Important Facts For Prelims
Hepatitis B: A Public Health Concern In India
- 30 Mar 2024
- 7 min read
Why in News?
A recent study by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, indicates that public awareness and knowledge regarding Hepatitis B, a potentially fatal disease leading to liver cirrhosis and cancer, is insufficient in India.
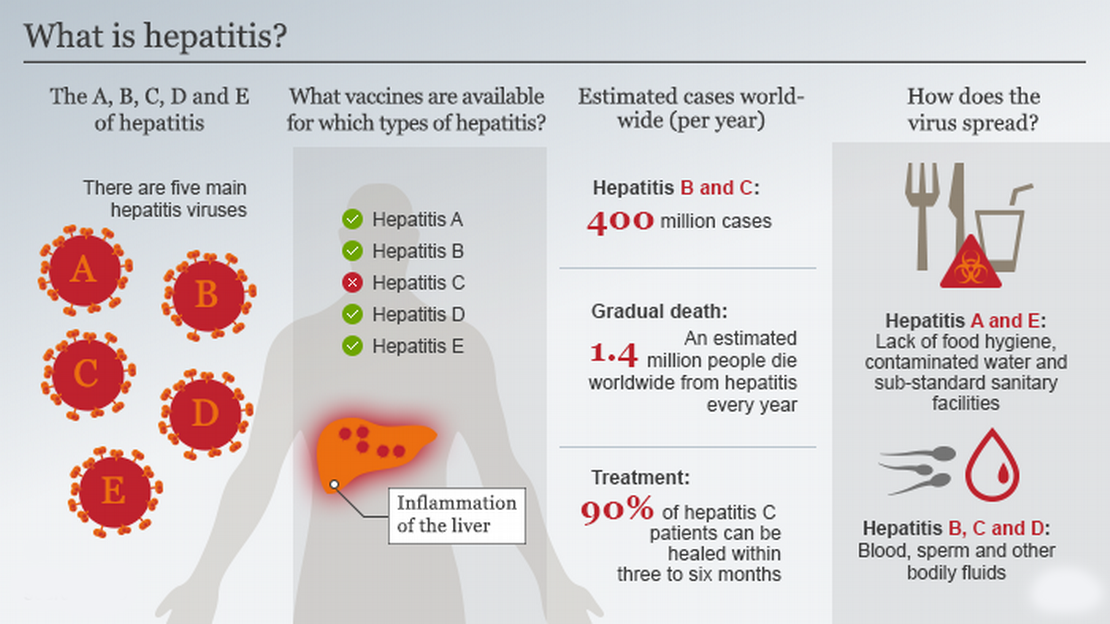
What is Hepatitis?
- About:
- Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver, characterised by irritation or swelling of the liver cells due to various causes.
- Liver inflammation can manifest as either acute, characterised by symptoms like jaundice, fever, and vomiting, or chronic, lasting over six months with no apparent symptoms.
- Symptoms:
- Some individuals infected with hepatitis may not exhibit symptoms, but common ones include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, joint pain, and jaundice.
- Causes:
- Hepatitis is typically caused by hepatotropic viruses, including A, B, C, D, and E, although other viruses like the varicella virus can also lead to the disease.
- SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing Covid-19 may injure the liver too.
- Additional causes encompass drug and alcohol misuse, liver fat accumulation (fatty liver hepatitis), or an autoimmune response where the body produces antibodies targeting the liver (autoimmune hepatitis).
- Hepatitis is typically caused by hepatotropic viruses, including A, B, C, D, and E, although other viruses like the varicella virus can also lead to the disease.
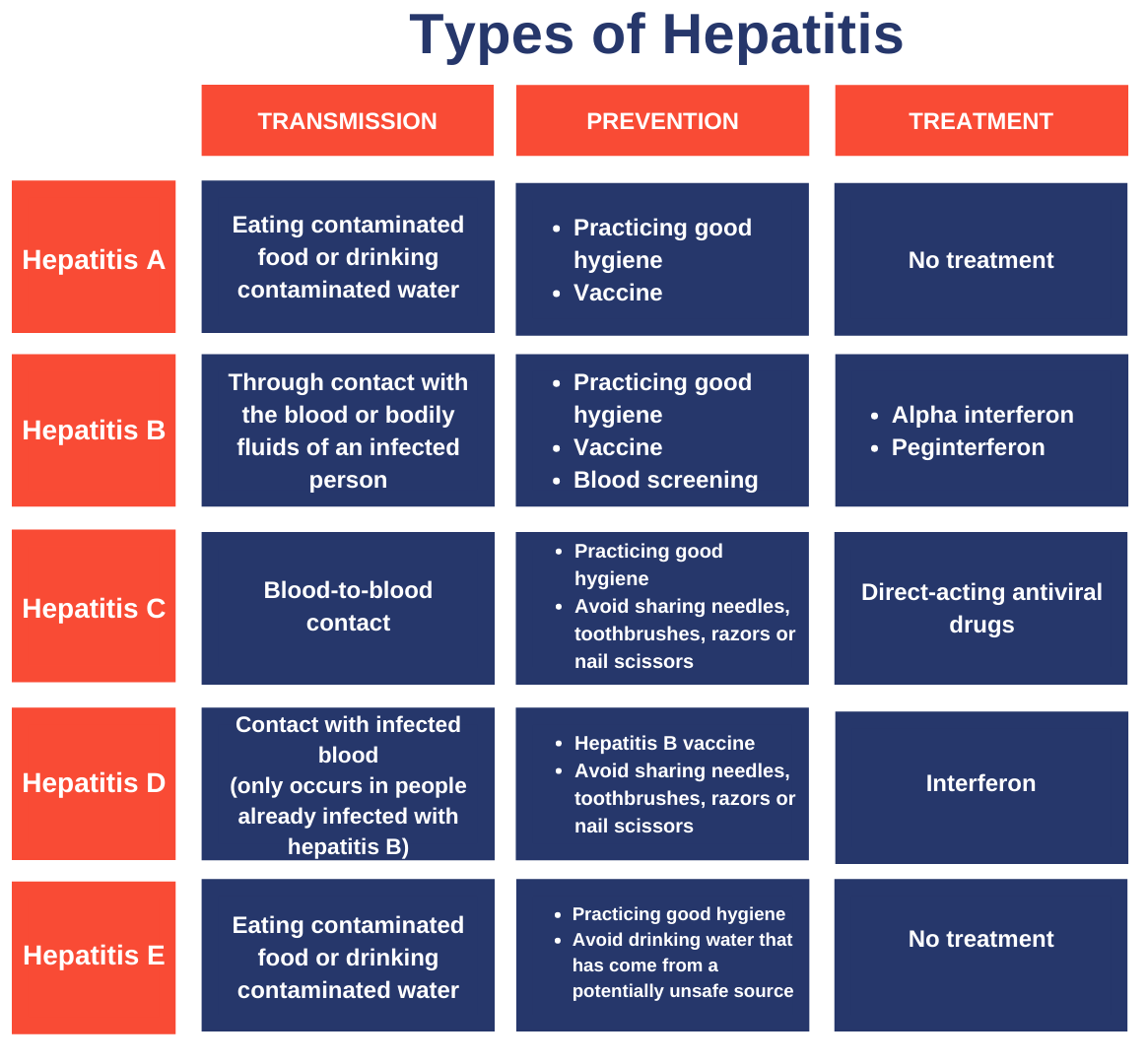
- Types of Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV):
- Hepatitis A is a liver inflammation that ranges from mild to severe, transmitted through contaminated food or water, direct contact with an infected person, and can be prevented with a vaccine, with most people recovering fully and gaining lifelong immunity.
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV):
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can cause acute or chronic liver disease, often transmitted from mother to child, through early childhood contact, or via sex or unsafe injections, but can be prevented by vaccines.
- Hepatitis B vaccines are highly efficacious in preventing HBV infection when administered before exposure to HBV.
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can cause acute or chronic liver disease, often transmitted from mother to child, through early childhood contact, or via sex or unsafe injections, but can be prevented by vaccines.
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV):
- Hepatitis C is a bloodborne virus causing both acute and chronic hepatitis, with severity ranging from mild to serious, including liver cirrhosis and cancer, primarily transmitted through unsafe health care, blood transfusions, injection drug use, and sexual practices.
- The cure rates exceeds 95% using Direct-acting antiviral medicines (DAAs), yet access to diagnosis and treatment is limited, and no effective vaccine exists.
- Hepatitis D virus (HDV):
- Hepatitis D, a virus dependent on hepatitis B virus (HBV) for replication, affects approximately 5% of individuals with chronic HBV infection worldwide, with co-infection or super-infection more prevalent among indigenous populations, dialysis patients, and drug users, posing a severe risk to liver health including the potential for cancer or fatality.
- Its prevention is possible through hepatitis B immunization, treatment efficacy remains limited.
- Hepatitis E virus (HEV):
- Hepatitis E, caused by HEV infection, is globally prevalent, particularly in East and South Asia, transmitted through contaminated water, with a licensed vaccine in China and some other countries and ongoing research for additional vaccines worldwide.
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV):
- Government Initiatives to Tackle Hepatitis:
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program: The National Viral Hepatitis Control Program aims to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health threat in the country by 2030.
- India's Universal Immunization Programme (UIP): India's Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) offers free vaccination against eleven vaccine-preventable diseases, including Hepatitis B, Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio, Pneumonia, Meningitis due to Haemophilus Influenzae type b (Hib), Measles, Rubella, Japanese Encephalitis (JE), and Rotavirus diarrhoea.
- Global Initiatives:
- WHO’s global hepatitis strategy
- Coalition for Global Hepatitis Elimination (CGHE)
- Global Hepatitis Programme
What are the Recommendations Made by the Survey?
- As per the survey, only 22.7% of participants had completed the full Hepatitis B vaccination course.
- Therefore it recommends, ensuring accessibility and reaching all segments of the population, especially those at high risk, is crucial for effective vaccination against HBV, alongside increasing overall vaccination efforts.
- The survey finds that only a quarter of those surveyed had sufficient understanding of the disease, encompassing its transmission, impact on the liver, and the crucial role of vaccination.
- Therefore to deal with widespread misconceptions and insufficient education on Hepatitis B the need for targeted information campaigns to address knowledge gaps is the way out.
- For this, people should be educated on the necessity of completing the entire vaccination regimen for optimal effectiveness, as it is not uncommon for individuals to miss the final dose after receiving one or two doses.
- It recommends educational campaigns should target the general public, especially women, older individuals, those with lower education levels, and rural residents, who showed lower knowledge scores and vaccination rates in the study.
- It concludes that comprehensive strategies, which integrate health literacy and vaccination coverage, are crucial for achieving national and global HBV control targets.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
(b) Hepatitis B unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
(c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses arc several times more than those infected with HIV.
(d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years
Ans: (b)
Q. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)