Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
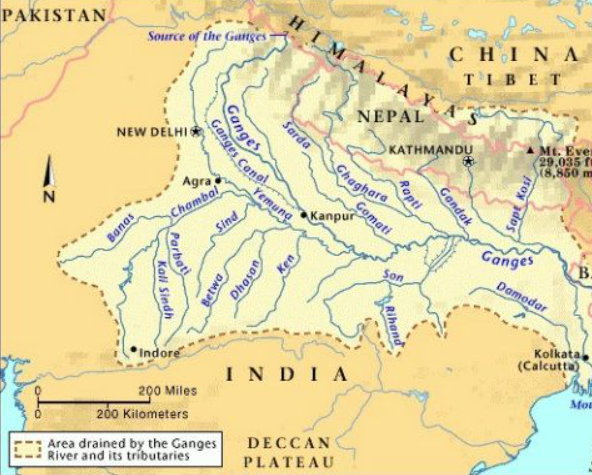
Sharda River
Why in News?
Several people drowned after being caught in the strong currents of the Sharda River near Devraghat in the Sitapur district.
Key Points
- About the Sharda River:
- Origin and Course:
- The Sharda River, also known as the Kali River in its upper reaches, originates in Uttarakhand.
- It rises in the Great Himalayas, on the eastern slopes of the Nanda Devi massif.
- Flowing generally south-southwest, the river forms the boundary between Uttarakhand (India) and western Nepal.
- After descending from the mountains, it enters the Indo-Gangetic Plain at Barmdeo Mandi in Nepal.
- As the river widens above the Sarda Barrage, it is referred to as the Sarda River.
- After crossing into India, the Sarda River flows southeastward through northern Uttar Pradesh.
- It eventually joins the Ghaghara River southwest of Bahraich, covering a total length of approximately 480 km (300 miles).
- Major Tributaries:
- Key tributaries of the Sarda River are Dhauliganga River, Goriganga River, Sarju River.
- Sarda Barrage and Canal System:
- The Sarda Barrage, located near Banbasa in Uttarakhand, plays a significant role in irrigation.
- It serves as the origin of the Sarda Canal, completed in 1930, which is one of northern India’s longest irrigation canals.
- Origin and Course:
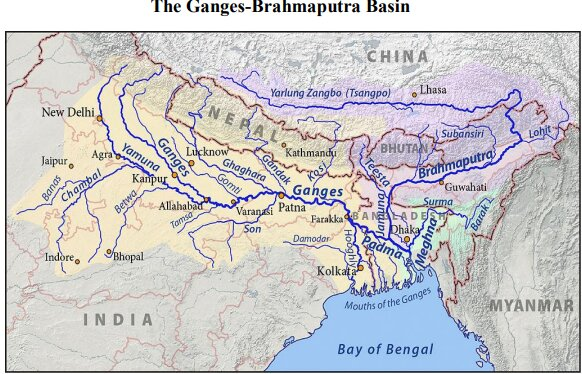
Ghaghara River
- Origin and Upper Course:
- The Ghaghara River is a major left-bank tributary of the Ganges River.
- It originates as the Karnali River in the high Himalayas of the southern Tibet Autonomous Region in China.
- Flowing southeast through Nepal, it descends from the mountains and cuts across the Siwalik Range.
- Formation of the River:
- After crossing the Siwalik Range, the river splits into two branches.
- These branches reunite south of the India-Nepal border, forming what is known as the Ghaghara River.
- Key Tributaries:
- Major tributaries that join the Ghaghara from the north include Kuwana River, Rapti River, Little Gandak River.
- These tributaries contribute significantly to the river’s volume and have helped shape the extensive alluvial plains of northern Uttar Pradesh.
- In its lower reaches, the Ghaghara is also known by other names Sarju River, Deoha.
- It was referred to as Sarabos by the 2nd-century Greek geographer Ptolemy.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Ghar-Ghar Shaurya Samman Initiative & Kargil Vijay Diwas
Why in News?
As part of the 'Ghar-Ghar Shaurya Samman' initiative, the Indian Army paid tribute to the valour of soldiers who laid down their lives in the Kargil War by presenting their families with a certificate of honour and a memento.
- As the country prepares to observe the 26th Kargil Vijay Diwas on 26th July 2025, this initiative exemplifies the Army's unwavering dedication to its soldiers and their loved ones.
Key Points
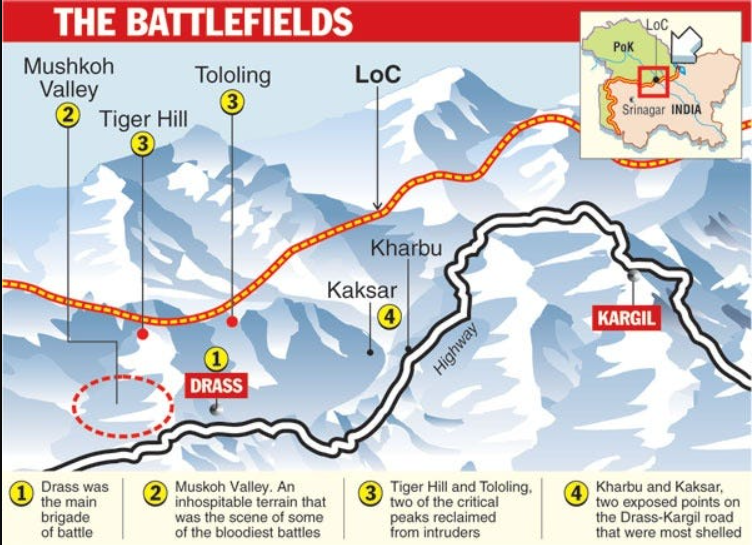
- Kargil Vijay Diwas:
- On 26th July, 1999, the Indian Army declared the success of Operation Vijay, marking victory in the nearly three-month-long Kargil conflict.
- Key battle sites included Tololing and Tiger Hill, known for their extreme altitudes and harsh terrain.
- During the Kargil War, the region was part of the former state of Jammu and Kashmir.
- After the 2020 reorganisation, Kargil now lies in the Union Territory of Ladakh, known for its rugged landscape and high-altitude terrain.
- Background:
- India and Pakistan have a history of conflicts, including a significant one in 1971 that led to the creation of Bangladesh.
- Post-1971, both nations faced ongoing tensions, particularly vying for control over the Siachen Glacier through military outposts on nearby mountain ridges.
- In 1998, both countries conducted nuclear tests, escalating tensions. The Lahore Declaration in February 1999 aimed to resolve the Kashmir conflict peacefully and bilaterally.
- During the winter of 1998-1999, Pakistani armed forces covertly trained and deployed troops across the Line of Control (LOC) to seize fortified positions overlooking NH 1A in the Drass and Batalik Sectors of Kargil, Ladakh.
- Indian troops initially mistook the infiltrators for terrorists or 'jihadis,' but it soon became clear that the attack was a well-organised military operation.
- It was fought in the summer of 1999 along a 170km mountain frontier, stretching from Mashkoh Valley to Turtuk in the Kargil sector.
- In response, India launched Operation Vijay, deploying over 200,000 troops to the region to counter the incursion.
- Significance of Kargil War Diwas:
- Since 1999, 26th July has been observed as Kargil Vijay Diwas to remember and honour the supreme sacrifices made by Indian soldiers during the war.
- The Kargil War memorial in Dras was built in 2000 by the Indian Army to commemorate the success of Operation Vijay in 1999.
- It was later renovated in 2014. It is also known as the "Dras War Memorial" due to its location in the town of Dras in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- The National War Memorial, inaugurated in 2019, is dedicated to soldiers who sacrificed their lives in various conflicts and missions, including the Sino-Indian war in 1962, Indo-Pak wars in 1947, 1965, and 1971, Indian Peace Keeping Force Operations in Sri Lanka 1987-90, and the Kargil Conflict in 1999.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Jal Ganga Sanvardhan Abhiyan
Why in News?
Launched on 30th March 2025, the Madhya Pradesh government’s Jal Ganga Sanvardhan Abhiyan has led to the successful revival of the Ghoda Pachhad River, a tributary of the Narmada, in Khandwa district.
Key Points
- Major Achievements of the Jal Ganga Sanvardhan Abhiyan:
- Water Harvesting Using ‘Ridge to Valley’ Approach:
- Authorities adopted the ‘Ridge to Valley’ model to build water conservation structures along a 33 km stretch.
- This approach focuses on conserving every drop of water at the ridge level and slowing surface run-off volume and velocity.
- As a result, the Ghoda Pachhad now flows again, raising hopes for year-round water flow in the region’s rivers.
- Efforts to Control River Pollution:
- The Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board surveyed major rivers including the Narmada, Chambal, Shipra, Betwa, Son, Tons, Tapti, Mahi, Sindh, and Ben Ganga.
- It has identified significant environmental concerns, including the discharge of around 450 million litres of domestic wastewater into rivers daily.
- To address this, the Urban Development Department is setting up Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) with a total treatment capacity of 869 million litres per day.
- This will substantially improve the water quality of the state’s rivers and contribute to cleaner, more sustainable water resources.
- Wetland Conservation and Ramsar Recognition:
- Madhya Pradesh increased its number of Ramsar Sites from one in 2002 to five by 2025.
- These include Sankhya Sagar, Sirpur Wetland, Yashwant Sagar, Tawa Reservoir and Bhoj Wetland.
- Indore became India’s first Wetland City, setting a benchmark in urban water management.
- Additionally, over 330 traditional wells and stepwells have been preserved in Indore, contributing to the revival of the region's historic water culture.
- Madhya Pradesh increased its number of Ramsar Sites from one in 2002 to five by 2025.
- Water Harvesting Using ‘Ridge to Valley’ Approach:
- Narmada River:
- About:
- The Narmada River flows westward through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra, covering a basin area of about 98,796 sq km.
- The river spans a course of approximately 1,300 km and is fed by 41 tributaries.
- The river originates from the Maikal Range in eastern Madhya Pradesh, near the Chhattisgarh border.
- An ancient Greek geographer referred to the Narmada as Namade, indicating its historical significance as a major route linking the Arabian Sea and the Ganga basin.
- It features numerous waterfalls, including the prominent Dhuandhar Falls, southwest of Jabalpur.
- Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh houses the Narmada Kund, regarded as the river's sacred origin.
- The Narmada River flows westward through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra, covering a basin area of about 98,796 sq km.
- Water Resource Development:
- The Narmada serves as a vital resource for hydroelectricity generation and irrigation.
- Major dams on the river include the Sardar Sarovar Dam (Gujarat), Indira Sagar Dam (Punasa, MP), Omkareshwar Dam, Bargi Dam, Maheshwar Dam.
- Narmada Bachao Andolan:
- Led by activists like Medha Patkar and Baba Amte, the Narmada Bachao Andolan (NBA) protested the displacement caused by dam projects.
- Their advocacy led to temporary halts by the Supreme Court and the World Bank, which withdrew from the project in 1993.
- In 2000, the Supreme Court allowed phased dam construction, conditional upon the rehabilitation of affected communities.
- Despite completion, the NBA continues to raise concerns over rising reservoir levels and risks to displaced populations.
- About:
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
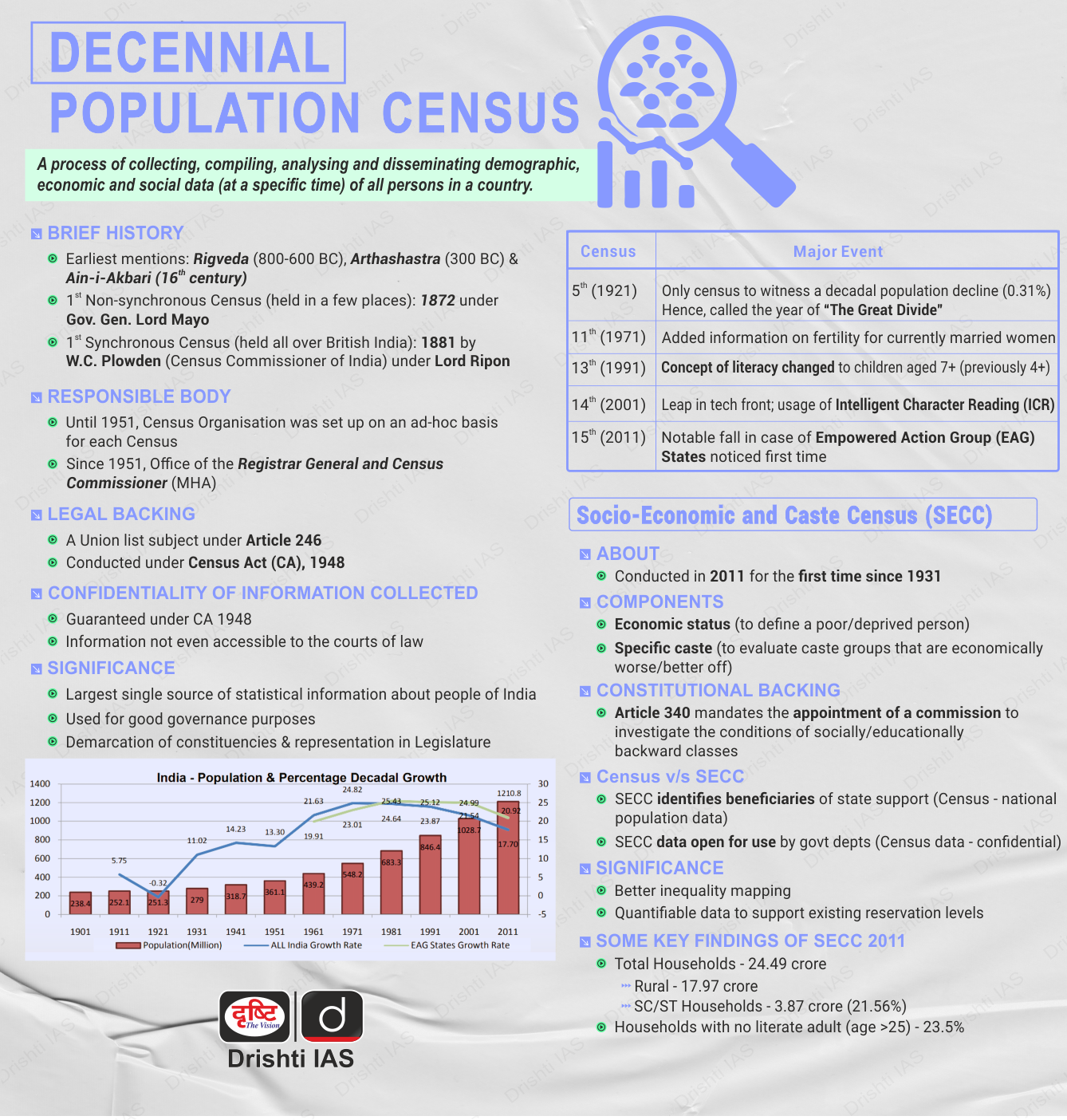
Centre Issues Notification for the 2027 Census
Why in News?
The central government has officially notified the conduct of the next decennial census in 2027, exercising its authority under Section 3 of the Census Act, 1948.
- This notification supersedes an earlier order from March 2019, which had initially set the schedule for the Census in 2021 but was delayed due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
Note: Under Section 3, the Central Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, declare its intention of taking a census in the whole or any part of the territories to which this Act extends, whenever it may consider it necessary or desirable to do so, and there upon the census shall be taken.
Key Points
- Updated Census Schedule:
- The Census will have a reference date of 1st March, 2027, for most parts of the country.
- However, regions like Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand, which face logistical challenges due to snow and difficult terrain, will follow an earlier reference date of 1st October, 2026.
- This adjustment allows for more accurate data collection in these areas.
- Census:
- About:
- The Indian Census is the largest source of demographic and socio-economic data on the country’s population.
- India's first synchronised census occurred in 1881 under W.C. Plowden, the then Census Commissioner of India.
- It has consistently provided detailed statistical information every 10 years, starting in 1872, when the first non-synchronous census was conducted across different regions of India.
- Legal Framework and Institutional Evolution:
- The Census Act of 1948 was enacted to create a legal framework for census operations and to define the roles of census officers.
- While the Act provides the legal framework, it does not mandate a specific frequency, making the decennial pattern a convention, not a constitutional requirement.
- In May 1949, the Government of India established a permanent Census organization under the Ministry of Home Affairs to systematize the collection of population and demographic data.
- The Office of the Registrar General was later tasked with implementing the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969, further expanding its role in maintaining vital statistics.
- The Census Act of 1948 was enacted to create a legal framework for census operations and to define the roles of census officers.
- About:
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Forest Fire in J&K
Why in News?
A massive forest fire erupted in the Bhaga village area near NH-144A in Reasi district, Jammu and Kashmir, spreading rapidly across hundreds of hectares of land.
Key Points
- Forest Fire Risk in J&K:
- In J&K, at least 1,747 square kilometres of forest area have been classified under the ‘High Risk’ zone for forest fires, while 62 square kilometres fall under the ‘Very High Risk’ category.
- As per official data:
- In 2022–23, a total of 1,553 forest fire incidents were reported, affecting an area of 2,774.21 hectares.
- In 2023–24, the number of incidents significantly declined to 607, impacting an area of 987.24 hectares.
- India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2023 and Forest Cover in J&K:
- The ISFR 2023 highlighted a substantial increase in forest cover which showed a rise of 34.78 sq km in the region’s forest area compared to the 2021 assessment.
- The report reveals that J&K has shown an increase of 398.12 sq km in forest cover in one decade from 2013 to 2023.
- According to the Report, the forest cover of J&K in 2013 was 20,948.27 sq km while in 2023 the forest cover increased to 21,346.39 sq km.
- J&K boasts of the highest number of forest types in the country, an impressive 43, along with the highest average growing stock of 296.22 cubic meters per hectare and the highest estimated carbon stock of 174.10 tonnes per hectare.
- Forest Fire:
- About:
- A forest fire refers to an uncontrolled blaze that spreads through vegetation taller than 1.8 metres.
- These fires often grow into major conflagrations, sometimes triggered by surface or ground fires that ignite upper tree canopies.
- When the flames leap to the top branches of trees (a phenomenon known as crowning), they can bypass the forest floor and undergrowth, rapidly intensifying.
- Such fires often lead to violent blowups and can evolve into firestorms, with erratic and extreme fire behaviour.
- Ecological Role of Forest Fires:
- Though typically viewed as destructive, many forest ecosystems depend on fire for their survival and regeneration.
- Natural events like lightning strikes in dry forests ignite fires that can benefit biodiversity.
- Related Government Initiatives:
- National Action Plan for Forest Fires (NAPFF), was started in 2018 with the goal of reducing forest fires by informing, enabling, and empowering forest fringe communities and incentivizing them to collaborate with state forest departments.
- The Forest Fire Prevention and Management Scheme (FPM) is the only government-sponsored programme dedicated to assisting states in dealing with forest fires.
- About:





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan