Important Facts For Prelims
Revised Startup Recognition Framework
- 07 Feb 2026
- 10 min read
Why in News?
India has revised the startup recognition framework under the Startup India Action Plan, marking a significant policy update as the Startup India initiative enters its second decade.
- In 2024, only about 10% of Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT)-recognised startups were deep tech, a level flagged as too low, prompting reforms to build a future-ready ecosystem aligned with India’s innovation, manufacturing, and emerging technology goals.
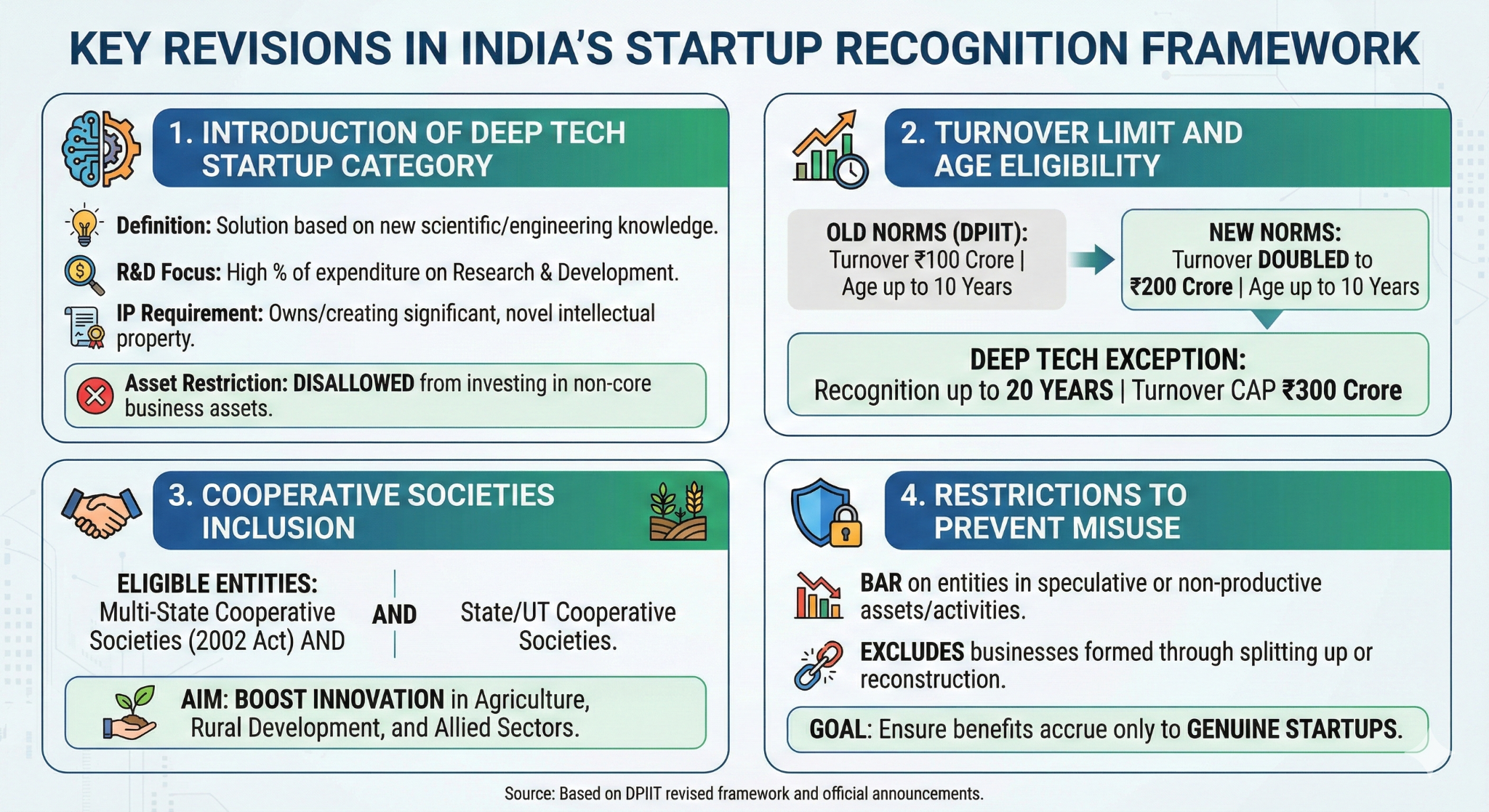
What are the Key Revisions in India's Startup Recognition Framework?
- Introduction of a Deep Tech Startup Category: A dedicated sub-category of startup has been introduced for "Deep Tech Startups" with specific criteria to identify genuine innovation:
- Definition: The entity must develop solutions based on new scientific or engineering knowledge, involving long development cycles, extended gestation periods, high capital and infrastructure needs, and significant technical or scientific uncertainty.
- R&D Focus: It must have a high percentage of expenditure on Research & Development relative to its revenue or funding.
- IP Requirement: The entity must own or be in the process of creating significant, novel intellectual property (IP) and be taking steps to commercialise it.
- Asset Restriction: During the recognition period, Deep Tech startups are explicitly disallowed from investing in assets or activities not integral to their core business.
- Authority: The DPIIT is the final authority that determines whether a company qualifies as a startup or a deep tech startup.
- It will decide this based on “guidance” from an Inter-Ministerial Board of Certification.
- Turnover Limit and Age Eligibility: Under the new DPIIT norms, the turnover limit for startup recognition has been doubled from Rs 100 crore to Rs 200 crore for entities up to 10 years from incorporation.
- For deep tech startups, the recognition period has been extended from 10 to 20 years from incorporation, with the turnover limit raised to Rs 300 crore.
- Cooperative Societies: Both Multi-State Cooperative Societies (under Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002) and Cooperative Societies (under State and Union Territory Cooperative Acts) are now eligible for startup recognition.
- This move specifically aims to boost innovation in agriculture, rural development, and allied sectors.
- Restrictions to Prevent Misuse: To ensure that benefits accrue only to genuine startups, the revised framework introduces stricter safeguards, including a bar on entities engaged in speculative or non-productive assets or activities, as notified by the government.
- It also clearly excludes businesses formed through the splitting up or reconstruction of existing enterprises from being recognised as startups.
Note: The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) is the custodian of the Rs 1 lakh crore Research and Development Innovation (RDI) Fund that is expected to invest in emerging technology and fund research over seven years.
- A part of these investments, which will be through secondary fund managers such as financial institutions, will go to deep tech startups.
What is the Startup India Initiative?
- About: The Startup India Initiative launched on 16th January 2016, led by DPIIT under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, has evolved into a full-stack platform supporting startups from ideation to scale.
- Startup India Action Plan: An Action Plan for Startup India was unveiled in 2016.
- The Action Plan comprises 19 action items spanning across areas such as “Simplification and handholding”, “Funding support and incentives” and “Industry-academia partnership and incubation”.
- The Action Plan laid the foundation of Government support, schemes and incentives envisaged to create a vibrant startup ecosystem in the country.
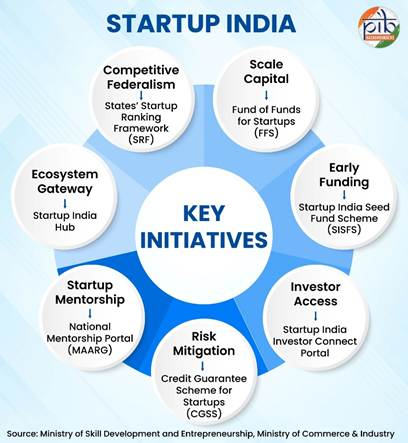
- Major Schemes & Support Pillars: The Fund of Funds for Startups channels a Rs 10,000 crore corpus through SEBI-registered Alternative Investment Funds to expand domestic risk capital.
- The Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups enables collateral-free lending via eligible financial institutions.
- The Startup India Seed Fund Scheme provides early-stage funding for proof of concept, prototyping, and market entry.
- The Startup India Hub acts as a single-window digital platform linking startups with investors, mentors, incubators, corporates, and government bodies.
- At the federal level, the States’ Startup Ranking Framework promotes competitive federalism by assessing startup policy performance across States and UTs.
- Mentorship and networking platforms such as Mentorship, Advisory, Assistance, Resilience, and Growth (MAARG) and Startup India Investor Connect Portal bridge founders with mentors and investors, strengthening the overall startup ecosystem.
- Impact & Achievements:
- Scale: India is now one of the world's largest startup ecosystems with over 2 lakh recognized startups.
- Unicorns: The number of unicorns (startups valued at USD 1 Billion+) has grown from just 4 in 2014 to over 120.
- Inclusivity: Over 45% of startups have at least one woman director, and nearly 50% of recognized startups come from Tier II and Tier III cities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the key objective of revising the Startup Recognition Framework?
To create a predictable, inclusive, and innovation-focused ecosystem while ensuring benefits reach genuine startups.
2. Who qualifies as a Deep Tech Startup under the new framework?
Startups based on scientific or engineering advancements with high R&D spend and ownership of novel intellectual property.
3. What changes have been made to turnover and age limits for startups?
General startups can now have up to Rs 200 crore turnover and 10 years’ age, while deep tech startups get 20 years and Rs 300 crore cap.
4. Why are cooperative societies included in startup recognition?
To boost innovation in agriculture, rural development, and allied sectors through cooperative-led entrepreneurship.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Stand Up India Scheme’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- Its purpose is to promote entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
- It provides for refinance through SIDBI,
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: C
Q. What does venture capital mean? (2014)
(a) A short-term capital provided to industries
(b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
(c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
(d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Ans: (b)