Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Discovery of Harappan Site in Rajasthan's Thar Desert
Why in News?
A new Harappan site has been found at Ratadiya Ri Dheri in Jaisalmer district, Rajasthan.
- The site was discovered by Dilip Kumar Saini, a history lecturer, and Parth Jagani, a local enthusiast.
Key Points
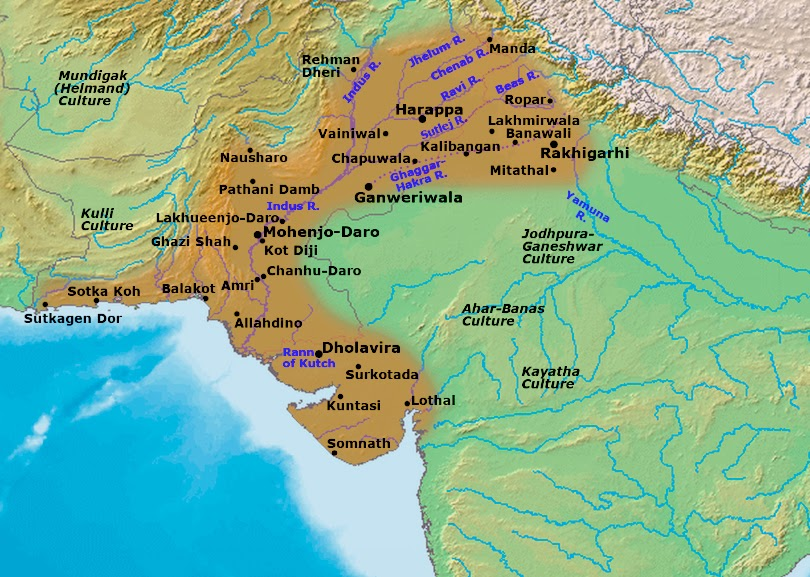
- About: The discovery of Ratadiya Ri Dheri is the first Indus Valley settlement found in Rajasthan's Thar desert.
- The site is located 17 km northwest of Sadewala, Pakistan, where Harappan traces were previously found.
- This discovery bridges an important gap in the archaeological map between Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Background: Before this, the most well-known Harappan site in Rajasthan was Pilibanga in the north, discovered by Italian Indologist Luigi Pio Tessitori in the early 20th century.
- Artefacts Found: The artifacts discovered include red pottery fragments such as bowls, pots, and jars, clay and shell bangles, terracotta objects, stone tools, and wedge-shaped bricks used in kilns.
- The kilns at the site resemble those found in Kanmer (Gujarat) and Mohenjo-daro (Pakistan), indicating the presence of a developed settlement.
- Dating and Significance: Archaeologists have dated the site to the mature urban phase of the Indus Valley Civilisation (2600 to 1900 BCE).
- The site is a rural Harappan settlement. It has been identified through terracotta cakes, pottery, stone tools, and chert blade fragments, linking it to the Sindh Harappan network.
- The artefacts, like the chert blades (a type of stone), show long-distance trade and resource sharing, typical of the Indus Valley cities.
Indus Valley Civilisation
- About: The Harappan Civilization, also known as the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), flourished around 2500 BCE along the Indus River.
- It was the largest of the four ancient urban civilizations alongside Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China.
- The IVC is classified as a Bronze Age civilization due to the discovery of numerous artefacts made from copper-based alloys.
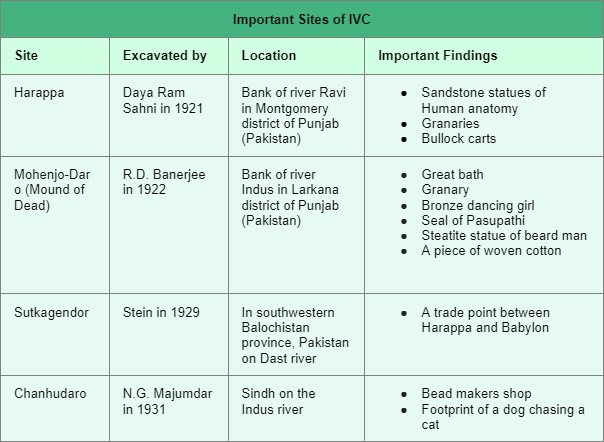
- Daya Ram Sahni first excavated Harappa in 1921-22, and Rakhal Das Banerji began excavating Mohenjo-daro in 1922.
- Sir John Marshall, DG of ASI, was responsible for the excavations that led to the discovery of the Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro sites of the IVC.
- Phases: As per NCERT, the total time span of the civilization ranges from 6000 BCE to 1300 BCE. Phases of the Civilization:
- Early Harappan (6000 BCE - 2600 BCE): This is the formative phase of the civilization.
- Mature Harappan (2600 BCE - 1900 BCE): The urban phase (Mature Harappan), which is the most prosperous phase of the civilization.
- Late Harappan (1900 BCE - 1300 BCE): The decadent phase, when the civilization began to decline.
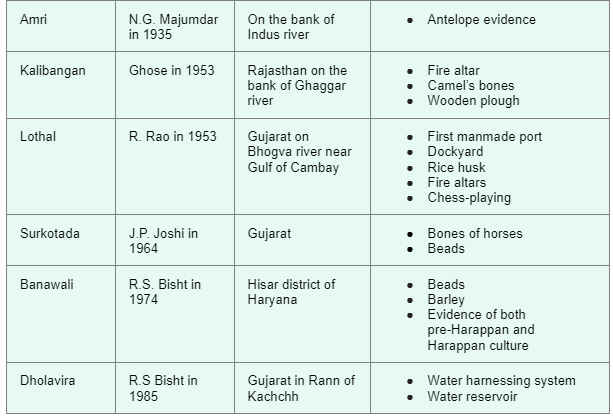
- Important Sites of Harappan Civilization:
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Holy Water Exchange Programme
Why in News?
On the third Monday (28th July 2025) of the sacred Shrawan month, Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath launched a historic holy water exchange programme between the Kashi Vishwanath Temple and the Shri Rameswaram Jyotirlinga.
Key Points
- Background: The exchange programme is part of Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Kashi-Tamil Sangamam initiative, aimed at fostering closer ties between the people of Kashi (Varanasi) and Tamil Nadu.
- Sacred Water and Sands Exchange: The exchange involved urns filled with sacred water and sands: from Prayagraj's Triveni Sangam (Holy confluence of Ganga, Yamuna, and mythical Saraswati) and Rameswaram Kodi Tirtham (Sacred water from the Rameswaram temple in Tamil Nadu).
- These were exchanged between the representatives of the Devakottai Zamindar Family Trust (DZFT) of Shri Rameswaram Jyotirlinga and officials of Kashi Vishwanath Temple Trust.
- The exchanged water will be used for the 'Jalabhishek' (ritual bathing) of both Lord Vishwanath and Lord Ramanathaswamy.
- Future Rituals: The Jalabhishek of Lord Vishwanath will take place on Shrawan Purnima, 9th August 2025, using the water brought from Rameswaram.
- Significance: This initiative strengthens the connection between Kashi and Tamil Nadu while reviving and preserving a sacred tradition for future generations, as described in the scriptures.
Kashi Tamil Sangamam
- About: It is a cultural initiative that aims to celebrate the deep-rooted historical and cultural ties and strengthen the ancient civilizational bond between Tamil Nadu and Kashi (Varanasi).
- The event aligns with the Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat initiative, emphasizing the integration of India’s diverse cultural heritage.
- The 3rd edition of Kashi Tamil Sangamam (KTS 3.0), a cultural confluence between Tamil Nadu and Kashi, took place in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh in February 2025.
- Historical Significance:
- The historical ties between Kashi (Uttar Pradesh) and Tamil Nadu date back to the 15th century when King Parakrama Pandya of Madurai traveled to Kashi to bring back a sacred lingam for his temple (Sivakasi, Tamil Nadu).
- The Pandya rulers also established the Kasi Viswanathar Temple in Tenkasi, located in southwestern Tamil Nadu, near the Kerala border.
- This deep-rooted spiritual and cultural connection underscores the essence of the Kashi Tamil Sangamam initiative.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Vipul Pancholi Appointed Chief Justice of Patna HC
Why in News?
Justice Vipul M. Pancholi was sworn in as the 45th Chief Justice of the Patna High Court (HC) at the Raj Bhavan in Patna, with Bihar Governor Arif Mohammed Khan administering the oath of office.
- He succeeded Justice Krishnan Vinod Chandran, who was elevated to the Supreme Court of India.
- Earlier, Justice Vipul served as an advocate in the Gujarat High Court and as a judge of both the Gujarat High Court and the Patna High Court.
Key Facts About Patna High Court (HC)
- Creation: The Patna High Court was established following a proclamation by the Governor-General of India in 1912, which promoted Bihar and Orissa to the status of a separate province.
- Foundation: The foundation stone of the Patna High Court building was laid on 1st December 1913, by Lord Hardinge, the Viceroy and Governor-General of India.
- The first Chief Justice of the Patna High Court was Sir Edward Maynard Des Champs Chamier (March 1916- October 1917).
- Post-Independence: After India became a republic in 1950, the Patna High Court's jurisdiction was extended, allowing it to issue writs under Article 226 of the Indian Constitution.
- The first Chief Justice of the Patna High Court in independent India was Sir Clifford Monmohan Agarwala (January 1948- January 1950).
Composition & Appointment of High Court Judges
- Composition: Each High Court consists of a Chief Justice and other judges as determined by the President.
- The President decides the strength of a High Court based on its workload.
- Appointment of High Court Judges: A High Court (HC) judge is appointed by the President under Article 217 of the Constitution.
- The Chief Justice is appointed by the President after consultation with the Chief Justice of India and the Governor of the state concerned.
- For the appointment of other judges, the chief justice of the concerned high court is also consulted.
- In case of a common high court for two or more states, the governors of all the states concerned are consulted by the President.
- The oath to a High Court judge is administered by the governor of that state.
- Qualifications of Judges: A person to be appointed as a judge of a High Court should have the following qualifications:
- He should be a citizen of India.
- He should have held a judicial office in the territory of India for ten years, or
- He should have been an advocate of a High Court (or High Courts in succession) for ten years.
- Minimum Age: The Constitution does not prescribe a minimum age for appointment as a judge of a High Court.
- Tenure of Judges: A judge of a High Court can hold office until he attains the age of 62 years.
High Courts in India
- Position: The High Court operates below the Supreme Court and above subordinate courts in India's judicial system.
- The High Court is the highest judicial body in the state (total 25 High Courts in India).
- Constitutional Provisions:
- High Court for each State: The Constitution of India provides for a High Court for each state (Article 214).
- Article 231 provides that the Parliament may by law establish a common High Court for two or more States or for two or more States and a Union Territory.
- Jurisdiction: Territorial jurisdiction is co-terminus with the state’s territory (or a common High Court’s jurisdiction is co-terminus with the territories of the concerned states and Union Territories).
- Articles 214 to 231: These deal with the organization, independence, jurisdiction, powers, and procedures of High Courts.
- High Court for each State: The Constitution of India provides for a High Court for each state (Article 214).
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Weather Information Network and Data System (WINDS) Project
Why in News?
The state government has allocated Rs 9.77 crore for the Weather Information Network and Data System (WINDS) project, out of a total of Rs 60 crore allocated for the current fiscal year (2025-26).
Key Points
- About: WINDS is a programmatic initiative to strengthen weather data infrastructure in the country and to provide good-quality weather datasets from a single digital platform.
- Launched by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare in July 2023, it is a national-level initiative that integrates the existing infrastructure and expertise available with the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), various State Governments, and public/private technical organizations.
- Objective: The WINDS project aims to provide hyper-local weather forecasting to boost agricultural productivity.
- Components: The project will involve the installation of weather stations and rain gauges at the block and panchayat levels.
- Weather Stations: A total of 308 automatic weather stations will be installed in selected blocks to provide precise and real-time weather data for local areas.
- Rain Gauges: Around 55,570 rain gauges will be set up across gram panchayats to measure rainfall and determine local rainfall patterns.
- Additional Infrastructure:
- 518 weather stations are under construction by the revenue department and the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Expected Benefits:
- Agricultural Productivity: With precise weather forecasts, farmers will be better prepared for extreme weather events like droughts, floods, and storms.
- This will help farmers take preemptive measures to protect their crops and plan for optimal harvesting times.
- Risk Assessment & Loss Estimation: WINDS will assist in estimating losses caused to horticultural crops during extreme weather conditions, helping stakeholders respond effectively.
- Crop Insurance & Agriculture Programs: The weather data will be used to decide crop insurance and aid in other agricultural programs, thus boosting overall productivity.
- Air Quality Monitoring: The project also focuses on improving air quality monitoring through the development of low-cost, reliable, sensor-based systems.
- Technological Advantage: WINDS employs advanced weather data analytics to provide actionable insights for agriculture.
- The system aims to generate hyper-local weather data, which will support farmers in making informed decisions regarding irrigation, sowing, and harvesting.
- Agricultural Productivity: With precise weather forecasts, farmers will be better prepared for extreme weather events like droughts, floods, and storms.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
CM Yogi Awards Over Jobs to Athletes
Why in News?
On the occasion of Nag Panchami, during the conclusion of the Uttar Pradesh Senior Wrestling Competition held at Gorakhnath Temple, CM Yogi Adityanath announced that over 500 athletes in Uttar Pradesh have been provided with government jobs as part of the state's commitment to promoting sports.
Key Points
- Wrestling Awards and Recognition: During the wrestling competition, the CM awarded prestigious titles such as UP Kesari, UP Kumar, and UP Veer Abhimanyu to the winners. The awardees included:
- UP Kesari: Jonty Bhati (Gautam Buddh Nagar) received ₹1.01 lakh and a mace.
- UP Kumar: Saurabh (Gorakhpur) received ₹1.01 lakh and a mace.
- UP Veer Abhimanyu: Monu (Gonda) received ₹51,000 and a mace.
- The CM also awarded ₹21,000 to third-place winners and ₹11,000 to the fourth-place winners in each category.
- Government Jobs for Athletes: Under the state’s sports policy, athletes who have excelled in Olympics, Asian Games, Commonwealth Games, World Championships, and National Games are being provided with government employment.
- Sports Infrastructure Development: CM emphasized the government’s efforts over the last eight years to develop sports infrastructure at the village, block, and district levels.
- Key developments include the construction of sports grounds at the village level, mini-stadiums at the block level, and full stadiums at the district level.
- Role of Sports in Personal and Social Development: Reflecting on the importance of sports, CM Yogi quoted a phrase from ancient Indian philosophy, “Sharir Madhyam Khalu Dharm Sadhanam”, meaning that a healthy body is essential for the fulfillment of religious duties.
Key Points of the Uttar Pradesh Sports Policy 2023
- Creation of Uttar Pradesh Sports Development Fund (UPSDF): ₹10 crore fund to support infrastructure, athletes, associations, and academies, especially those lacking resources.
- Institutional Support: Formation of a State Sports Authority to manage sports policy, talent mapping, and infrastructure development.
- Centers of Excellence & Infrastructure:
- Up to 14 sports-specific Centres of Excellence under the PPP model.
- Five High Performance Centres for elite training.
- Sports centers in every district with improved facilities (hostels, fitness experts, diet experts).
- Focus on district, block, and village-level sports infrastructure (stadiums, mini-stadiums, playgrounds).
- Athlete Development: Athletes divided into three tiers: Grassroots (beginner), Developmental (talented) and Elite (top performers).
- Focus on Inclusivity:
- Special emphasis on women’s participation and para-athletes (with exclusive coaches).
- Cashless health insurance up to ₹5 lakh for registered players, coaches, and families under the Ayushman scheme.
- State pension for players who represented UP nationally/internationally.
- Promotion of E-Sports and Indigenous Games: First state in India to include e-sports in official policy.
- Encouragement of indigenous/local games.
- Linkage with Education: 40 minutes of sports, physical education, or yoga included in school timetables.
- Promotion of sports nurseries/academies in schools.
- Sports Industry and Tourism: Support for making UP a hub for sports goods manufacturing (e.g., Meerut cluster).
- Boosting sports tourism.
- Comprehensive Talent Search & Khelo India Integration: Active participation in Khelo India University Games.
- Talent identification through university and academy competitions.
- Health and Welfare Measures: Eklavya Sports Fund for injury treatment and welfare.
- Personal accident insurance for athletes and coaches.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh to Establish 5 Seed Parks
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government is aiming to make the state self-reliant in high-quality seed production by establishing five state-of-the-art seed parks across different agro-climatic zones.
Key Points
- About: The seed parks will address region-specific crop needs and ensure the availability of quality seeds, with an investment of Rs 2,500 crore over the next three years.
- The agriculture department has identified six large farms with existing infrastructure (ranging from 200 to 400+ hectares), which will be leased to private entities for seed production.
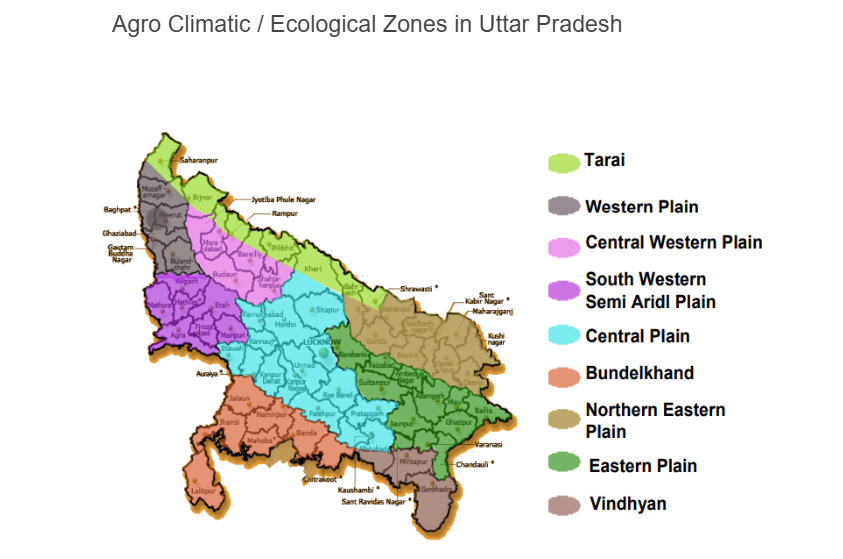
- Locations: The Seed Parks will be established in Western UP, Terai, Central UP, Bundelkhand, and Eastern UP.
- The first seed park, named after former Prime Minister Chaudhary Charan Singh, will be established in Attari, Lucknow. It will feature facilities for seed production, processing, storage, speed breeding, and hybrid laboratories.
- Model: The government is using a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model, offering incentives to private investors, with land leases for 30 years, extendable up to 90 years.
- Benefit: Uttar Pradesh, with its large agricultural base, stands to benefit greatly from this initiative. Key benefits include:
- Job Creation: Across all five parks, approximately 6,000 direct jobs and 15,000 indirect jobs will be generated, benefiting nearly 40,000 seed-producing farmers.
- Self-Reliance in Seed Production: The state expects to save around Rs 3,000 crore annually by producing seeds locally, strengthening the local economy, and creating jobs in production, logistics, and transport.
- Seed Replacement Rate (SRR): This initiative is expected to improve the SRR, directly impacting crop yields.
- Potential Yield Improvement: Officials estimate that better seed availability could narrow the yield gap by 15-20%.
- Uttar Pradesh has the largest cultivable land and the highest irrigated area in the country, but lags behind states like Punjab and Haryana in per-hectare yields.
- Quality Issues: The establishment of these seed parks will ensure better seed quality for farmers across Uttar Pradesh.
- Poor-quality seeds, identified in 3,630 out of 1,33,588 tested samples in the 2023-2024 Seed Test Report, lead to low germination rates, delayed re-sowing, wasted investments in land preparation and fertilizers, and ultimately, reduced crop yields.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP’s 1st Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI)
Why in News?
The LPS Cardiology Institute in Kanpur has become the first government medical college in Uttar Pradesh to offer TAVI (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) for heart valve replacement in elderly patients.
- TAVI avoids open-heart surgery by implanting a new valve without intense invasive procedure. It promises to reduce risks and improve the quality of life for senior heart patients.
Key Points
- TAVI: TAVI is a minimally invasive procedure that involves implanting a new aortic valve using a catheter inserted through a vein in the patient's leg.
- Unlike traditional open-heart surgery, TAVI avoids the need for large incisions, reducing recovery time and risks, especially for elderly patients.
- Procedure and Benefits: The new valve, made from the membrane of animal hearts, is implanted in place of the damaged valve.
- Unlike metal valves, which come with higher risks, animal membrane valves have a longer lifespan of 15 years.
- Global Significance and History: The TAVI technique was pioneered by German specialist Dr. Alain Kreebeyer in the early 1990s and was first implemented in 2002.
- India adopted this innovative procedure in 2010.
- India adopted this innovative procedure in 2010.
Human Heart
- Function: Pumps blood throughout the body via blood vessels, supplying oxygen and nutrients, and removing waste products.
- Heart Wall:
- Epicardium: Outer layer.
- Myocardium: Middle muscular layer (responsible for heart contraction).
- Endocardium: Inner lining.
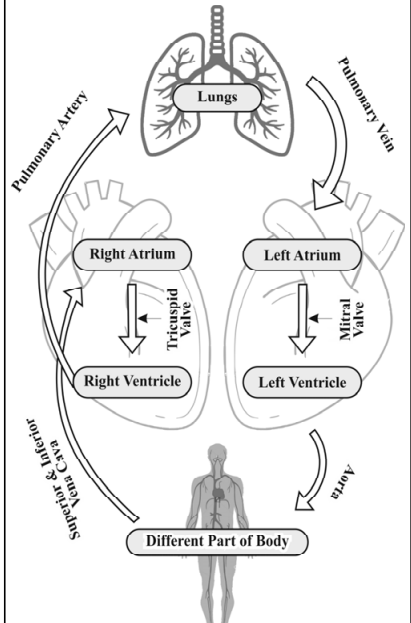
- Chambers of the Heart:
- Atria (upper chambers): Receive blood.
- Ventricles (lower chambers): Pump blood.
- Right Heart: Right atrium + right ventricle.
- Left Heart: Left atrium + left ventricle.
- Septum: Divides the left and right sides of the heart.
- Heart Valves: Prevent backflow of blood, ensuring one-direction flow.
- Pacemaker and Heart Rhythm: Controlled by the Sinoatrial (SA) Node, generating electrical impulses.
- Heart rate: 60-100 beats per minute at rest.
- Blood Flow:
- Deoxygenated Blood: From body → right atrium → right ventricle → lungs (oxygenated).
- Oxygenated Blood: From lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → body.
- Tachycardia:
- Heart rate > 100 beats per minute.
- Caused by stress, medications, or underlying heart conditions.
- Key Figures:
- William Harvey: Discovered blood circulation.
- Dr. Christian Barnard: First successful heart transplant in 1967.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Delhi to Adopt UP's Digital Grievance Redressal Model
Why in News?
Delhi is set to adopt Uttar Pradesh (UP)'s Integrated Grievance Redressal System (IGRS) and the CM Dashboard to improve governance and ensure efficient grievance management.
Key Points
- About: IGRS is a comprehensive grievance redressal system in Uttar Pradesh aimed at promoting good governance through the use of advanced technology and involving all stakeholders.
- Key Features:
- Citizens can easily and conveniently file grievances, track them across various platforms, and receive timely and satisfactory responses in terms of both quality and resolution.
- The system allows citizens to interact transparently with Government Departments/Offices, facilitating a smooth communication process.
- All complaints, regardless of the source, are centralized on a single platform, enhancing accessibility, monitoring, and effective resolution by relevant departments.
UP-DARPAN Dashboard (CM Dashboard)
- UP-DARPAN Dashboard for the Chief Minister helps in analytical review of projects/schemes through department ranking, district ranking, Timeline Series, and Statistical Graphical reports.
- D A R P A N (Dashboard for Analytical Review of Projects Across Nation) is a configurable multilingual product of the National Informatics Centre (NIC).
- It facilitates the presentation of real-time data on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) of selected government schemes/projects to all the levels (State, Division, District) of officers for planning, evaluation, and monitoring.
- DARPAN provides seamless authentication and integration with the user repository through secure APIs for automatic update of data on a predefined frequency.
- D A R P A N (Dashboard for Analytical Review of Projects Across Nation) is a configurable multilingual product of the National Informatics Centre (NIC).
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Satish Prasad Singh: Bihar's Shortest-Serving CM
Why in News?
As Bihar heads toward the 2025 Assembly Elections, the state’s political history is being revisited, with particular focus on its leaders. Among them, Satish Prasad Singh, the sixth Chief Minister of Bihar, holds the record for the shortest tenure as CM, serving just 4 days.
Key Points
- Shortest Tenure as CM: Satish Prasad Singh created history by serving as Bihar’s Chief Minister for just four days, from 28th January 1968 to 1st February 1968.
- His term was marked by political instability, as he was appointed as a stopgap CM before the rise of B.P. Mandal.
- Political Beginnings: Satish Prasad Singh, born in Khagaria, was deeply influenced by socialist ideologies from an early age.
- His political career was shaped by his dedication to social justice and the farmers' cause.
Longest-serving Chief Minister
- Nitish Kumar is currently the longest-serving Chief Minister in Bihar with a total tenure of over 18 years (as of 2025). He broke the previous record held by Sri Krishna Sinha, who served for 17 years and 52 days.
- Longest Continuous Term: Sri Krishna Sinha still holds this record with 14 years and 314 days of uninterrupted service.
- Nitish Kumar's longest continuous term: 8 years and 239 days (2005-2014, with brief interruption by Jitan Ram Manjhi).
- CM Who Has Taken Maximum Number of Oaths: Nitish Kumar holds the record for taking the maximum number of oaths as Chief Minister (sworn in 9 times as the CM of Bihar).
- Bihar has experienced President's Rule 8 times since its formation as a state (Total 37 terms including 8 periods of President's Rule).
Note
- Under the Government of India Act 1935, the heads of provincial governments in British India were officially designated as "Prime Ministers" or "Premiers" (not Chief Ministers).
- Mohammad Yunus (1 April 1937 – 19 July 1937) was the first Prime Minister of Bihar Province, serving for 109 days under the Muslim Independent Party. Notably, he was the first person to take the oath as 'Prime Minister' in all of British India.
Complete List of Bihar Chief Ministers (1947-2025)
|
S. No. |
Name |
Tenure |
Political Party/Alliance |
|
1 |
Sri Krishna Sinha |
15 Aug 1947– 31 Jan 1961 |
Indian National Congress |
|
2 |
Deep Narayan Singh |
1 Feb 1961 – 18 Feb 1961 |
Indian National Congress |
|
3 |
Binodanand Jha |
18 Feb 1961 – 2 Oct 1963 |
Indian National Congress |
|
4 |
Krishna Ballabh Sahay |
2 Oct 1963 – 5 Mar 1967 |
Indian National Congress |
|
5 |
Mahamaya Prasad Sinha |
5 Mar 1967 – 28 Jan 1968 |
Jana Kranti Dal |
|
6 |
Satish Prasad Singh |
28 Jan 1968 – 1 Feb 1968 |
Shoshit Dal |
|
7 |
Bindeshwari Prasad Mandal (B.P. Mandal) |
1 Feb 1968 – 22 Mar 1968 |
Shoshit Dal |
|
— |
President's Rule |
29 Jun 1968 – 26 Feb 1969 |
— |
|
8 |
Harihar Singh |
26 Feb 1969 – 22 Jun 1969 |
Indian National Congress |
|
9 |
Bhola Paswan Shastri |
22 Jun 1969 – 4 Jul 1969 |
Indian National Congress |
|
— |
President's Rule |
4 Jul 1969 – 16 Feb 1970 |
— |
|
10 |
Daroga Prasad Rai |
16 Feb 1970 – 22 Dec 1970 |
Indian National Congress |
|
11 |
Karpoori Thakur |
22 Dec 1970 – 2 Jun 1971 |
Samyukta Socialist Party |
|
12 |
Bhola Paswan Shastri |
2 Jun 1971 – 9 Jan 1972 |
Indian National Congress |
|
— |
President's Rule |
9 Jan 1972 – 19 Mar 1972 |
— |
|
13 |
Kedar Pandey |
19 Mar 1972 – 2 Jul 1973 |
Indian National Congress |
|
14 |
Abdul Gafoor |
2 Jul 1973 – 11 Apr 1975 |
Indian National Congress |
|
15 |
Jagannath Mishra |
11 Apr 1975 – 30 Apr 1977 |
Indian National Congress |
|
— |
President's Rule |
30 Apr 1977 – 24 Jun 1977 |
— |
|
16 |
Karpoori Thakur |
24 Jun 1977 – 21 Apr 1979 |
Janata Party |
|
17 |
Ram Sundar Das |
21 Apr 1979 – 17 Feb 1980 |
Janata Party (Secular) |
|
— |
President's Rule |
17 Feb 1980 – 8 Jun 1980 |
— |
|
18 |
Jagannath Mishra |
8 Jun 1980 – 14 Aug 1983 |
Indian National Congress |
|
19 |
Chandrashekhar Singh |
14 Aug 1983 – 12 Mar 1985 |
Indian National Congress |
|
20 |
Bindeshwari Dubey |
12 Mar 1985 – 13 Feb 1988 |
Indian National Congress |
|
21 |
Bhagwat Jha Azad |
14 Feb 1988 – 10 Mar 1989 |
Indian National Congress |
|
22 |
Satyendra Narayan Sinha |
11 Mar 1989 – 6 Dec 1989 |
Indian National Congress |
|
23 |
Jagannath Mishra |
6 Dec 1989 – 10 Mar 1990 |
Indian National Congress |
|
24 |
Lalu Prasad Yadav |
10 Mar 1990 – 28 Mar 1995 |
Janata Dal |
|
— |
President's Rule |
28 Mar 1995 – 5 Apr 1995 |
— |
|
25 |
Lalu Prasad Yadav |
5 Apr 1995 – 25 Jul 1997 |
Janata Dal / Rashtriya Janata Dal |
|
26 |
Rabri Devi |
25 Jul 1997 – 11 Feb 1999 |
Rashtriya Janata Dal |
|
— |
President's Rule |
11 Feb 1999 – 9 Mar 1999 |
— |
|
27 |
Rabri Devi |
9 Mar 1999 – 2 Mar 2000 |
Rashtriya Janata Dal |
|
28 |
Nitish Kumar |
3 Mar 2000 – 10 Mar 2000 |
Samata Party |
|
29 |
Rabri Devi |
11 Mar 2000 – 6 Mar 2005 |
Rashtriya Janata Dal |
|
— |
President's Rule |
7 Mar 2005 – 24 Nov 2005 |
— |
|
30 |
Nitish Kumar |
24 Nov 2005 – 17 May 2014 |
Janata Dal (United) |
|
31 |
Jitan Ram Manjhi |
20 May 2014 – 22 Feb 2015 |
Janata Dal (United) |
|
32 |
Nitish Kumar |
22 Feb 2015 – 20 Nov 2015 |
Janata Dal (United) |
|
33 |
Nitish Kumar |
20 Nov 2015 – 26 Jul 2017 |
Janata Dal (United) - Mahagathbandhan |
|
34 |
Nitish Kumar |
27 Jul 2017 – 16 Nov 2020 |
Janata Dal (United) - NDA |
|
35 |
Nitish Kumar |
16 Nov 2020 – 9 Aug 2022 |
Janata Dal (United) - NDA |
|
36 |
Nitish Kumar |
10 Aug 2022 – 28 Jan 2024 |
Janata Dal (United) - Mahagathbandhan |
|
37 |
Nitish Kumar |
28 Jan 2024 – Present |
Janata Dal (United) - NDA |
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Polygamy in Haryana and Haryana Family Identity Card
Why in News?
Recent data from the Haryana Family Identity Card (Parivar Pehchan Patra (PPP)) has revealed that several individuals in the state have two or more wives.
- The data has been voluntarily shared by these individuals, reflecting personal details such as the number of wives and their children.
Key Points
- Details from PPP Data: There are 2779 people in Haryana who have two or more wives.
- Of these, 2761 individuals have two wives, while 15 people have three, and 3 individuals reported having more than three wives.
- Regional Statistics: The highest number of people with two wives is found in Nuh, where 353 individuals have two wives.
- Other districts with significant numbers include Ambala (87), Bhiwani (69), and Faridabad (267), among others.
Family Identity Card (Parivar Pehchan Patra) Scheme
- Background: The PPP scheme was formally launched in July 2019 to achieve the Haryana government’s vision for ‘paperless’ and ‘faceless’ delivery of schemes, services, and benefits offered by the state government.
- Under this, each family is considered a single unit and gets an 8-digit unique identification number, called family ID.
- Family IDs are also linked to independent schemes like scholarships, subsidies and pensions, so as to ensure consistency and reliability.
- It also enables automatic selection of beneficiaries of various schemes, subsidies and pensions.
- Objective: The primary objective of Parivar Pehchan Patra (PPP) is to create authentic, verified and reliable data of all families in Haryana.
- Benefits of PPP:
- Family as a Unit: Union government’s Aadhaar card contains an individual's details and does not cater to the entire family as a unit.
- Although the ration card system is there, it is not updated and does not contain adequate family records.
- Smooth Service Delivery: Government services and schemes such as social security pensions, ration cards and birth, death, caste and income certificates etc. are being delivered by various departments of the Haryana government through PPP.
- Beneficial for Migrant Workers: Registration IDs are provided to those who live in Haryana but have not completed residency requirements.
- This enables the State government to provide benefits such as rations from fair price shops, benefits of labour schemes, street vendors’ support schemes, etc.
- Family as a Unit: Union government’s Aadhaar card contains an individual's details and does not cater to the entire family as a unit.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan