Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh's First AYUSH University
Why in News?
President Droupadi Murmu inaugurated Uttar Pradesh’s first AYUSH University, named Mahayogi Guru Gorakhnath AYUSH University, in Gorakhpur.
- The President highlighted the spiritual and historical legacy of the region, stating that it is also the birthplace of Paramhansa Yogananda.
Key Points
- Spiritual and Historical Legacy of Gorakhpur:
- The Nath Tradition:
- The Nath tradition, rooted in the teachings of Shri Adinath, Matsyendranath, and Guru Gorakhnath, traces its origins to Gorakhpur.
- Over time, this spiritual lineage has spread across India and reached several countries worldwide, influencing diverse yogic and ascetic practices.
- Role in India’s Freedom Struggles:
- Gorakhpur holds not just spiritual significance but also a deep historical connection to India's freedom movements.
- From monk-led uprisings in the 18th century to the Revolt of 1857- First War of Independence, this region has been a centre of resistance.
- The sacrifices of freedom fighters like Babu Bandhu Singh and Ram Prasad Bismil are closely linked to this sacred land, highlighting its legacy of courage and patriotism.
- The Nath Tradition:
- About Guru Gorakhnath:
- Gorakhnath, who likely flourished around the 11th century CE, is regarded as a revered Hindu yogi and the spiritual founder of the Kanphata yogis, a sect of ascetics known for practising Hatha Yoga.
- The Kanphata yogis emphasise both physical discipline and spiritual mastery, aligning with the principles of Hatha Yoga.
- Hatha Yoga, associated closely with Gorakhnath’s teachings, is a philosophical and spiritual system that uses control over the body as a path to spiritual perfection.
- This school of thought blends asceticism with intense yogic discipline, marking a departure from ritualistic or purely devotional practices.
- Gorakhnath, who likely flourished around the 11th century CE, is regarded as a revered Hindu yogi and the spiritual founder of the Kanphata yogis, a sect of ascetics known for practising Hatha Yoga.
Paramhansa Yogananda
- About:
- Paramhansa Yogananda (1893–1952) was the first Indian yoga master to establish permanent residence in the Western world.
- He played a pivotal role in introducing Indian spiritual philosophy to Western audiences in the early 20th century.
- A Lasting Spiritual Legacy:
- While his early presence in the West had a remarkable cultural impact, Yogananda's enduring legacy lies in the spiritual awakening he inspired.
- He continued to lecture and write actively until his death in 1952, promoting a blend of Kriya Yoga, meditation, and universal spirituality.
- His seminal work, Autobiography of a Yogi, published in 1946, sparked a spiritual revolution in the West.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
NAVYA Initiative Launched in UP
Why in News?
NAVYA – Nurturing Aspirations through Vocational Training for Young Adolescent Girls was launched in Sonbhadra district of Uttar Pradesh to empower adolescent girls.
Key Points
- NAVYA Initiative for Empowerment:
- NAVYA is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship and the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It will be implemented across 27 aspirational districts in 19 states, ensuring that marginalised and underserved regions are prioritised.
- It is a pilot initiative aimed at equipping adolescent girls aged 16–18 years with a minimum qualification of Class 10, with vocational training mainly in non-traditional job roles.
- It aligns with the Viksit Bharat@2047 vision and promotes women-led development and reinforces the Government’s commitment to building a skilled, self-reliant, and inclusive workforce, positioning young girls as agents of socio-economic transformation.
- The programme will draw upon schemes like Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) and other flagship skill development schemes.
- NAVYA is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship and the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- The Skill India Mission was launched by the Government in 2015, under which the flagship scheme PMKVY is implemented.
- It aims at vocational training and certification of Indian youth for a better livelihood and respect in society.
- PMKVY is implemented by the National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC) under the guidance of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rainwater Harvesting in Jaipur
Why in News?
A rainwater harvesting and irrigation project was inaugurated at Kukas in Jaipur district, Rajasthan, following the creation of a 15-crore-litre water conservation capacity.
Note: 80% of Rajasthan's area faces groundwater depletion; 50% of drinking water and 60% of irrigation rely on rapidly declining aquifers.
- Over-extraction leads to high salinity, fluoride and nitrate contamination, causing serious health risks in many regions.
Key Points
- Direct Benefits for Smallholder Farmers:
- Over 6,000 villagers, primarily smallholder farmers and livestock rearers, will directly benefit from the project.
- It is projected to increase farm income by Rs 5 crore annually and ensure long-term drinking water security for over 10,000 rural households.
- These ponds are designed to capture rainwater directly from each farm, and many have already started filling during the ongoing monsoon.
- By the end of the monsoon, the ponds are expected to become a permanent water source for rain-fed fields in the region.
- This will reduce dependence on rapidly depleting groundwater sources and promote sustainable agriculture.
- Over 6,000 villagers, primarily smallholder farmers and livestock rearers, will directly benefit from the project.
- Strategic Partnership:
- The project is a collaboration between the Atomic Power Evolution Awareness Foundation and Hero MotoCorp’s Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) wing ‘Hero We Care’.
- It is being implemented in the Kukas region, where the Kacherawala River has dried up and over 200 wells and handpumps are defunct.
- Groundwater levels in the region have dropped to depths of 1,000 feet, making surface water conservation critical.
- India's Initiatives Related to Water Conservation:
Water Harvesting System
- About:
- A water harvesting system refers to a technique or structure designed to capture, store, and use rainwater, surface runoff, or other sources of water for various purposes, such as agriculture, domestic use, and groundwater recharge.
- It is a sustainable water management practice aimed at conserving water and addressing water scarcity.
- A water harvesting system refers to a technique or structure designed to capture, store, and use rainwater, surface runoff, or other sources of water for various purposes, such as agriculture, domestic use, and groundwater recharge.
- Types:
- Rainwater Harvesting (RWH): Collecting and storing rainwater through methods like rooftop collection and underground storage to conserve water.
- Groundwater Recharge Systems: Techniques such as recharge wells that allow rainwater to seep into the ground to maintain and improve groundwater levels.
- Surface Water Harvesting: Collecting rainwater from land or open fields using ponds and reservoirs for irrigation and other uses.
- Urban Water Harvesting: Capturing rainwater in cities from rooftops and surfaces to reduce pressure on municipal water systems and manage stormwater.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
New Reserved Areas Near LAC and LoC
Why in News?
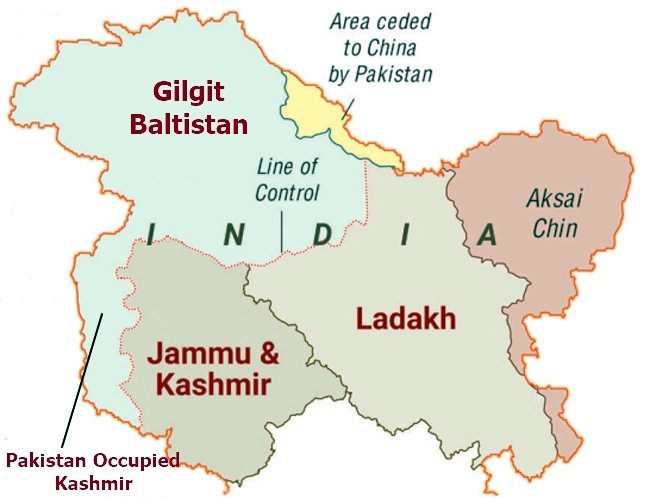
The Ladakh administration has declared 52 villages along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) as reserved areas, allowing residents to access reservation benefits in recruitment and other sectors.
Key Points
- Official Declaration of Areas Along the LAC:
- The issued notification is under the Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Act, 2004, as amended by the Ladakh Reservation (Amendment) Regulation, 2025.
- The notification includes:
- 18 revenue villages in Leh district situated along the Line of Control (LoC) and LAC.
- 34 revenue villages in Kargil district along the LoC.
- In total, 52 villages have been declared as adjoining the LAC.
- Reservation Benefits for Border Residents:
- Residents of these officially declared villages will now be eligible for reservation benefits.
- These benefits cover recruitment and other welfare sectors, aiming to support communities living in strategically sensitive and remote areas.
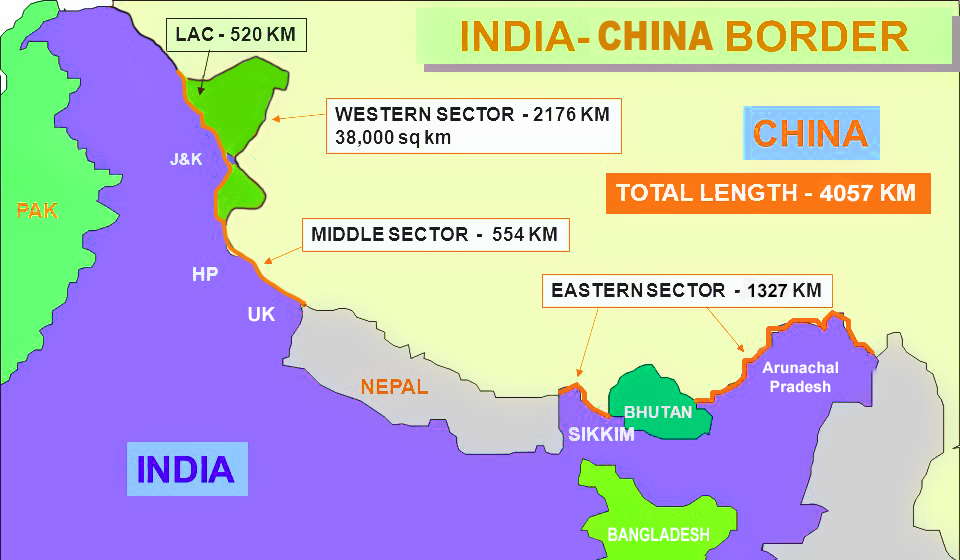
Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- It serves as the boundary separating Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory.
- The India-China Border is not fully demarcated which has led to tensions between the countries.
- This demarcation is categorized into three sectors:
- Eastern sector encompassing Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim.
- Middle sector spanning Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh.
- Western sector located in Ladakh.
Line of Control
- The Line of Control (LoC) emerged from the 1948 ceasefire line negotiated by the United Nations (UN) after the Kashmir War.
- It was designated as the LoC in 1972, following the Simla Agreement between the two countries.
- LoC is demarcated up to the Siachen Glacier (Point NJ9842)- the world's highest battlefield.
- LoC is delineated on a map signed by the Director General of Military Operations (DGMO) of both armies and has the international sanctity of a legal agreement.
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
New Commandant of the Pune’s Military Institute of Technology
Why in News?
Rear Admiral V. Ganapathy, a distinguished Indian Navy Flag Officer, has taken charge as Commandant of the Military Institute of Technology (MILIT), Pune.
Key Points
- Military Institute of Technology (MILIT):
- Background:
- The MILIT was established on 19 January 2012, after being carved out from the Defence Institute of Advanced Technology (DIAT)—a Deemed University and grants-in-aid institution under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Administrative Transition and Reorganisation:
- From 2012 to 31st March 2015, MILIT functioned under HQ DRDO as its 52nd lab.
- On 1st April 2015, MILIT was reconstituted as an Armed Forces Training Institute (AFTI) under the Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (IDS).
- Location and Composition:
- Background:
Indian Navy
- The East India Company's naval arm came under the British Crown on 1st May 1830, becoming the Indian Navy, and was later renamed Her Majesty's Indian Navy in 1858.
- The Indian Navy adopted the Vedic invocation to Lord Varuna, "Sam no Varunah," as its emblem motto, meaning "Be auspicious unto us, O Varuna."
- On 21st October 1944, Navy Day was celebrated for the first time.
- Since 1972, Navy Day has been celebrated on 4th December to honor the successful 1971 naval operations in the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Karachi harbor missile attack, and to pay tribute to war martyrs.




























.jpg)







.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan