Science & Technology
Bioremediation in India
- 04 Dec 2025
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Bioremediation, Biotechnology, Synthetic biology, Biosensing,
For Mains: Need for Bioremediation, Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Why in News?
India is revisiting bioremediation as pollution from sewage, industrial waste, pesticides, plastics, and oil spills continues to strain the country’s soil, water, and air. With traditional clean-up technologies proving costly and unsustainable, bioremediation is emerging as a promising, science-backed alternative.
What is Bioremediation?
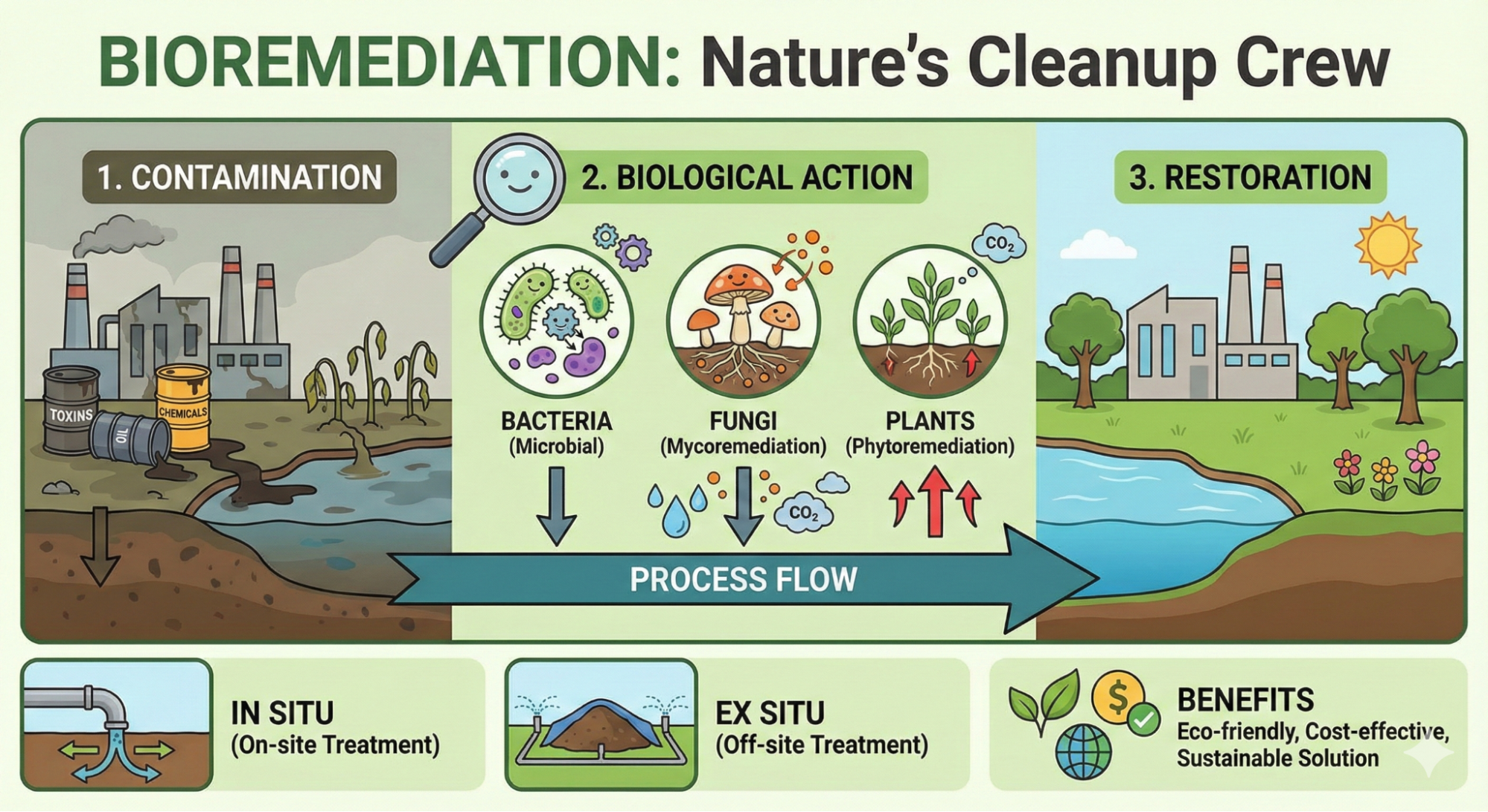
- About: Bioremediation is the use of living organisms (bacteria, fungi, algae, or plants) to break down or neutralise toxic pollutants.
- These organisms convert contaminants like oil, pesticides, plastics, and heavy metals into harmless end-products such as water, carbon dioxide, or organic acids.
- It is a cost-effective, eco-friendly method compared to chemical or mechanical clean-up technologies.
- Types:
- In situ bioremediation: Treatment takes place at the contaminated site itself.
- Example: oil-eating bacteria sprayed on an ocean spill.
- Ex situ bioremediation: Contaminated soil or water is excavated or pumped out, treated in a controlled facility, and returned after cleaning.
- In situ bioremediation: Treatment takes place at the contaminated site itself.
- Advancements in Bioremediation: Modern bioremediation combines traditional microbiology with biotechnology and synthetic biology.
- Genetically modified (GM) microbes are now designed to break down stubborn chemicals like plastics and oil residues.
- Synthetic biology enables “biosensing” organisms that change colour when they detect toxins, offering early contamination warnings.
- New biotechnologies help identify useful biomolecules and reproduce them under controlled conditions, allowing their use in settings like sewage plants or agricultural fields.
- Development of nanomaterials and microbes–nanocomposite systems are useful for faster pollutant capture.
- Bioremediation Status in India: Bioremediation is expanding in India but remains mostly in pilot stages.
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) supports projects through its Clean Technology Programme.
- IITs have developed cotton-based nanocomposites for oil spills and identified pollutant-degrading bacteria.
- Startups such as Econirmal Biotech now supply microbial formulations for soil and wastewater treatment.
Why Does India Need Bioremediation?
- Severe Pollution: Rapid industrialisation and urban growth continue to burden rivers like the Ganga and Yamuna, which receive thousands of liters per day of untreated sewage and industrial effluents every day.
- Multiple Contaminant Types: Widespread oil leaks, pesticide residues, and heavy-metal pollution degrade ecosystems, contaminate groundwater, and increase long-term public-health risks.
- Limitations of Traditional Clean-up: Mechanical and chemical remediation is expensive, energy-intensive, and often generates secondary pollution.
- Bioremediation provides a cheaper, sustainable, and decentralised solution—critical in a country where resources for environmental restoration are limited.
- Leverages India’s Rich Biodiversity: Indigenous microbial species, naturally adapted to high temperatures, salinity, acidity, and varied ecological conditions, consistently outperform imported strains, improving recovery efficiency.
- Suitable for large-scale contamination: India has extensive polluted stretches e.g., over 300 polluted river stretches identified by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) where biological clean-up is far more feasible than conventional methods.
- India's Technology Gaps: Large-scale adoption is limited by technical gaps like site-specific microbial knowledge and complex pollutants, as well as regulatory challenges, including the absence of uniform national standards.
International Practices in Bioremediation
- Japan: Uses microbial and plant-based systems as part of its urban waste management strategy.
- European Union: Funds cross-country bioremediation projects to clean oil spills and rehabilitate mining-affected areas.
- China: Prioritises bioremediation under its soil pollution control laws, deploying genetically improved bacteria to restore contaminated industrial sites.
What are the Opportunities and Risks of Bioremediation for India?
|
Opportunities |
Risks |
|
Helps restore polluted rivers, lakes, and wetlands |
Release of genetically modified organisms may cause unintended ecological impacts |
|
Enables reclamation of contaminated land and industrial sites |
Inadequate testing or poor containment can worsen pollution problems |
|
Creates jobs in biotechnology, environmental consulting, and waste management |
Lack of public awareness may lead to resistance or misuse of new technologies |
|
Supports national missions like Swachh Bharat, Namami Gange and National Clean Air Programme, ensuring long-term ecological restoration. |
Weak monitoring systems and absence of strong biosafety guidelines and certification systems can limit safety and effectiveness |
How Can India Scale Bioremediation Effectively?
- Develop national guidelines for bioremediation and biomining protocols and microbial applications with input from DBT, CPCB, and State Pollution Control Boards.
- Biomining is the process of using microorganisms to extract metals of economic interest from rock ores or mine waste.
- Create regional bioremediation hubs linking universities, industries, and local bodies.
- Support startups and community projects through DBT–BIRAC.
- Strengthen biosafety norms for GM organisms, expand certification and training for field-level staff, and adopt real-time monitoring through biosensors and digital dashboards to track advances in bioremediation.
- Improve public engagement to build trust and awareness about microbial solutions.
Conclusion
Bioremediation offers India a sustainable and affordable pathway to restore polluted ecosystems while supporting SDG 6 (Clean Water) and SDG 13 (Climate Action). With strong standards, skilled manpower, and public trust, it can become a key pillar of long-term environmental recovery.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Bioremediation can reduce remediation costs and environmental footprints compared to conventional methods. Discuss |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is bioremediation?
Bioremediation is the use of living organisms (microbes, fungi, algae, plants) to degrade or neutralise pollutants like oil, pesticides, plastics and heavy metals into harmless products.
2. How does bioremediation support national missions like Namami Gange?
Bioremediation offers decentralised, low-cost treatment for sewage and organic pollution, complementing infrastructure upgrades under Namami Gange and Swachh Bharat to restore river health.
3. What are the main risks of bioremediation?
Risks include unintended ecological impacts from genetically modified organisms, inadequate testing, poor containment, and weak monitoring — necessitating strict biosafety guidelines and certification.
Summary
- Bioremediation uses microbes and biotech to safely break down pollutants, offering a cheaper and greener alternative to conventional clean-up methods.
- India needs it due to severe river, soil and groundwater pollution, with 300+ polluted stretches identified by CPCB and rising industrial waste.
- India’s efforts are growing through DBT, IITs and startups, though adoption is slowed by technical gaps and lack of national standards.
- Strong biosafety rules, regional hubs, and public awareness are essential to scale bioremediation and support missions like Swachh Bharat and Namami Gange
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
PrelimsQ. In the context of solving pollution problems, what is/are the advantage/advantages of bioremediation techniques? (UPSC Prelims 2017)
- It is a technique for cleaning up pollution by enhancing the same biodegradation process that occurs in nature.
- Any contaminant with heavy metals such as cadmium and lead can be readily and completely treated by bioremediation using microorganisms
- Genetic engineering can be used to create microorganisms specifically designed for bioremediation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and
Ans. (c)