutions, and multilateral bodies, continuing the momentum of investment and collaboration in the state.
Key Facts About Rajasthan
- Rajasthan is the largest State in the country in terms of area.
- It is spread over the geographical area of about 3.42 lakh square kilometres, which is 10.41% of India's total land area.
- It is located in the northwest part of the country and is surrounded by the States of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) for 2023-24 is USD 182.02 billion, with a GSDP growth rate of 8.03% at constant prices (2011-12).
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
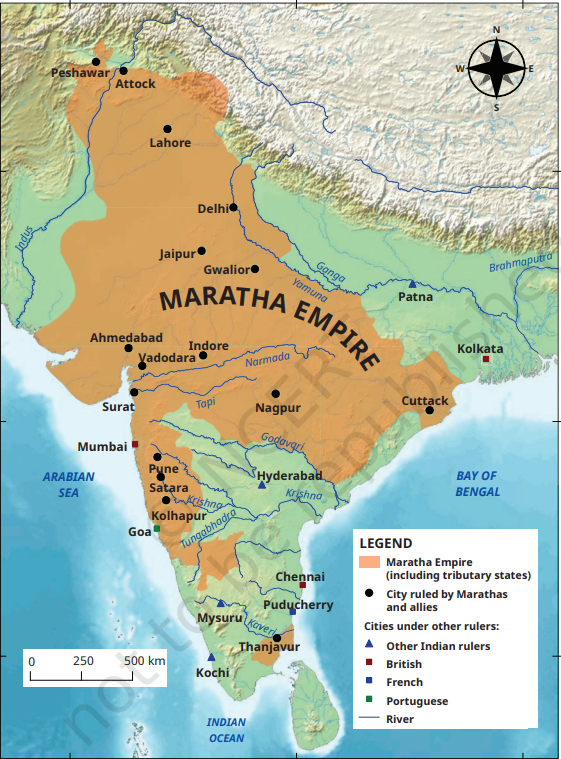
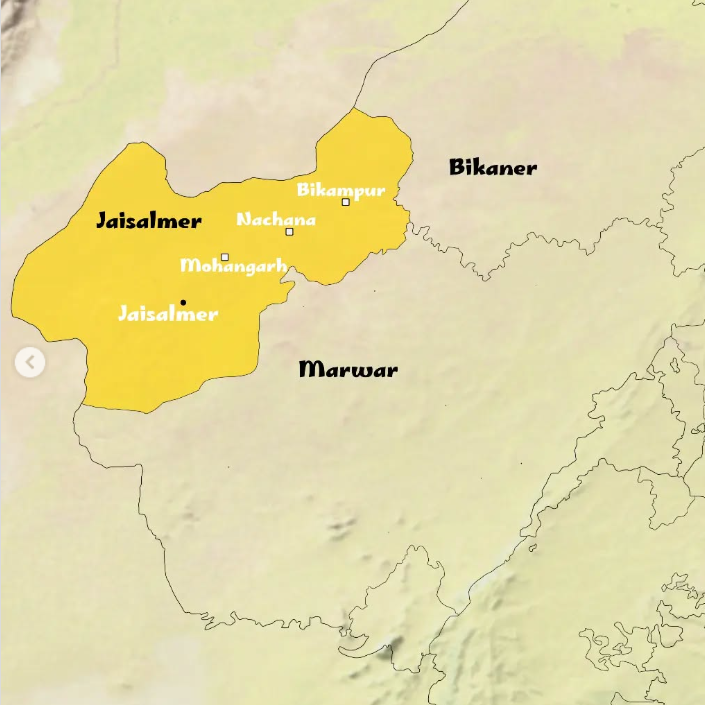
Controversy Over Jaisalmer as Part of Maratha Empire
Why in News?
A historical controversy has erupted following a claim in the NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) textbook where Jaisalmer is depicted as part of the Maratha Empire.
Historians' Arguments on Maratha Relations with Jaisalmer
- Rajput’s Arguments: The royal family of Jaisalmer, led by Chaitanya Raj Singh, the 44th Maharawal of Jaisalmer, has strongly objected to this portrayal, calling it a grave historical error and highlighting that there is no evidence of Maratha influence in Jaisalmer—a region that remained independent throughout various invasions, including those by the Mughals and the British.
- Historical accounts reveal that the region’s Rajput rulers defended their sovereignty, and there was no Maratha intervention or taxation in Jaisalmer.
- Maratha’s Arguments: Maratha historians cite the 1752 Ahadnama (a pact between Mughal Emperor Ahmad Shah Bahadur and Maratha commanders Malharrao Holkar and Mahadji Shinde) and argue that, while the Marathas did not have direct day-to-day control, Rajput states, including Jaisalmer, were made to pay chauth and sardeshmukhi taxes.
- Pandurang Balkawade (historian from Pune) points to Peshwa administration records showing regular collection of chauth from the Ajmer (Mewar) region.
Jaisalmer
- Location & Significance: Jaisalmer, often referred to as the "Golden City," is located in western Rajasthan, close to the Pakistan border and the Thar Desert.
- Its prominent landmark is the Jaisalmer Fort, also known as Sonar Qila (Golden Fort), which is unique for being a living fort.
- Historical Background: Jaisalmer was founded in 1156 by Rawal Jaisal, a descendant of the Yaduvanshi clan. After being passed over for the throne of Lodurva, Jaisal sought a new capital, guided by the prophecy of sage Eesul (local hermit).
- Cultural Heritage: Jaisalmer’s cultural and architectural beauty is shaped by its Rajput heritage, with influences from the Bhati Rajputs.
- Geological Significance: The Wood Fossil Park (Aakal) in Jaisalmer shows fossils from the Thar Desert for a glimpse into geological history, dating back 180 million years.
- Post-Independence: Jaisalmer State signed the Instrument of Accession with India on 7th April 1949, merging with the Indian Union.
Marathas
- Origin & Language: The Marathas (speak Marathi language) are native to the Deccan Plateau, mainly present-day Maharashtra.
- Shivaji Maharaj & the Rise of Maratha Power:
- Born (1630): Shivaji, from the Bhonsle clan, aimed to establish Swarājya (sovereignty).
- Military Campaigns: At 16, he began capturing forts in the Pune region, growing his influence.
- Utilized guerrilla tactics against the Bijapur Sultanate, including defeating General Afzal Khan.
- After Shivaji’s death, Sambhaji (Shivaji’s son) became the Chhatrapati. He was captured and executed by Aurangzeb.
- Maratha Structural Transformation:
- Decentralization: After Shivaji’s death, the Maratha power became more decentralized, with the Peshwa gaining influence.
- Expansion: The Marathas expanded across India, briefly controlling parts of Lahore, Attock, and Peshawar.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Flash Floods in Uttarkashi District
Why in News?
Flash floods, triggered by heavy rainfall, have caused widespread devastation along the Kheer Ganga river in Uttarkashi district, Uttarakhand.
- The floods, which hit the town of Dharali, a popular tourist spot situated 8,600 feet above sea level, have resulted in significant loss of life, with many others feared missing.
Key Points
- Reasons for Flash Floods:
- Experts suggest that a glacier collapse or a glacial lake outburst (GLOF) upstream, rather than a cloudburst, likely triggered the flash flood in Dharali village.
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) recorded minimal rainfall during the disaster, well below the typical levels that cause cloudburst-induced flooding, leading experts to suggest the possibility of a glacier burst or GLOF, supported by satellite images showing significant glaciers and glacial lakes above Dharali.
- Disaster Risk:
- According to the Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Uttarakhand is home to 1,266 glacial lakes, ranging from small to large bodies of water, some of which pose significant downstream threats.
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has identified 13 glacial lakes as high-risk, with five classified as extremely dangerous.
- Such disasters occur when water accumulates at high elevations and is suddenly released—heavy rainfall alone cannot trigger such catastrophic events.
Flash Flood
- Definition: Flash floods are sudden increases in water levels during or immediately after intense rainfall. They are highly localized and short-lived events, typically occurring within 6 hours of rainfall.
- Causes:
- Flash floods are primarily caused by intense rainfall that overwhelms the soil’s absorption capacity and drainage systems.
- Apart from heavy rain, flash floods can also result from rapid snowmelt due to sudden temperature rise, dam or levee breaches, ice or debris jams, and sudden glacial lake outbursts.
- Additionally, urbanisation with impervious surfaces like roads and buildings increases runoff, reducing water absorption and intensifying flood risks.
Glacial Lake Outburst (GLOF)
- About: A GLOF is a type of catastrophic flood that occurs when the dam containing a glacial lake fails, releasing a large volume of water.
- This type of flood is typically caused by the rapid melting of glaciers or the buildup of water in the lake due to heavy precipitation or the inflow of meltwater.
- In February 2021, Chamoli district in Uttarakhand witnessed flash floods which are suspected to have been caused by GLOFs.
- Causes:
- These floods can be triggered by a number of factors, including changes in the volume of the glacier, changes in the water level of the lake, and earthquakes.
- According to the NDMA (National Disaster Management Authority), glacial retreat due to climate change occurring in most parts of the Hindu Kush Himalayas has given rise to the formation of numerous new glacial lakes, which are the major cause of GLOFs.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
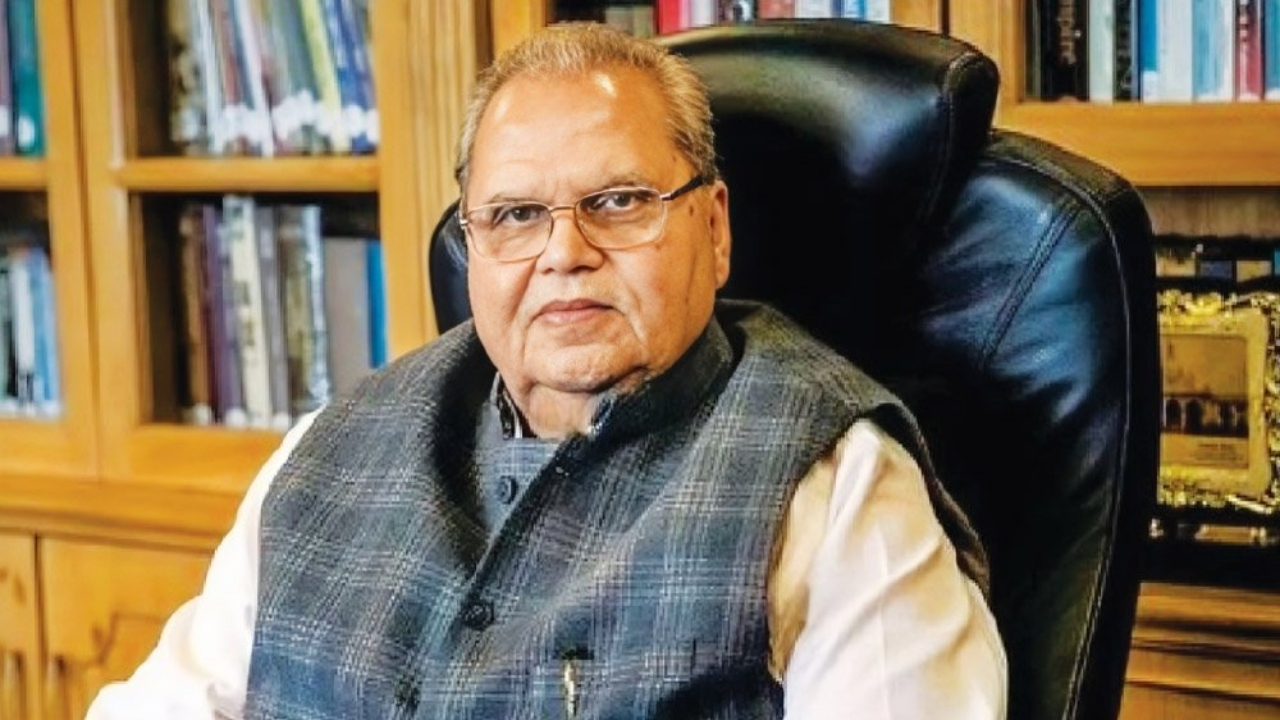
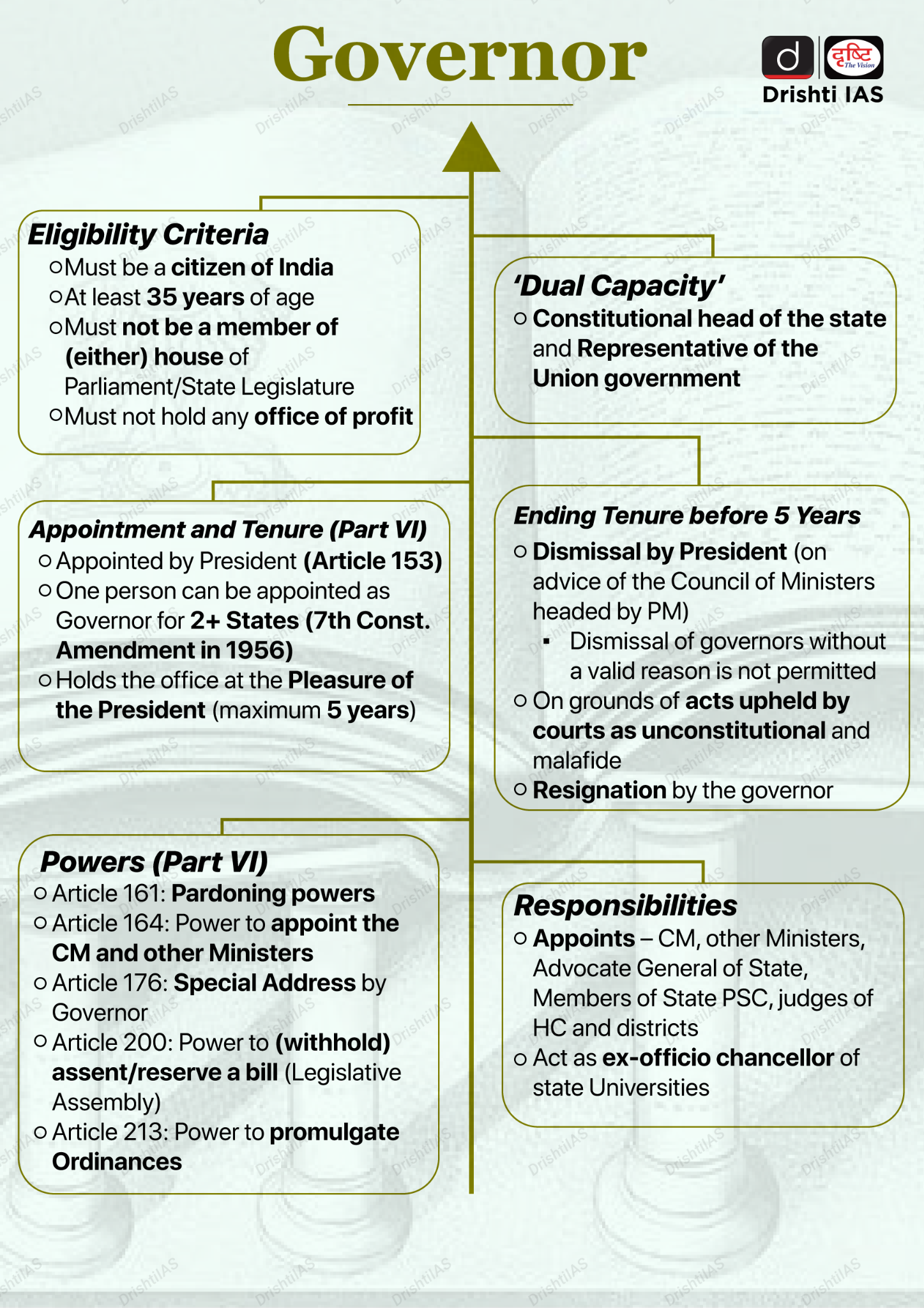
Former Governor Satyapal Malik Passes Away
Why in News?
Former Governor Satyapal Malik passed away at the age of 79 on 5th August 2025, after battling a prolonged illness.
- He served as the Governor of five states, including Jammu and Kashmir, and played a pivotal role during the historic abrogation of Article 370 in 2019.
Key points
- Early Life: Malik was born on 24th July 1946, in Hisawada village, Uttar Pradesh.
- Political Journey of Satyapal Malik:
- Student Politics: Began his political career in 1965 at Meerut College.
- Member of Legislative Assembly: Elected as MLA for Baghpat in 1974.
- Rajya Sabha: Entered the Rajya Sabha in 1980.
- Rejoined the Rajya Sabha in 1984 after a brief period of change.
- Lok Sabha: Elected to the Lok Sabha from Aligarh in 1989.
- Governor Positions:
- Bihar (2017–2018)
- Odisha (Additional charge in 2018)
- Jammu and Kashmir (2018–2019)
- Goa (2019–2020)
- Meghalaya (2020–2022)
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Maharashtra Startup, Entrepreneurship, and Innovation Policy 2025
Why in News?
The Maharashtra state cabinet has approved the Maharashtra Startup, Entrepreneurship, and Innovation Policy 2025, aimed at fostering innovation and entrepreneurship across the state.
Key Points
- About: The policy focuses on creating 1.25 lakh entrepreneurs and 50,000 startups over the next five years.
- Maharashtra is already leading the country with 29,146 startups (18% of India's total), and seeks to build an even more robust ecosystem for innovation.
- Key Objectives:
- Create 1.25 lakh entrepreneurs and 50,000 startups in 5 years.
- Encourage startups led by women and youth through targeted support.
- Enhance Maharashtra's position as a leading hub for innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Financial and Infrastructure Support:
- Maha-Fund (Rs 500 crore): Financial assistance for 25,000 early-stage entrepreneurs from a pool of 5 lakh youth. This will follow a three-stage selection process and will include mentoring, incubation, and funding support.
- Maharashtra Innovation City: A 300-acre innovation hub bringing together startups, corporates, educational institutions, and the government to foster research and development.
- Departmental Innovation Fund: All state departments will be required to allocate 0.5% of their annual funds towards promoting innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Startup Week Incentives: Startups selected during the Maharashtra Startup Week will get opportunities to work directly with government departments, with pilot work orders worth up to Rs 25 lakh.
- Support for Incubators and Regional Hubs:
- Micro-incubators will be established in ITIs, polytechnics, and educational institutions across Maharashtra to ensure organized infrastructure for innovation.
- Regional innovation hubs will be set up in each administrative division to promote local entrepreneurial ecosystems.
- Financial Assistance and Recognition:
- Compensation for Patents & Certifications: Financial support for patent registration, product quality certifications, and participation in domestic and international exhibitions.
- Loan Assistance: A special mechanism will be created for startups that have secured work orders from public institutions or trusted customers.
- Implementation Agency: The policy will be executed through the Maharashtra State Innovation Society.
Key Facts About Maharashtra
- It is the most industrialised state in India and has maintained its leading position in the industrial sector in the country.
- At current prices, Maharashtra’s gross state domestic product was estimated at Rs. 49.39 trillion (USD 578.31 billion) in 2025-26.
- According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), between October 2019-December 2024, the FDI inflow in Maharashtra stood at Rs. 6,71,863 crore (USD 85.73 billion).
- Maharashtra ranked first for the highest FDI reception.
- Maharashtra had 12 Special Economic Zones (SEZs) with valid in-principal approvals, 51 SEZs with formal approvals, and 45 SEZs with notified approvals.
- As of October 2020, the state had 37 exporting SEZs across diversified sectors, including textiles and apparel, food processing, footwear and leather products, multi-product, pharma, and IT SEZs.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan