Governance
Net Neutrality in India
- 11 Nov 2023
- 13 min read
This editorial is based on “A telco double dip attempt that threatens Net neutrality” which was published in The Hindu on 07/11/2023. It talks about the importance of upholding net neutrality principles which lies in fostering an environment that promotes innovation, nurtures healthy competition, and prioritizes consumer welfare.
For Prelims: Net- Neutrality,Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), Over-The-Top (OTT) players,Telecom Service Providers (TSPs), Content delivery networks (CDNs), Facebook's Free Basics, Prohibition of Discriminatory Tariffs for Data Services Regulations (2016),Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)..
For Mains: About Net neutrality, Significance of Net Neutrality, Regulatory Status of Net Neutrality in India, Key Debates on Net Neutrality in India,Way Forward for an Inclusive Digital Landscape in India.
Recently, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) initiated a consultation on the regulation of Over-The-Top (OTT) services in response to the government's request.
- Telecom companies argue that OTT services, such as Netflix and Amazon Prime, should share the costs of bandwidth, claiming that they benefit from the telecom companies' infrastructure.In this context, Net Neutrality debate has resurfaced.
What is Net Neutrality ?
- 'Net- Neutrality' refers to the concept of non-discrimination of internet traffic by intermediate networks on any criteria. The network should be neutral to all the information being transmitted through it.
- All communication passing through a network should be treated equally i.e. independent of its content, application, service, device, sender or recipient address.
- Net neutrality ensures that everyone has equal access to information and services on the internet, regardless of their financial resources or the size and power of the websites they use.
- Origin of the Term: The term "net neutrality" was popularized by Tim Wu, a professor at Columbia Law School, in his 2003 paper titled "Network Neutrality, Broadband Discrimination."
- Key principles of Net Neutrality include:
- The stakeholders in the internet space who are impacted by net neutrality include :
- The consumers of any internet service
- The Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) or Internet Service Providers (ISPs),
- The Over-the-top (OTT) service providers (those who provide internet access services such as websites and applications),
- The government, who may regulate and define relationships between these players
- Also, TRAI is an independent regulator in the telecom sector, which mainly regulates TSPs and their licensing conditions, etc.
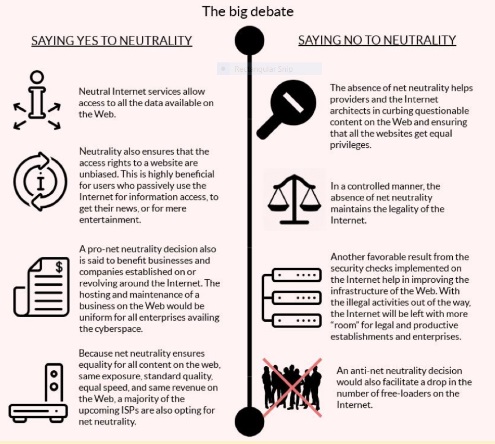
Why does Net Neutrality Matter ?
- Preserves an Open Internet: Net neutrality ensures free and unrestricted access to information, ideas, and services.
- Without net neutrality, individual ISPs can provide higher connection speeds to certain websites or throttle access to others. At the most extreme, an ISP could block access to some material altogether.
- Promotes Consumer Choice: Net neutrality allows consumers to freely choose the content, applications, and services they want to access without restrictions.They are not limited to a pre-selected set of offerings determined by ISPs.
- Protects Freedom of Expression: Net neutrality safeguards freedom of expression by allowing people to organize, communicate, and mobilize supporters without interference, making it a vital tool for democratic engagement.
- Fosters Innovation: An open internet encourages innovation and competition. Startups, small businesses, and entrepreneurs have equal opportunities to launch new services and reach users without the need to strike deals with ISPs.
- Prevents Anti-Competitive Practices: Without net neutrality, ISPs could engage in anti-competitive behavior by favoring their own content or services or those of their partners. Net neutrality rules prevent such discriminatory practices and maintain fair competition.
What is the Regulatory Status of Net Neutrality in India?
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) plays a central role in regulating and ensuring net neutrality in India.The regulation of net neutrality in India is marked by a series of following developments :
- Airtel Zero and VoIP Controversy (2014):
- In 2014, Bharti Airtel introduced the "Airtel Zero" scheme, which raised concerns about zero-rating and potential violations of net neutrality.
- Airtel's move to charge extra for Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services like Skype and WhatsApp also sparked controversy.
- TRAI Consultation (2015):
- In 2015, TRAI released a consultation paper on over-the-top (OTT) services and net neutrality, seeking public feedback.
- TRAI's 2016 Regulations:
- In 2016, TRAI ruled in favor of net neutrality by prohibiting differential rates for data services
- TRAI's "Prohibition of Discriminatory Tariffs for Data Services Regulations, 2016" put an end to zero-rating services like Facebook's Free Basics, ensuring non-discriminatory pricing.
- TRAI's Recommendations in 2017:
- TRAI extended non-discriminatory principles to content treatment.
- License agreements between the government and ISPs should be amended to prevent content discrimination.
- TRAI's Consultation Paper on 5G Digital Transformation,2023 :
- It aims to identify policy challenges and formulate an effective framework for the rapid adoption and optimal utilization of new technologies within the 5G ecosystem.
What are Some of the Key Debates on Net Neutrality in India?
- Perspective of Telecom Companies:
- Revenue Decline:
- Over the last ten years, telecom companies have witnessed a reduction in revenue, primarily from conventional services such as voice calls and SMS.
- The proliferation of free competing OTT services has been a key factor in this decline.
- Infrastructure Enhancement:
- TSPs contend that they make substantial investments in network infrastructure and assert the need for incentives, like differential pricing, to sustain these investments and facilitate the expansion of internet penetration.
- Telecom companies perceive OTT platforms as deriving benefits from the infrastructure they have established and sustained.
- Hence, these companies urge OTT content providers, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ Hotstar, to contribute to the expenses associated with bandwidth.
- Disparity in Taxation :
- Telecom companies contend that OTT services encounter a disparity in taxation and licensing fees, resulting in an imbalanced competitive landscape.
- Revenue Decline:
- Perspective of OTT Platforms:
- Exclusive Role of Internet Providers :
- OTT providers highlight that telecom companies serve as conduits for Internet access; they do not own it. Consumers remunerate these companies for access through data plans.
- The use of OTT services leads to increased data consumption, contributing to telecom companies' revenue growth.
- Demand for Net Neutrality:
- Net neutrality is crucial to prevent internet fragmentation and ensure equal access, preventing discrimination by TSPs, which could stifle innovation and restrict access to smaller-scale, innovative OTT services
- Net neutrality supporters believe in maintaining a free, open, and nondiscriminatory internet for a democratic exchange of ideas and knowledge, ethical business practices, fair competition, and ongoing innovation.
- Content Delivery Network Provision:
- OTT platforms already cover expenses related to content delivery networks (CDNs) to amplify the internet's capability for delivering content.
- OTT services compete in their own market based on content variety and quality, streaming quality, ease of navigation, and device availability.
- Telecoms' Liberty to Increase Prices:
- Telecom companies can adjust their prices to cover costs, as they capitalize on the demand created by OTT content and infrastructure investments.
- Exclusive Role of Internet Providers :
- Concerns for Consumers:
- Additional Costs :
- Supporters of net neutrality contend that imposing extra costs on OTT platforms might be transferred to subscribers, leading to higher fees or diminished service quality.
- Critics of net neutrality argue that preserving open competition in internet services is crucial for safeguarding consumers' access and choice.
- Additional Costs :
What is the Way Forward for an Inclusive Digital Landscape in India?
- Regulation Clarity: The TRAI should continue to provide regulatory clarity and guidance on net neutrality. This includes defining and enforcing net neutrality principles that prevent discriminatory practices, while also allowing for reasonable network management.
- Multi-Stakeholder Approach: Consider a balanced approach that acknowledges the interests of both telecom companies and OTT service providers. Finding a middle ground that ensures fair competition and innovation while allowing telecom companies to recover investments is crucial.
- Transparency: Encourage transparency in how ISPs manage their networks and how they cooperate with OTT providers. This transparency can help ensure that any network management practices are reasonable and non-discriminatory.
- Continual Assessment: Regularly assess the impact of net neutrality regulations on the telecom industry and OTT providers. This assessment should consider the evolving nature of the internet and its services.
- Public Awareness and Education: Increase public awareness and education about the importance of net neutrality, its principles, and how it impacts consumers. Informed consumers can play a role in formulating regulations for net neutrality.
- Global Best Practices: Take a look at global best practices and examples of successful net neutrality regulations in other countries. These can provide insights and lessons for India's regulatory framework.
Conclusion :
Settling the net neutrality debate in India requires a balanced and inclusive approach that considers the interests of all stakeholders while ensuring that the principles of net neutrality are upheld to preserve a free and open internet. As technology continues to evolve, policymakers must remain vigilant to adapt regulations accordingly, ensuring a dynamic and inclusive digital landscape for all.
|
Drishti Mains Question : Examine the historical development and importance of Net Neutrality in India. Discuss the fundamental principles and obstacles related to net neutrality regulations and propose suggestions for a well-balanced regulatory framework within the country. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims :
Q. Which of the following is/are the aims/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains :
Q. Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) based Projects/Programmes usually suffers in terms of certain vital factors. Identify these factors, and suggest measures for their effective implementation. (2019)