Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Revival of Mandal Dam Project
Why in News?
The Jharkhand government has approved the relocation of seven villages situated in the submergence zone of the Mandal Dam in the Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR).
Key Points
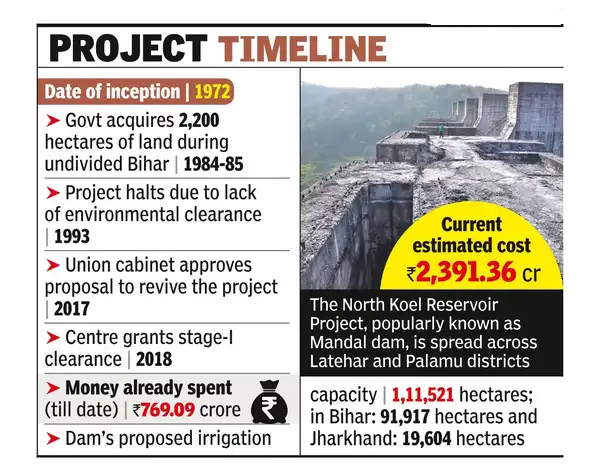
- About the Mandal Dam Project: The Mandal Dam is located in the PTR covering parts of Garhwa, Latehar, and Palamu districts in Jharkhand on the North Koel River, a tributary of the Sone River.
- The project was originally conceived decades ago but has remained non-functional due to local opposition and lack of consensus on rehabilitation and environmental concerns.
- A task force was also set up in 2015 to speed up the clearances.
- The project gained momentum when the Prime Minister laid its foundation stone in January 2019.
- PTR will benefit from the project as the vacated land will be submerged, forming a large water body that can help reduce the persistent problem of human-animal conflict in the districts.
- The project was originally conceived decades ago but has remained non-functional due to local opposition and lack of consensus on rehabilitation and environmental concerns.
- Relocation of Villages: Seven villages, including Kutku, Bhajna, Khura, Khaira, Saneya, Chemo, and Meral, will be relocated.
- Each household will get one acre of land and Rs 15 lakh as compensation.
- The relocated area will be developed as a model cluster to provide better living conditions for the villagers.
Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR)
- PTR is located on the Chhotanagpur plateau in western Latehar district, Jharkhand.
- 'Betla National Park' is situated within 226.32 sq km of the Palamu Tiger Reserve, which is spread over a total area of 1,129.93 sq km.
- The project area is constituted mainly of Sal forests, mixed deciduous forests and bamboo groves.
- The reserve zone is the watershed area for 3 important rivers Koel, Burha and Auranga.
- It was constituted in 1974 under Project Tiger and is one of the first nine tiger reserves established in the country at the inception of the project.
- It was the first sanctuary in the world to conduct a tiger census using pugmark counts, done in 1932.
- The keystone species include Tigers, Elephants, Leopards, Grey Wolf, Gaur, Sloth Bear, Four- horned Antelope, Indian Ratel, Indian Otter and Indian Pangolin.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Tuberculosis Elimination Camp and Healthy Liver Mission
Why in News?
The Governor of Madhya Pradesh honoured stakeholders of the 100-day Ni-Kshay Shivir Abhiyan and launched the state-wide Healthy Liver Mission in Bhopal.
Key Points
100-Day Ni-Kshay Shivir Abhiyan
- Under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Program, the state conducted special health camps to identify TB cases, ensure timely treatment, and raise public awareness about the disease.
- The campaign enabled citizens to receive testing and consultations through the joint efforts of the health department, NGOs, public representatives, and civil society.
- Under this campaign, over 5,000 Gram Panchayats have been declared TB-free.
- Seoni and Betul districts have secured the highest number of TB-free Gram Panchayats for three consecutive years.
- Kanhar (Mandla), Patwa (Balaghat), and Sawarwani (Chhindwara) have achieved TB-free status.
- The state government is striving for 100% coverage under the initiative, aiming to eliminate TB from the state by 2028.
Healthy Liver Mission
- This initiative is aimed at combating liver-related diseases.
- India leads the world in fatty liver disease prevention, with Madhya Pradesh emerging as the top-performing state in the country.
- The mission will focus on awareness, early detection, treatment, and prevention of conditions such as hepatitis B and C, fatty liver, and cirrhosis.
- Under this, the health department will conduct screening camps, provide medical training, offer consultations, and distribute free medicines statewide.
National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- In 2020, the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP) was renamed the NTEP with the goal to eliminate TB in India by 2025, five years ahead of the global target of 2030.
- The program is guided by the National Strategic Plan (2017-2025) under the strategic pillars: Detect – Treat – Prevent – Build (DTPB).
- The NTEP focuses on early diagnosis, quality-assured treatment, engaging private providers, contact tracing in high-risk areas, and addressing social determinants through a multi-sectoral approach.
- The programme recorded its highest-ever case notifications, reporting 25.5 lakh TB cases in 2023 and 26.07 lakh cases in 2024.
- Under NTEP, India introduced improved drug-resistant TB treatments, including a safer, shorter all-oral Bedaquiline regimen, increasing success rates from 68% in 2020 to 75% in 2022.
- The mBPaL regimen (Bedaquiline, Pretomanid, Linezolid) offers 80% success for MDR-TB, reducing treatment duration to six months.
Fatty Liver Disease
- Fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis) is the buildup of excess fat in liver cells.
- It becomes unhealthy when fat exceeds 5% of liver cells (hepatocytes), affecting liver function and metabolism.
- It is of 2 types- NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) & Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Tribes Advisory Council (TAC) Meet in Jharkhand
Why in News?
Jharkhand Chief Minister Hemant Soren chaired the Tribes Advisory Council (TAC) meeting.
- The aim is to implement Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) rules, ease land sale norms, improve tribal welfare, and preserve tribal culture and traditions in the state.
Key Points
Tribes Advisory Councils (TACs)
- Constitutional Provision: As per Article 244(1) of the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution:
- TACs must be established in each state with Scheduled Areas.
- The President may direct the formation of TACs in states with Scheduled Tribes but no Scheduled Areas.
- Objective: TAC is responsible for advising on issues related to the welfare and advancement of Scheduled Tribes in the State whenever referred to it by the Governor.
- Council Composition:
- TAC shall consist of not more than 20 members.
- Around three-fourths must be Scheduled Tribe (ST) representatives from the State Legislative Assembly.
- States with TACs in Scheduled Areas: TACs have been formed in the following 10 states with Scheduled Areas — Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha and Rajasthan.
- States with TACs but No Scheduled Areas: West Bengal, Tamil Nadu and Uttarakhand.
Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act, 1996
- About:
- The PESA Act was enacted on 24th December 1996 to ensure self-governance for people living in tribal areas, called Scheduled Areas, through traditional village assemblies known as Gram Sabhas.
- The Act extended the provisions of Panchayats by providing self-tribal rule to the tribal areas of Fifth Schedule states.
- Legislation:
- The Act defines Scheduled Areas as those mentioned in Article 244(1), which states that the Fifth Schedule applies to Scheduled Areas and Scheduled Tribes in states other than Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- Significant Provisions:
- The PESA Act establishes the Gram Sabha as a forum for community participation in the development process. It is responsible for identifying development projects, preparing development plans, and implementing these plans.
- The Act mandates the establishment of village-level institutions, including the Gram Panchayat, the Gram Sabha, and the Panchayat Samiti, to carry out development activities and provide basic services to the community.
- Gram Sabha and the Gram Panchayat are granted significant powers and functions related to managing natural resources and regulating economic activities.
- The Act provides for the protection of land rights of tribal communities in the Scheduled Areas, requiring their consent before any land is acquired or transferred.
- The Act safeguards the cultural and social practices of tribal communities in the Scheduled Areas, prohibiting any interference in these practices.
Note
- Jharkhand has the 12th largest tribal population in India, comprising 8.3% of the country’s Scheduled Tribes.
- Major Tribes of Jharkhand:
- Gondi (one of the largest groups in India)
- Munda (one of India's largest scheduled tribes)
- Santal (largest tribe in the Jharkhand state of India in terms of population)
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Railway Stations Redeveloped under Amrit Bharat Scheme (ABSS)
Why in News?
The Prime Minister inaugurated three redeveloped railway stations in West Bengal—Kalyani Ghoshpara, Panagarh, and Joychandi Pahar, as part of the nationwide launch of 103 Amrit Stations under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS).
Key Points
- Amrit Bharat Station Scheme:
- About & Objective:
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme was launched in December 2022 by the Ministry of Railways.
- The scheme aims to redevelop 1309 stations nationwide.
- The redevelopment will provide modern passenger amenities along with ensuring well-designed traffic circulation, inter-modal integration, and signage for the guidance of passengers.
- Focused efforts will enhance the stations’ greenery and visual appeal to create a more inviting environment for passengers.
- Under this scheme, local products will be showcased and sold under the ‘One Station One Product’ scheme.
- Integrated Approach to Urban Development:
- The redevelopment is planned with a holistic approach to urban development, treating the stations as "City Centres."
- This approach aims to integrate both sides of the city and create well-designed traffic circulation, inter-modal connectivity, and clear signage for passengers' guidance.
- About & Objective:
Note
- The Indian Railways ranks as the world's fourth-largest railway network, encompassing a track length of 67,368 km. Only the US, China, and Russia have larger networks.
- It's also the world's second-largest network managed under a single administration, spanning 115,000 km.
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites:
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites,
- Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus in Mumbai, Nilgiri Mountain Railway, and Kalka Shimla Railway.
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites,
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Vidya Samiksha Kendra (VSK)
Why in News?
Uttarakhand Chief Minister Pushkar Singh Dhami has announced the inclusion of private schools under the ambit of the Vidya Samiksha Kendra (VSK).
- This initiative aligns with the state’s broader vision to enhance educational outcomes through data-driven governance.
Key Points
- Vidya Samiksha Kendra (VSK):
- About:
- It is a digital infrastructure ecosystem that tracks and analyses data about student enrolment, attendance, academic performance, and teacher training to help administrators monitor school education progress.
- It enables transformative impact through data-driven decision-making aligned with the New Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and various education schemes.
- VSK Implementation in Uttarakhand:
- Uttarakhand is the first state in India to implement the Gujarat model of VSK.
- About:
- Infrastructure Development:
- Construction is underway for 141 Pradhan Mantri Schools for Rising India (PM SHRI schools) and Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Residential Schools.
- Virtual classrooms have been established in several schools across 13 districts to enable technology-driven learning.
- Focus on Educational Enhancements:
- NCERT textbooks are implemented in all government schools to ensure quality education.
- Scholarships awarded to meritorious students from Class 6 to 12 in both government and private schools.
- The new Medhavi Chhatra Protsahan Scholarship Scheme sends meritorious Class 10 and 12 students on educational tours across India.
- Sports and Employment:
- The state government is emphasizing sports promotion.
- Players winning national-level medals will be offered government jobs as incentives.
PM SHRI School
- PM SHRI School is a centrally sponsored scheme to develop over 14,500 schools across India, managed by Central, state/UT governments, local bodies, Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS), and Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti (NVS).
- It is being implemented from 2022-23 to 2026-27.
- The scheme aims to provide a safe, inclusive, and resource-rich learning environment where every student feels welcomed and cared for.
- It aligns with the NEP 2020, nurturing students to become engaged, productive, and responsible citizens.
- The scheme promotes quality school education and helps inform policy, practice, and implementation.
Schemes Related to Education in Uttarakhand
- Mukhyamantri Medhavi Chhatra Protsahan Yojana: For meritorious students of Class 10 and 12 to go on educational tours across India.
- Chief Minister Higher Education Encouragement Scholarship Scheme: Scholarships for meritorious students pursuing graduation and post-graduation in government colleges.
- Nanda Gaura Yojana: Financial assistance for girls from poor families.
- Child Benefit Scheme (UKBOCWWB): Financial aid for children of registered building and construction workers. Supports students from Class I to higher education or professional courses.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)


