Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme (RIPS)
Why in News?
The Rajasthan government has disbursed ₹765.78 crore in investment incentives under the Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme (RIPS) for the 2024-25 fiscal year.
Key Points
- About: RIPS 2024 is the Rajasthan government’s flagship scheme to promote investments across manufacturing, services, renewable energy, MSMEs, startups, and sunrise sectors.
- Launched at a UK roadshow in October 2023, the scheme operates until 31st March 2029, with potential revisions as needed.
- Priority Sectors and Categories:
- Manufacturing, services, sunrise sectors, MSMEs, startups, industrial infrastructure, logistics, warehousing, R&D, and global capability centers.
- Special focus on women, youth, and startups; logistic infrastructure requires minimum investments ranging from ₹2 crore (warehouse or cold chain) to ₹50 crore (multi-modal logistics parks).
- Key Incentives:
- Capital Subsidy: Up to 28% of eligible investment for some sectors.
- SGST Reimbursement: Up to 75% of State GST for a defined period.
- Stamp Duty Reimbursement: Up to 75% exemption and reimbursement for the remainder.
- Renewable Energy Focus: 100% exemption of electricity duty, 75% exemption in stamp duty and conversion charges (remainder reimbursed), banking and transmission exemptions, and dedicated benefits for green hydrogen and energy storage.
- Eligibility:
- For new/expansion investments and for projects starting commercial production within the operative policy period or two years from entitlement, whichever is later.
- Eligible entities may access single-window clearance through the Rajnivesh portal, streamlining applications and approvals.
- Implementation and Scale:
- Rajasthan has signed MoUs worth ₹35 lakh crore as per the 2024 Rising Rajasthan Global Investment Summit, with over ₹4.12 lakh crore under implementation.
- Regular partnership conclaves and roadshows to attract both domestic and global investors.
- The Rajasthan government will host the Rising Rajasthan Partnership Conclave in Jaipur on 11-12 December 2025 to further strengthen partnerships with industry leaders, institutions, and multilateral bodies, continuing the momentum of investment and collaboration in the state.
Key Facts About Rajasthan
- Rajasthan is the largest State in the country in terms of area.
- It is spread over the geographical area of about 3.42 lakh square kilometres, which is 10.41% of India's total land area.
- It is located in the northwest part of the country and is surrounded by the States of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) for 2023-24 is USD 182.02 billion, with a GSDP growth rate of 8.03% at constant prices (2011-12).
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
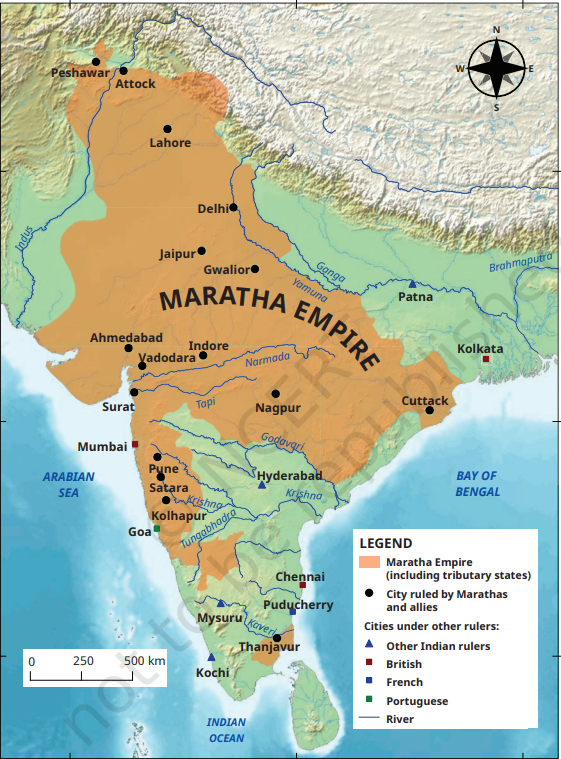
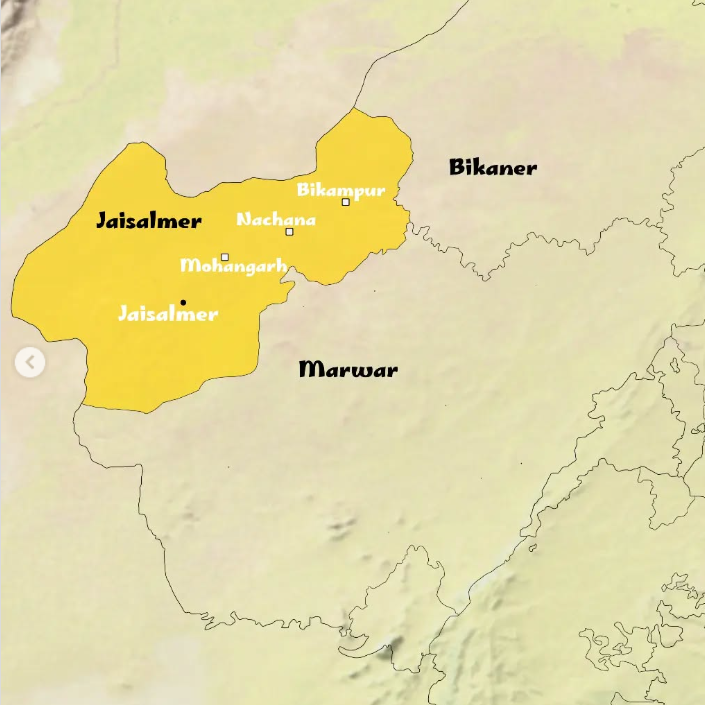
Controversy Over Jaisalmer as Part of Maratha Empire
Why in News?
A historical controversy has erupted following a claim in the NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) textbook where Jaisalmer is depicted as part of the Maratha Empire.
Historians' Arguments on Maratha Relations with Jaisalmer
- Rajput’s Arguments: The royal family of Jaisalmer, led by Chaitanya Raj Singh, the 44th Maharawal of Jaisalmer, has strongly objected to this portrayal, calling it a grave historical error and highlighting that there is no evidence of Maratha influence in Jaisalmer—a region that remained independent throughout various invasions, including those by the Mughals and the British.
- Historical accounts reveal that the region’s Rajput rulers defended their sovereignty, and there was no Maratha intervention or taxation in Jaisalmer.
- Maratha’s Arguments: Maratha historians cite the 1752 Ahadnama (a pact between Mughal Emperor Ahmad Shah Bahadur and Maratha commanders Malharrao Holkar and Mahadji Shinde) and argue that, while the Marathas did not have direct day-to-day control, Rajput states, including Jaisalmer, were made to pay chauth and sardeshmukhi taxes.
- Pandurang Balkawade (historian from Pune) points to Peshwa administration records showing regular collection of chauth from the Ajmer (Mewar) region.
Jaisalmer
- Location & Significance: Jaisalmer, often referred to as the "Golden City," is located in western Rajasthan, close to the Pakistan border and the Thar Desert.
- Its prominent landmark is the Jaisalmer Fort, also known as Sonar Qila (Golden Fort), which is unique for being a living fort.
- Historical Background: Jaisalmer was founded in 1156 by Rawal Jaisal, a descendant of the Yaduvanshi clan. After being passed over for the throne of Lodurva, Jaisal sought a new capital, guided by the prophecy of sage Eesul (local hermit).
- Cultural Heritage: Jaisalmer’s cultural and architectural beauty is shaped by its Rajput heritage, with influences from the Bhati Rajputs.
- Geological Significance: The Wood Fossil Park (Aakal) in Jaisalmer shows fossils from the Thar Desert for a glimpse into geological history, dating back 180 million years.
- Post-Independence: Jaisalmer State signed the Instrument of Accession with India on 7th April 1949, merging with the Indian Union.
Marathas
- Origin & Language: The Marathas (speak Marathi language) are native to the Deccan Plateau, mainly present-day Maharashtra.
- Shivaji Maharaj & the Rise of Maratha Power:
- Born (1630): Shivaji, from the Bhonsle clan, aimed to establish Swarājya (sovereignty).
- Military Campaigns: At 16, he began capturing forts in the Pune region, growing his influence.
- Utilized guerrilla tactics against the Bijapur Sultanate, including defeating General Afzal Khan.
- After Shivaji’s death, Sambhaji (Shivaji’s son) became the Chhatrapati. He was captured and executed by Aurangzeb.
- Maratha Structural Transformation:
- Decentralization: After Shivaji’s death, the Maratha power became more decentralized, with the Peshwa gaining influence.
- Expansion: The Marathas expanded across India, briefly controlling parts of Lahore, Attock, and Peshawar.
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
Birth Anniversary of Pingali Venkayya
Why in News?
On 2nd August, PM Modi paid tributes to Pingali Venkayya on his 149th birth anniversary, highlighting his immense contribution in designing India's national flag, a symbol of the nation's unity, diversity, and independence.
- He also urged citizens to support the Har Ghar Tiranga movement by unfurling the Tricolour at their homes.
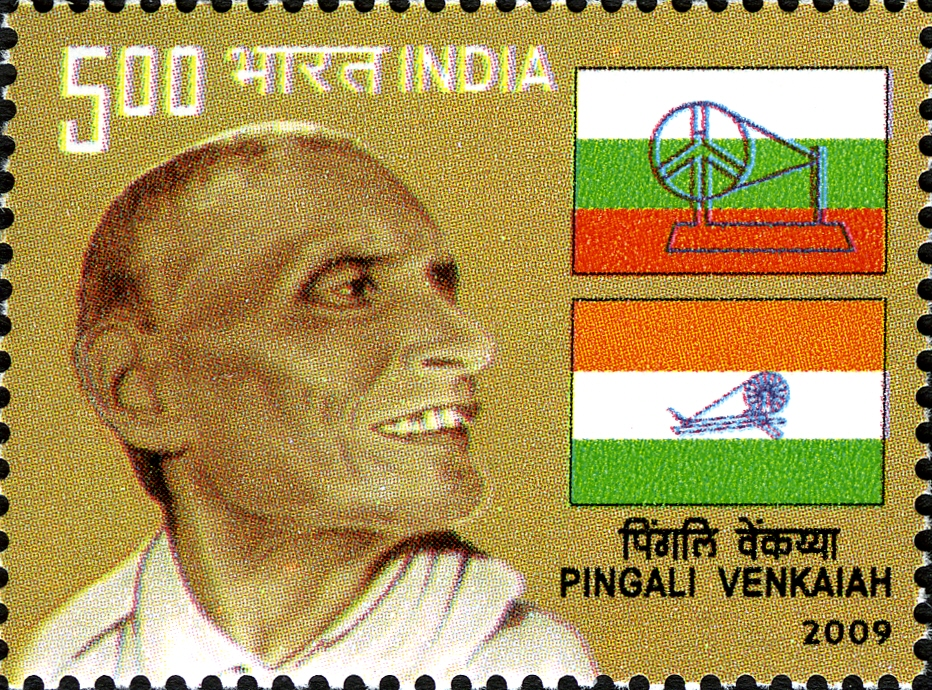
Pingali Venkayya
- He was born on 2nd August 1876 in Bhatlapenumarru village, near Machilipatnam, Andhra Pradesh, and passed away on 4th July 1963 at the age of 86.
- He fought the Second Boer War (1899-1902).
- In 1913, he delivered a lecture in Japanese in Bapatla, Andhra Pradesh, called ‘Japan Venkayya’.
- He was also known as Patti Venkayya for his research into the Cambodia Cotton.
- In 2009, a postage stamp was released for his contribution.
Evolution of Flag
- In 1916, Pingali Venkayya published a booklet titled A National Flag for India, featuring nearly 30 designs for a potential Indian flag, inspired by flags of other nations.
- Venkayya’s design for the National Flag was finally approved by Mahatma Gandhi in a Congress meeting in Vijayawada in 1921.
- The initial flag, called the Swaraj flag, consisted of two red and green bands (representing the Hindus and the Muslims religious communities). The flag also had a charkha, which represented Swaraj.
- Mahatma Gandhi advised Venkayya to add a white band to represent peace.
- The Flag Committee (1931) replaced the red with saffron and placed saffron on top followed by white and then green. The charkha was placed on the white band in the middle.
- The colors stood for qualities and not communities i.e., the saffron for courage and sacrifice, white for truth and peace, and green for faith and strength. The charkha stood for the welfare of the masses.
- Post-Independence, a national flag committee under President Rajendra Prasad replaced the charkha with the Ashok Chakra.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan