- Filter By :
- Geography
- History
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Indian Society
-
Q. “The oceans play a critical role in the Earth’s climate system.” Examine the influence of ocean currents and phenomena like El Niño on Indian weather patterns. (250 words)
04 Aug, 2025 GS Paper 1 GeographyApproach :
- Briefly introduce the role of oceans in Earth's climate system.
- Examine the influence of ocean currents and phenomena like El Niño on Indian weather patterns.
- Conclude with a suitable way forward.
Introduction :
Oceans cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface and act as massive reservoirs of heat and moisture. Through large-scale circulations such as ocean currents and complex climate phenomena like El Niño and the La Niña, and the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) significantly influence the Earth’s climate system, including the Indian monsoon, cyclones, and rainfall distribution.
Body :
Role of Oceans in the Earth’s Climate System:
- Storing and transporting solar energy through surface and deep currents.
- Regulating atmospheric temperatures via latent heat transfer.
- Influencing wind patterns and cloud formation, which in turn affect precipitation and pressure belts.
- This complex ocean-atmosphere interaction defines regional climates, including that of the Indian subcontinent.
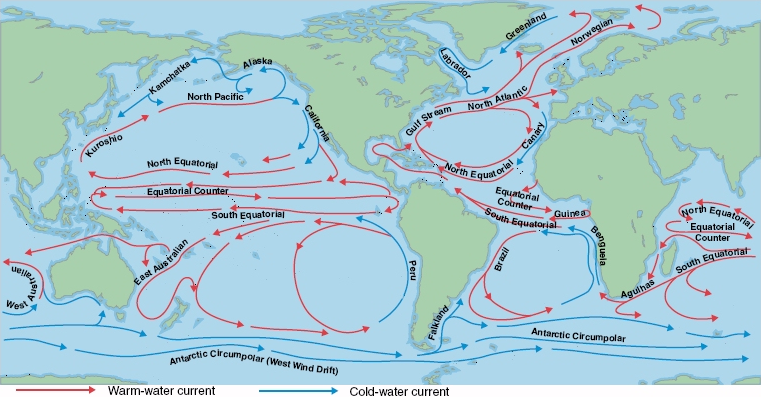
Influence of Ocean Currents on Indian Weather
- Warm currents (e.g., Agulhas Current) near the equator increase evaporation, feeding the monsoon system with moisture.
- Cold currents (e.g., West Australian Current) suppress rainfall by reducing evaporation.
- The Somali Current, unique for its seasonal reversal, influences Arabian Sea upwelling and marks the onset of the southwest monsoon.
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) affects rainfall intensity:
- Positive IOD: Warmer western Indian Ocean leads to enhanced rainfall over India.
- Negative IOD: Cooler western Indian Ocean suppresses monsoon activity.
- Example: In 2019, despite a weak El Niño, a strong positive IOD helped deliver a near-normal monsoon in India.
El Niño, La Niña and Their Impact on India
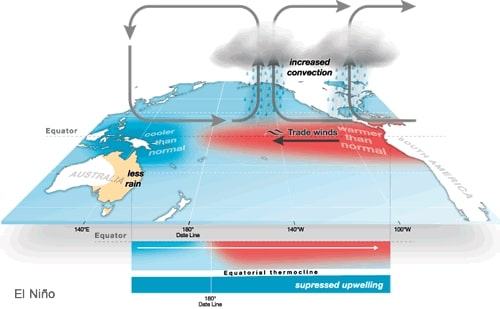
El Niño:
- El Nino is a climate pattern that describes the unusual warming of surface waters in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It is the “warm phase” of a larger phenomenon called the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- El Niño involves oceanic and atmospheric phenomena with the appearance of warm currents off the coast of Peru in the Eastern Pacific, which weakens the trade winds and the Walker Circulation. This reduces the moisture-laden winds reaching India.
- In India, El Niño generally tends to weaken the monsoon, resulting in drier-than-average conditions and reduced rainfall. This can lead to droughts, water shortages, and agricultural losses.
- The 2015 El Niño led to a monsoon deficit of 14%, causing widespread agricultural distress.
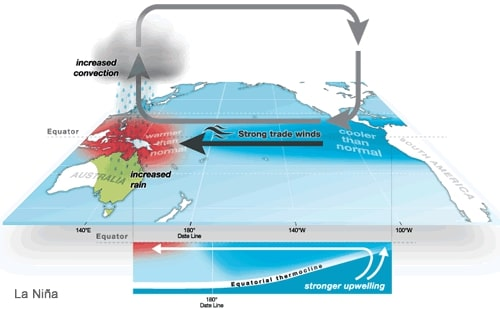
La Niña
- La Nina, the “cool phase” of ENSO, is a pattern that describes the unusual cooling of the tropical eastern Pacific.
- In the La Niña phase, trade winds strengthen, pushing larger volumes of water toward the western Pacific, leading to cooler temperatures in the eastern Pacific.
- It results in above-normal rainfall, which can lead to floods in some regions while benefiting water reservoirs and agriculture in others.
- The most recent La Nina phase lasted from 2020 to 2023.
Conclusion:
Oceans are integral to the global and regional climate systems. For India, ocean currents and ENSO-related events play a decisive role in determining monsoon strength, agricultural output, and disaster preparedness. Strengthening ocean monitoring systems, such as ARGO floats and real-time satellite data, and enhancing monsoon forecasting models are crucial for climate resilience and sustainable development.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF