-
Q.“Cloud seeding offers temporary respite from smog but cannot substitute long-term emission control.” Critically examine the viability of cloud seeding as a tool in India’s air pollution mitigation strategy. (150 words)
05 Nov, 2025 GS Paper 3 Bio-diversity & EnvironmentApproach :
- Briefly define cloud seeding.
- Critically examine the viability of cloud seeding as a tool in India’s air pollution mitigation strategy
- Suggest comprehensive measures to curb air pollution in India
- Conclude with a suitable way forward.
Introduction:
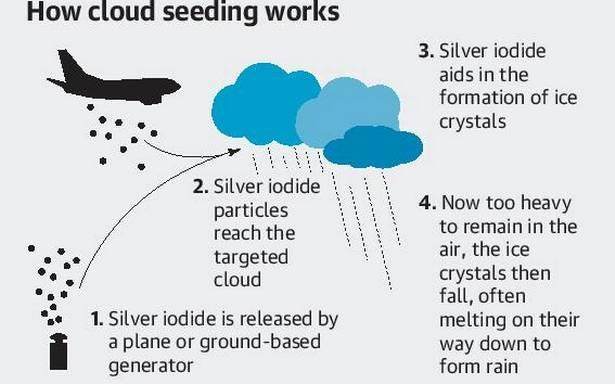
A 2024 report by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, defines cloud seeding as a weather modification technique that involves introducing ‘seed’ particles into suitable clouds to enhance rainfall.
- To induce artificial rainfall, suitable clouds are injected with salts such as silver iodide, potassium iodide, or sodium chloride, which act as the ‘seed’ to promote condensation and droplet formation.
Body :
The Viability of Cloud Seeding
- International Success and Applications of Cloud Seeding:
- It can aid temporary particulate matter reduction by triggering rainfall that washes out PM2.5/PM10.
- It could serve as an emergency response tool in acute air-quality episodes when other measures lag.
- Used since the 1940s mainly to boost rainfall in drought-prone or water-scarce regions (e.g., USA, China, UAE).
- It can serve as short-term relief during droughts, support agriculture, and act as an emergency air-quality intervention.
- Pakistan’s 2023 artificial rain experiment in Lahore showed minimal rainfall but helped reduce AQI temporarily, with pollution rebounding after a few days.
- Limitations of Cloud Seeding:
- Cannot induce rain without suitable clouds and adequate moisture.
- Effects are temporary, with rainfall lasting from a few hours to a couple of days.
- Measuring precise effectiveness is difficult due to natural atmospheric variability
- Chemicals used pose potential environmental risks such as soil and water contamination; long-term effects require monitoring.
- In 2025, the Delhi government and IIT Kanpur conducted cloud seeding experiments to induce artificial rain, but the effort saw limited success because of low atmospheric moisture.
Comprehensive Measures to Curb Air Pollution in India
- Enforce BS-VI norms strictly across all cities.
- Mandate Real Driving Emissions (RDE) testing and strengthen EIAs.
- Implement an effective vehicle scrappage policy to retire old, polluting vehicles.
- Invest in Green Energy Corridors, smart grids, and AI-based load management.
- Scale up Pusa Decomposer, biochar, and residue-based bioenergy plants.
- Provide MSP-linked incentives and machinery support to promote residue management.
- Enforce dust-control norms: smog guns, water sprinkling, and covering construction sites.
- Promote permeable pavements, green buffers, and street-side plantations.
- Enhance powers and resources of the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM).
Conclusion:
Every breath we take is a gift from the planet-safeguarding air quality is safeguarding life itself.Thus,India must align its pollution control efforts with SDG 3 (Health), SDG 7 (Clean Energy), SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities), and SDG 13 (Climate Action) by strengthening emission norms, promoting renewables, managing waste sustainably, and fostering inclusive, science-based governance to ensure clean air, public health, and environmental justice for future generations.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF