Facts for UPSC Mains
Year End Review-2025: Department of Biotechnology
- 18 Dec 2025
- 11 min read
Why in News?
The Department of Biotechnology's (DBT) 2025 Year-End Review shows India's biotechnology sector grew from USD 10 billion in 2014 to over USD 165.7 billion in 2024, with a USD 300 billion projection for 2030.
- This growth has positioned India as the world's 12th largest biotech hub, the 3rd largest in the Asia-Pacific, the 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally, and the largest vaccine manufacturer.
Summary
- India’s biotech sector grew from USD 10 billion (2014) to 165.7 billion (2024), aiming for USD 300 billion by 2030.
- Key advances include healthcare innovations, high-yield gene-edited crops, space biomanufacturing, and technology transfers.
- Strategic initiatives like BioE3 Policy, National Biofoundry Network, regulatory reforms, and E-YUVA scheme have strengthened innovation, commercialization, and youth-led biotech development.
What are the Key Initiatives in India’s Biotechnology Sector?
- Infrastructure and Policy Initiatives: India’s 1st National Biofoundry Network launched to strengthen indigenous biomanufacturing capabilities.
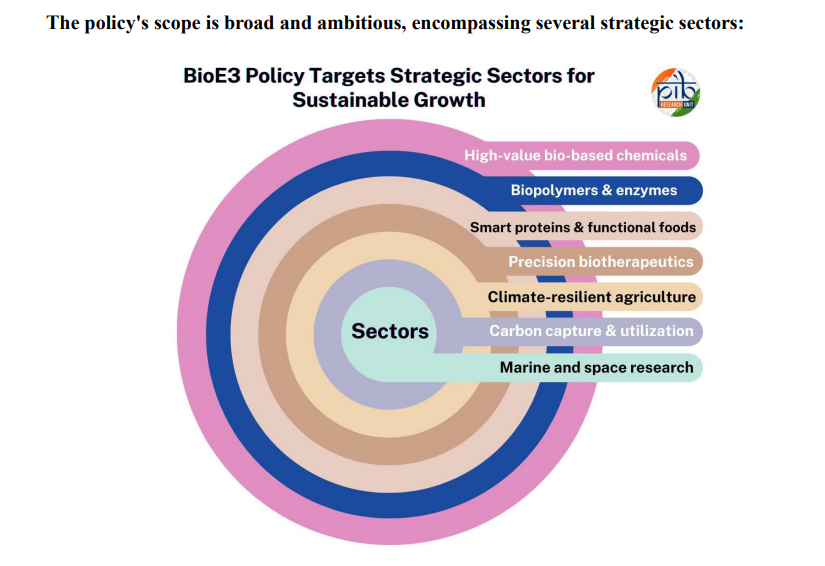
- BioE3 Policy implementation across 6 thematic sectors including bio-based chemicals, precision biotherapeutics, and climate-resilient agriculture.
- D.E.S.I.G.N for BioE3 Challenge launched to empower youth-led innovation for sustainable bioeconomy.
- BioE3 Policy implementation across 6 thematic sectors including bio-based chemicals, precision biotherapeutics, and climate-resilient agriculture.
- Guidelines on Stacked Plants: Guidelines on Genetically Engineered Plants Containing Stacked Events, 2025 notified to ensure biosafety and innovation.
- Stacked refers to combining two or more transgenes—such as those for herbicide tolerance (HT) and insect resistance (Bt)—into a single crop.
- GenomeIndia Project 2020: Creation of a national genomic database with 10,000 accessible whole genome samples under the GenomeIndia Project.
- One Day One Genome Project 2024: It highlights India's unique microbial diversity and its vital roles in ecosystems, agriculture, and health. A core feature is the daily public release of one fully annotated microbial genome, focusing on bacterial strains isolated in India.
- Biomedical Research Career Programme (BRCP) Phase-III (2025-26 to 2037-38): It aims to nurture top scientific talent for cutting-edge and translational biomedical research, strengthen research systems, reduce regional disparities, and build globally impactful research capacity.
Biotechnology
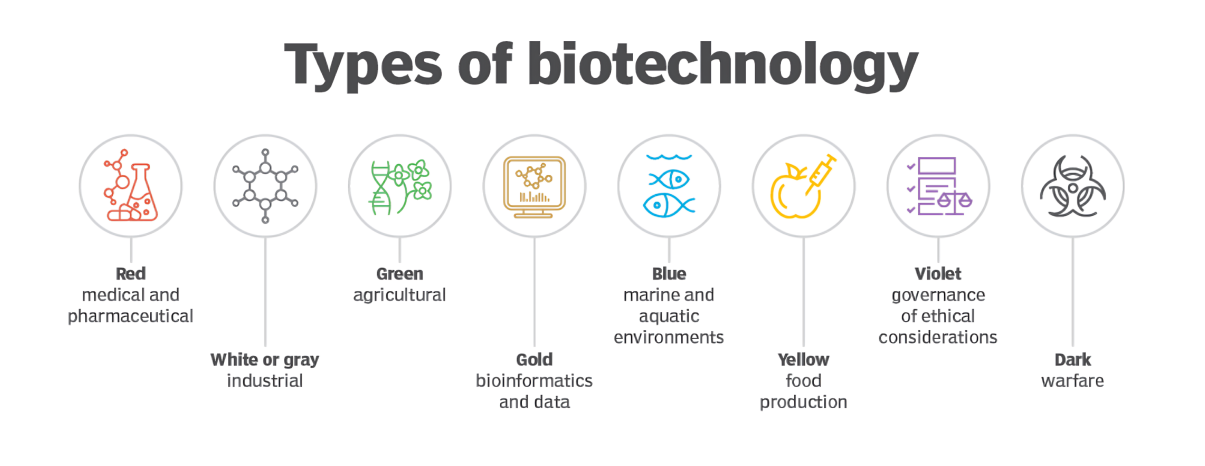
- About: Biotechnology harnesses cellular and biomolecular processes to develop products and technologies that improve human life and protect the environment.
- Types:
- Applications:
- Healthcare (Red): Enables advanced drugs, vaccines (e.g., rapid Covid-19 production), personalized/gene therapies, and stem cell research for tissue regeneration.
- Agriculture (Green): Develops crops resistant to pests, drought, and diseases, and enhances nutritional profiles (e.g., vitamin-A fortified Golden Rice) to improve food security.
- Environment (White): Uses microorganisms for bioremediation (cleaning pollutants) and produces sustainable biofuels, bioplastics, and biodegradable materials to support a circular economy.
- Economic Growth: Creates jobs and provides a competitive global edge through innovation.
- Climate & Materials: Helps capture CO₂, produces cleaner biofuels, and engineers novel bio-based materials for industries like fashion and aerospace.
What are the Key Achievements of the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) in the Year 2025?
- Healthcare & Research: Indigenous AI-driven models developed for pregnancy dating and preterm birth prediction with 66 genetic markers identified.
- Dare2eraD TB programme: 18,000 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) isolates sequenced for comprehensive drug-resistant TB mapping.
- GARBH-INi Cohort: 12,000 pregnant women enrolled with 14 lakh biospecimens and 1 lakh ultrasound images archived.
- Commercialization of Lactobacillus Crispatus: Consortia of beneficial Lactobacillus crispatus (lactic acid-producing bacteria) isolates have been developed and transferred to a leading Indian nutraceutical company for application in nutraceutical and cosmetic products.
- Agricultural Biotechnology Innovations: High-yielding gene-edited rice cultivar (DEP1 mutation) showing 20% increased yield over wild type developed.
- Rice variety ADT 39-Sub1 with submergence tolerance released in 2025. Drought-resistant rice variety 'Arun' developed for variable climatic conditions.
- Two drought-tolerant chickpea varieties (ADVIKA and SAATVIK) contributed to 30% of total breeder seed indent developed.
- Space Biomanufacturing: Microalgae demonstrated two-fold growth increase in microgravity.
- A proof of concept for growing cyanobacteria on urea in microgravity has been achieved, potentially enabling the use of human waste (CO2 and urea) to produce nutritional supplements for astronauts on long-term space missions.
- India’s 1st human muscle stem-cell experiment revealed microgravity as an accelerated model of muscle aging (sarcopenia).
- Technology Transfer and Commercialization: Engineered Glucoamylase Secreting yeast strain developed for 1G ethanol production (50% reduction in external glucoamylase requirement).
- Multiple technology transfers including white rust resistance mustard varieties to eight seed companies.
- E-YUVA scheme scaled to 19 pre-incubation centres across 15 states, supporting 460+ Fellows.
- North-Eastern Region Development: Value-added products from wild apples and theaflavin extraction technology developed. 218 beneficiaries including farmers trained through targeted interventions.
- A Network project on Large Cardamom is under implementation with the Sikkim State S&T Council in collaboration with iBRIC+.
- Strategic Partnerships: Centre-State BioE3 Cells initiated. International collaborations with the United Kingdom (FEMTECH, (Women-Orientated Health Tech)), Switzerland (One Health).
Conclusion
Driven by policies like BioE3, cutting-edge research, and strong public-private partnerships, India's biotechnology sector has grown transformatively, positioning the country as a global leader in sustainable bio-economy and self-reliance.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyze the contributions of biotechnology to climate-resilient agriculture in India, with reference to recent developments in gene-edited crops and drought-resistant varieties. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is the projected value of India’s biotechnology sector by 2030?
India’s biotechnology sector is projected to reach USD 300 billion by 2030, positioning it among the world’s top biotech hubs.
Q. What is the National Biofoundry Network?
The National Biofoundry Network is a DBT initiative to strengthen indigenous biomanufacturing capabilities and support innovation in biotech startups.
Q. What are the key objectives of the BioE3 Policy?
The BioE3 Policy focuses on six thematic sectors, including bio-based chemicals, precision biotherapeutics, and climate-resilient agriculture, promoting a sustainable bioeconomy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q. How can biotechnology help to improve the living standards of farmers? (2019)
Q. Why is there so much activity in the field of biotechnology in our country? How has this activity benefited the field of bio pharma? (2018)