Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
New Colonel of the Regiment of Garhwal Rifles
Why in News?
Lieutenant General Dinesh Singh Rana, Commander-in-Chief of Andaman & Nicobar Command, has officially taken over as the 23rd Colonel of the Regiment of Garhwal Rifles in a ceremony held at the Garhwal Rifles Regimental Centre in Lansdowne, Uttarakhand.
- He succeeds Lieutenant General NS Raja Subramani.
Key Points
- Garhwal Rifles:
- The Garhwal Rifles is an infantry regiment of the Indian Army, established in 1887 as the 39th (Garhwal) Regiment of the Bengal Army.
- It became part of the British Indian Army and was later incorporated into the Indian Army after India’s independence.
- The soldiers of the Garhwal Rifles mainly come from the seven Garhwal districts of Uttarakhand:
- Uttarkashi, Chamoli, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal, Dehradun, Pauri Garhwal, and Haridwar.
- The Garhwal Scouts are stationed at Joshimath and are nicknamed “The Snow Leopards.”
- It has a strong legacy of valor, courage, and service to the nation, reflecting the proud tradition of Garhwali warriors.
- The regiment earned distinction in both World Wars and in multiple post-independence conflicts.
- It played a significant role in the 1962 Sino-Indian War and the Indo-Pakistan wars of 1965 and 1971.
- The Garhwal Rifles is famous for its role in peacekeeping missions, such as Operation Pawan in Sri Lanka.
- The regiment’s motto is “Yudhaya Krit Nishchaya” (Fight with Determination).
- The regiment’s insignia features a Maltese cross, similar to the defunct Rifle Brigade (Prince Consort’s Own).
- The Garhwal Rifles has won several prestigious awards, including three Victoria Crosses and one Ashoka Chakra.
- The Garhwal Rifles is an infantry regiment of the Indian Army, established in 1887 as the 39th (Garhwal) Regiment of the Bengal Army.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
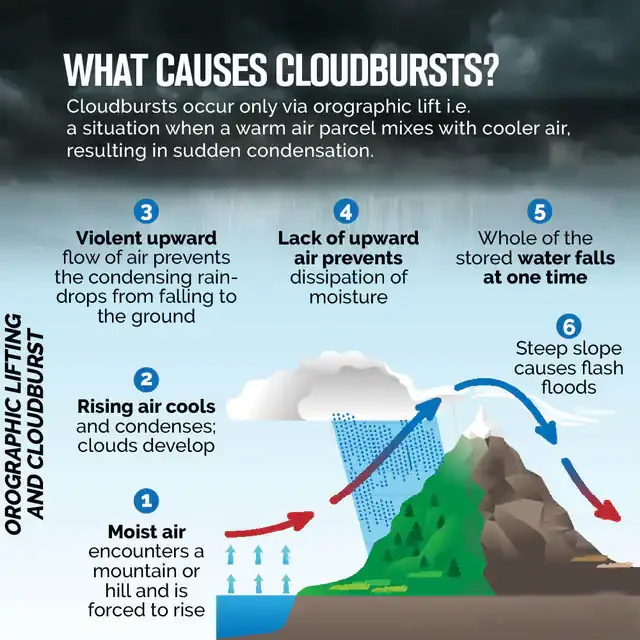
Cloudburst in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
A cloudburst in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand caused landslides, disrupted key pilgrimage routes, and left several workers missing.
- Districts prone to flash floods and landslides have been placed on high alert.
Key Points
- About Cloudburst:
- A cloudburst is a sudden, intense rainstorm that results in more than 10 cm of rain in less than an hour over a small area (approximately 10 km²).
- It can also be accompanied by hail and thunder. Cloudbursts are common in mountainous areas, especially in the Himalayas.
- Due to their localised nature, cloudbursts are hard to predict or detect but can unleash sudden, devastating rainfall, leading to flash floods and landslides.
- Landslide:
- Definition: A landslide is the downward movement of rock, soil, or debris on a slope due to gravity.
- It is a form of mass wasting, where earth materials move down a slope under the influence of gravity.
- Causes: Natural factors like heavy rainfall, earthquakes, and water seepage weaken slopes, while human activities such as deforestation and construction increase risks. Geological factors, such as soil composition and terrain, also affect slope stability and can lead to landslides.
- Definition: A landslide is the downward movement of rock, soil, or debris on a slope due to gravity.
- Flash Floods:
- Definition: Flash floods are sudden increases in water levels during or immediately after intense rainfall.
- They are highly localized and short-lived events, typically occurring within 6 hours of rainfall.
- Causes: Flash floods are primarily caused by intense rainfall that overwhelms the soil’s absorption capacity and drainage systems.
- Apart from heavy rain, flash floods can also result from rapid snowmelt due to sudden temperature rise, dam or levee breaches, ice or debris jams, and sudden glacial lake outbursts.
- Additionally, urbanisation with impervious surfaces like roads and buildings increase runoff, reducing water absorption and intensifying flood risks.
- Definition: Flash floods are sudden increases in water levels during or immediately after intense rainfall.




























.jpg)







.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan