Haryana Switch to Hindi
Arjan Singh Memorial Hockey Tournament 2025
Why in News?
The Indian Air Force conducted the 6th edition of the Marshal of the Air Force Arjan Singh Memorial Hockey Tournament from 29 April to 06 May 2025 at the Raghbir Singh Bhola Hockey Stadium, Chandigarh.
Key Points
- Details of the Tournament:
- Twelve teams, including Air Force Hockey Teams and teams from two foreign countries, participated in the tournament.
- The tournament commemorates Marshal of the Air Force Arjan Singh DFC (Distinguished Flying Cross), a legendary figure in IAF history.
- Arjan Singh’s unmatched passion for hockey and inspirational leadership in both military and sports spheres continues to motivate air warriors.
- Final Match:
- The final match featured a contest between Indian Railways and Rail Coach Factory, Kapurthala.
- Indian Railways won the match by scoring 3–1 in the tie-breaker after a 2-goal draw.
- Awards and Felicitations:
- Medals, trophies, and cash awards were presented during a befitting award ceremony.
- Winners received Rs 3,00,000/-
- Runners-up received Rs 2,00,000/-
- Prominent international hockey players were also felicitated for their contributions.
- Medals, trophies, and cash awards were presented during a befitting award ceremony.
Air Force Marshal Arjan Singh
- He was born in 1919 in Lyallpur (now in Pakistan), was commissioned into the Royal Indian Air Force in 1939 and awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross (DFC) for his role in the Burma Campaign during World War II.
- He became Chief of Air Staff in 1964 at the age of 44.
- During the 1965 Indo-Pak war, his decisive leadership enabled the IAF to repel Pakistan’s offensive in Akhnoor within hours, earning him the Padma Vibhushan.
- In 2002, he became the only IAF officer to be conferred the Five-Star rank of Marshal of the Air Force.
- Post-retirement, he served as ambassador and Lt Governor of Delhi.
Indian Air Force
- Background:
- The Indian Air Force was established in 1932 during World War II to support the Royal Air Force of the United Kingdom in its war against Japan.
- To stop the Japanese army's progress into India, the IAF was utilised to target Japanese bases in Burma.
- In 1945, King George VI bestowed the prefix "Royal" in recognition of the IAF's accomplishments. After India became a republic in 1950, this honorary title was abolished.
- After the independence of the nation, it evolved into the Indian Air Force in 1950.
- The Indian Air Force was established in 1932 during World War II to support the Royal Air Force of the United Kingdom in its war against Japan.
- About:
- President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces,
- The fourth-largest air force in the world is the Indian Air Force.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Motto of India Air Force: Touch the sky with Glory.
- It was taken from the eleventh chapter of the Bhagavad Gita.
- The Chief of Air Staff, an air chief marshal is responsible for the operational command of the air force.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Operation Sankalp
Why in News?
Security forces killed Naxalites during an encounter in the forests of Chhattisgarh’s Bijapur district, as part of Operation Sankalp, a massive counter-insurgency initiative.
Key Points
- About Operation Sankalp:
- Security forces launched Operation Sankalp on 21 April based on intelligence inputs about the presence of senior cadres of the Maoist battalion no. 1, Dandakaranya Special Zonal Committee (DKSZC), and the Telangana state committee of Maoists.
- The operation targets Maoist strongholds in the Karregutta hills and surrounding forest areas along the Chhattisgarh–Telangana border.
- Forces Involved:
- Around 28,000 security personnel are taking part in the operation.
- These include units from the District Reserve Guard (DRG), Bastar Fighters, Special Task Force (STF), Chhattisgarh Police, Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), and its elite CoBRA unit (Commando Battalion for Resolute Action).
- Area of Operation:
- The operation covers nearly 800 sq km in the forested and hilly terrain straddling Bijapur (Chhattisgarh) and Mulugu and Bhadradri-Kothagudem (Telangana), located over 450 km from Raipur.
- Forces have seized:
- Over 400 improvised explosive devices (IEDs)
- Around 2 tonnes of explosive materials
- More than 6 tonnes of rations, medicines, daily-use items, and other Maoist belongings
District Reserve Guard (DRG)
- The District Reserve Guard (DRG) is a specialized police unit in Chhattisgarh, established in 2008 to combat Maoist violence.
- It consists of specially trained personnel operating in affected districts, conducting anti-Maoist operations, search and seizure, and gathering intelligence.
- The DRG collaborates with other security forces, like the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), to counter the Maoist insurgency.
Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF)
- The CRPF was initially established as the Crown Representatives Police in 1939 in response to political turmoil and unrest within the princely states.
- The force was renamed the Central Reserve Police Force in 1949.
- Sardar Vallabh Bhai Patel, the then Home Minister, envisioned a multifaceted role for the CRPF, aligning its functions with the evolving needs of a newly independent nation.
- COBRA:
- It is a special operation unit of the Central Reserve Police Force of India proficient in guerrilla tactics and jungle warfare. Originally established to counter the Naxalite movement.
- CoBRA is deployed to address insurgent groups engaging in asymmetrical warfare.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Global Service Centre in UP
Why in News?
To attract global investment, the Uttar Pradesh government has approved the Global Capability Centres (GCC) Policy.
Key Points
- About the Policy:
- The policy aims to drive UP toward its ambitious goal of becoming a USD 1-trillion economy.
- Officials expect the policy to attract global players in IT, banking, healthcare, engineering, and next-generation technologies.
- The policy offers attractive incentives and has been framed after studying global best practices.
- Technologies Covered by GCCs:
- GCCs being set up in UP include cutting-edge domains such as:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning
- Cloud Computing
- Cybersecurity
- Robotic Process Automation
- Engineering design and development
- GCCs being set up in UP include cutting-edge domains such as:
- Sectors and Companies Already on Board:
- Global firms in banking, financial services, insurance, automotive, electronics, and semiconductor manufacturing have begun operations in UP.
- Microsoft has laid the foundation for a 10,000-seater development centre in Noida.
- MAQ Software has set up a 3,000-seater engineering centre.
- The state is also working to attract GCCs to Varanasi, Kanpur, and Prayagraj, alongside Noida and NCR.
Global Capability Centers (GCCs)
- GCCs represent offshore establishments set up by companies to deliver a range of services to their parent entities.
- Operating as internal entities within the global corporate framework, these centres offer specialised capabilities including IT services, research and development, customer support, and various other business functions.
- GCCs play a crucial role in capitalising on cost efficiencies, tapping into talent reservoirs, and fostering collaboration between parent enterprises and their offshore counterparts.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs) can provide a fertile ground for GCCs to flourish by offering several advantages like tax breaks, simplified regulations and streamlined bureaucracy.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
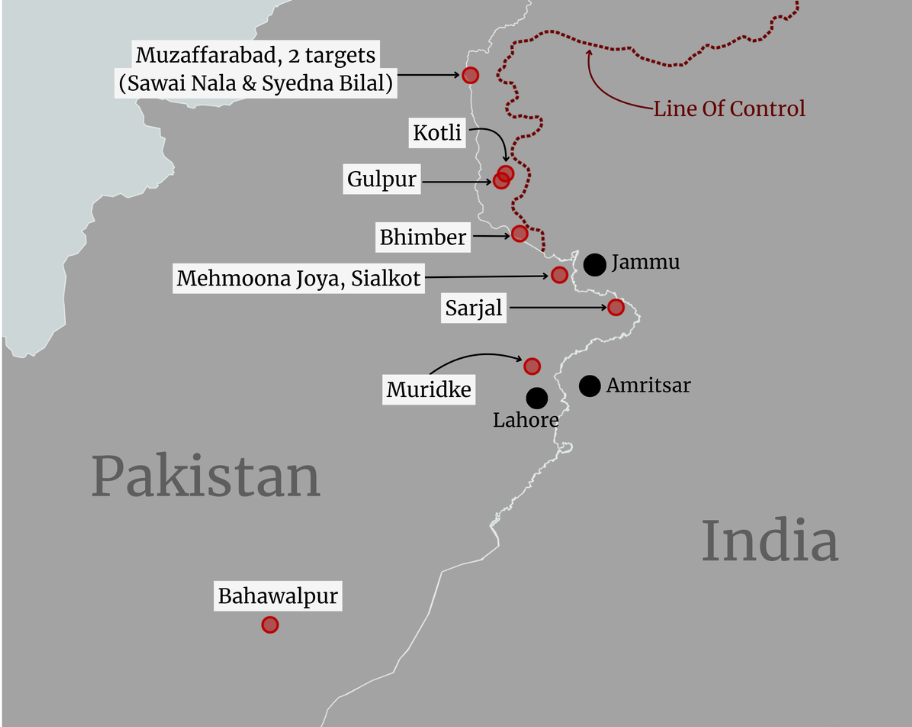
Operation Sindoor
Why in News?
India retaliated against the April 2025 Pahalgam terrorist attack by launching Operation Sindoor, targeting nine terrorist infrastructure sites across Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Jammu and Kashmir (PoJK).
Key Points
- Operation Sindoor:
- It was executed through the coordinated efforts of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, conducted from Indian territory.
- Unlike past operations with aggressive names meant to project strength, this operation’s name was chosen as a personal tribute to the victims, particularly the widows of the Pahalgam attack.
- Intelligence and probe agencies confirmed that the targeted camps were linked to banned terrorist groups including Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), and Hizbul Mujahideen.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Security Measures Activated in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
Uttarakhand Chief Minister held a high-level meeting with senior officials and directed them to ensure robust security across all border areas of the state, while maintaining strict surveillance over any suspicious activity in the frontier regions.
Key Points
- Sensitive Border Districts Identified:
- Uttarkashi and Chamoli share borders with China.
- Champawat and Udham Singh Nagar share borders with Nepal.
- Pithoragarh shares its border with both China and Nepal.
- Enhanced Security During Char Dham Yatra:
- CM emphasised heightened security along the Char Dham Yatra route, where lakhs of pilgrims are currently registered.
- He instructed that all security arrangements for the pilgrimage sites be activated without delay.
- Protection of Strategic Infrastructure:
- The meeting reviewed the security of key establishments, dams, power plants and instructed all departments and police forces to stay on high alert.
- Emergency Preparedness Measures:
- He directed that supplies of food grains and essential goods be ensured at district and tehsil levels.
- Hospitals must remain alert with proper arrangements for essential medicines.
- Role of Civil Defence and Volunteers:
- CM called for training of civil defence groups and voluntary organisations in relief and rescue operations.
- Curbing Rumours and Misinformation:
- The CM emphasised the need to disseminate accurate, verified information to the public.
- He instructed officials to monitor social media strictly and take action against those spreading rumours.
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Kolkata Air Toxicity
Why in News?
A new study by Kolkata-based Bose Institute revealed that PM 2.5 becomes significantly more toxic when pollution levels exceed 70 micrograms per cubic metre of air.
Key Points
- Key Findings of the Study:
- A new long-term study conducted in Kolkata revealed that PM2.5 toxicity spikes sharply when pollution levels cross 70 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m³).
- According to the researchers, the toxicity continues to rise until it stabilises around 135 µg/m³.
- Study Duration and Area Covered:
- The analysis covered seven years of data (2016–2023).
- Air samples were collected from eastern Kolkata and the northern and southern zones of the city.
- Violation of National Standards:
- India's national PM2.5 standard is 60 µg/m³ (24-hour average).
- From October to February, this threshold was breached on about 75% of winter days in Kolkata's metropolitan region.
- Health Hazards of PM2.5:
- PM2.5 particles can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing asthma, COPD, cardiovascular issues, and pulmonary fibrosis.
- The toxicity is linked to oxidative stress, which can damage human cells through molecules like peroxides, hydroperoxides, and hydroxyls.
- Scientific Insight on Toxicity:
- Researchers explained that toxicity rises due to chemical components from biomass and solid waste burning, with vehicular emissions contributing to a lesser extent.
- The study was limited to winter months, when PM2.5 levels peak in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- Emission Trends Post-NCAP:
- Under the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) launched in 2019, Kolkata received over Rs 636 crore between 2019 and 2023.
- Post-NCAP, emissions declined from:
- Vehicles by 33%
- Industries by 39%
- Road dust by 42%
- Biomass Burning Remains Unchecked:
- Despite NCAP, there was no notable reduction in biomass and waste burning emissions.
- The study attributes this to:
- Open-air burning of dry leaves in winter
- Widespread use of biomass for cooking among economically weaker sections due to high LPG refill costs.
- These practices remain largely unsupervised, contributing to continued high air toxicity.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- It was launched by the MoEFCC in January 2019.
- It is the first-ever effort in the country to frame a national framework for air quality management with a time-bound reduction target.
- It seeks to cut the concentration of coarse (particulate matter of diameter 10 micrometer or less, or PM10) and fine particles (particulate matter of diameter 2.5 micrometer or less, or PM2.5) by at least 20% in the next five years, with 2017 as the base year for comparison.
- The plan includes 102 non-attainment cities, across 23 states and Union territories, which were identified by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) on the basis of their ambient air quality data between 2011 and 2015.
- Non-attainment cities: These are those that have fallen short of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for over five years.
Particulate Matter (PM)
- Particulate matter, or PM, refers to a complex mixture of extremely small particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. These particles come in a wide range of sizes and can be made up of hundreds of different compounds.
- PM10 (coarse particles) - Particles with a diameter of 10 micrometres or less.
- PM2.5 (fine particles) - Particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometres or less.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



